Steel, a man-made alloy of iron and carbon, is in constant demand today in a wide variety of industries. Without it, it is difficult to build cities, install pipelines, produce transport, equipment, various units and parts.
The share of iron in the steel alloy must be at least 45%. All properties of steel, and, ultimately, of rolled metal products obtained from it, depend on the content of carbon and alloying elements.
One of the most popular grades of raw materials is steel 45. Characteristics and properties determine its popularity in the rolled metal market. It belongs to the category of structural carbon quality steels.
Explanation and chemical composition
The presence of the number 45 in the name of the raw material brand “reports” a content of about 0.45% carbon (C). The remaining “ingredients” were distributed as follows: silicon (Si) - from 0.17 to 0.37, chromium (Cr) - up to 0.25, manganese (Mn) - 0.5 - 0.8, nickel (Ni) – up to 0.25, copper (Cu) – up to 0.25, phosphorus (P) – up to 0.035, sulfur (S) – up to 0.04, arsenic (As) – 0.08.
Some physical and technological characteristics
- Weight (specific): 7826 kg/m3.
- Hardness of steel 45: HB = 50 HRC (after hardening).
- Forging temperature: from 1250 to 700 o C with subsequent cooling in air (for parts whose cross-section varies up to 400 mm).
- Turning is recommended in the hot-rolled state.
- Welding options: RDS, KTS (with heating). Further heat treatment is required.
- Flock sensitivity: low
- Tendency to become brittle when tempered: none.
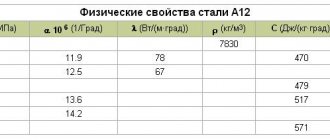
Mechanical and physical properties can be viewed in the table:
Steel grade 09g2s, what it is made of and where it is used
In the production of machine parts, pipeline elements, supports and other welded metal structures, 09g2s steel is more often used, which is associated with its operational and mechanical properties. Grade 17g1s is also used in the manufacture of electric-welded and seamless pipes, machinery, pipeline fittings, and heat exchangers.
Despite the overlap in the scope of application, the brands differ in their chemical composition, which determines the difference in physical and mechanical properties. Therefore, the choice of material depends on the operating conditions and design documentation.
Features of steel grade 45
Steel 45 has increased characteristics of strength, endurance, is well processed, and is affordable. It has found application in almost all areas of industry, where there are constant mechanical loads and difficult temperature conditions. Products made of steel 45, for example, the extremely popular circle and hexagon st45, can withstand differences in the range from 200 to 600 o C.
If we compare some characteristics of raw materials of grade 45 and, for example, grade 35, then the influence of the proportion of carbon in the alloy composition becomes obvious. Thus, 0.42 - 0.5% versus 0.32 - 0.4% (respectively) indicates increased hardness characteristics of steel 45.
If steel 35 is classified as limitedly weldable, then steel 45 (GOST 1050-88) is very difficult to weld. This is perhaps the first of the latter’s “disadvantages”. The second is susceptibility to corrosion due to the presence of nickel and chromium.
Steel 35 is usually used for the manufacture of parts of not too high strength, subjected to light and medium loads during operation: these are axles, cylinders, crankshafts, connecting rods, while grade 45 raw materials are used to make more reliable parts with improved strength characteristics.
Comparative characteristics of raw materials can be found here:
Characteristics of steel 17g1s-u
Steel grade 17g1s-u is also included in the group of lightly alloyed structural materials. The letter “y” at the end of the abbreviation means “strengthened”, i.e. the alloy has high strength. The decoding of the 17g1s-u brand implies enhanced special characteristics.
According to the state standard (GOST 19282-73), the chemical composition can be modified by certain components. So, to increase the strength of the material, calcium, titanium, and aluminum are introduced into it. The first two components are added in a volume of 0.03%, and the last - 0.05%.
The alloy is used in general purpose structures, which consist of welded, bolted, riveted devices. Forgings, stampings, flanges, fittings, bends and other connecting components of main pipelines with increased corrosion resistance are made from it.
Welding of rolled products is carried out without restrictions.
About steel processing 45
In mechanical engineering, grade 45 steel is first heat treated. After normalization, any mechanical “decor” (milling, turning) is simpler and easier. This is how various shafts, gears, cylinders, spindles, and cams are obtained.
After finishing heat treatment or hardening, the completed parts can “boast” greater resistance to wear. At the exit, they are cooled in water and subjected to low-temperature tempering (200-300 o C), the hardness indicators are about 50 HRC.
Application area
17G1S steel is used to create pipelines operating under a pressure of 7.5 MPa, parts subject to heating, and load-bearing structures. To give the metal anti-corrosion properties, cladding is used, which allows you to create a multilayer material. It is intended for:
- parts of special machines, passenger cars, carriages;
- creation of rolled products;
- use as a shaped element in a pipeline (maximum thickness – 60 mm);
- heat exchangers;
- gas and oil pipelines;
- heating systems;
- pipelines made of electric-welded or seamless pipes.
Due to the plastic properties and ease of creating a weld, high quality electric welded pipes with longitudinal and spiral connections are ensured. Before starting work, no heat treatment or other manipulations with the metal will be required.
Steel grade 17G1S is characterized by resistance to mechanical stress and ease of creating a welded joint, therefore it is widely used in construction. The cold resistance of the material allows you to create cooling systems, as well as use it in conditions of low temperatures.
Impact strength is determined based on the operating temperature, chemical composition and type of heat treatment of the steel. These parameters are decisive when choosing a metal grade depending on operating conditions.
Assortment of products made from St. 45, GOST standards
According to current standards, a sufficient number of well-known rolled metal products are made from grade 45 steel - hot-rolled steel circle. 45, sheet, square st45, pipes.
Long products, including shaped steel, are manufactured according to the strict requirements of GOSTs: 1050-88, 10702-78, 2590-2006 and 2591-2006, 2879-2006, 8509-93 and 8510-86, as well as 8239-89, 8240-97.
- To produce a calibrated rod, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of standards 1050-88, 8559-75 and 8560-78, 7417-75,
- sheet metal: thick (GOST 1577-93, 19903-74), thin - GOST 16523-97,
- stripes (GOSTs 103-2006, 1577-93, 82-70),
- ground rod – GOST 14955-77,
- steel strips 45 – GOST 2284-79,
- forged blanks - GOST 8479-70, 1133-71,
- pipes - standards 8732-78, 8731-74, 8733-74, 8734-75, and also 21729-76,
- wires - GOST 17305-91, 5663-79.
Mechanical characteristics
| Section, mm | holiday t, °C | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | d4 | y, % | kJ/m2, kJ/m2 | Brinell hardness, MPa |
| Seamless cold-deformed pipes, heat-treated as delivered in accordance with GOST 30563-98 | ||||||||
| — | ≥265 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — | |
| Straight-seam electric welded pipes according to TU 1303-002-08620133-01 as delivered (the wall thickness is indicated in the cross-section) | ||||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥325 | 470-620 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥343 | — |
| 20-25 | — | ≥305 | 460-610 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥343 | — |
| 6-10 | — | ≥345 | 490-640 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥393 | — |
| Sections and shaped rolled products made of high-strength steel as delivered in accordance with GOST 19281-89 (strength class indicated) | ||||||||
| 20-100 | — | ≥265 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| 20-32 | — | ≥295 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| ≤20 | — | ≥325 | ≥450 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| ≤10 | — | ≥345 | ≥480 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥255 | ≥420 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥590 | — |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| ≤10 | — | ≥345 | ≥490 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥325 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | ≥50 | ≥290 | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥185 | ≥345 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 20 | ≥295 | ≥405 | ≥30 | — | ≥66 | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥265 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥590 | — |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥325 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥176 | ≥440 | ≥16 | — | ≥42 | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥165 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 100 | ≥270 | ≥415 | ≥29 | — | ≥68 | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 100-300 | — | ≥245 | ≥450 | ≥19 | — | ≥42 | ≥390 | 120-179 |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| 20-32 | — | ≥305 | ≥460 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 21-32 | — | ≥305 | ≥460 | ≥21 | — | ≥50 | ≥240 | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥145 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 200 | ≥265 | ≥430 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 300-500 | — | ≥245 | ≥430 | ≥17 | — | ≥35 | ≥390 | 120-179 |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| 32-60 | — | ≥285 | ≥450 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 21-32 | — | ≥176 | ≥430 | ≥16 | — | ≥42 | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥195 | ≥355 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 300 | ≥220 | ≥435 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 100 | — | ≥245 | ≥470 | ≥22 | — | ≥48 | ≥490 | 143-179 |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| 60-80 | — | ≥275 | ≥440 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 33-50 | — | ≥285 | ≥450 | ≥21 | — | ≥50 | ≥230 | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥175 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 400 | ≥205 | ≥410 | ≥27 | — | ≥63 | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| ≤10 | 630-640 | ≥345 | ≥490 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 174-217 |
| Rolled thick sheets and wide-band universal ones in delivery condition GOST 19282-73 | ||||||||
| 80-160 | — | ≥265 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Thick plates are in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5034-91. Samples across the rolling direction | ||||||||
| 33-50 | — | ≥176 | ≥420 | ≥16 | — | ≥42 | — | — |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 20-160 | — | ≥155 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheets 34 mm thick in delivery condition HB 112-127 (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| — | 500 | ≥185 | ≥315 | — | — | ≥63 | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| 10-20 | 630-640 | ≥325 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 174-217 |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 300 | — | ≥195 | ≥355 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| 20-32 | 630-640 | ≥305 | ≥460 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 167-207 |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 300 | — | ≥175 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| 32-60 | 630-640 | ≥285 | ≥450 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 167-207 |
| Blanks after the main heat treatment in the delivery condition according to TU 302.02.122-91 (sheets and sheet stamped blanks - transverse samples, forgings - longitudinal samples) | ||||||||
| 300 | — | ≥155 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| 60-80 | 630-640 | ≥275 | ≥440 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 143-197 |
| Long products. Normalization at 930-950 °C | ||||||||
| — | — | ≥300 | ≥460 | ≥31 | — | ≥63 | — | — |
| Sheet 2-18, 19-22 categories, heat-treated, in delivery condition (GOST 5520-79) and Blanks for pipeline fittings parts made of rolled steel and stamped: Quenching in water from 930-940 °C (curing 2.5-4.0 hours depending on the thickness and weight of the workpiece) followed by tempering | ||||||||
| 80-160 | 630-640 | ≥265 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥588 | 143-197 |
| Long products. Normalization at 930-950 °C | ||||||||
| — | — | ≥220 | ≥420 | ≥25 | — | ≥56 | — | — |
| The sheet is in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5241-93. Quenching + Tempering (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥325 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Long products. Normalization at 930-950 °C | ||||||||
| — | — | ≥180 | ≥360 | ≥34 | — | ≥67 | — | — |
| The sheet is in delivery condition according to TU 14-1-5241-93. Quenching + Tempering (transverse samples) | ||||||||
| 20-32 | — | ≥295 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| 32-50 | — | ≥265 | ≥430 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| 8-10 | — | ≥345 | ≥490 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Hot rolled sheet as delivered. No heat treatment | ||||||||
| 2-3.9 | — | — | ≥490 | — | ≥17 | — | — | — |
| Rolled thick sheet and broadband universal rolled metal in delivery condition GOST 19282-73. Quenching + Tempering | ||||||||
| 10-32 | — | ≥365 | ≥490 | ≥19 | — | — | — | — |
| 32-60 | — | ≥315 | ≥450 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — |
| Long-section hot-rolled products from continuously cast evacuated steel with a diameter of 80-173 mm. Quenching in oil from 910-930 °C + Tempering at 640-660 °C, cooling in water or oil | ||||||||
| — | — | ≥300 | ≥460 | ≥24 | — | — | ≥600 | 120-179 |
| Thin sheets of high strength steel in delivery condition GOST 17066-94 | ||||||||
| 0.5-3.9 | — | ≥345 | ≥490 | — | ≥19 | — | — | — |
| 0.5-3.9 | — | ≥345 | ≥460 | — | ≥19 | — | — | — |
| Seamless hot-deformed pipes for oil and gas pipelines according to TU 14-3R-44-2001, heat-treated, as delivered (for group B - KCU-40 °C, for group B - KCU-60 °C) | ||||||||
| — | ≥265 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — | |
| — | ≥265 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥294 | — | |
| — | ≥265 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | ≥294 | — | |
| Seamless hot-deformed pipes according to TU 14-159-1128-2008 as delivered (Dн=57-219 mm, wall thickness 4-25 mm) | ||||||||
| — | ≥265 | 470-588 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — | |
| Seamless hot-deformed, cold-resistant pipes in accordance with GOST 30564-98, TU 14-3R-1128-2007, TU 14-3-1128-2000 in delivery condition | ||||||||
| — | ≥265 | ≥470 | ≥21 | — | — | — | — | |
| Electric-welded straight-seam oil and gas pipeline pipes in delivery condition according to TU 14-3-1573-96 (transverse samples; in the cross-section column - outer diameter, wall thickness in brackets; in the KCU column the value KCU-40 °C is indicated) | ||||||||
| 530 (7-12) | — | ≥340 | ≥490 | ≥20 | — | — | ≥294 | — |
| Electric-welded straight-seam oil and gas pipes in delivery condition according to TU 14-3-1573-96 (transverse samples; in the section section - outer diameter; in the KCU column the value KCU-60 °C is indicated) | ||||||||
| 630, 720, 820, 1020 | — | ≥340 | ≥490 | ≥20 | — | — | ≥294 | — |