If you need to carry out welding work yourself, the question arises: what type of welding machine to purchase. Welding is the creation of permanent connections between welded parts at the atomic level. The welded connection is one of the strongest and therefore is used quite often.
During electric welding, heating and melting of the metal occurs due to the formation of an electric arc between the end part of the electrode and the surface to be welded. Sources of arc formation and maintenance are divided into several types:
- Transformer.
- Inverter.
- Rectifiers.
- Welding units based on internal combustion engines.
Let's consider two types that are most widely used: a welding machine based on a transformer and an inverter source of electric arc.
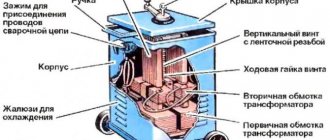
Transformer welding machine
This is the simplest of welding machines that uses alternating current. It works using a transformer that regulates the mains voltage to the welding voltage. Transformer or induction welding machines are divided according to the following criteria:
- Power (the greater the welding current, the thicker the metal it can be processed).
- The number of posts, that is, jobs (how many people can work at the same time).
- Voltage (single-phase or three-phase network).
Its advantage is a simpler and more reliable design, low cost, and high maintainability.
Transformer welding machine
The disadvantages include the dependence of the arc on power surges, large weight and overall dimensions, and strong heating during work.
Why is an inverter more expensive?
No matter how stupid it sounds, an inverter air conditioner has an additional component - a voltage inverter. It is responsible for the speed of the compressor. The more filling there is in a technique, the more expensive it costs.
The operation of a voltage inverter is based on switching a constant voltage source to periodically change the polarity of the voltage at the load terminals. The switching frequency is set by control signals generated by the control circuit (controller).
Article about Voltage Inverters on Wikipedia
The main difference in the structure of conventional non-inverter models from inverter ones is the presence of a voltage inverter. Without it, it is impossible to regulate the operation of the compressor. In simple words, the principle of operation can be explained as follows:
In conventional split systems, the signal from the temperature sensor is processed by the air conditioner control board. It gives a signal when to turn on or turn off the compressor.
In inverter models, the control board responds to the temperature sensor readings. It calculates at what speed the compressor should operate and what voltage is needed for this. The board gives a command to the inverter, which converts standard 220V into the required voltage. The speed of the compressor depends on the voltage applied to it. The smaller it is, the lower the speed.
What is an inverter?
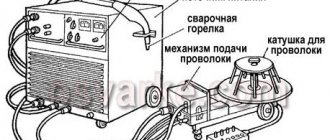
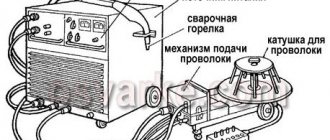
An inverter welding machine or simply an inverter is one of the energy sources for electric arc welding, which is based on the use of high frequency current . Its operation is carried out by power electronics and a small transformer.
Inverter welding machine
Its advantages are considered to be low energy consumption, compactness, low weight and size, and fairly high quality seams.
The negative aspects of the inverter include the relatively high cost, fear of moisture, dust and low temperatures (typical of budget models), sensitivity to voltage surges, and expensive repairs.
What is a welding inverter?
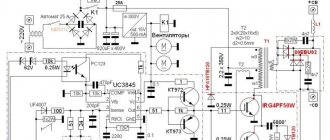
This type of welding machine is characterized by the ability to convert direct electric current into alternating current. This unit contains the following main components:
- rectifiers - network and frequency;
- filter;
- frequency converter - the inverter itself;
- transformer;
- Control block.
This is how a welding inverter works.
Alternating current from the electrical network, which has a frequency of 50 Hz, is supplied to the network rectifier. After this, the current is correspondingly rectified and then smoothed through a filter. Next, it is fed to an inverter, in which it is converted into an alternating voltage with a high frequency - approximately several tens of kHz. Then, through a transformer, the current voltage is reduced to a level of about 50-60 V, while its strength increases to approximately 100-200 A. Then the current is rectified using a frequency rectifier - already during the arc welding process.
The frequency converter - inverter - can be adjusted by the welder, thereby ensuring optimal operating parameters of the unit. To do this, another functional element of the inverter welding machine is used - the control unit.
Main advantages of inverters:
- low weight and dimensions;
- high energy efficiency of welding;
- high welding precision.
- units in many cases require special storage conditions - in terms of temperature, air humidity;
- sensitivity to low temperatures;
- high price, high cost of maintenance and repair.
What do an inverter and a transformer welding machine have in common?
The similarity of these devices in their purpose is the formation and maintenance of an electric arc. But there are still some points that unite them:
- The devices under consideration are united by the presence of a transformer, but of different sizes. Due to the preliminary receipt of high frequency current, inverters do not need to use large transformers. To obtain a current of 160 A, a transformer weighing 0.25 kg is needed. To obtain the same current in inductive devices, a transformer weighing 18-20 kg is required.
- Possibility of smooth current adjustment. Transformer devices have this opportunity due to changing the size of the air gap in the magnetic circuit.
- The devices are powered from a household (220V) or industrial (380V) network.
- Most welding machines have short circuit protection.
What is the difference between an inverter and a welding machine and what characteristics are important
Today, inverters are increasingly used for welding work. Their production and sales are growing, and their use is becoming commonplace. Inverter welders today can be found in a small workshop, a large industrial enterprise, a construction site, or simply in a private home. What are their differences from ordinary (transformer) welding machines? Let's look at six parameters that are important for any device, and how the inverter differs from traditional devices in these parameters. We especially note that Resanta welding machines are sold at the link https://www.avtogen.ru/svarochnye_invertory/brand-is-resanta/, look at the prices.
What is the difference between an inverter and a transformer source of electric arc?
- The dimensions and weight of a transformer-type welding machine are larger than that of an inverter. Industrial designs can weigh more than one hundred kilograms.
- Operating principle. In the inverter, the alternating current of the network is converted by the primary rectifier into direct current, then again into high-frequency alternating current and then again changes to direct current at the secondary rectifier. In transformer-type welding machines, the current strength changes due to changes in the position of the magnetic core, that is, the core of the step-down transformer or the inclusion of a different number of turns of windings in the circuit.
- The inverter has a more stable arc due to the stability of the welding current, which affects the quality of the seam.
- The difference is in the design. The inverter is more complex and can be equipped with the following additional functions: HOT START - increasing the initial current to improve ignition of the welding arc. ARC FORCE - increasing the welding current to speed up the melting process and prevent sticking, that is, the arc is forced. ANTI-STICK – reduction of current when the electrode sticks to increase the time it takes to tear it off and protect against overload.
- The process of learning to work on a transformer is more complex and time-consuming. However, having mastered these skills, you can easily work on an inverter.
- The inverter produces direct current, the transformer operates on alternating current with a household power supply frequency of 50 Hz.
- The power factor of the inverter is the highest of all welding equipment, and the efficiency exceeds transformer analogues by 20-30%.
- Wide range of welding current changes.
- The inverter has such an indicator as the intermittency coefficient (IC). It determines the time of continuous operation at maximum welding current. That is, if the CP is 50%, then after 10 minutes of operation it needs 5 minutes to cool down. Such requirements are not imposed on a transformer welding machine.
- Possibility of using electrodes designed for both direct and alternating current.
Today there is a fairly wide selection of welding equipment on the market from various manufacturers. The choice of welding machine should be made based on the tasks that will be performed with its help.
Repair and constructionComment
Transformer or inverter: which is better?
So now you know what a transformer and an inverter are and what are their differences. At this stage, you probably have a question: “Which welding is better, an inverter or a transformer?” We'll disappoint you, but there is no short answer. Because there are many nuances. But first things first.
First of all, a transformer and an inverter are two completely different devices. They have different devices, different operating principles, and different configuration methods. Even the dimensions and weight differ.
Inverters are more beginner-friendly because they come with additional features that make welding easier. But at the same time they are less reliable and not powerful enough. Transformers are difficult to master, and here the quality of the seam directly depends on the selected settings and the skill of the welder himself. But they are much more powerful and provide you with more opportunities in the future.
A simple conclusion follows from this: transformers are necessary for those who seriously want to master welding, but are not ready to spend a lot of money on a powerful inverter. A transformer for a relatively low price will give you much more options than a household inverter. But you will have to spend a lot of time studying the theory of setting up such a device.
But the inverter will appeal to all summer residents and garage craftsmen who need to weld something up a couple of times a year. They don’t want to spend a long time figuring out the settings and fiddling with transporting the device. But to get a more powerful device, they will have to buy an expensive professional inverter or the same transformer.
What about rectifiers?
Experienced craftsmen have probably noticed that in this article we did not talk about another interesting type of welding equipment. We are talking about rectifiers. Many beginners have not even heard of such devices, although a rectifier may be an ideal option when choosing a first welder.
A rectifier is in many ways similar to a transformer. It is just as bulky and powerful. But there is one key difference. The fact is that the transformer welding machine uses alternating current. Hence there are many difficulties with igniting the arc and making a seam. The rectifier does not have this drawback. It, like the inverter, welds using direct current. Therefore, it is easier for a beginner to light an arc and generally operate the device.
Most rectifiers are also designed for manual arc welding, so you won’t have any problems with this. A rectifier is as reliable as a transformer because it contains rare electronic components. Not a single cheap household inverter can compare in reliability with a rectifier or transformer.
That is why, asking the question “Which is better: a welding transformer or an inverter?” remember the rectifier. This is an excellent device for both beginners and practicing masters.
Differences between an inverter air conditioner and a conventional one
Longer service life . The compressor does not experience stress when turned on constantly. It wears out more slowly, and this is the heart of any air conditioner.
Costs more . An inverter split has an additional unit - an inverter. Accordingly, it cannot cost the same as a regular, non-inverter model. But the price gap is narrowing every year.
Less electricity consumption . An inverter air conditioner does not have the starting currents required to start the compressor. They can significantly affect energy consumption. The COP of inverter air conditioners is higher due to the size and volume of the evaporator and condenser.
Precise temperature maintenance . Indoor temperature will fluctuate between 0.5-1 degrees. For start-stop systems, this range is within 2-4 degrees.
Few people will tell you about this
Small temperature changes are not noticeable. But your body reacts to them. If it gets a little cooler, your metabolism speeds up and your body begins to produce more heat. If it gets warmer, the processes slow down, but not immediately.
It's a little stressful, but still stressful. It is generally harmless, but in some people it can cause fatigue, malaise, and decreased vitality. If you are weather dependent, or have small children in the family, start-stop air conditioning is a bad option.
Fast heating and cooling . When turned on for the first time, it warms or cools the room faster than a regular on/off air conditioner.
There are no power surges in the network . To turn on the compressor of a non-inverter air conditioner, a high starting current is required. Because of this, there may be voltage drops; it can drop to 170V. The inverter system starts the compressor only once when turned on.
Expensive repairs . It takes more time to determine the breakdown. Some spare parts are difficult to obtain and are expensive. Repairs should be performed by a professional who is familiar with electronics.
Wide operating temperature range . When a conventional air conditioner cannot cope, an inverter air conditioner can work. At the same time, its COP will always be greater than 1. It will produce more heat or cold than it will consume electricity.