Flux Welding Wire
The welding process requires not only the correct selection of consumables, which includes various types of welding wire, but also the necessary modes of the procedure, protective equipment, and so on. One of the frequently used consumables is flux. It performs protective functions and also improves the weldability of metals. Its use is almost always desirable, especially if it is selected accordingly. To simplify the selection and use procedure, flux-cored welding wire is produced.
Flux Welding Wire
This option already contains flux, which is perfectly suited to the wire material itself and the purpose for which it is used. It is worth noting that similar varieties are available in almost all types of wire, no matter what metal it is used for. Such brands perform best in automatic welding, but are used equally well in semi-automatic and manual mode. Here you do not need to choose the proportions of addition, perform any preparatory procedures, etc., since everything is immediately ready for use. This filler material is suitable for both beginners and professionals.
Flux Welding Wire
Naturally, welding wire with flux will cost more than ordinary wire. But the fact that additional materials do not need to be purchased and use becomes more convenient completely overcomes these shortcomings. Often, flux-cored welding wire is somewhat thicker due to the content of additional substances inside. Its design assumes the presence of a rod inside, which consists of flux. Thus, it can be bent, a part can be cut off, and other procedures can be performed, but the substance to improve welding will always be present, and in the same proportion.
The most widely used welding wire with flux is found in industry, joining metal structures, in automatic devices, and so on. Many experts rely on it when choosing high-quality metal processing for critical repairs. For a product to truly meet its stated quality, it must meet accepted standards. Flux-cored welding wire is produced in accordance with GOST 26271-84.
Advantages
- No additional use of flux or its calculation in a certain proportion is required;
- The welding process becomes better and the percentage of defects decreases;
- The use of wire becomes simpler and more efficient;
- Many negative nuances of difficult-to-weld metals fade into the background thanks to correctly selected additional consumables;
- The connection speeds up, since welding with flux-cored wire allows it to come into contact with the base metal faster;
- For automatic devices, this is one of the best options, which guarantees a more reliable connection;
- There is no risk that any extra elements will get into the molten seam with the flux.
Flaws
- The welding wire for submerged arc welding has a relatively high cost, so the cost of the joining process is not always profitable;
- Such varieties are not as common as standard ones;
- In some cases, the problem of poor weldability cannot be solved and additional means are still required;
- The thickness of such material is higher, which complicates the selection of the required diameter for the selected operating mode.
Physicochemical characteristics
Flux-cored welding wire for semi-automatic machines has good ductility and interacts well with the feed system on the machine. At the same time, the material has greater wear resistance, which makes it easier to move, store and contact with other surfaces. This is done to protect the flux layer from damage. Automatic submerged arc welding welding wire has a lower melting point than the base metal. The properties of the steel material make it possible to work with both low-carbon and high-carbon workpieces.
Flux Welding Wire
Improved welding properties due to selected soft metals and the presence of additional elements ensure stable arc burning when using argon arc welding. The material contains a minimal amount of hydrogen and other substances that negatively affect the condition of the seam and can cause cracks, pores and other defective elements. This results in the formation of a relatively small slag crust on the surface, so that it can be removed without problems.
Varieties
Submerged arc welding wire varies in diameter and in the base metal to which the welding will be carried out. This determines which flux will be used:
- For steel - the material is divided depending on the level of alloying, as it can be used for high-alloy steels to replace those elements that are lost during heat treatment. This also applies to stainless steel welding.
- For copper - 08 mm flux welding wire, which is designed to work with copper parts, helps improve the connection of this refractory metal at normal temperatures.
- For aluminum - when welding aluminum, flux is required, so this product will be an excellent option to do everything with the highest quality and reduce the likelihood of defects.
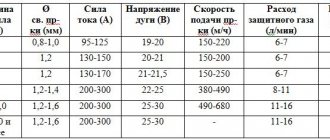
Specifications
| Parameter | Tensile strength, (MPa) | Yield strength, (MPa) | Relative elongation, % | Impact, KV cut | What gas can be used for protection? | |
| 0, degrees Celsius | -20, degrees Celsius | |||||
| Minimum value | 480 | 400 | 22 | 47 | 27 | CO2 |
| Maximum value | 580 | 490 | 27 | 120 | 103 |
Features of choice
Flux-cored welding wire 0.8 mm is used for the thinnest parts. For other procedures, 2 mm is suitable if the metal thickness is 2-4 mm. Thicker versions up to 6 mm are often used for production. When choosing, you need to pay attention not only to the diameter, but also to the composition, since this is a more important parameter. It should be as similar as possible to the base metal. There is no need to select flux, since everything is already determined automatically by the manufacturer. For private use in small volumes, it is better to buy welding wire for semi-automatic machines with flux in cassettes, and for large-scale work - in coils.
"Important!
There is flux-cored wire for welding without gas, as one of the most richly supplied with additional substances option, but for critical connections it is still better to use it in a protective gas environment or use another option.”
Welding Features
The main feature of flux-cored wire welding is the absence of lengthy preparations. The only thing that will have to be done here is to bevel the edges of the joint if the metal thickness is more than 4 mm, and also treat it with solutions if the metal is prone to forming an oxide film. Wire for automatic submerged arc welding, as well as its other varieties, has everything necessary to ensure a high-quality connection in the area for which it is used.
The main thing here is to set the feed speed correctly, since due to the presence of additional materials, the melting temperature can be noticeably lower than that of flux-free analogues and the base metal. This is well manifested due to the fact that the wire begins to melt without any problems, even when working with small thicknesses, it does not lead to burning of the metal.
Manufacturers and popular brands
svarkaipayka.ru
Which flux wire is best for cooking without gas?
The most popular brand of flux-cored wire for semi-automatic machines without gas is self-shielding wire E71T-GS. This wire ensures quick filling of the weld and greater metal transfer. However, such flux-cored wire is not very suitable for performing delicate work.
Self-shielding wire Spark E71T-8 can provide a much better quality semi-automatic weld. This is the most preferred wire option for semi-automatic machines without gas for welding body metal.
In addition to multi-passability, the wire provides low thermal impact; it can be welded in all spatial positions. Thus, it turns out that not all flux-cored wire is intended for welding without a protective gas atmosphere.
I hope the article will be useful not only to novice welders who have encountered difficulties when welding semi-automatically without gas.
Features of submerged arc welding
24.10.2017
Welding wire with flux, in accordance with GOST 8713 of 1979, is intended for permanent connection of parts made of steel and alloys with the inclusion of an iron-nickel base. Using this type of welding work, you can perform joints of any complexity. Training a specialist for semi-automatic submerged arc welding does not require a lot of time and money. The flux itself is a granular powder that, when burned, creates a protective layer of gas and slag.
Effect of protective coating
Electric arc welding under a layer of protective powder is a simple, but high-quality and reliable connection of various metal structures and parts.
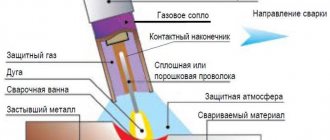
The peculiarity of submerged arc welding lies in the connection of molten metal of two parts under a layer of special granular powder. At high temperatures of the electric arc, the metal and flux melt. The film formed when the granules melt protects the weld pool from exposure to oxygen and the environment and prevents metal from splashing.
Important! A thin layer of slag appears on the seam, which allows the welded joint to cool evenly. The crust is easily removed from the surface of the seam. It is necessary to perform removal for visual control of welding quality.
To remove slag, just hit it lightly with a hammer and it will crumble. Before this, it is necessary to remove the remaining flux from the parts; it can be used at the next joint.
Working methods
To make a connection using submerged arc welding, two methods are most common.
Connection using semi-automatic welding. To ensure optimal feed speed of flux-cored wire, the welder selects the appropriate operating mode on the machine, taking into account the thickness of the metal and the type of connection. The arc is directed manually. At the same time, the wire feed speed, current strength and angle of inclination of the holder are the main factors affecting the quality of the work performed.
The automatic (robotic) welding scheme is designed for connecting butt and corner parts. In this case, the machine sets the direction of arc movement, wire feed speed and carriage travel. Such a device produces a high-quality seam at high welding speed.
One of the varieties of the automatic method allows you to weld with two electrodes at once - this is the tandem method. In this case, the electrodes run parallel to each other and are in the same plane, which makes it possible to increase the weld pool when the electric arc is instantly excited. The flux protects the seam from oxygen and ensures uniform cooling.
Types of fluxes
Each substance included in the flux is intended for welding certain metals and alloys. When choosing a brand of flux, it is taken into account whether the steel to be welded is high-alloy or high-carbon, or whether non-ferrous metals, alloys, and so on will be welded.
According to the production method, fluxes are divided into two types:
- unfused (baked and ceramic) – granules with alloying additives that ensure high quality welded joints;
- fused - with inclusions of glass or pumice.
Baked and ceramic fluxes are made by grinding a base material and combining the solution with liquid glass. They are used to add alloying additives to the weld body. Fused fluxes are made by sintering base materials.
Fluxes for seam protection are produced separately for electric and gas welding. They differ in chemical composition. Granules, which contain a certain amount of fluorides and chlorides, are intended for electric arc welding with remelting of slags with active metals. These are salt granules.
The combination of saline and oxide solutions allows the use of mixed fluxes for weld penetration of alloy steel. Oxide flux is intended for joining structural steels with a high fluorine content.
Welding wire classification
Semi-automatic welding is performed with flux-cored wire without gas to improve the quality of joining parts. The mechanical performance of the welding joint depends on the type of rods and chemical composition.
Important. Steel wire for submerged arc welding must comply with GOST 2246 of 1970 and be used depending on the material of the parts.
Wire is made from three types of steel:
- alloyed;
- highly alloyed;
- structural, low-carbon.
The cross-section of the cores, depending on the thickness of the metal, is made with a diameter of no more than 12 mm. Supplied in coils no more than 80 m long. At the request of customers, winding on cassettes or reels is possible. Steel wire should be stored in dry rooms. When rust forms, the coils are treated with gasoline or kerosene. For welding aluminum parts, the wire is made according to GOST 7871 and
16130. For this purpose, copper-plated wires are produced and most often used, which do not require processing during welding.
Features and Benefits
The advantages of semi-automatic and automatic welding under a protective layer of flux allow this type of permanent connection to occupy one of the leading places.
High level of performance
According to this characteristic, the advantage over manual welding is at least 6 times, some experts believe that it is much more. But this is not the limit; by increasing the operating coefficient of the welding machine, the amount of labor productivity increases. Another reason for achieving such results is the use of high current values during welding.
A dense layer of flux material does not allow the metal to spread, while good weld formation occurs. At higher current values, this equipment can reliably provide penetration of even thick metal without extensive cutting of edges. Therefore, productivity increases even more. The time required to clean up splashes and heavy metal spreading is reduced.
Improved seam quality
The quality of the connection increases due to the fact that the molten metal is not exposed to oxygen and other atmospheric substances. There is a wide choice of welding wire material available. By using the brand that is best suited for welding, you can obtain a weld with a homogeneous composition.
It becomes possible to give the seam an excellent shape, with the required seam leg. Thanks to the protective film that forms when the flux burns, there are no undercuts, lack of penetration, pores or cracks in the seams. Finally, there is no need to replace electrodes, so the seam is smooth and without tears.
Economical consumption of materials and improved working conditions for the welder
When welding with submerged arcs, wire consumption is reduced by up to 35%, when compared with welding with electrodes. The material is not wasted in the form of cinders and metal spattering. With this method, carbon monoxide is released in smaller quantities; the specialist’s eyes and face are not exposed to strong ultraviolet radiation, as with electric welding.
Equipment
We produce 2 types of equipment for submerged arc welding of parts. In the first type, welding wire with a thickness of no more than 3 mm is used. The design principle of such a welding machine involves self-adjustment of the arc (voltage on it), while the wire is fed at a constant speed.
The second type is equipment in which the current is automatically adjusted depending on the feed speed of the welding wires. The diameter of the electrode wire for such equipment starts from 3 mm.
We produce semi-automatic welding machines and devices for automatic welding. They produce universal machines that can be used for welding with flux-cored wire, submerged arc welding, MIG, as well as electric arc gouging. The current reaches values of 300…1500 A.
Modern automatic models are equipped with a mechanism that allows you to collect unmelted flux and send it back to the loading container. There is a seam proportionality control function. Self-propelled vehicles (tractors, suspended heads) are common in industry, allowing automatic welding of voluminous and extended structures. If the welding machine is equipped with a laser, this makes it possible to monitor the position of the electrode. Moreover, the screen can be installed at a distance of about 20 meters.
Application area
It is necessary to understand where submerged arc welding is used, which is rightfully considered one of the main methods for obtaining a permanent connection. Welding is performed in the lower position, for connecting parts end-to-end, overlapping, for corner connection methods.
Previously, the method was used only for welding metal structures made of structural steels. With the development of new technologies, it became possible to weld all types of steel and nickel alloys. For this purpose, a wire suitable in its composition is used.
Titanium and its alloys, copper and copper-based alloys, aluminum alloys and pure metal - these materials are successfully and reliably joined using submerged arc welding.
Using the submerged arc method, complex building structures, bridges, pipes, tanks, sea and river vessels are welded. It is economically profitable to use this method for sheets with a thickness of 6 mm or more.
It is important to choose the right operating mode, wire material and type of flux. The seam will be able to withstand large temperature changes and exposure to aggressive environments. A joint made by a professional will withstand very high pressure and will be reliable in conditions of complete vacuum.
Similar articles
svaring.com
Classification and labeling
All modern flux-cored wire, both domestic and imported, is divided into types according to seven characteristics:
- The purpose of the resulting connection.
- Strength characteristics of the seam (tear resistance and impact strength).
- Composition of the inner core.
- The type of protective coating formed during the welding process.
- The position in space of the parts being welded in relation to the electrode (options are possible here - only vertically, only horizontally, only in the lower horizontal plane, only in the lower vertical plane, in any position).
- The metals being connected can be steel (alloyed or not), non-ferrous metals, alloys.
- The ability to form external gas protection or not (in the latter case, a carbon dioxide cylinder is needed).
In Russia, according to a number of sources, the most popular and widespread brands are:
- ER70S-6;
- E71T-1;
- E71T-GS;
- T-8;
- T-GS;
- BlueWeld 802208;
- Forte.
If you need to connect metal made no thicker than 2 mm, 0.8 mm wire In the case where the thickness of the part is greater, but does not exceed 5 mm , use 2 mm in diameter. For really massive parts to be connected, you need to use a diameter of about 6-8 mm or more.
Depending on the material of the parts to be joined by welding, three types of wire can be distinguished:
- For welding aluminum parts. When working with this material, it is impossible to do without flux.
- For welding copper parts. The most common is 0.8 mm in diameter.
- For steel products. Involves preliminary preparation of the connection site.
Welding flux-cored wire for semi-automatic machine
When performing semi-automatic welding without gas, flux-cored wire is widely used.
Flux-cored welding wire
This allows you to increase work productivity, reduce the time required to form a seam and, as a result of welding, obtain a reliable and high-quality connection.
Features of flux welding semi-automatically without gas
When welding stainless steel products with flux wire, the connection is made without splashing drops of metal, and the crust obtained during the operation of the semi-automatic machine reliably protects both the arc and the metal from the harmful effects of the atmosphere.
In order to cook stainless steel products semi-automatically without using gas, use flux-cored wire of the following diameters:
Not all flux-cored wires are suitable for welding without gas.
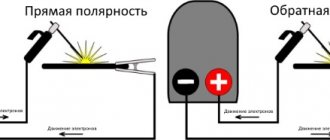
There can be several problems when flux-cored wire does not cook without gas. Firstly, this is an incorrect connection of the semi-automatic device, we are talking about polarity. With direct polarity, the minus is connected to the burner, with reverse polarity, the plus is connected. This is, firstly.
Secondly, in fact, not any flux-cored wire can be used to cook without gas. Yes Yes exactly. A salesperson in a store can tell you anything to make you buy his product quickly. However, in fact, when you come home and start cooking with flux-cored wire, you may encounter exactly the same problem that was mentioned above.
What do you need to know? There are two classes of flux-cored wire - self-shielding and for gas-shielded welding. That is, in simple words, even if it is flux-cored wire, gas may still be required for a semi-automatic device. It is for this reason that semi-automatic welding without gas, using wire alone, may not work.
For welding without gas, you need a special flux-cored wire marked S. The marking of flux-cored wire for gas welding is almost the same, but only with a different letter at the end, for example: FCAW-G, that is, “gas-shielded.” In simple words, such flux-cored wires require an external gas environment when welding, and nothing else.
Flux Wire Welding
Welding in a ceiling position is a process that is accompanied by a certain technology. You can make seams in this position using several methods of electrode movement, a certain current strength, specific types and methods of welding. This article describes how to weld a ceiling seam.
Strict requirements are imposed on the assembly of pipelines of any type. Depending on the purpose and metal, different welding methods are used, different types of pipe joints are used, etc. In this article we will provide general information on the assembly and welding of different types of pipelines.
In this article we will talk about cutting metals with gas. Namely, we will dwell on what gases are usually used and what types of burners exist. Let's talk about the features of oxygen cutting of metal: what materials it is suitable for, how it is carried out, etc.
stalevarim.ru