Scope of application and features
Processing materials on a lathe involves securing a cylindrical workpiece into a three-jaw chuck. Due to the perpendicular feed of the cutting tool, the specified thickness of the metal is removed. All this allows you to grind the workpiece to the required size.
When performing certain jobs, simply fixing the workpiece in the chuck is not enough. To ensure safety, obtain the required cleanliness and accuracy, additional support of the part by the tailstock is required.
In what cases is it necessary to use a rotating center:
- The length of the workpiece is 5 times the diameter.
- Turning of heavy parts at high speeds (high speed and feed).
- Large thickness of chips removed.
- When finishing will take place on a grinding machine.
Features and benefits of using centers:
- Long service life.
- Resistance to high loads.
- Possibility to increase processing speed.
- Improving equipment performance.
- Versatility - can be used on manual machines and CNC equipment.
- High quality parts.
You might also be wondering how to properly mount a DRO on a lathe?
The disadvantages of the device include radial runout. If, according to technical requirements, this error is unacceptable, finishing is practiced using a fixed center in gentle modes.
Normal, reverse, rotary turning center
Turning center
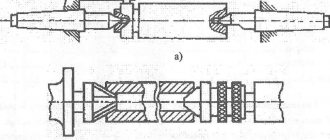
Various types of centers are used on lathes. The most common center is shown in Fig. 37, a. It consists of a cone 1, on which the workpiece is mounted, and a conical shank 2. The shank must fit exactly into the conical hole of the headstock spindle and tailstock quill.
Parts with external cones at the ends are processed in reverse centers (Fig. .37, b).
Fig 37 - Centers: a - normal, b - reverse center
The top of the center cone must exactly coincide with the axis of the shank. To check, the center is inserted into the spindle hole and rotated. If the center is in good condition, then the top of its cone will not “beat”.
The front center rotates together with the spindle and the workpiece, while the rear center is in most cases stationary; the rotating part rubs against its surface. Friction heats up and wears out both the conical surface of the rear center and the surface of the center hole of the part. To reduce friction, it is necessary to fill the center hole of the part at the rear center with a thick lubricant of the following composition: grease - 65%, chalk - 25%, sulfur - 5%, graphite - 5% (chalk, sulfur and graphite must be thoroughly ground).
Lack of lubrication leads to burning of the end of the center, as well as damage and scuffing of the surface of the center hole.
When turning parts at high speeds (v>75 m/min), rapid wear of the center occurs and the center hole of the part is developed. To reduce wear on the rear center, its end is sometimes equipped with a hard alloy; It is better, however, to use rotating centers.
Rice. 38 - Rotating center inserted into the tailstock quill
In Fig. 38 shows the design of a rotating center inserted into the conical hole of the tailstock quill. Center 1 rotates in ball bearings 2 and 4. Axial pressure is perceived by thrust ball bearing 5. The tapered shank 3 of the center body corresponds to the conical hole of the quill.
When processing heavy parts at high cutting speeds, as well as when cutting large-section chips, the rotating centers have insufficient rigidity, as a result of which the part can be pressed out and strong vibrations during operation are possible. To avoid these phenomena, rotating centers built into the tailstock quill are used.
Rice. 39. Rotating center built into the tailstock quill
In Fig. Figure 39 shows the design of such a center. In the front part of the quill 1 there is a bored hole in which the front thrust 3 and rear radial 2 bearings for the bushing 4 are installed. The axial force is perceived by the thrust ball bearing 3. The bushing 4 has a conical hole into which the center 5 is inserted. Using the stopper, connect bushing 4 to the quill; the bushing will not rotate. In this case, a drill or other axial tool (countersink, reamer) can be installed in the tailstock.
Similar materials
Price
| Type | Lathe | Type of work | Landing | Price, rubles |
| Fixed | JET | MK-3 | 500 | |
| Rotating | JET | MK-2 | 1800 | |
| Rotating | JET | MK-5 | 3000 | |
| Rotating | JET | for medium work | MK-3 | 2000 |
| Rotating | JET | for light work | MK-2 | 2800 |
| Rotating | JET | for heavy work | MK-5 | 3000 |
| Rotating | Tekhosnastka-S BT-5592 | for processing parts with center holes | A-1-3-N | 2050 |
| Rotating | Tekhosnastka-S BT-5598 | for processing parts with center holes | A-1-6-U | 11500 |
Design of rotating centers
The rotating center consists of a shaft and a conical tip. It is the working part that fixes the part. Rotation is ensured by a built-in ball bearing. It increases the efficiency of equipment, reduces friction and heating.
The standard tip angle is 60º. Such equipment is used in most cases when processing is carried out in standard modes. To work with heavy parts, a center with a tip angle of 90º is required.
The diameter of the tapered shank may vary depending on the tool model. To install the device in the tailstock, you will need a Morse taper 5.
Center rotating
Returning goods of proper quality
We draw your attention to the fact that, in accordance with Art. 26.1 of the Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights” The buyer has the right to refuse the goods at any time without giving reasons before its transfer, and after the transfer of the goods - within 7 days.
Returning a product of good quality is possible provided that the specified product has not been used, its presentation, consumer properties, as well as a document confirming the fact and conditions of purchase have been preserved.
In case of refusal of the goods, the company shall refund the funds paid by the Buyer under the contract, with the exception of the costs of delivery of the returned goods from the Buyer, within 10 days from the date the Buyer submits the corresponding demand.
Exchange of goods of good quality
According to Art. 25 “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” The buyer has the right to exchange goods of good quality for a similar product from the seller from whom this product was purchased, if the specified product does not fit in shape, dimensions, style, color, size or configuration. The Buyer can exchange the product for a suitable one within 14 days, not counting the day of purchase.
Exchanges are made only if the marketable appearance and consumer properties of the goods are preserved, a sales receipt or other document confirming payment is available, and also if the specified goods have not been used. If a similar product is not on sale, the Buyer has the right to demand a refund of the money he paid for the specified product.
In case of refusal of the goods, the company returns the funds paid by the Buyer under the contract, with the exception of the costs of delivery of the returned goods from the Buyer, within 14 days from the date the Buyer submits the corresponding demand. In addition, by agreement with the seller, the Buyer can exchange the product when an analogue goes on sale.
Returning goods of inadequate quality
If defects in the goods are detected, the Buyer has the right:
- Request a replacement for a product of the same brand (model);
- Request a replacement for the same product of a different brand (model) with a corresponding recalculation of the purchase price;
- Demand a proportionate reduction in the purchase price;
- Refuse to execute the sales contract and demand a refund of the amount paid for the goods.;
The return of goods of inadequate quality is carried out at the expense of the seller.
The above conditions for returning/exchanging goods do not apply to goods made according to the Buyer’s individual order.
Rincom admits that there may be erroneous or inaccurate information about the product located on our website www.rinscom.com. To avoid unpleasant situations, we kindly ask you to contact our managers for clarification of information about the product.
Varieties
In turning, several types of rotating center are used. According to their purpose, equipment is divided into two types:
- Thrust center - the pointed tip rests against the end of the part. You must first make a centering hole.
- Fungal - has a tip of a larger diameter with a truncated cone. Used for fixing parts with an internal hole (pipes, hollow shafts).
By design:
- With permanent roller (type A).
- With replaceable nozzle (type B).
The use of type B allows you to use one device for processing products with different dimensions. Removable attachments make it easier for the cutter to approach the workpiece. Such equipment is often used when turning shaped parts.
Centers for lathes are made of high-strength alloy steel. Depending on the complexity of the process, they can be regular or enhanced. The latter are used when working with heavy products. Reinforced is durable and resistant to high loads.
Specifics of operation
Before starting work, the turner must take into account runout errors. It occurs due to wear of the bearings or tip, or insufficiently rigid fixation. If the requirements do not allow such an error, it is better to use other equipment.
What nuances need to be taken into account when processing in centers:
- The axes of the spindle and center must coincide, otherwise there will be processing errors. When turning parts with a high accuracy class, allowances must be left for finishing.
- The clamping force should securely fix the workpiece, but not interfere with its rotation.
- When working at high speeds, lubricant must be used to reduce tip wear.
Important!
The runout of the rotating center leads to radial runout of the part relative to the axis. Further processing of the same workpiece on another machine may lead to misalignment.
If strong runout is detected, the conical tip must be ground with a special tool, which is attached to the tool holder. After checking with a template, if the result is satisfactory, you can begin metalworking.
Important!
When turning at high speeds, the center tip wears out and the center hole breaks. To extend the life of the equipment, the tip is treated with a protective lubricant.
Rotating Centers for Lathes
In this article we will talk about turning centers, their design, types and operating features.
One of the most common workpieces processed on lathes are shafts, and shafts of various lengths. In order to achieve the required surface quality, they must be secured sufficiently rigidly and reliably. This is done in the most effective and proven way - on one side the shaft is clamped into the chuck, and on the other it is pressed by the center. In most cases, this is done using a rotating center that is installed in the tailstock quill.
In what cases is it necessary to use a rotating center:
- The length of the workpiece is 5 times the diameter.
- Turning of heavy parts at high speeds (high speed and feed).
- Large thickness of chips removed.
- When finishing will take place on a grinding machine.
Advantages of using centers:
- Long service life.
- Resistance to high loads.
- Possibility to increase processing speed.
- Improving equipment performance.
- Versatility - can be used on manual machines and CNC equipment.
- High quality parts.
Design of rotating centers
The rotating center consists of a conical tip, a shaft and a bearing housed in a steel housing. The bearing largely determines what modes the center can operate in; it also reduces friction.
For standard operating conditions, a center with a tip angle of 60º is used; for heavy operating conditions, it is advisable to use a center with a tip angle of 90º.
Varieties
Depending on the characteristics of the tasks being solved, there are several types of center turning:
- Thrust center - used at low processing speeds. You must first make a centering hole.
- Thrust with a cut cone - used when cutting the end
- Rotating - used at high processing speeds, where a persistent one can no longer be used.
- Fungal - has a tip with a truncated cone. Used for fixing parts with an internal hole (pipes, hollow shafts).
- With rotating nut - for easy removal from the tailstock
- With interchangeable tips - the ability to machine a wide range of parts using just one center
Centers for lathes are made of high-strength alloy steel. Depending on the complexity of the process, they can be regular or enhanced. The latter are used when working with heavy products. Reinforced is durable and resistant to high loads.
Specifics of operation
Before starting work, the turner must take into account runout errors. It occurs due to wear of the bearings or tip, or insufficiently rigid fixation. If the requirements do not allow such an error, it is better to use other equipment.
What nuances need to be taken into account when processing in centers:
- The axes of the spindle and center must coincide, otherwise there will be processing errors. When turning parts with a high accuracy class, allowances must be left for finishing.
- The clamping force should securely fix the workpiece, but not interfere with its rotation.
- When working at high speeds, lubricant must be used to reduce tip wear.
Important!
The runout of the rotating center leads to radial runout of the part relative to the axis. Further processing of the same workpiece on another machine may lead to misalignment.
If strong runout is detected, the conical tip must be ground with a special tool, which is attached to the tool holder. After checking with a template, if the result is satisfactory, you can begin metalworking.
Important!
When turning at high speeds, the center tip wears out and the center hole breaks. To extend the life of the equipment, the tip is treated with a protective lubricant.
Sources:
1) catalog Bison-Bial 2015
2) https://vseostankah.com/tokarnye-stanki/vrashhayushhijsya-tsentr-nepodvizhnyj-gribkovyj.html
3) https://mekkain.ru/library/czentr-upornyij.html