Types of metal straightening
The operation is divided into two subtypes:
Manual straightening and straightening of metal is used in home workshops and in the manufacture of unique products. The set of tools is simple, but requires a highly qualified worker - a straightener.
Manual straightening of metal
Machine straightening is used in industry. The equipment is massive and complex, but has high productivity and process automation capabilities. In addition, the machine straightening operation is often combined with bending and cutting of sheet blanks, including it as part of a single technological complex.
Machine straightening of metal
The operation can be carried out at room temperature. Working at temperatures of 0C and below is unacceptable - the material loses its ductility and becomes brittle. Sometimes the workpiece has to be heated to 140-400C to increase ductility.
Metal straightening
Straightening is used in cases where it is necessary to eliminate distortion of the workpiece shape - waviness, warping, dents, bending, bulging, etc. Metal can be straightened both cold and heated. Heated metal is easier to straighten, which is also true for other types of plastic deformation, such as bending.
At home, straightening should be done on an anvil or a massive plate of steel or cast iron. The working surface of the stove must be smooth and clean. To make the impact noise less loud, the stove should be placed on a wooden table, which can also be used to level the stove so that it is in a horizontal position.
A special metalworking tool is required for editing. You cannot do it with any hammer that is at hand; the metal may not only not be straightened, but also get even larger defects. The hammer must be made of a soft material - lead, copper, wood or rubber. In addition, you cannot straighten metal with square-headed hammers: it will leave marks in the form of nicks on the surface. The hammer head should be round and polished.
Sheet metal straightening
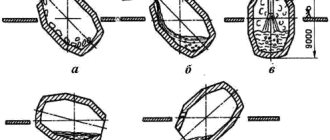
The complexity of the sheet metal straightening operation also depends on the type of defect.
The most difficult cases are a combination of different types of defects, for example, a waviness of the edge and a bulge in the center of the sheet at the same time.
Convex
The convexity is corrected by blows along the circle, starting from the outer side of the defect and gradually reducing the radius of the circle, moving from the edge to the center of the defect. The force of the blows becomes less, and the frequency increases.
Read also: Hair dryer for welding PVC film
Editing a convexity in the center of a metal sheet
If there is more than one bulge on the workpiece, they should be combined into one large one. You should hit between local defects, achieving their unification, and then act as described above.
Waviness of edges
Straightening of sheet metal with wavy edges is carried out starting from the edges of the sheet and gradually moving towards its center. After stretching the workpiece in the middle, the wavy edges are smoothed out.
Thin sheets
Small thickness workpieces cannot be straightened with strikers due to the high probability of the formation of tears and creases.
Straightening thin sheet metal
To straighten thin sheet metal, extended surfaces of metal or wooden smoothing bars are used. The workpiece is smoothed from different sides, gradually increasing the pressure.
Metal straightening and straightening
(cold method) Straightening and straightening are operations for straightening metal, blanks and parts that have dents, bulges, waviness, warping, curvature, etc. The metal is straightened both in a cold and in a heated state. The choice of method depends on the deflection, size and material of the product .
Straightening is done by hand on a straightening plate or anvil; machine on rollers or presses. For straightening, hammers with a round, smooth, polished head are used. Flats (wooden or metal bars) are used when straightening thin sheet and strip metal. Metal editing. The curvature of parts is checked by eye or by the gap between the plate and the part. When editing, it is important to choose the right places to strike. Editing is done on an anvil. Straightening of strip metal . The strip is placed on the correct slab so that it lies convexly upward, touching the slab at two points. The blows are applied to the convex parts.
Straightening the bar. After checking by eye, the boundaries of the bends are marked with chalk on the convex side. Then the rod is placed on a plate or anvil so that the curved part is convex upward and struck with a hammer. Editing sheet metal with bulges, identifying warped areas, determining where the metal is bulging the most. Editing begins from the edge closest to the bulge, along which one row of blows is applied with a hammer. Then blows are struck on the second edge. After this, a second row of blows is applied along the first edge and they move again to the second edge and so on until they gradually approach the bulge. Straightening parts that are bent after hardening is called straightening. Depending on the straightening, hammers with a hardened striker or special straightening hammers with a rounded side of the striker are used. Equipment for straightening at enterprises uses machine straightening on straightening rollers and presses. Welded joints with warping are subjected to cold straightening. Manually using wooden and steel hammers on plates, anvils, etc. Cold straightening is performed especially carefully. Labor safety : work with a serviceable tool (correctly mounted hammers, no cracks on the handles or chips on the hammers); To protect your hands from impacts and vibrations of the metal, work in gloves: hold the workpiece firmly on the plate or anvil. Metal bending. Bending is a method of metal forming by pressure, in which a workpiece or part thereof is given a curved shape. Bending is performed with hammers (preferably with soft strikers) in a vice, on a plate or using special tools. devices. Thin sheet metal is bent with mallets, wire products with a diameter of up to 3 mm are bent with pliers or round nose pliers. Only plastic material is bent. When bending parts at right angles without rounding on the inside, the bend allowance is taken from 0.5 to 0.8 of the thickness of the material. Mechanization of bending works. Profiles (strip, sectioned metal) with different radii of curvature are bent on three- and four-roller machines. The machine is preliminarily set up by positioning the upper roller relative to the two lower ones by rotating the handle. When bending, the workpiece must be pressed by the upper roller to the two lower ones. Bending and flaring of pipes Pipes are bent by manual and mechanized methods, in hot and cold conditions, with and without fillers.
The bending method depends on the diameter and material of the pipe, and the bending angle. Hot bending of pipes is used for diameters greater than 100 mm. When hot bending with filler, the pipe is annealed, marked, and one end is closed with a wooden or metal plug. The diameters of the plugs (plugs) depend on the internal diameter of the pipe. For small-diameter pipes, plugs are made of clay, rubber or hardwood; they are made in the form of a conical plug with a length equal to 1.5...2 pipe diameters, with a taper of 1:10. For pipes of large diameters, plugs are made of metal. When bending hot pipes, wear gloves. The pipes are heated with blowtorches in forges or the flame of gas burners until they have a cherry-red color. It is recommended to heat the pipes once, since repeated heating degrades the quality of the metal. Cold bending of pipes is performed using various devices. A simple device for bending pipes with a diameter of 10...15 mm is a plate with holes, in which pins are installed in appropriate places to serve as stops during bending. Pipes with a diameter of up to 20 mm are bent in a device that is attached to the workbench using a hub and a plate. Mechanization of pipe bending . For the mass production of parts from pipes of the largest diameters, manual pipe bending devices and lever pipe benders are used, and for bending pipes of large diameters (up to 350 mm), special pipe bending machines and presses are used. Pipe bending into a ring is carried out on a three-roller bending machine. Flaring (rolling) of pipes involves expanding (rolling) the ends of pipes from the inside using a special tool (rolling). The flaring process consists of putting a flange with grooves machined in its hole onto the end of the pipe, then inserting a flange with rollers into the pipe and rotating it. The most productive is rolling on special rolling machines and various mechanisms. Defects. When bending metal, defects most often are oblique bends and mechanical damage to the processed surface as a result of incorrect marking or fastening of parts in a vice above or below the marking line, and incorrect application of blows. Safety . When bending, the following safety requirements must be met: secure the workpiece firmly in a vice or other devices; work only on working equipment; Before starting work on bending machines, read the instructions; perform the work carefully so as not to damage your fingers; work in gloves and buttoned-up gowns.
Section 1. Mechanical work
Editing hardened metal (straightening)
Soft strikers are not used for straightening. They are made from a high-strength alloy and are given a rounded shape or the sharp side is rounded.
Editing hardened metal (straightening)
To straighten hardened metal, blows are directed along the concave area of the part. As the material on the concave side stretches, the workpiece will straighten. The operation is carried out on a hemispherical straightening headstock, along which the part is gradually moved up and down.
To straighten a hardened square with a violation of the right angle, two techniques have been developed. If the corner has become acute, the blows are directed near the inner corner. If the angle has turned into an obtuse one, the blows are directed to the area at the top of the outer corner. The material in the affected area is stretched and the right angle is restored.
Round metal straightening
The method is similar to working with a strip. Irregularities are marked with chalk, the workpiece is positioned with the convex side up. The blows are directed from the periphery of the defect to its center.
Round metal straightening
When the main defect is corrected, reduce the impact power and rotate the part around the longitudinal axis to avoid deformation in the other direction. Square and rectangular rolled products are straightened using the same method.
Straightening metal twisted in a spiral
The unwinding method is used here. One end of the spiral is fixed in a vice fixed to a straight plate, the other in a hand clamp.
Straightening metal twisted in a spiral
After partial unwinding of the spiral, it is pressed against the plate and straightened like a round piece, determining the curvature in the light.
Basic methods of straightening metal
The choice of method is influenced by the nature and cross-sectional area, grade and type of alloy, and the size of the defect relative to the overall size of the product.
Depending on the method of applying stress to metal workpieces, there are three methods of straightening metal:
- cold bending;
- cold stretching;
- local heating
Straightening metal by pulling
Heating is carried out with gas burners or induction.
Cold straightening of shafts
When operating machines, the shafts develop defects: bending; wear of working surfaces; Damage to threads, keyways and splines. The bending of the shafts is determined in the centers of a lathe, special devices or on prisms using stands with indicators (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Determination of shaft bending using an indicator head on prisms
Shaft bending is eliminated by straightening: cold or hot. Cold straightening is performed under pressure. It should be borne in mind that during cold straightening, as a result of the appearance of cold hardening in the metal, internal stresses arise, the magnitude of which is higher, the greater the amount of deformation during straightening. In addition, during cold straightening, the required shape of the shaft is not always maintained (the shafts can return to their distorted shape). Therefore, it is recommended that after cold straightening, heat the shafts to 400...450 °C, hold for 1 hour and cool slowly.
Editing using the Buravtsev method . It was called “elemental cold editing.” In the process of straightening according to the Buravtsev method, a press is also used (Fig. 3). The know-how lies in a special device with the help of which the surface layer of the shaft journal is plastically deformed so that instead of the usual tensile stresses, compressive stresses are created in it. In this case, the fillet is not affected, which means that the fatigue strength of the crankshaft after straightening not only does not decrease, but even increases. Moreover, having gotten rid of the disadvantages of previously known methods, element-by-element cold straightening allows you to restore any crankshafts (both cast iron and steel) of any engines (from motorcycles to excavators) with almost any deflection. At the same time, the editing accuracy is very high. For example, it is possible to ensure a mutual runout of the main journals of 0.01 mm with an initial runout of over 1 mm.
Rice. 3. Shaft editing using the Buravtsev method
Over the years of using the method of element-by-element straightening in practice, factual material has been accumulated on the further “fate” of straightened crankshafts of both domestic cars and foreign cars, including trucks and buses. Statistics have shown that these crankshafts do not return to a bent state over time. There were no complaints related to shaft breakage, which indirectly indicates their high fatigue strength.
Straightening of shafts by work hardening . The method is suitable for straightening crankshafts whose runout does not exceed 0.03...0.05% of the shaft length. It is produced by peening the cheeks with a pneumatic hammer with a special head. The crankshaft is placed on prisms with the upper main journals or installed in the centers. The duration of straightening and the depth of hardening (deformation of the cheek) depend on the force and number of blows per unit time. It is not recommended to make more than three or four blows on the same place; The effectiveness of straightening is monitored by measuring the shaft runout. The inner and outer sides of the cheek (from the crankpin side) are subject to work hardening, depending on the direction of the shaft runout. Straightening the crankshaft cheeks does not reduce its fatigue strength.
For what purposes is metal straightening used?
The configuration of a part may be disrupted during its initial processing, transportation or storage. Such blanks are unsuitable for further use, but are not irrevocable, final defects. Metal straightening is used to return the workpiece to the shape determined by the design and technological documentation.
Read also: Collapsible racks VAZ 2114
Straightening metal to return the workpiece to its shape
Sometimes, in order to reduce production costs, an enterprise deliberately purchases workpieces of improper shape, in which case the operation is included in the technological process. Planned straightening of metal can also be included in the technical process after heat treatment operations that cause a change in the shape of the part. Otherwise, the work will be unplanned, and its cost is included in unplanned losses.
Straightening equipment
The foundation of any tool kit is the right slab. It must be perfectly smooth, massive and stable, for which it is cast from impact-resistant cast iron or steel, and is equipped with longitudinal and transverse stiffeners to strengthen the structure. They are installed on a massive concrete base.
Metal straightening tools
Straightening hammers should be softer than the workpiece material. Therefore, they are equipped with wooden or rubber strikers. To work with steel sheets, hammers with soft strikers made of copper or lead are used. The firing pin must have a rounded shape. A square-shaped striker is not suitable, as it will leave characteristic marks on the sheet workpiece - nicks. The mass of the slab should be in a ratio of approximately 100:1 to the mass of the hammer.
To work with sheet workpieces, a backing plate made of dense rubber is also used, with a large number of tubercles of the same height formed on it. Under impacts, the metal itself finds its place, and the productivity of the process increases noticeably compared to a bare steel straightening plate.
To work with thin sheets, special equipment is used - smoothers and supports. To work with hardened parts, cylindrical or hemispherical straightening heads are used.
In a home workshop, an anvil or a massive metal plate is used.
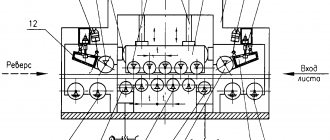
Enterprises use special mechanized leveling complexes with mechanical sheet feeding and automated correction of defects. In some, the workpiece is pulled between massive rotating rollers rotating in opposite directions. In others, the operation takes place on a regular plate by lowering a wide press.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Plumbing
Tool
Materials
Equipment for straightening/straightening
Manual straightening/straightening of metal sheets and structural elements made from them is carried out using hammers on special equipment - straightening headstocks, as well as straightening plates.
Straightening headstocks
For the manufacture of these devices, heat-treated steel alloys are used. The working surface of the straightening head can be:
- in the form of a flat circle on a cylindrical base, the radius of which (designation R) ranges from 150 mm≤R≤200 mm:
- spherical. This is the lateral surface of a cylinder truncated along the plane of symmetry and along the edges.
Also, in home workshops, a railway rail, cut to a length of 0.5 m to 1 m, is often used as a straightening headstock. It is convenient to move it along the slab. In addition, the rail is not subject to deformation and remains practically motionless when the workpiece is struck with a hammer.
Correct slabs
Straightening slabs are available in two modifications.
- Manufacturing material – cast iron. Execution – design with side ribs or solid.
- Manufacturing material – steel.
The slab must be heavy and sufficiently stable so that hammer blows do not cause it to shake. As for the requirements for the condition of its surface, they are standard: it must be perfectly smooth, and without the presence of foreign particles in the form of dirt and remnants of metal fragments that interfere with obtaining a high-quality result of straightening work.
The slabs must be installed on supports. They can be either metal or wood. But the most important thing is that these stands provide, in addition to stability, the required horizontal position. To make straightening easier, you need to have enough space around the slab.
There is another interesting option for such equipment. The material used to make the correct slab is dense rubber with many small protrusions, or rather, even tubercles with the same height. Under the influence of impacts, the metal itself determines its place. As a result, there is a significant increase in the productivity of the straightening process when compared with the use of a conventional leveling plate made of steel.
Hammers
The following key requirement is imposed on hammers used for straightening: they must be softer than the material of the workpiece being processed. In view of this, for straightening sheet steel, an impact tool with lead or copper strikers is usually used. Moreover, these elements should be characterized by a rounded shape. A square-shaped firing pin will leave nicks on the metal plate upon impact. When it comes to processing soft metals or non-ferrous alloys, it is necessary to use hammers equipped with rubber or wood strikers.
Convenience of work will be ensured if the ratio of the weight of the impact tool and the same parameter of the correct plate is equal to 1:100.
Metal straightening
Metal straightening is the process of straightening unevenness in rolled metal, wire, parts and other metal products.
The narrow end of the hammer head is used to pull out the steel sheet and simultaneously round the edge. If you put a steel sheet on an anvil and evenly accelerate the metal with the narrow end of the striker, then after a while the material will stretch, and due to this its edge will be rounded.
When working with a hammer, you must constantly monitor its correct position in your hand. The hammer should be swung with the whole arm, not the hand. By swinging your entire arm, the power and accuracy of the strike increases.
When performing any work with a hammer, the straightening support plays an important role.
The support is a very effective tool that helps straighten deformed areas of a metal sheet. In this case, the sheet is processed using an appropriate accelerating hammer or smoother.
Another type of hammer is the sediment hammer. This is a very important tool for working with sheet metal.
When straightening convexities with a settling hammer, blows are applied in a circle from the edge of the convexity to its center.
Then a support with appropriate roundness is placed on the back side of the metal sheet. Using a sediment hammer, carefully strike the sheet. With each blow, the metal is compressed, and thus the sheet is leveled and becomes flat.
Body straightening technology
Before starting work on restoring the body, a thorough inspection and selection of the technology by which straightening will be carried out is necessary. If necessary, those parts that require correction and those that make it difficult to access the area in need of repair are dismantled.
There are many ways to straighten a body, but they all work based on four technologies. Repair using a specific technology depends on the type and form of damage and the properties of the metal.
Let's consider the main technologies for straightening a car body:
- paintless vacuum straightening using PDR technology. Paintless Dent Repair – straightening technology using vacuum suction cups. PDR can be used on large, regularly shaped dents without damaging the paintwork. Using a vacuum suction cup, such dents are simply “pulled” back by air pressure without the use of straightening hammers. However, this method is contraindicated if the metal has cracks.
Do-it-yourself regular body straightening is the most common type, used using hammers, anvils, and spoons. Used for complex metal damage. The main problem with this technology is excessive stretching of the metal and the formation of poppers (playing metal). Recently, a similar problem has been corrected by a spotter
straightening with hot shrinkage - this technology is used as a last resort when conventional straightening does not bring results. With this method, the metal is heated with a torch and the metal is given the required shape in a spiral.
straightening aluminum - straightening and straightening of metal in this case is carried out using a method directly opposite to straightening dents on steel parts. Straightening of parts made of aluminum and its alloys is carried out from the center of the dent to its edges by knocking out or extruding. It should be noted that aluminum alloys cannot be straightened using a spotter, so their straightening is carried out from the inside of the part. If it is impossible to repair the damage using the “cold” method, the metal is heated to 150–200 degrees.