Tool steel is an alloy or carbon steel intended for the manufacture of cutting and measuring tools, cold and hot deformation dies, and machine parts that experience increased wear under moderate dynamic loads.
In terms of shape, size and maximum deviations, metal products meet the requirements:
- hot-rolled round steel - GOST 2590-88;
- hot-rolled square steel - GOST 2591-88;
- hot-rolled hexagonal steel - GOST 2879-88;
- forged square and round rods - GOST 1113-88;
- stripes - GOST 103-76, GOST 4405;
- calibrated rods, coils - GOST 7417, GOST 8559, GOST 8560 of h11 and h12 qualifications;
- rods with special surface finishing - GOST 14955 grades h11 and h12.
Tool alloy steel GOST 5950-2000
Alloy steel is steel into which, during the alloying process, special elements are introduced in certain quantities to provide the required properties. Such elements are called alloying elements. They can increase the strength and corrosion resistance of steel and reduce the risk of brittle fracture.
Alloying of steel can be carried out at various stages of metal production and consists of introducing alloying elements into the melt or charge. During the alloying process of steel, the introduced elements can form special chemical compounds with the steel base. Such intermetallic, carbide and nitride elements have high hardness and strength, chemical resistance, heat resistance, etc. Uniform distribution throughout the entire volume of the solid solution and a sufficient amount of these elements in the steel give the metal the necessary properties when alloying steel.
The following chemical elements are used to alloy steel: manganese (Mn) - G; silicon (Si) - C; chromium (Cr) - X; nickel (Ni) - H; copper (Cu) - D; nitrogen (N) - A; vanadium (V) - F; niobium (Nb) - B; tungsten (W) - B; selenium (Se) - E; cobalt (Co) - K; beryllium (Be) - L; molybdenum (Mo) - M; boron (B) - P; titanium (Ti) - T; aluminum (Al) - Yu.
Pure metal elements are not usually used when alloying steel. More often, ferroalloys (iron alloys) and alloys (auxiliary alloys) are used for alloying steel. This is more economical and allows one to avoid a number of technological difficulties in the process of steel alloying.
GOST 5950-2000 regulates the standards for the production of rods, strips and coils of hot-rolled, forged, calibrated and with special surface finishing from tool alloy steel, as well as the standards of chemical composition for steel 3Х2МNF, 4ХМНФС, 9ХФМ, ingots, billets, strips, pipes, forgings and other metal products.
Classification of alloy steels
By the number of alloying elements:
- highly alloyed - the total mass of alloying elements is more than 10%;
- medium alloyed - the total mass of alloying elements is more than 2.5-10%;
- low-alloy - the total mass of alloying elements is up to 2.5%.
By purpose:
- I - for the manufacture of tools used for processing metals and other materials in a cold state;
- II - for the manufacture of tools used for metal forming at temperatures above 300°C.
According to the method of further processing:
- a - hot-rolled and forged metal products for hot forming and cold drawing without control of structural characteristics;
- b - hot-rolled and forged metal products for cold machining with a full range of tests.
By quality of workmanship:
- regular;
- high quality - A.
By quality and surface finish:
- hot-rolled and forged: 2GP - for subgroup "a", 3GP - for subgroup "b" of improved quality, 4GP - for subgroup "b" of ordinary quality;
- calibrated - B and C;
- with special surface finishing - B, D, D.
By manufacturer:
- — EI;
- Zlatoust Metallurgical Plant - ZI.
Alloy tool steel grades
Grades of tool alloy steel of group I: 13Х, 8ХФ, 9ХФ, 11ХФ (IH), 9ХФМ, Х, 9Х1, 12Х1 (120Х, EP430), 6ХС, 9Г2Ф, 9ХВГ, 6ХВГ, 9ХС, В2Ф, ХГС, 4ХС, ХВСГФ, ХВГ , 6ХВ2С, 5ХВ2СФ, 6ХЗМФS (EP788), 7ХГ2ВМФ, 9Х5ВФ, 8Х6НФТ (85Х6НФТ), 6Х4М2ФС (DI55), Х6ВФ, 8Х4В2МФС2 (EP761), 11Х4В2МФ3° C2 (DI37), 6Х6В3МФ S (EP569, 55Х6В3СМФ), Х12, Х12МФ, Х12Ф1 , X12VMF.
Grades of tool alloy steel of group II: 5ХНМ, 5ХНВ, 5ХНВС, 7Х3, 8Х3, 4ХМФС (40ХСМФ), 4ХМНФС, 3Х2МNF, 5Х2МНФ (DI32), 4Х3ВМФ (3И2), 3Х3М3Ф, 4Х5 МФС, 4Х4ВМФС (DI22), 4 H5MF1S (EP572) , 4X5V2FS (EI958), 4X2V5MF (EI959), X3V3MFS (DI23), 05X12N6D2MFSGT (DI80).
Designation of the steel grade: the first numbers are the mass fraction of carbon in tenths of a percent, then the letters are the substance used as an alloying element, the numbers after the letters are the average mass fraction of the corresponding alloying element in whole units of percent. The initial figure is omitted if the carbon content is at least 1%. The letter “A”, in the middle of the steel grade is the nitrogen content, at the end is high-quality steel. For example, steel 5ХНМ - 0.5 C, 1 Cr, 1 N1, up to 0.3 Mo.
Non-standard alloy steels produced, for example, are designated by the appropriate combination of letters (in this case “EI”), followed by the serial number of the steel. For example, EI959, EP761, DI80, etc.
Application of tool alloy steel
| steel grade | Application area |
| X12MF | Parts for working under pressure of about 1400-1600 MPa. Profiling rollers of complex shapes, standard gears, rolling dies, sections of forging dies, complex punching dies and punches of cutting and perforating dies, punches and dies of cold extrusion for high pressures. Not applicable for welded structures. |
| 4-9ХС, ХВГ | Critical parts with increased wear resistance, bending fatigue strength, contact loading, and elastic properties. Drills, reamers, taps, dies, combs, cutters, machine dies, stamps for cold work. Not applicable for welded structures. |
| 4Х5МФС | Small hammer dies, large hammer and press inserts for hot deformation of structural steels and non-ferrous alloys in large-scale and mass production, injection molds for aluminum, zinc and magnesium alloys. |
| 3Х3М3Ф | Tools for hot deformation on crank presses and horizontal forging machines that undergo intense cooling during operation (usually for small tools), injection molds for copper alloys, knives for hot cutting. |
| R6M5, R6M5K5, R6M5F3, R6M5K8, R18, R7M2F6, R12MF5, R9M4K8, R10M4K14, R12M3K5F2, R12M3K8F2, R12M3K10F2, R12M3K10F2 | Disc cutters, reaming drills, countersinks, taps, broaches; worm cutters, end cutters, disk cutters; Shavers. |
Technological properties
| Name | Meaning |
| Weldability | Not applicable for welded structures. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | Not inclined. |
| Forging temperature | Start - 1125 °C, end - 750 °C. |
| Flock sensitivity | not sensitive. |
| Microstructure | The microstructure of unannealed tape with a thickness of up to 2.2 mm according to TU 14-1-2993-80 must correspond to: lamellar perlite - no more than 6 points; cementite mesh - no more than 3 points. |
| Features of product production | Wire rod according to TU 14-1-505-73 is supplied by the Beloretsk Metallurgical Plant. |
Tool carbon steel GOST 1435-99
Carbon steel is a steel that does not contain alloying elements, but contains carbon in varying concentrations: up to 0.25% - low-carbon steel, 0.24-0.6% medium-carbon steel, more than 0.6 - high-carbon steel.
GOST 1435-94 regulates the standards for the production of rods and strips forged, hot-rolled, calibrated and with special surface finishing from tool carbon (non-alloy) steel, as well as the standards for the chemical composition for ingots, billets, sheets, strips, wire and other metal products.
Classification of carbon steels
By purpose:
- high-speed - P;
- ball bearing - Ш;
- electrical engineering - E.
By chemical composition:
- quality;
- high quality - A.
By purpose, depending on the mass fraction of chromium, nickel and copper:
- 1 - for all types of products, except patented wire and tape;
- 2 - for patented wire and tape;
- 3 - for products of all types, manufactured with repeated heating, increasing the possibility of steel graphitization, as well as for products that require increased hardenability (except for rolled products for cores, patented wire and strip).
According to the method of further processing:
- a — hot-rolled and forged products for hot forming (upsetting, upsetting), cold drawing;
- b - for cold machining (turning, milling, etc.).
By quality and surface finish:
- for hot-rolled and forged steel: 2GP – for subgroup “a”, 3GP – for subgroup “b”;
- for calibrated steel - B and C.
- for rolled products with special surface treatment - B, D, D.
According to the condition of the material:
- steel without heat treatment;
- heat-treated steel - TO;
- cold-worked rolled products - NG (for calibrated bars and with special surface finishing).
Carbon tool steel grades
Grades of tool carbon steel: U7, U8, U8G, U9, U10, U11, U11A, U12, U13, U13A, U7A, U8A, U8GA, U9A, U10A, U12A.
Designation of steel grade: Y - carbon, the number following it is the average mass fraction of carbon in tenths of a percent, G - increased mass fraction of manganese.
Applications of Carbon Steel Tools
| steel grade | Application area |
| U7(A) | Woodworking tools (axes, chisels, etc.); small pneumatic tools (chisels, crimpers, etc.); forging dies; needle wire; plumbing tools: hammers, sledgehammers, screwdrivers, pliers, wire cutters, etc. |
| U8(A), U8(G, GA), U9(A)) | Tools used in conditions that do not cause heating of the cutting edge and when processing wood: cutters, axes, chisels, saws, etc. Knurling rollers, plates and cores for injection molds of tin-lead alloys. For plumbing tools (rivet presses, punches, screwdrivers, pliers, wire cutters). For profiles of simple shape and lower accuracy classes; cold-rolled strip 0.02-2.5 mm thick. |
| U10A, U12A) | Cores. |
| U10, U10A) | Needle wire. |
| U10(A), U11(A)) | Tools used in conditions that do not cause heating of the cutting edge and when processing wood: hand and machine cross-cutting and carpentry saws, twist drills. For cold stamping dies (drawing, heading, trimming, cutting) of small sizes; for calibers of simple shape and lower accuracy classes; for knurling rollers, files, metalwork scrapers, etc. Files, scrapers, cotton tape 0.02-2.5 mm thick. |
| U12(A)) | Hand taps, files, bench scrapers; dies for cold stamping (edged, die-cut) of small sizes and without cross-sectional transitions; cold heading punches and stamps of small sizes, simple shapes and low accuracy classes. |
| U13(A)) | Tools with reduced wear resistance (without heating the cutting edge): files, razor blades and knives, scalpels, scrapers, engraving tools. |
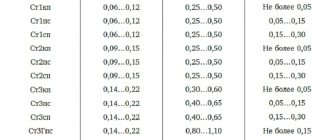
Mechanical characteristics
| Section, mm | σB, MPa | d4 | d10 | Brinell hardness, MPa | HV, MPa |
| Flattened tape of medium strength 0.1-4.0 mm according to GOST 10234-77 in delivery condition (delivery condition is indicated) | |||||
| — | 740-1270 | — | — | — | — |
| — | ≤780 | — | ≥8 | — | — |
| Cold-rolled, heat-treated strip (0.05-1.30 mm) for spring parts and springs in accordance with GOST 21996-76 and flattened strip (0.15-2.00 mm) in accordance with GOST 21997-76 (strength group of the strip is indicated) | |||||
| — | 1270-1570 | — | — | — | 375-485 |
| — | 1580-1860 | — | — | — | 486-600 |
| — | ≥1860 | — | — | — | ≥600 |
| Gradation of property indicators of finished heat-treated parts according to OST 1 90005-91 | |||||
| — | — | — | — | 44-48 | — |
| Annealed cold-rolled strip of the highest quality category | |||||
| 0.08-3 | ≤750 | ≥10 | — | — | — |
| Cold-rolled strip (strength class indicated) | |||||
| 0.1-4 | 750-900 | — | — | — | — |
| 0.1-4 | 900-1050 | — | — | — | — |
| 0.1-4 | 1050-1200 | — | — | — | — |
Tool high-speed steel GOST 19265-73
Rods and strips made of tool high-speed steel are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of GOST 19265-73.
Tool high-speed steel is used for the manufacture, most often, of cutting tools. High-speed tool steel combines high heat resistance (600-6500C depending on composition and processing) with high hardness, wear resistance (at elevated temperatures) and increased resistance to plastic deformation.
Weldability of high-speed steel: when electric butt welding with steel 45 and 40X, the weldability of tool steel is good.
Tool high-speed steel can be produced by steel alloying or without it. In the latter case, it will be one of the types of carbon steel. Depending on what type it belongs to, high-speed tool steel has the properties and classification of alloy steel or carbon steel.
Grades of tool high-speed steel
Grades of tool high-speed steel: R18, R6M5, R9K5, R9K9, R6M5K5, R6M4K9, R6M5F3, R9M4K8, etc.
Designation of steel grade: P - high-speed steel, number - tungsten content in tenths of a percent, M, K - alloyed with molybdenum or cobalt, respectively.
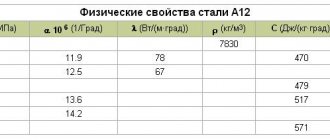
physical characteristics
| Temperature | E, GPa | G, GPa | r, kg/m3 | l, W/(m °С) | R, NOM m | a, 10-6 1/°С |
| 0 | 207 | 79 | 7745 | — | — | — |
| 100 | — | — | 7726 | 49 | 253 | 113 |
| 200 | — | — | 7717 | 48 | 329 | 121 |
| 300 | — | — | 7690 | 46 | 418 | 129 |
| 400 | — | — | 7686 | 43 | 525 | 136 |
| 500 | — | — | 7655 | 40 | 646 | 142 |
| 600 | — | — | 7622 | 37 | 789 | 147 |
| 700 | — | — | 7586 | 33 | 943 | — |
| 800 | — | — | 7568 | — | 1155 | 152 |
| 900 | — | — | 7523 | — | 1198 | — |
| 1000 | — | — | — | — | — | 14 |