Welding inverter device
Until recently, the inverter device was quite simple in terms of operation. Over time, engineers added electronics to it, which increased the functionality of the unit. The most interesting thing is that this does not make the price of the welding inverter higher. As the sales trend shows, it is gradually decreasing, which makes everyone happy.
Attention! The term "inverter" does not refer to the welding process. This is not a technique. This is the power source of the device.
What is the operating principle of an inverter-type welding machine?
- It operates from an alternating current network with a voltage of 220 or 380 volts and a current frequency of 50 Hz. Plugs into a regular outlet if we are talking about a household welding inverter.
- The welding current entering the inverter passes through the filter, where it is smoothed out and becomes constant.
- The resulting electrical energy passes through a block of transistors (with a high switching frequency), the result is again alternating current only with a higher frequency - 20-50 kHz.
- Next, the current voltage is converted, it is reduced to 70-90 volts at the inverter output. According to Ohm's law, a decrease in voltage results in an increase in current. At the output (at the end of the electrode) there will be a current equal to 100-200 amperes. This is the welding current.
It is the high frequency of current that is the main technical solution in inverter welding machines. It allows you to achieve maximum advantages over other power sources for the electric welding arc. In inverters, the current required for welding is achieved by changing the high-frequency voltage. In conventional welding transformers, this process occurs due to a change in the electromotive force (EMF) of the induction coil, which is the main part of the transformer.
It is the preliminary conversion of electricity that allows the use of small-sized transformer units in inverters. For comparison, we can give the following example. If you need to obtain a current of 160 amperes at the output, then for this you will need to install a transformer weighing 300 g in the inverter. The same current at the output of conventional welding transformers will be obtained if a transformer with a copper wire (coil) weighing 20 kg is installed in it.
Why is this happening? The main element of a transformer-type welding machine was the power transformer itself with primary and secondary winding coils. It was the coil that made it possible to reduce the alternating voltage and obtain high currents at the output of the second winding, suitable for inverter welding of metals. A dependence appears from the voltage drop to the current increase. In this case, the length of the copper wire on the secondary winding decreased, but its diameter increased. Hence the large dimensions of the welding machine and its heavy weight.
Recommended for low power conditions
Conventional models of welding inverters operate reliably in the voltage range from 190 to 240 volts. For markets in developing countries and special operating conditions, leading equipment manufacturers offer specially modified inverters that can operate at lower input voltages. Which inverter is better? When choosing a device, you need to pay attention to the following parameters and features:
- sufficient input voltage range for the area of use;
- Wide range of operating current settings;
- stability of open circuit voltage;
- “hot start” and “anti-stick” options;
- operating temperature range suitable for the climate zone;
- possibility of long-term continuous operation.
A number of models meet these conditions.
Fubag IR 200
The first unit is presented by a well-known German company with factories in China. The new product works stably with electrodes with a diameter of 1.6-5 mm when the voltage drops to 150 volts. Operating current range: 5-200 amperes. The device is equipped with a hot start and arc stabilization option. Retains performance from -10 to +40°C.
Svarog ARC -160
The simplest and most reliable low-power model of a well-known brand is compact and provides a stable arc with input fluctuations from 160 to 245 volts.
The output current adjustment range is 20-160. The device is equipped with a hot start and is capable of working with both conventional fusible electrodes and infusible tungsten electrodes. The disadvantages include the short duration of continuous operation: 40% of the total time.
Interskol ISA 160
The third model also has low power, the current varies from 20 to 160 amperes.
During testing, it showed stable operation at a minimum supply voltage of 155 volts. The device has a hot start, anti-sticking and forced arc mode, as well as a stable open circuit voltage. Can work without interruption thanks to an efficient cooling system.
Aurora PRO Inter 200
This new product stands out for the capabilities of its stabilizer and PFC unit.
The test confirmed the ability to cook effectively even from 140 volts. In this case, the operating current develops from 20 to 200 amperes. Supports work with a 100-meter extension cord if the wire cross-section is 2.5 mm2 or more. Can work continuously up to 60% of the total time. All of the listed models are compact and modest in weight, not exceeding 8 kg . Of course, when working at the lower limit of the supply voltage, you should not rely on the maximum welding current and 5 mm electrodes.
But 1.6 and 2 mm will cook stably, without sticking and annoying burns of thin workpieces and small parts. During prolonged operation, wear and tear on the parts and components of the device's power supply will increase.
It is also important to consider the reputation of the manufacturer . Little-known companies that have recently appeared on the market often offer their products at a low price compared to well-known brands. At the same time, they promise miracles that contradict the law of conservation of energy, for example, operation at an input voltage of 90 volts. This can only mean one thing: a clear example of false advertising. In this case, the input voltage will be close to the output voltage, and no matter how much it is converted, it will not be possible to maintain the required current parameters.
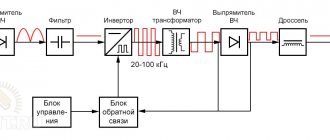
Schematic diagram of the inverter apparatus
In inverter-type welding machines, the opposite is true: they are small in size and weight. But how to obtain high-frequency voltage if its frequency in the network is only 50 Hz? The basic inverter circuit of the device, which consists of powerful transistors, comes to the rescue. They can switch with a voltage frequency of 60-90 kHz.
But for transistors to work, a constant current is required. It is obtained through the use of a rectifier. This block is a combination of two elements: a diode bridge, which rectifies the alternating voltage of the network, and filter capacitors, with the help of which smoothing occurs. The output of the rectifier produces a constant voltage of more than 220 volts. This is the first stage of voltage and current conversion.
The resulting voltage is the power source for the operation of the entire circuit of the device. And since powerful key transistors are connected to a transformer (step-down), they will switch at a high frequency. Accordingly, the welding unit itself will operate at such a high frequency. For all this to work (transform), it is necessary to install a large number of additional elements into the circuit.
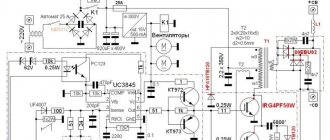
To understand the circuit diagram of a welding inverter, you need to consider any model.
Additional functions of inverter welding machines
The presence or absence of service functions is not critical, but it makes life a lot easier, especially for a beginner. Their set is usually standard:
- “Hot start” HOT START - affects the ignition of the arc. When igniting, an additional impulse is given, which makes it easy to start welding.
- “Arc Force” - ARC FORCE - when the electrode suddenly approaches the metal, the welding current automatically increases. This prevents the electrode from sticking.
- “Anti-stick” - ANTI STICK - turns off the power when the electrode gets stuck, turns it on after it comes off. A convenient function, especially relevant for novice welders.
There are some other useful features. For example, indication and automatic shutdown when overheating. This is a useful addition - it is not always possible to keep track of the time or the overheating indicator. Automatic shutdown saves you from burnout and expensive repairs.
A welding machine for manual electric arc welding allows you to weld almost all metals, except non-ferrous ones
Pay attention to the package: in addition to the welding machine, there is usually a power cable (sometimes it is removable, sometimes it is stationary), two welding cables - one with a clamp for attaching to the part, the second with an electrode holder. It is better if the cables are light, flexible and long. But such luxury is not always available. More often, working cables are about 2 meters long, which is not always convenient. When looking at the cables, pay attention to how they are terminated, soldered (preferably) or clamped/rolled.
Pay attention to the warranty period, as well as how close the nearest service center is to your home/dacha. The lack of a service network is an alarming sign. This means that even if there is a warranty breakdown, you will have to repair it yourself, for money. You won’t send your device for repairs across half of our rather large country...