Features of the use of cored wire
Welding with it is often used when installing large metal structures in unusual conditions (for example, at a height or, on the contrary, underground). Despite the fairly high quality of the seam, it is not suitable for welding highly loaded joints and pipes designed for significant operating pressure.
Flux-cored wire for semi-automatic machines has a wide range of grades - they differ in sheath material and powder composition. This must be taken into account when welding different metals or their alloys. Each of them requires its own variety.
Another feature of working with it is to set straight polarity on the semi-automatic welding machine before starting work. Since this is usually done by switching the terminals inside the device body, it is also worth calibrating the pressure rollers that ensure the supply of consumables from the reel.
The rollers should press on it with just enough force to ensure its movement and fixation. Any deformation by pressure rollers is unacceptable - this will lead to damage and jamming of the wire in the cable channel of the semi-automatic welding machine.
And finally, you should take care of the burner tip. Before the flux-cored wire for a semi-automatic machine appears when fed from the torch, the tip must be unscrewed. And only after it comes out, screw it back on, but without the nozzle. Since gas is not supplied, there is no need for a nozzle.
The main thing is to choose the optimal ratio of the diameter in the tip and the thickness of the supplied electrode - they should be as close as possible, but not coincide. It is recommended to coat the tip itself ahead of time with a special substance that protects against the adhesion of drops of melt and slag.
Let's sum it up
The wires used for semi-automatic welding are made of metal if we are talking about shielding gas. They can be made of flux, which will work in a similar way to gas.
The use of such wires will result in poor-quality seams. But sometimes powder additives are indispensable in work.
In many cases, the technician is unable to move the large device. If metalworking is carried out in a difficult location, then cored cables will be indispensable.
Even though there are pros and cons to this wire, sometimes they are not comparable to other materials. If you have had experience working with such wire, then write about it in the comments. We wish you success in your work!
Primary requirements
All its varieties must meet four groups of requirements:
- When melting there should be no significant spattering, and the melting process itself should be uniform;
- The electric arc between the workpiece and the electrode (which is the tip of the wire protruding from the torch) should occur without difficulty and be stable. A draft and even wind should not be a hindrance for her.
- The slag formed during work should be distributed evenly and not penetrate deep into the seam. It should come off easily from the metal.
- The seam itself, with the usual qualifications of the welder, should be smooth, without pores or cracks.
Total information
The core cable is considered an empty tunnel that is produced from metal. There may be flux inside it, which is combined with metal powder. You can work with this type of wire if we are talking about semi-automatic equipment without using gas.
If the wire is made in the CIS countries, it is needed for a certain steel. We are talking about durable black metal and low carbon options. There are fewer other types.
The cable may have a specific function, or be ordinary. Wire is an impurity matter. You can work with them when there is metalworking in any workshop type of welding. Common wires are used in factories and for everyday purposes.
The cored wire works so that the arch ignites easily and burns stably. In this case, the cables melt slowly and there is no spattering.
Slag separation occurs in the inner part of the wire. It comes off easily when you need to clean the surface. To do this, it is important to reduce the temperature of the part. The connection will be smooth if you already have experience working with a welding inverter.
Operational Features
As already mentioned, it is used to weld metals with direct polarity.
- Straight polarity means that the positive contact of the welding machine is connected to the workpiece itself with a ground cable, and the negative contact is connected to the electrode via a welding cable
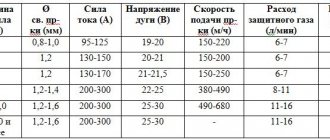
In the settings of the welding machine, the minimum feed speed and operating voltage are set. For example, when using a 1.2 mm diameter, the optimal feed speed would be 2 meters per minute and the voltage would be 14 V.
It is common for her to form a thick slag layer on the seam made. If the seam is planned to be multi-pass, then this slag must be carefully removed with a metal brush and hammer.
In general, according to reviews, the seam is almost always quite rough, has large scales and sagging. If the welder acts carelessly and hastily, lack of penetration may occur. This is virtually inevitable when working with an intermittent electric arc.
How to use cored wire
If you have once worked with natural welding using electrodes, then the new method will not bring difficulties for you. Powder additive is similar to conventional metalworking using electrodes. In this case, flux is used.
You can work in several ways. It is possible to feed wires independently, as well as to hold them in your hands. Another option is that you place the wires in the device and make the process simple.
9 times out of 10, when working with cored wires, you need to use static current and the opposite polarity. Certain cable models require the use of active current.
Types of cored wire
Flux-cored wire for semi-automatic machines is divided into four types according to the nature of its design:
- simple tubular shape;
- with one bend of the shell;
- with two shell bends;
- two-layer.
Its overall dimensions vary in a wide range of diameters - from 0.8 mm to 2.5 mm.
A simple tubular one can have slight nuances in its design - it can either be seamlessly drawn from one piece of metal, or bent from a sheet of metal into a cylinder with a butt joint. There may also be an overlap connection between the workpiece and the shell.
A special powder is evenly placed inside the wire. Its composition may vary depending on the purpose of the parts being welded and the characteristics of their further operation.
In general, the powder consists of ferroalloys, minerals and other chemicals of complex composition. In any proportion, they create a protective layer of neutral gas that separates the melt from atmospheric oxygen. In addition, the gas released by the powder:
- alloys;
- deoxidizes;
- stabilizes the electric arc;
- simplifies the formation of a uniform seam.
Depending on the composition of the powder, self-shielding wire for semi-automatic machines is divided into types:
- Fluorite;
- Fluorite-carbonate;
- Rutile;
- Rutile-fluorite;
- Rutile-organic.
All of the above types have self-protective properties. To weld with them, there is no need for an additional carbon dioxide cylinder.
Pros of work
The first thing you need to know is that you can operate a semi-automatic without using gas. A cylinder operating on a gas installation is not needed. The wire is intended for metalworking without gas.
It contains fluxes in its interior. When the wire burns, it comes out into the outer part of the apparatus. In this case, a cloud appears that has the characteristics of gas compounds.
With this technology, metal processing is possible in any location, even in hard-to-reach ones. Do not transport heavy cylinders. The only thing you need to do is thread the wire into the machine and feed it into the weld pool yourself.
Features of welding technique
Fundamentally, welding using it does not differ from welding using widely used consumable electrodes. The formed weld seam is clearly visible throughout the work, which facilitates application in several stages.
- A feature of flux-cored wire is the intensive formation of slag covering the seam. It is recommended to clean it immediately after formation with a suitable tool (for example, a wire brush). Otherwise, there is a risk of slag getting into the working area and, as a result, the appearance of defects and a decrease in mechanical strength
Due to the peculiarities of the technology, the seam formed is inferior in strength to that created using consumable electrodes. Therefore, to prevent an even greater decline in quality indicators, you need to carefully adjust the feed rollers before starting work. This will stabilize the feed and eliminate accidental deformations, jams and breaks.
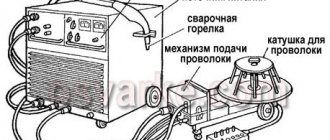
Working with a semi-automatic machine
Semi-automatic welding machines have long ceased to be a technical novelty. They migrated from the professional environment to the everyday environment. The popularity of MIG and MAG machines is due to the fact that to work with them, the requirements for welding skills are minimal. Knowing the correct current and wire feed speed settings makes it easy to get a quality connection.
Semi-professional devices are inexpensive compared to professional ones and are available to those who want to do the repairs themselves. But there is a drawback that minimizes the use of these devices - a heavy gas cylinder.
The welding process takes place in a protective environment. Inert gases are used as it: argon, helium, carbon dioxide. Their choice depends on the metals being connected. Structural steel grades are most often welded. They use carbon dioxide. It is pumped under a pressure of 55 atm. in a cylinder whose weight is more than 60 kg. Therefore, this type of welding has a number of disadvantages:
- The need for periodic refilling of cylinders. Gas stations are not located in every locality.
- Low mobility. To transport gas cylinders, a special device is required.
- Once every few years, the cylinder needs to be re-examined, which incurs time and financial costs.
It is possible to weld with wire without carbon dioxide, but the quality of the connection will be very low. When working at low currents, the wire will stick to the surface because the welding arc will be unstable. At high current, the weld pool will spatter and the seam will become porous.
A solution has been found: enclose powdered flux inside the semi-automatic welding wire, which, when melted, will create a protective environment. In terms of its external parameters, such wire does not differ from ordinary wire and is suitable for working with the drawing mechanism of the device.
Technology and some of its disadvantages
Flux-cored welding wire is welded on semi-automatic machines and used on automatic lines. The consumable material is fed into the welding zone at a constant speed. The arc heats the bath and distributes the melt evenly in a non-contact manner - without touching the edges of the parts being joined.
The welding process is carried out using alternating current, the polarity is reversed. The quality of the seam complies with GOST 26271-84. Uniform wire feed and a stable arc allows you to make any seams of complexity, position and length without joints. Productivity is 2–4 times higher than when working with solid wire.
PPs are excellent at welding parts, but they also have disadvantages:
- relatively high cost;
- narrow specialization of each brand of consumables;
- it is difficult to weld sheets up to 1.5 mm thick;
- low viscosity and ductility; when bent, the wire breaks;
- feeding is carried out by special rollers with reduced compression only;
- Only the pulling mechanism on the handle is used.
When welding with self-shielding wire, the weld pool is difficult to see under the submerged arc. The cost of powder welding is justified when making long seams. When welding short sections, a lot of waste is left.
The use of flux-cored wire on semi-automatic machines significantly increases the productivity and quality of the seam. For home use with a small amount of work, it is expensive. In workshops and production, where you need to weld well and quickly, you can get by with the efforts of welders with low grades, without inviting expensive specialists.
Is welding possible without gas?
Semi-automatic welding requires inert (or carbon dioxide) gases, melting filler wire and flux. This technology is called MIG/MAG.
With its help, working welders obtain strong connections, the quality of which cannot be complained about. Manual electric arc welding (MMA) produces this effect with difficulty.
But the first option includes many details: a gas environment, the semi-automatic device itself and wire. The last two elements cannot be excluded, but without the first one a seam may turn out.
The main disadvantage of MIG/MAG is the gas. The cylinders with it are large and difficult to carry. In places where there is little space or there is no stable platform for work, there is no place to install a gas supply system.
If there is a lot of material for soldering, the cylinders need to be changed or refilled, but in hard-to-reach places this is not easy due to the fact that the refill cannot be carried with you along with all the other equipment. Is it possible to refuse the gas environment in these cases?
Welders believe that they can do the job in the same way as with gas, but without the latter. They decide that a semi-automatic machine with filler wire will make good seams without the influence of gas.
But will they be as dense and neat as those obtained in a gaseous environment? Let's tell you further.
Principles of classification
According to the shape of the shell, tubes made of metal sheets are distinguished:
- round, with edges joined end-to-end;
- with lock-type bends;
- multilayer.
According to the use of a protective environment, a distinction is made between PP - gas-protective, flux-cored wires for welding in a gas environment and PS - self-protective, which does not require additional consumables.
In addition to indicating the type of wire, the marking uses a letter designation of the spatial position of the seam, which is performed with this electrode.
Steel grades are not reflected in the markings ; they must be looked at in the technical specifications for each type of cored wire.
Gas-protective
The gas shield wire requires covering the top of the weld pool. For this, argon or other inert gas is used. Used for welding carbon and low-alloy steels . It has positive technical characteristics and advantages over other electrodes:
- stable arc;
- slag easily comes to the surface;
- no porosity;
- low spatter;
- the slag is easily separated.
PP is characterized by deep penetration. It is used to create butt, corner and overlap joints when creating metal structures and pipelines .
Self-protective
Self-shielding wire for a semi-automatic machine is suitable for working in any spatial position of a seam in field conditions. It does not require any additional consumables. During operation, a cloud of molten gas-forming charge forms above the bath. An even layer of flux is applied to the seam, completely covering the hot joint in a wide strip.
PS is used for welding outside equipped places , outdoors for welding alloy steels, stainless steel, non-ferrous alloys and cast iron. And also for soldering various parts made of aluminum and its alloys. Stainless steel is welded with electrodes containing a high content of chromium, nickel and ferromanganese in the core.