Not every welder can handle the process of welding stainless steel. This is due to the technical characteristics of this material. More difficulties arise when welding stainless steel with ferrous metal. To create a strong connection between these materials, it is necessary to choose the right welding mode and take into account a number of features.
Welding pipes from different metals
Is it possible to weld ferrous metal with stainless steel?
If we talk about production, the technology of welding stainless steel with ferrous metal, then it is initially incorrect due to the difference in materials, their properties, and technical characteristics. However, the connection can be made.
Since enterprises require compliance with GOSTs, this method of joining metals is in demand in small workshops. But to obtain a good connection, you need to know the chemical composition of the components being welded and have practical experience working with them.
Pipeline welding
To connect pipes made of different materials, electrodes with rutile or basic coating are used. With fusible consumables, work is carried out with a current of reverse polarity. Welding pipes with constant parameters has the following advantages:
- Possibility of use when working with thin-walled pipes;
- high quality seam;
- ease of execution;
- minimum amount of splashes generated during operation.
When using non-fusible tungsten electrodes, set straight polarity. This method of welding pipes has the following positive characteristics:
- reliable protection of the oxygen weld pool;
- stability of the electric arc;
- corrosion resistance of the seam.
Difficulties in welding dissimilar steels
Welding stainless steel with ferrous metal causes certain difficulties. This is due to differences in the technical characteristics and chemical composition of the two steels. These include:
- The weakest point after the work is the solder joint. This is explained by the fact that the two materials have a difference in the coefficient of linear expansion. Because of this, internal stresses remain after the welding process.
- Uneven penetration occurs due to differences in thermal conductivity. This negatively affects the strength of the finished seam.
- Effect of carbon migration. Impairs the anti-corrosion protection of the finished product. Because of this, the seam will quickly become covered with a layer of rust.
Recommendations and nuances
- Sometimes stainless steel welding is performed in the Double Pulse mode - double pulse. In this mode, two pulses (low and high) are superimposed on the welding base current. During a high pulse, highly efficient welding is achieved, and during a period of low pulse, the metal cools down, eliminating the formation of smudges and warping. During a high pulse period, the welding drop is “driven” into the melt zone, without causing short circuits, and during a low period, the metal cools, eliminating the formation of sagging and smudges. . In the Double Pulse mode, ideal heat transfer between the melting filler material and the stainless steel bath is achieved, and the quality of the weld is improved. The “Double Pulse” mode is implemented in the TRITON ALUMIG 250P Dpulse Synergic device.
- Welding is carried out with reverse polarity. Welding with direct polarity is carried out only using submerged arcs.
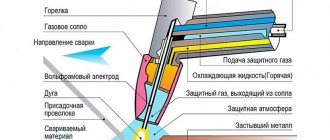
- A mixture of carbon dioxide and argon is used as a shielding gas.
- The filler wire overhang should be within 6-12 millimeters. Adjust the average flow rate of the gas mixture within 6-12 m³/min.
- Welding is carried out with the torch angled backwards to achieve deep penetration and the correct shape of the seam. Forward angle welding is used for thin sheet metals when a shallow penetration depth is required with a wide weld shape.
By following the recommendations described above and the correct settings of the inverter semi-automatic machine, you can achieve high-quality welding of stainless steel products.
Tool
To carry out the work, it is necessary to prepare a welding machine, additional tools, consumables, and wire of a certain chemical composition. List of required devices and materials:
- Inverter welding machine.
- Stainless steel filler wire.
- Electrodes (the quantity depends on the size of the seam, the number of parts to be welded).
Separately, it is necessary to talk about the choice of electrodes. There are several main types of consumable metal rods with a special coating:
- OZL-25B - used for joining heat-resistant steels.
- NIAT-5 - used for welding austenitic materials.
- TsT-28 - used for welding nickel-based alloys.
- E50F - used for joining heat-resistant metals.
We must not forget about setting up the welding material. Principles for selecting modes:
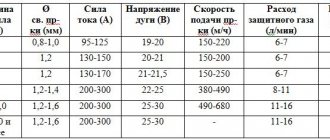
- For a part thickness of 1 mm, direct current of up to 60 A is used (electrode 2 mm in diameter).
- With a workpiece thickness of 2 mm, an alternating current of up to 80 A is set (electrode 3 mm in diameter).
- With a part thickness of 4 mm, a direct current of up to 130 A (4 mm electrode) is used.
If the current is too high, the materials will be damaged.
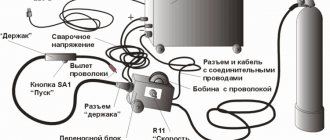
Inverter with mask and electrodes
Electrodes used
Having understood the welding technology, you can move on to the question of what electrodes and filler wire should be used for welding ferrous metal and stainless steel. The wire used in the process of welding two different steels must contain at least 30% of the base material. The degree of alloying must be the same or higher than that of the metals being welded. In the case of stainless steel and black, the main material is stainless steel (as it has the highest degree of alloying). The rest of the filler material is nickel and manganese.
Electrodes for welding
In principle, a good welded joint for not very critical structures can be obtained without the use of special consumables. Most often, a stainless electrode or a stainless filler wire is used to connect stainless and ordinary steel. Such electrodes contain an increased amount of alloying components, which make it possible to compensate for their burnout during the heating process.
If you need to weld any critical structure, you should pay attention to special transition electrodes for welding dissimilar or difficult-to-weld steels. When using them, a special intermediate (or buffer) layer is fused, which allows the parts to be connected. The most commonly used electrodes are OZL-312 (in cases where the chemical composition of steels is generally unknown) and NII-48G.
Technologies for welding stainless steel and ferrous metal
There are several features of welding stainless steel with ferrous metal:
- Stainless steel has a high coefficient of linear expansion. Because of this, large gaps are required between the workpieces being connected.
- It is necessary to quickly cool the metals being welded to maintain corrosion resistance.
- You should only work with short electrodes, up to 350 mm long. Using long coated rods will cause them to overheat during the work process.
- The welding current should be reduced by 20% due to the low thermal conductivity of stainless steel. This will help maintain the technical characteristics of the finished product.
TYPES OF STAINLESS STEEL
Austenitic steels. They contain at least 20% chromium and 4.5% nickel.
Duplex steels. Their chromium content reaches 25%, 1.5% nickel and a slight admixture of nitrogen.
Ferritic steels. Up to 29% chromium is allowed in their composition.
Martensitic steels. Their chromium content is insignificant, no more than 13%, and nickel maximum 4%.
Multicomponent steels. Minimal amounts of chromium and nickel and include a wide range of other enhancing impurities.
In this case, chromium is a reinforcing component, due to which strength and corrosion resistance increase significantly. Cold deformation is simplified and weldability, appearance and wear resistance are improved.
Stainless steel markings:
- A number indicating the percentage of carbon;
- Letter designations that give an idea of what kind of impurity is contained in this alloy: X-chrome, N-nickel, etc. After them come digital designations of the percentage of impurities.
This is interesting: Coolants (cutting fluids) for lathes
How to weld stainless steel with ferrous metal?
You can weld stainless steel to ferrous metal by using:
- High alloy steel electrodes to fill the seam. Nickel-plated rods can be used.
- Alloyed electrodes for surfacing black steel edges. The seam is then created using clad steel that fills the seam.
Before welding you need:
- Prepare nickel-based consumables.
- Heat the electrodes. The optimal temperature is up to 210 degrees for 1 hour.
- Connect DC current.
- Clean metal surfaces from dirt, plaque, scorch, and rust.
Recommendations:
- If gas welding is used, rapid cooling of the finished seam cannot be performed. The part should cool on its own.
- It is recommended to apply flux to the work area to make a better connection.
- When using a tungsten rod, do not forget to sharpen its tip.
- Gas shielded welding is preferred because the finished weld will be stronger.
- When welding, you need to capture more ferrous metal. This will create a stronger seam at the molecular level.
- Movements should be careful and unhurried.
Processing stainless steel after welding
When welding stainless steel semi-automatically in the MIG/MAG mode, a porous oxide layer is formed on the surface of the workpiece. At the same time, chromium, which is contained in the metal, weakens the properties of steel, exposing it to corrosion. To eliminate these defects, it is necessary to carry out careful preparation and processing of products after completion of the welding process.
Before starting work you must:
- clean the working surface of the workpiece from traces of oil, rust, etc.;
- degrease the surface of the product using acetone or solvent.
At the end of the welding cycle, the appearance of the seam should be checked and, if necessary, cleaning and grinding should be carried out.
How to check the quality of the connection?
There are three ways to check a seam:
- Cover the joint surface with kerosene. You should not skimp on the amount of liquid during testing. If kerosene comes out on the other side, the seam is bad.
- The second option is to use acetone. It is applied in the same way as kerosene. Droplets appearing on the other side of the seam indicate the presence of microcracks and through holes.
- The industrial method for testing the strength of seams is the hydraulic method. After this is done, you need to inspect the connection visually. If defects appear, the part is rejected.
If the master knows that the connection is weak, he will not use testing methods associated with the destruction of parts. Any unevenness, cracks, or depressions indicate improper work.
Acetone for checking the seam
Control of welded joints
To assess the strength of the connection between iron and stainless steel, the following methods are used:
- Treating the seam with kerosene. If liquid comes out from the reverse side, the connection is poor quality.
- Using acetone. It is applied in the same way as kerosene. Drops appearing on the reverse side indicate the presence of through defects.
- Hydraulic method. Used in industrial environments. After supplying water under pressure, inspect the connection.
- Ultrasound methods. They are used when high demands are placed on the quality of metal structures.
Security measures
Welding work is carried out in strict compliance with safety regulations:
- Never use faulty equipment. Check the device in advance, inspect the working elements and wires for possible breakdowns.
- The electrodes must be new, with the working layer intact. Cracked rods should not be used.
- Prepare your workplace in advance. Remove all flammable mixtures away and clear the table of unnecessary objects that may interfere with welding work.
- Welding is considered a harmful technological process. Therefore, you need to use a welder’s mask, protective overalls, gloves, and durable shoes.
- Place a rubber mat under your feet to prevent electric shocks.
- The room in which welding work is carried out must be equipped with a good ventilation system.
- For convenience, it is advisable to carry out work on a metal work table.
When working with cylinders filled with inert gases or oxygen, it is necessary to wipe off any oil leaks in the work area.
Any welder knows how difficult it is to weld stainless steel parts together. The process becomes more complicated if you need to connect stainless steel with ferrous metal. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the components of materials, select electrodes, and the operating mode of the device. During the work process, you need to take into account the advice of professionals.
Methods
The most popular method for welding stainless steel and ferrous metals is electric welding. This method has earned recognition and popularity due to its low cost and small number of auxiliary manipulations. Unfortunately, when choosing electric welding, you often have to sacrifice the quality of the connections. The reason for this is the different viscosity indicators of stainless steel and ferrous metals. At the arcing temperature, steel can spread, while ferrous metal remains quite viscous.
High fluidity limits the welder's actions. It is almost impossible to apply a vertical or ceiling seam. When working with dissimilar metals, you have to use transition electrodes adapted for stainless steel and ferrous metal. The electrodes themselves, or rather their rods, are made of stainless steel.
Gas welding is characterized by the presence of filler material, presented in the form of stainless steel wire. When gas welding, steel is less fluid, so this method has some advantages compared to arc welding. A special flux allows you to increase the efficiency of melting ferrous metal. The disadvantage of gas welding is increased safety requirements, as well as a large amount of preparatory work.
Experts call argon arc welding the best way to weld stainless steel and ferrous metal. There is no need to use coated filler wire as argon does a great job of protecting the weld pool. With all the advantages of the listed methods, it should be noted that welding stainless steel and metal does not always pay off, since the financial costs are prohibitively high.
The determining factor in choosing one of the listed welding methods will be the goal and the existing conditions.
- When carrying out minor household repairs at home, the most optimal solution is electric arc welding with stainless steel electrodes. Naturally, high mechanical loads on the structure are excluded.
- Gas welding will provide a more reliable connection. But it is available only in specialized workshops. A private master is unlikely to agree to purchase expensive equipment that also takes up a lot of space. In industry and production, semi-automatic TIG machines are used for argon arc welding. The quality of the resulting seams is high, but the process itself is associated with material costs.