Where is alloy wire used?
Most often, SV08G2S wire is used when carrying out work on automatic and semi-automatic welding machines in industrial conditions. Using it, you can carry out manual welding of various steel products. Using this consumable material, you can obtain a high quality welded joint. The seam is smooth and clean.
Areas of application
Wire of this brand is indispensable when performing the following operations:
- formation of a bead on the connecting seam;
- filling the space between the edges of the workpiece being welded.
When performing welding work, this hardware is the main element of technological processes. Welding in such areas as:
- construction;
- mechanical engineering;
- aircraft and shipbuilding.
Also note that this alloy welding wire can be used as an effective filler material. One of the characteristic features is a high deposition rate. This ensures high quality performance of complex surfacing activities.
Recently, high-alloy welding wire has been actively used when performing work in a gas atmosphere. To create such an environment, argon or a mixture of this gas with others is usually used. Carbon dioxide is often used to form this environment. The choice in favor of the latter is dictated by its lower cost compared to argon. When welding work is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment, direct current is used. Please note that this environment is recommended for welding work on carbon steel products.
Main advantages
Wire of similar markings allows you to make high-quality sealed seams; during welding, the arc is characterized by stable combustion, regardless of the equipment used: it is budget class or for professionals. Restarting the arc when it suddenly goes out is not a problem even for beginners.
When welding in shielding gas, the metal practically does not spatter, the seam joint has a pleasant appearance, which is important when repairing structures that remain in plain sight. With this connection, additional processing or grinding is not used, as it is unnecessary. When using a copper tip, its melting during long-term operation is insignificant, because the wire marked SV08G2S has absolutely no effect on it.
Flux-cored and gas-protective flux-cored wire
To get the job done in the field or in open buildings, flux cored welding wire was developed. The seams are of high quality, mechanization of the process takes less time, and less time is spent on cleaning the metal from splashes. This type of wire has two subtypes: self-protective powder wire and gas-protective powder wire.
Gas-protective is designed for welding with a semi-automatic and automatic welding machine; low-alloy and carbon steels can be welded; welding is carried out in a protective gas environment. This can be carbon dioxide, argon, or mixtures of them. This method has a high degree of metal penetration, which allows welding of lap, corner, and butt joints even in one pass, depending on the specific case each time.
Types
There are several types of low carbon steels with:
- flux core;
- high degree of surfacing;
- flux core;
- core made of metal powder.
These are new types of welding wire, with their help it is possible to make high-quality welding of metal parts, the welding speed increases, the degree of metal spattering decreases, the deposition rate is high, and low smoke is observed during welding. This fact is also very important; the smoking effect is especially small when welding metals in an argon environment or in a protective gas environment, which consists of a mixture of gases with a high argon content.
Self-shielding flux-cored wire is also called flux-cored wire, or self-shielding. It has a core containing the necessary slag-forming and weld-protecting additives. This eliminates the use of bottled gas, which is also beneficial, since the use of bottled gas involves waste of time, transportation costs, waste of money and increased danger in the workplace, because the cylinders are under high pressure. In addition to these problems, cylinders require periodic certification.
When welding semi-automatically using gas, a protective pool is formed, the gas comes out of the nozzle and hits the molten metal of the parts being welded and creates conditions for high-quality welding. Wire, when welding occurs without the use of gas, creates protection and high-quality welding of metal in a different way. During the melting of the wire, the flux that is included in the composition melts at the same time and forms a protective layer in the welded area, which is not removed by the air flow. Thus, it is advisable to use this type of welding in open areas with high wind speeds, i.e. in field conditions.
Receiving process
Wire 08G2S is a common brand because it is universal - it is used to weld low-alloy steels and metals containing carbon. It is ideal for the work of novice welders and experienced craftsmen, sold in cassettes for professional use weighing 15 kg or more, a compact version - in 5 kg spools.
During long-term storage, the wire does not unwind, since the rows are wound tightly. For production purposes, welding wire of this marking is sold in coils from 250 kg to a weight of more than a ton. Such packaging has a beneficial effect on the wire and, when passing through the automatic feeder, does not wear out the parts due to twisting. The cost in packaging is much cheaper than wound on reels or cassettes.
Where are welding jobs needed?
It may even be that some people may need welding work in a domestic environment, but the overwhelming majority of welding work is required in a production environment, where welding is considered almost an integral function of production. When a situation arises in which it is necessary to weld metals together, the question also arises of how this work should be performed, what welding machine and materials should be used to do this, and similar issues.
There are various methods of welding metals, various consumables. They are selected depending on what metals need to be welded. If you need to weld non-ferrous or refractory metals, you should use a welding additive of a certain type.
How is the grade of material selected?
Such a question may well seriously puzzle a beginner, but if you understand everything consistently, then there is nothing overly complicated in this matter. There is a list that indicates what type of welding certain metals should be.
Recommendations
When purchasing welding wire, you should remember some rules that will reduce the likelihood of purchasing counterfeit or low-quality products:
- you should purchase materials from manufacturers and suppliers who have certificates that indicate what standards the wire meets and whether it is even genuine;
- It is recommended to buy consumables in large stores; from trusted sellers who are able to provide storage under appropriate conditions.
Wire Types
There are several types of wire based on their chemical composition. Different grades, depending on the impurities contained, are used when welding a wide variety of types of metals:
- High-alloy wire contains many additional additives.
- Medium alloy wire contains fewer additives, which allows it to be used in most types of welding work.
- Low-alloy wire has a minimum content of impurities and contains approximately 0.2 percent carbon, which makes it possible to weld carbon metals or steel alloys.
The acceptability of the wire to the metal depends on the amount and percentage of impurities such as carbon or nickel.
Deposition coefficient
Surfacing work is carried out in production to correct minor defects in welding, as well as to give surfaces improved physical properties. The wire deposition coefficient (hereinafter abbreviated as CNC) is one of the most important parameters of welding materials.
The specific value of the KNI is determined:
- The chemical composition of the resulting compound.
- The presence of a joint coating - with a high percentage of copper content or not.
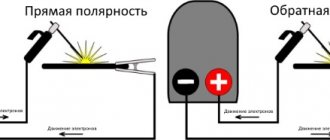
- The polarity of the welding current is direct or reverse.
- Type of current - direct or alternating.
The deposition rate is 8.5 g/Ah and does not fall below.
Types of aluminum wire and rules for its use
Aluminum welding wire for semi-automatic machines consists of individual rods or coils of a certain diameter. In any case, they are hermetically sealed. The first feature of using this material is connected with this.
Electrodes for working on aluminum are not recommended for use when carrying out important work that requires high quality. They are suitable not for industrial purposes, but for home and household purposes.
The fact is that aluminum under normal conditions is covered with a durable and elastic oxide film. Its melting point is about 2500º C. At the same time, the melting of pure aluminum is not higher than 600º C. For alloys the situation is not much different.
To effectively clean and degrease aluminum and its alloys, it is recommended to supplement mechanical cleaning with the use of chemicals (for example, white spirit, acetone or a special hot alkaline bath)
A consequence of this feature of aluminum and its alloys is the need to first remove the oxide film from the surface of the parts being joined (for example, with a mechanical or hand tool). The electrode itself must be initially free of oxide.
If the package of electrodes is not completely used up, it must be sealed again with silica gel added inside to absorb moisture.
Aluminum wire for semi-automatic machines When choosing a wire for welding aluminum alloys, you need to consider what qualities are required from the future weld:
- Seam tensile strength.
- Plasticity of the connection.
- Corrosion resistance.
- Resistant to cracking from heat.
The diameter of the aluminum wire for semi-automatic welding without gas should be 0.3-0.5 mm greater than the thickness of the parts it welds
It is most convenient to use the table below.
When using welding electrodes, you need to remember the need for their preliminary preparation. In a special purchased or home-made oven, preliminary uniform heating of the electrodes and their so-called roasting are carried out. This will allow you to form a very high-quality seam.
Aluminum does not change its color when heated, unlike many other metals, so you need to be especially careful when working with it - it’s easy to burn through
In addition to preliminary preparation of the electrodes, you always need to prepare the parts to be connected. They need to be heated evenly in advance. And ensure that this uniform heating is maintained throughout the formation of the seam.
An alkaline bath is the most effective way to comprehensively remove oxide films and degrease aluminum parts. To do this, you need to make a special solution of 2 liters of pure water, 100 g of trisodium phosphate, 100 g of soda and 50 g of liquid glass. The solution must be heated to a temperature of 60-70º C
It is also necessary to take into account that aluminum tends to cool unevenly and, as a result, crack. Of course, this is compensated by the plasticity of this metal. But if the welds are placed too close to each other (about 10-15 mm), cracks will certainly appear.
Molten aluminum and its alloys are very fluid. That is why all seams are made in one layer in one pass. Where possible, it is recommended to use molten metal containment liners
Distinctive features
When choosing welding materials, both production technologists and home craftsmen are faced with a serious question. He needs to find wire or electrodes that provide high quality seam joints, are unpretentious to welding conditions, and, last but not least, are not too expensive. When compared, SV08G2S wire comes out ahead in many respects.
SV08G2S has the following features compared to other welding materials:
- promotes stability of the electric arc, reduces the risk of electrode sticking to the surface of the workpiece;
- supports a wide range of welding modes;
- compatible with most types of welding machines;
- allows you to minimize the splashing of molten metal;
- facilitates re-ignition of the welding arc;
- helps save other consumables, such as copper tips.
Automatic wire welding
The combination of these features allows us to weld strong and durable seams, with high-quality edge penetration, uniform in composition and with a minimum of porosity and other defects.
Application area
The wire is produced in different sections, so it is used to connect thin-walled and thick metals: for example, in everyday life a diameter of 2 mm is often used to repair small parts, and a cross-section of 6 mm is used in the engineering industry for welding the base of machine tools or other powerful metal structures.
Copper-coated welding wire SV08G2S-O and its application:
- manual welding, when argon and its mixture with CO2 are used for protection, and an infusible tungsten electrode is used,
- semi-automatic version with argon protection,
- as an alloying additive for the weld pool, when the melting flux forms a protective cloud from possible oxidation, and the solidifying slag forms a solid surface with similar protective properties during the crystalline formation of the weld.
SV08G2S-O has better compatibility with all manufactured semi-automatic machines, helps to reliably join manually any carbon steel with high quality seams . Well-known experts in welding technologies note the special uniqueness of wire with such markings for forming a seam bead and uniformly filling the gaps between the edges of parts with molten metal.
Description and technical characteristics of welding wire SV-08G2S
SV-08G2S (PSG-0302) is one of the most versatile types of welding wire used in mechanized welding processes. This wire is suitable for use in both automatic welding machines and semi-automatic welding devices. Copper-plated wire is used for welding in shielding gases (CO2 or a mixture of CO2 with 20% Ar content). SV-08G2S wire allows you to use pure CO2 when welding, which significantly reduces the cost and speeds up production processes. For highly loaded structures, when welding with SV-08G2S wire, you can use a gas mixture of CO2 (80%) and Ar (20%). In such a gas mixture, a weld made using copper-plated wire SV-08G2S will have the highest impact strength and tensile strength. This type of wire can be used by any welding machines in any spatial positions.
During production, SV-08G2S welding wire is coated with a protective layer of copper. Copper-plated wire has a long shelf life and is less susceptible to chemical and physical influences during storage. Currently, copper-plated welding wire marked SV-08G2S is produced by many factories in Russia, the CIS countries, China and Turkey.
Oddly enough, even with so many suppliers, choosing a welding wire is not such an easy task. When choosing a welding wire supplier, you need to carefully select the supplier and clearly know which manufacturing plant produces the welding wire you have chosen. This is especially true for the choice of copper-plated welding wire SV-08G2S - it is one of the most popular and is produced by many factories in large volumes.
Thus, using low-quality wire for welding can backfire not only for the customer, but also for an overly economical or simply inattentive contractor. Welding seams filled with such wire have reduced strength and toughness. And welding equipment operates with increased wear, and the more expensive the welding machine used in the work, the more dubious the benefits of using low-quality wire seem. The protective layer of copper peels off, the wire crumbles, contaminating the internal parts of the welding feed mechanisms and clogging the guide spiral (channel) through which the wire flows to the torch. This in turn leads to production downtime and additional costs for equipment.
is part of the ITS group of companies and is one of the largest manufacturers and suppliers of welding equipment. Welding wire SV-08G2S produced at the factories of the ITS group of companies is subject to the most stringent control for compliance with technical standards. Control of the physical and chemical characteristics of the wire is carried out for compliance with GOST 2246-70 and the technical specifications of NPF "ITS" TU1211-022-11143754-2005. The control unit is every 250! kg welding wire.
Copper-plated welding wire SV-08G2S, produced at the plants of the ITS group of companies, has successfully passed all certification tests for its use on highly loaded structures and high-risk objects controlled by Rostechnadzor.
Where can I buy
Suppliers and manufacturers of Sv-08G2S wire, as well as other consumables, are collected in a separate section of our website.
Sections: Welding wire
Tags: alloyed welding wires, wire for argon arc welding, copper-plated welding wire, polished welding wire, steel welding wire
Previous: Deca Welding Wire Next: ER70S Welding Wire
Steel welding wire
Welding wire made from low-carbon steels can contain up to 0.12% carbon. Wire grades Sv-08, Sv-08A and Sv-08AA are made from boiling steel, and grades Sv-08GA, Sv-10GA and Sv-10G2 are made from semi-quiet steel. Boiling steels are prone to the formation of CO and CO2 at high temperatures. They come out of the weld pool well before the weld metal crystallizes. Wire made from mild steels is prone to pore formation, spatters more, and generally has slightly worse weld formation characteristics. Therefore, such wire can be used for gas and electroslag welding where the crystallization period of the weld is longer. This facilitates the complete release of gases to the surface.
For welding and filling gaps between edges, filler wire and rods with a chemical composition similar to the base metal are used. You cannot weld with a brand of wire of unknown composition.
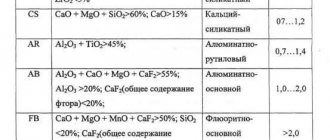
Table 2. Grades of steel welding wire (according to GOST 2246-70 standard)
| Wire | Symbol |
| Low carbon (6 grades) | Sv-08, Sv-08A, Sv-08AA, Sv-08GA, Sv-10GA and Sv-10G2 |
| Alloyed (30 grades) | Sv-08GS, Sv-12GS, Sv-08G2S, Sv-10GN, Sv-08GSMT, Sv-15GSTYUTSA (EP-439), Sv-20GSTUA, Sv-18KhGS, Sv-10NMA, Sv-08МХ, Sv-08ХМ, Sv -18KhMA, Sv-08KhNM, Sv-08KhMFA, Sv-10KhMFT, Sv-08KhG2S, Sv-08KhGSMA, Sv-10KhG2SMA, Sv-08KhGSMFA, Sv-04Kh2MA, Sv-13Kh2MFT, Sv-08Kh3G2SM, Sv-08KhMNFBA, Sv-08KhN2M , Sv-10HN2GMT (EI-984), Sv-08HN2GMTA (EP-111), Sv-08HN2GMYu, Sv-08HN2G2SMYu, Sv-06N3, Sv-10H5M |
| High alloy (41 grade) | Sv-12X11НМФ, Sv-10Х11НВМФ, Sv-12Х13, Sv-20Х13, Sv-06Х14, Sv-08Х14GNT, Sv-10Х17Т, Sv-13Х25Т, Sv-01Х19Н9, Sv-04Х19Н9, Sv-08Х16Н8М2 (EP-377), Sv -08Х18Н8Г2Б (EP-307), Sv-07Х18Н9ТУ, Sv-06Х19Н9Т, Sv-04Х19Н9С2, Sv-08Х19Н9Ф2С2, Sv-05Х19Н9Ф3С2, Sv-07Х19Н10Б, Sv-08Х19Н10Г2Б (EI-898), Sv-06Х19Н1 0M3T, Sv-08Х19Н10М3Б (EI -902), SV-04X19N11M3, Sv-05X20N9FBS (EI-649), Sv-06X20N11M3TB (EP-89), Sv-10X20N15, Sv-07X25N12G2T (EP-75), Sv-06X25N12TYU (EP-87), Sv- 07Х25Н13, Sv-08Х25Н13БТУ (EP-389), Sv-13Х25Н18, Sv-08Х20Н9Г7Т, Sv-08Х21Н10Г6, Sv-30Х25Н16Г7, Sv-10Х16Н25AM6, Sv-09Х16Н25М6AF (EI-981А), Sv-01Х23 N28M3D3T (EP-516), Sv -30Х15Н35В3Б3Т, Sv-08N50 and Sv-06Х15Н60М15 (EP-367) |
see also
Cored wire
Designations in the marking of welding wire
The marking of welding wire has a certain order, which is responsible for the data transmitted by the letters and numbers contained in the brand name. This shortens its length, making everything more compact, and helps to better reveal the necessary nuances of the content.
The first number that stands in front of all letter designations and often somehow stands out from the main mass, at least in that it stands apart, is the diameter.
Behind the number is a letter designation that reveals the purpose of the wire. There may be two options here. The first of them is “Np”, which means surfacing wire, the second “Sv” - welding wire. If there are also numbers next to these letters, then they indicate the carbon content of the material. For example, if Sv2, then the carbon content in hundredths will be 0.2%, and if Sv06, then the carbon content will be 0.06%.
Example of welding wire marking
After indicating the type of material and carbon content in it, there may also be separate letters that give an indication of the purity of the composition in terms of harmful impurities. Often such impurities are phosphorus and sulfur. In the marking these are the letters “A” and “AA”. If we look at the example of SV08, then in the absence of letters, 0.04% of the admixture content of phosphorus and sulfur is allowed, in the SV08AA brand - up to 0.02%, and in the SV08A brand - up to 0, 03%.
The following is a list of alloying elements in the composition. The following designations exist:
- M – molybdenum;
- C – silicon;
- N – nickel;
- X – chromium;
- C – zirconium;
- D – copper;
- F – vanadium;
- T – titanium;
- G – manganese;
- Yu – aluminum.
Not all letters have numbers behind them. There is a peculiar feature here. If the number does not appear, then the content of this element in the wire is only 1 percent. If there is a number after the letter, then it shows the percentage of content. For example, 2 is 2%, and 25 is 25%.
After indicating the chemical composition, one of the methods for melting the wire is indicated, which can be very important under critical conditions of use. There are the following basic designation methods:
- VI – smelting in vacuum induction furnaces;
- VD – smelting in vacuum arc furnaces;
- Ш – smelting using electroslag remelting.
If the same wire can be used for the production of electrodes, then the letter “E” is placed in the designation. If it has only one application and is used exclusively for gas welding, then no additional designation is given.
Wire with a copper-plated surface is often produced. In this case, the letter “O” is added at the end - copper-plated.
At the very end of the brand there is a GOST according to which it is manufactured. To reduce this, many manufacturers miss this point, but in full labeling all this must be present.
ASSORTMENT
2.1. The wire diameters and maximum deviations along them must correspond to those indicated in the table. 1.
Table 1
mm
| Nominal wire diameter | Maximum deviation for wire intended | Nominal wire diameter | Maximum deviation for wire intended | ||
| for welding (surfacing) | for the manufacture of electrodes | for welding (surfacing) | for the manufacture of electrodes | ||
| 0,3 | -0,05 | — | 2,5 3,0 | -0,12 | -0,09 |
| 0,5 | -0,06 | ||||
| 0,8 | -0,07 | ||||
| 1,0 | -0,09 | — | 4,0 5,0 6,0 | -0,16 | -0,12 |
| 1,2 | |||||
| 1,4 | |||||
| 1,5 | |||||
| 1,6 | -0,12 | -0,06 | 8,0 | -0,20 | -0,16 |
| 2,0 | 10,0 12,0 | -0,24 | — | ||
(Changed edition, Rev., No. 2).
2.2. For highly alloyed wire subjected to pickling, maximum deviations in diameter are allowed 50% more than those indicated in the table. 1.
2.3. The ovality of the wire should not exceed half the maximum deviation in diameter.
Examples of symbols:
Welding wire with a diameter of 3 mm, grade Sv-08A, intended for welding (surfacing), with a non-copper-plated surface:
Wire 3 Sv-08A GOST 2246-70
Welding wire with a diameter of 4 mm, grade Sv-04Х19Н9, intended for the manufacture of electrodes:
Wire 4 Sv-04Х19Н9 - E GOST 2246-70
Welding wire with a diameter of 2 mm, grade Sv-30Х25Н16Г7, intended for welding (surfacing), from steel made by electroslag remelting:
Wire 2 Sv-30Х25Н16Г7-Ш GOST 2246-70.
Welding wire with a diameter of 1.6 mm, grade Sv-08G2S, intended for welding (surfacing), with a copper-plated surface:
Wire 1.6, Sv-08G2S - O GOST 2246-70
Welding wire with a diameter of 2.5 mm, brand Sv-08KhGSMFA, intended for the manufacture of electrodes from steel smelted in a vacuum induction furnace, with a copper-plated surface:
Wire 2.5Sv-08KhGSMFA-VI-E-O GOST 2246-70
Characteristics of welding wire SV08G2S, application features and tips
To obtain a high-quality weld, it is necessary to select appropriate materials, called consumables. Welding wire SV08G2S has high characteristics in most respects and is used in many industries. Technical specifications for products are reflected in GOST No. 2246 of 1970.
Application Feature
For welding carbon, low-alloy steels belonging to group 1 with strength class up to K54. The use of this wire reduces the risk of electrode “sticking” and reduces the intensity of metal spattering. Provides the ability to work with various types of welding equipment.
| Section (mm) | ||||
| 0,8 | 1 | 1,2 | 1,6 | |
| Electrode extension (mm) | 8 – 12 | 8 – 14 | 10 – 15 | 15 – 20 |
| Recommended current (A) | 60 – 150 | 80 – 180 | 90 – 220 | 120 – 350 |
| Voltage (V) from 18 to | 22 | 24 | 28 | 32 |
Seam characteristics
- Temporary tensile strength – from 500 (MPa).
- Limit fluidity – 400 (MPa).
- Elongation (relative) – from 18%.
- Viscosity (impact) – from 50 J/cm2 (at t0 = 20 0C).
Decoding of markings
- St – for welding.
- 0.8 – percentage of carbon (and in hundredths).
- G – alloying chemical element (manganese).
- The next number “2” is its content (in %).
Delivery specifics
SV08G2S wire comes to the market, as a rule, in coils of 15 or 5 kg. However, the best option is to purchase the material in packaging (without winding on a reel) - 80, 250 kg. In this case, minimal wear on the feed system is ensured, since the wire comes out “directly”. And its cost per unit of weight is lower.
The wire can be either non-copper-plated or copper-coated (designated with the letter “O”). The latter option is subject to “hard” calibration, which reduces tip wear.
What can be replaced
In practice, it often happens that due to a lack of necessary material, in order to avoid downtime and disruption of the work schedule, it is necessary to look for a “backup” option, using one or another product with similar characteristics, the use of which will not negatively affect the quality of operations. SV08G2S wire can be replaced with samples such as “ER” 70-S or 49, OK 12-51, Novofil G3Si1 or W10.
Price
It depends on many components (section, with copper plating or not, manufacturer, volume of purchase). Approximate price – from 64 rubles/kg. For example, copper-plated wire 1.2 mm weighing 15 kg will cost about 1,450 rubles.
ismith.ru
Technical requirements
Welding wire Sv08G2S GOST2246-70 has technical characteristics:
- tensile strength 550 MPa;
- impact strength 70 J/cm2;
- yield strength 450 MPa.
Requirements are made for the continuity of the metal. Pores and chemical inclusions are not allowed.
Copper-plated solid wire is distinguished from other consumables by its positive technical qualities:
- burning resistant:
- long arc welding;
- high strength and tightness of the seam;
- easy initial and re-ignition of the arc;
- low splashing;
- long service life of tips.
Melting of copper-plated wire occurs evenly, which significantly reduces spattering . The seam is smooth, without ridges. Due to this, material consumption is almost 40% less compared to light-colored types of wire.
Classification
The characteristics by which welding wire is classified are as follows:
- purpose;
- type of surface;
- structure;
- chem. composition.
Depending on their purpose, products can be general or special purpose. Special-purpose wire is intended to perform specific work - underwater welding, welding of reinforcement, tank welding, etc. This wire has a chemical composition that simplifies the above work and helps obtain a welded joint of the highest quality.
General purpose wire is intended for welding, used in surfacing work and in the manufacture of various types of electrodes (the letter E is present in the marking).
Depending on the type of surface, the wire is produced non-copper-plated and copper-plated (the letter O is present in the marking). Copper-plated wire is used for welding structures and products made of carbon or low-alloy steel. Its purpose is to create anti-corrosion protection for the seam, as well as to promote stability of the arc. This is especially true when carrying out gas welding.
According to the structure, the wire can be solid, powdered or activated. The composition of the steel from which the wire is made is of great importance when choosing it for welding a specific grade of metal and depends on the symbol - marking. Wire designation
Chem. The composition of the steel grades from which the wire is made is specified in GOST 2246-70 and according to it there are 6 grades made from steel grades with low carbon content, 30 grades from alloy steel and 41 grades from high-alloy steel. The wire is considered low-carbon if its total content of alloying elements is less than 2.5%, alloyed if the total content of these elements is in the range from 2.5 to 10%, and high-alloyed - more than 10%. The wire has a symbol that indicates the quantitative content of various elements in its composition.
The marking consists of numbers and letters, where the numbers are the number of elements that make up the wire in %, and the letters are the name of the chemical element. Welding wire may contain the following elements:
- A (N) – nitrogen;
- B (Nb) – niobium;
- B (W) - tungsten;
- D (Cu) – copper;
- M (Mo) - molybdenum;
- H (Ni) – nickel;
- C (Si) - silicon;
- T (Ti) - titanium;
- Yu (Al) - aluminum;
- F (V) - vanadium;
- X (Cr) – chromium;
- Z (Zr) – zirconium.
A number must be placed before the marking. After it, St. is written with a hyphen. The number indicates the Ø of the wire in mm, and St. indicates that it is intended for welding. After St there are numbers indicating the amount of carbon (in hundredths of a percent). At the end of the marking there may be letters:
- A – the content of phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S) in steel is reduced;
- AA - the wire is made of metal, which has a minimum amount of P and S, i.e. the metal is purified as much as possible from these impurities.
Sulfur and phosphorus negatively affect weldability, therefore, when welding critical structures, be sure to choose wire grades with a reduced amount of them.
An example of a symbol for the most used grade of wire when carrying out welding work and its explanation:
3-Sv08G2S
Where:
- 3 – diameter in mm;
- Sv – welding wire;
- 08 – contains 0.08% carbon;
- G2 – contains 2% manganese;
- C – contains up to 1% silicon.
Sv08G2S is also used for manual arc welding, when performing surfacing work and when performing work using semi-automatic and automatic machines. It is used to weld critical pressure vessels, structures made of various steels, pipelines, boilers, etc. Solid diameter wire is available in Ø from 0.3 to 12 mm.
Decoding the brand
SV08G2S stands for as follows:
- SV – welding;
- 08 – carbon content, % – 0.08;
- G – presence of manganese in the composition;
- 2 – amount of manganese, in% – 2;
- C – the presence of silicon in the composition, since there is no number after the letter “C”, this means that the silicon content does not exceed one percent.
Reference. Manufacturers produce two modifications of wire: copper-plated and uncoated. The marking of the first variety contains the letter “O”.
Copper-plated welding wire is also in high demand, since its use results in slight wear of copper tips and an increase in conductivity, which ensures arc stability and increases the strength and durability of the weld. It is important not to confuse copper coated steel wire with all copper consumables.
Wires for welding: standard requirements and types
Standard and designation
To carry out high-quality welding work during construction or repair, welding wire GOST 2246-70 is used. It was introduced on January 1, 1973 and is currently in force with amendments and additions. It applies to cold-rolled steel made from low-carbon, alloy and non-alloy steel. Defines technical specifications, grades and classification.
The text provides examples of symbols for welding wire with interpretation. For example, welding wire Sv-08G2S–0 GOST 2246–70.
- It is designed for welding, which is designated “St”.
- It has a copper-plated surface - the letter “O”.
- The number “08” indicates a low carbon content of 0.08%, that is, low carbon.
- “G2” determines the manganese content - 2%.
- “C” - silicon, after which there is no number, this means its share is less than 1%.
- The total amount of alloying elements, that is, elements added to impart certain qualities and properties, is more than 2.5%. In this case, it is considered doped.
It is used when working with automatic and semi-automatic devices, as a rule, in ship, aircraft, mechanical engineering and construction. It is also used for gas-shielded arc welding.
Characteristics
Welding seam made by semi-automatic welding Welding wire provides reliable welding with an even and clean seam, and also fills the gap between the edges of the metal. This brand has a low content of impurities: phosphorus and sulfur. These are harmful substances, which together amount to less than 0.03%. It also contains a small amount of chromium - 0.2% and nickel - up to 0.25%. There is practically no titanium and molybdenum.
How to install a new coil of wire in a semi-automatic welding machine Its diameter can be from 0.8 to 5 mm. Copper coating - up to 0.15 mm. According to the time of tensile strength, it is divided into two groups.
According to GOST, it is rolled up, depending on the cross-section, in rectangular coils or large-sized coils weighing up to 1 ton. And in this form it is delivered to the consumer. In skeins it should be one piece and rolled in rows. The skeins are tied in three places. Each is attached with a label with the manufacturer's name, brand and batch number. For each batch of welding wire there is a certificate, which also indicates the condition of its surface, chemical composition, test result and weight.
Chemical composition
Welding wire JULI SV08G2S. Photo Welding Technologies
The chemical composition of materials for welding is determined by GOST 2246–70. In accordance with Gosstandart, the wire contains the following elements:
- carbon (C) – 0.05-0.11;
- silicon (Si) – 0.7-0.95;
- manganese (Mn) – 1.8-2.1;
- chromium (Cr) – no more than 0.2;
- nickel (Ni) – no more than about.25;
- sulfur (S) – no more than 0.025;
- phosphorus (P) – no more than 0.03.
Wire without copper coating may contain copper, no more than 0.25%. GOST allows for a nitrogen content of no more than 0.01.
Alloyed wires containing vanadium, aluminum and other elements are not produced.