Types of sewer systems according to SNiP.
Attention! When designing and installing external sewage systems, they rely on the rules of SNiP.
The sewerage network includes individual pipes installed in a single system, having the appearance of a branched communication. The pipeline moves wastewater from buildings to tanks where the water is purified and recycled.
Types of sewerage:
1. external type, involves laying pipes with treatment facilities on the street.
2. internal type, represented by a structure inside buildings.
Liquid flows through pipes using pressure or by gravity, so there are pipelines:
1.non-pressure type.
2.pressure type.
Important ! Non-pressure sewerage and water supply systems are laid at an angle of inclination so that the wastewater moves naturally to the processing site. Polyethylene is considered a common material option for sewer pipes.
The pressure type of pipeline operates from a pump that supplies pressure to remove wastewater. Pressure networks are characterized by increased structural strength; polyvinyl chloride is considered the best material.
Classification of sewerage by type of purpose:
1.production networks.
2.household networks.
3.storm networks (for the movement of waste water after rain and snow)
The economic and household type of network is divided into:
1.central network.
2.autonomous network.
The central system transports the wastewater of the entire city, while the autonomous system is laid to serve a private building, sometimes a couple of houses.
The method of laying external systems implies:
1. general alloy systems.
2.semi-separate systems.
The all-alloy network moves domestic wastewater and rainwater through a single pipeline. In a semi-separate network, wastewater of different natures is transported separately, but ultimately they flow into one place. A separate type of communication transports wastewater in different ways into separate containers.
Features of installation work
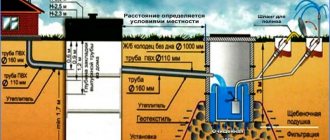
By observing SNiP during installation work, it is possible to improve the performance of the sewer system and increase its durability. To effectively drain wastewater naturally, it is very important to set the correct slope of the pipeline. According to SNiP, pipes must be laid at an angle towards the storage well. As a rule, the slope is approximately 2-3 centimeters for every meter of pipeline. As for the cross-section of sewer pipes, pipes with a diameter of 100-110 mm are sufficient to organize drainage from one private house. If the system serves several private houses, then a pipeline with a diameter of at least 200 millimeters is needed.
An important point in design is determining the location for the construction of a prefabricated well. When determining the location, it is necessary to take into account what type of water collector will be installed. This can be a storage well or a septic tank, which not only accumulates, but also processes wastewater. In both cases, it is recommended to select the lowest location on the site to install the wastewater collection point. If preference is given to a simple storage well, then it will need to be emptied periodically using a sewer truck. In this case, it is recommended to choose a place to build a collection point not only in the lowest place, but also as close as possible to the roadway.
Also, do not forget about the construction of intermediate inspection wells at pipeline turns and every 25 meters on straight sections. The presence of inspection wells will simplify the maintenance of the system, especially at turns, where there is always a high probability of sewer pipe clogging.
External type of sewerage.
Using the external method, different types of sewer systems are laid:
1. The design in the form of a routing involves the installation of networks from the beginning of the wastewater to the place where it is collected in the reservoir. The method is used for private and apartment buildings, if construction requirements are met. Pipes are laid only vertically.
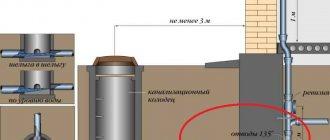
Important! In this case, the distance from the outside wall of the house to the sewer pipes should be over three meters. Tracing is used if it is possible to connect to the main sewer system.
2.Street-type sewerage consists of a complex pipeline system with wells. This type of communication is laid on every street in the city; through it, wastewater from all houses enters the main sewer pipeline and is sent for treatment.
3.Collectors are needed to collect wastewater and redirect it. Sewage can be redirected to the next collection device, which is located near the collection pool or in its area. Collectors operate by gravity or under pressure, transporting liquid.
4. Treatment structures represent the last point for the movement of wastewater; here sewage is collected for treatment. After treatment activities, water flows into reservoirs for further use.
Important! Country houses that do not have a single sewer network are equipped with an autonomous cleaning system.
Sewer pipes can be laid in different ways, this is influenced by factors such as:
1. turns.
2.bends.
3.height of groundwater flow.
All pipelines are laid at a certain angle, which is determined by the cross-section of the pipe. Sometimes the system requires the installation of a pump or technical well.
External sewer networks
There are several types of sewerage systems laid externally.
Trace. This design is mounted from the starting point to a special collection tank. Tracing can be installed even in an apartment building (subject to all building codes and regulations). Pipe laying is carried out only in a vertical plane. It is worth noting that there must be a distance of at least 3 m from the outer wall of the building to such communication. Installation of the trace can only be carried out if it is possible to connect to the central sewer network.
External sewerage consists of pipes, collectors and wells
Street sewer network. Such a system is represented by a complex system of pipes and wells. The laying of such communications is carried out on all streets of the city. Through the street sewer network, wastewater is transported to the central sewer system and further to treatment facilities.
Collectors. Such structures are “engaged” in collecting wastewater, as well as redirecting it if necessary. Redirection of wastewater occurs from one collector to another, located near the sewer basin or on its territory. The principle of operation of collectors is quite simple - they transport wastewater under pressure or by gravity.
Treatment facilities. They are the final destination for wastewater. In such facilities, wastewater is concentrated and purified. After purification, water is usually discharged into reservoirs, after which it is again used for economic purposes.
Helpful information! Private areas that do not have the ability to connect to a central sewer system can be equipped with autonomous treatment structures.
The laying of sewer lines is carried out differently depending on the specific case. Installation features are determined by the following factors:
- bends;
- turns;
- the level at which groundwater flows.
Sewage of any type must be equipped with treatment facilities
In any case, communication should be located on a slope. Changing the slope level depends on the pipe cross-section. In addition, in some cases, pumps or inspection wells are installed.
What does the external sewage system consist of?
The sewerage system laid outside the building has a complex design, including bends with pipes, inspection hatches, slopes, and containers. Installation is carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNiP, taking into account safety precautions.
The sewerage system consists of such elements as:
1.pipeline, which contains pipes of different sizes and lengths.
2. wells, their number depends on the situation, there are:
-revision type.
- drainage type.
-variable type.
- rotary type.
4.releases and receivers. Through outlets, waste water flows into a cleaning tank.
5.local treatment structures: septic tanks or aerators. The number of treatment facilities is determined by the regulations. After the cleaning procedure, wastewater is absorbed into the ground or flows into water bodies. Sometimes it is collected in containers for further use in everyday life.
Attention! Autonomous sewerage must include a septic tank or aerator.
5.pumping station. These structures are not used for all types of sewage systems, but are used only when it is necessary to supply wastewater for treatment in parts.
6. from elements that help the system operate, for example, installation equipment.
What is included in external sewer networks?
An external sewer network is a complex system that includes various structural elements: pipes, turns, slopes, various wells, tanks, etc. Their installation is regulated by SNiP and must be carried out taking into account safety regulations.
Let's consider the main components that are included in external sewer networks:
1. Pipeline. It is mounted from pipes, which may have different cross-sectional indicators depending on the specific case. In addition, pipes can be of different lengths.
2. Wells. Mounted depending on need. These structures are represented by four main types:
- auditing;
- drainage;
- differential;
- rotary.
3. Receivers and releases. Through outlets, wastewater is unimpededly transported to the treatment tank.
4. Local treatment facilities. These include: septic tanks, aerators and other devices that perform cleaning functions. The number of such devices must comply with the required regulations. It is worth noting that treatment plants, after direct purification of water, discharge it into the soil or reservoir. In some cases, water after purification is collected in tanks, after which it is used for various agricultural needs.
The local wastewater disposal system must be equipped with a septic tank or aerator
5. Swap stations. Not used in all external sewerage networks. As a rule, they are used in cases where portioned supply of wastewater to treatment plants is necessary.
6. Auxiliary elements. These include various additional devices with the help of which the external sewer network is installed and operated.
Design according to SNiP
The design of the sewerage system should be carried out in conjunction with the water supply network, as well as the irrigation system. Water pipelines with sewerage are laid taking into account water consumption data in each individual case.
During the installation of sewer pipelines, sanitary and construction standards and requirements must be adhered to. Otherwise, accidents may occur during operation. These standards must be observed by both public and private companies, as well as individuals installing an autonomous external sewer system in a country house or country house.
Before starting to create a project, the characteristics of the area and the sewer type are determined: all-alloy, semi-separate, or separate.
Important! When creating a project and laying communications, they take into account the type of soil on the site, the climatic conditions of the area, and the height of the groundwater.
The requirements for external sewerage networks are specified in SNiP 2.04.03 - 85; according to the rules, the sewerage system must be designed taking into account the environmental features of the site.
Factors that determine the features of sewerage installation:
1.soil type. The composition and characteristics of the soil are determined before designing the network. The composition of the soil determines the installation method; this is important if the soil is unstable.
Attention! You should also take into account the terrain of the site in order to calculate the slope angle and network elevations.
2.level of groundwater occurrence and its quantity.
3. features of the climate in the area, this factor affects the type of thermal insulation of the pipeline.
4.the amount of wastewater planned to be processed. Their volume is determined by the number of people who will use the sewerage; the presence of industrial facilities and other public buildings also affects the amount of drainage.
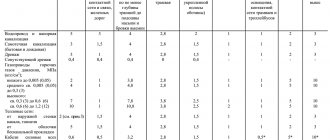
5. It is necessary to calculate the distance of laying the sewerage pipeline from houses, industrial buildings, the location of pumping stations, and structures for cleaning.
SNiP rules regulate the arrangement of pipeline crossings along rivers, roads, and ravines. The project indicates how the transition will be carried out.
What are the advantages of working with us?
When working on projects, we adhere to the principles that have created the image of our company as a reliable partner, and first of all these are:
- attention to the economic interests of the customer and taking into account his legal requirements for the development of a utility network project with the highest indicators of reliability, efficiency, ease of implementation at minimal cost;
- compliance with contractual deadlines for the development of a complete package of project documentation;
- strict adherence to GOST, SP (Code of Rules) and industry standards for owners of utility lines, which facilitates the acceptance of utility networks built according to our projects by regulatory and administrative authorities;
- willingness to take on and carry out additional activities to resolve issues that arose with the customer already in the process of developing a utility network project.
But the main thing in our work is that we don’t just promise, but constantly deliver, and our projects receive their material embodiment in various regions of the country from Moscow and the region to the Far North.
What materials are used for external sewage systems.
An important point during the installation of a sewer system is the selection of suitable pipe material and other structural elements. The pipes carry wastewater that has an aggressive composition, so the network materials must be resistant to this environment.
Attention! Most often, a modern material is used for the external sewer network - polymer.
Popular materials suitable for installation work:
1.polyvinyl chloride.
2.polypropylene.
3.polyethylene.
4.cast iron.
5. steel.
Most often, pipes made of polymeric materials, including plastic, are used. Metal pipelines require more labor-intensive installation.
If an open version of the gasket is used, then the polyethylene material is not suitable; it changes from exposure to sunlight, losing properties and breaking down. If it is necessary to use polyethylene pipes in these conditions, a protective casing is required. They can use old steel pipes.
The most reliable option is the use of polyvinyl chloride pipes. The material has a low price, high strength, and is resistant to UV rays. Pipe installation is simple compared to rolled steel pipes. PVC pipes have different ratios of cross-section, length, and wall thickness. The parameters can be found in a special table.
PVC pipes can be used for pressure and non-pressure networks.
Preparatory work and installation stages
The simplest technical diagram of an external water supply system includes the following elements:
- pumping station;
- locking mechanism;
- a storage tank, which is needed to maintain optimal pressure parameters;
- devices that regulate the water supply process;
- pipeline.
All work must be regulated by regulations SNiP 2.4.2-84, SNiP 3.5.4-85*. Can be:
- ground: on supports and overpasses with subsequent insulation or its absence;
- underground: characterized by the laying of trenches.
For the installation of an external water supply at a summer cottage, it is more advisable to give preference to the latter option. Implementation may require special equipment and machinery, but if the area is small, you can dig them yourself.
The stages of installing an external water supply include the following processes:
- Preparing the soil and digging trenches (pipe depth of at least 0.5 m).
- Laying pipes and connecting them.
- If necessary, insulate elements of the water main.
- Sealing the entry point of the pipeline into the house.
Finally, the system must be checked for leaks.
Carrying out excavation work
Excavation of soil and preparation of trenches for the pipeline is carried out using the following technology:
- On a personal plot, the approximate location of the pipeline network is outlined and earth is excavated according to the dimensions; the depth of the trench depends on the approximate depth of soil freezing. As a rule, it ranges from 1.5-1.8 meters. The value of this parameter is also influenced by the duration of low temperatures in the region, soil density and soil moisture. The optimal trench width is 50 cm.
- The bottom of the trench must be leveled. If the soil is loose, it is additionally compacted. Before laying the pipes, install a bed made of gravel or sand.
- Pipes are placed on the prepared cushion; pits must be made at the joints.
After laying and compacting, the pipeline is covered with sand or gravel to a depth of 10-15 cm, then the removed soil is used.
The outside of the pipes is smooth or corrugated.
Attention! Non-pressure pipes are installed in gravity systems.
Non-pressure PVC pipes are used for laying external sewerage, which is installed at an angle. The fluid flow speed in the pipes should not exceed eight meters per second.
Pressure pipes are used for communications, discharging wastewater through a pump. The operating pressure for pipes made of this material can be at least ten atmospheres.
Corrugated PVC products are used for problem areas. Installing them does not require the use of special equipment. Pipes can be installed in pressure and non-pressure networks. There is a special table to determine the relationship between pipe diameter and wall thickness.
Sometimes it is appropriate to lay a sewer network from reinforced concrete or asbestos-cement pipes. The products are used for the installation of large systems made of large cross-section pipes. The material does not have high strength; they can only be used in non-pressure systems.
GOSTs and TU
| Document's name | Link for review |
| System of design documents for construction. External networks. Water supply and sewerage. Working drawings. | GOST 21.604-82 |
| Cast iron hatches for inspection wells. Specifications | GOST 3634—89 |
| Concrete and reinforced concrete structures for sewer, water and gas pipeline wells. Specifications | GOST 8020—90 |
| Ceramic sewer pipes. Specifications | GOST 286—82 |
| Water purification devices. General requirements for efficiency and methods for determining it | GOST R 51871-2002 |
| Cast iron sewer pipes and fittings for them | GOST 6942-98 |
| Polymer pipes with a structured wall and fittings for them for external sewerage systems. Specifications | GOST R 54475-2011 |
| Polymer sewer wells | GOST 32972-2014 |
| Compact units for treating domestic wastewater. Types, parameters and sizes | GOST 25298-82 |
| Sewerage. Terms and Definitions | GOST 25150-82 |
| Sanitary drainage fittings. Specifications | GOST 23289-94 |
| Manholes for inspection wells and stormwater inlets. Specifications | GOST 3634-99 |
| Pipes and fittings made of polyethylene for internal sewerage systems. Specifications | GOST 22689-2014 |
| Pressure pipes made of polyethylene. Specifications | GOST 18599-2001 |
| Dynamic pumps. Test methods | GOST 6134-2007 |
| Soils. Permeability Field Test Methods | GOST 23278-78 |
Types and features of networks by location
Internal sewer networks are installed plumbing and piping systems that are located inside a facility. They can be made of cast iron, plastic, metal alloys.
External sewer networks carry out the task of draining wastewater and household waste from the facility. Their design is quite complex and includes cleaning systems, as well as large pumping stations. There are several types of external sewer networks:
- separate - having several channels for the removal of wastewater of different composition and nature;
- semi-separate - operates on the same principle as separate external sewerage, but has one significant difference - wastewater is processed in a single collector;
- general - all types of waste and waste are transported in a single stream.