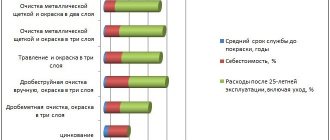
The method of electroplating metals was invented quite a long time ago. With its help, you can improve the mechanical properties of the material and expand the scope of use of the finished product. Electroplating means a sample processing cycle according to a strict algorithm of actions.
Galvanization is a method of coating one metal with another by electrolysis.
History of appearance and development
Historians claim that the technology of galvanic deposition, or rather its variety called galvanoplasty, appeared in 1838. The author of the idea was researcher Boris Jacobi. In the course of numerous experiments, the scientist invented an unusual method of processing metal blanks and began to actively introduce it into various areas of industry. Soon electroplating began to be used at mints and organizations that produced printing devices or equipment for artistic activities.
The method was named not after the discoverer, but the Italian scientist Luigi Galvani, who tried to process products electrochemically almost at the same time as Jacobi.
In what cases is galvanic coating of metal required?
Electroplating of metal is, in fact, an electrochemical process in which, in addition to the workpiece, an electrolyte, two electrodes and an electric current take part. An electrolyte is a conductive liquid in which, under the influence of an electric current, metal molecules are released, which then settle on the surface of the workpiece and cover it with a thin film.
A distinctive feature of galvanic coating is that the metal is not simply applied to the desired surface, but its molecules penetrate into the surface layer of the product.
The technology began to be used in 1838 thanks to the scientist Boris Jacobi. He was the first to actively introduce electroplating into various areas of production. Then his invention began to be used by mints, artists, craftsmen, and industrial enterprises.
However, this method of protecting metals from corrosion owes its name to the Italian scientist Luigi Galvani, who began studying electrochemical technology for processing products almost at the same time as Boris Jacobi.
Electroplating of metals serves various purposes. For example, to perform galvanic chrome plating, the workpiece is coated with a layer of nickel. In most cases, such layers are intended to enhance the protective and decorative characteristics of products. Also, using electroplating, you can create exact copies of parts, including those with complex surface topography. This process is called galvanoplasty.
The advantages of electroplating metals are as follows:
- They are characterized by uniform thickness and the highest level of coating density.
- Electroplating is also suitable for processing parts with complex shapes.
- Galvanic coating of metals significantly increases their decorative and protective properties.
- Adjusting the thickness of the galvanic layer is quite simple.
The essence of the galvanic process
Galvanization is a special electrochemical process that results in the formation of a thin metal coating on the original workpiece. Processing consists of several main cycles:
- Prepare an electrolyte with a suitable composition (varies depending on the type of material and the desired result).
- Dipping 2 anodes into the prepared solution, which are connected to the positive contact of the DC source.
- Immersion of the workpiece in the galvanizing mixture, placing it between the anodes and connecting it to a contact with a negative value. As a result, the workpiece will become a cathode.
- Closing the electrical circuit.
Galvanization results in the formation of a thin metal coating.
Galvanic cycles that occur in such a circuit involve the movement of charged particles of the deposited metal present in the electrolytic solution to the negatively charged cathode and subsequent deposition on the surface. This leads to the appearance of a metallic film.
The essence of the galvanic method of metal coating
It is impossible to understand what electroplating is without understanding the essence of this electrochemical process. Galvanic processing of parts, in which their surface is coated with a thin metal layer, consists of a number of main stages:
- preparing an electrolyte solution, the composition of which will be different in different cases;
- immersing two anodes in an electrolyte solution, which are connected to the positive contact of a direct current source;
- immersing the part to be protected in an electrolytic solution, placing it between two anodes and connecting it to the negative contact of a current source (in this case, the part being processed will act as a cathode);
- closing the formed electrical circuit.
The essence of galvanic processes occurring in an electrical circuit is as follows: positively charged particles of the applied metal present in the electrolytic solution, under the influence of electric current, are directed to a negatively charged cathode - the part, settling on its surface and forming a thin metal film on it.
Purposes of metal galvanization
There is a wide range of purposes for which galvanization can be used. If galvanic chromium plating is to be performed, the sample should be coated with a nickel layer. In most cases, this technology is used to improve the protective and decorative properties of samples. Electroplating can also be used to obtain exact copies of parts that have complex relief. Under such conditions the process is called galvanoplasty.
No less popular is the galvanizing of ferrous metals through galvanization. This treatment is intended to form an anti-corrosion galvanized coating on the surface. Metal parts galvanized by this method can be used for a long time in a humid environment, interact with salt or fresh water and still not lose their initial properties.
Electroplating can be applied to a metal surface for various purposes.
High-quality galvanizing is mandatory in the production of pipe products, technical tanks, components of roofing or building structures.
Electroplating is also indispensable in jewelry making. It is used to improve the decorative qualities of processed samples. The process involves the distribution of gold or silver on the product, restoration of damaged surfaces and other actions aimed at improving the appearance of the jewelry.
What kind of electroplating will he do for you?
We have the most modern equipment for electroplating at our disposal, so we will provide the customer with all current coating options:
— zinc coating (zinc plating) – gives products shine and prevents the formation of rust;
— nickel coating (nickel plating) makes the metal part resistant to external influences;
— copper coating (copper plating), which we do upon pre-order, forms a durable protective film for parts;
- plating with gold or silver (gilding and silvering), which is carried out on special orders of sufficient volume, will provide a combination of an extremely expensive appearance and reliable protection against corrosion;
— chrome coating (chrome plating) qualitatively improves the aesthetics of products, while making them more durable and increasing protection from aggressive external environments;
— brass coating (brass plating) gives the products a stylish decorative look;
— etching removes the surface layer from the product, which allows you to remove oxides and rust and detect internal defects. The procedure becomes an excellent preparation for applying the topcoat;
— aluminum electroplating creates a galvanic coating on this difficult-to-process material and solves the difficulties associated with its surface oxide film.
Specialists carry out all the necessary operations, competently selecting the mode of the electrolytic process to suit the conditions of the order.
Three good reasons to outsource your order
Electroplating methods
The formation of a protective film by distributing another metal is performed using 2 technologies:
- Cathode sputtering. If the layer is slightly damaged, rust forms on the main product. This is due to the reaction of the surface coating itself.
- Anodic application. The method is characterized by greater efficiency compared to the previous version. If there is a threat of development of corrosion processes, they occur only in the surface layer. The main part of the product does not lose its initial external properties for a long time. In addition, the material remains protected from negative environmental influences.
Interesting: Resistance welding
Metal galvanization
Coating the surfaces of finished products with an additional layer allows you to solve many technical and aesthetic problems. One of the most common methods of applying such coatings is metal galvanization. This method belongs to the category of electrochemical processes occurring in a container filled with an electrolyte. Electroplating forms a new layer due to the penetration (diffusion) of molecules into the surface layer of the workpiece, forming a thin film. As a result of this process, a layer with new physical and mechanical properties is obtained.
Key Benefits
Electroplating has important advantages that make it a popular metal processing method. Experts note the following points:
- Metal coating is performed on any type of initial samples, regardless of their shape or configuration.
- The finishing layer has a high density and uniform thickness.
- The surface is characterized by good adhesion to the treated coating.
- The protective and decorative properties of the processed parts are at a high level.
- The thickness of the metal layer, which is applied by electroplating, can be adjusted without much difficulty.
Metal coating is carried out regardless of the shape.
In addition, the technology is well developed and does not require any complex operations during implementation.
Its implementation is not accompanied by large financial investments.
Metal compatibility
Contact corrosion occurs when two dissimilar metals interact. Thus, it is forbidden to connect aluminum sheets with a copper rivet, as this will lead to the formation of a strong galvanic couple.
Different metals have different electrode potentials. When in contact with an electrolyte, one becomes a cathode and the other an anode. During the chemical reaction, corrosion begins, in which copper (cathode) mercilessly destroys aluminum (anode).
Almost all dissimilar materials that come into contact with each other are not protected from rust formation, because... even moisture particles contained in the air can turn into electrolyte and trigger an electrode potential.
You can check the compatibility of galvanic pairs using the table:
| Aluminum | Brass | Bronze | Copper | Cink Steel | Iron | |
| Aluminum | D | N | N | N | D | ABOUT |
| Copper | N | ABOUT | ABOUT | D | ABOUT | N |
| Lead | ABOUT | ABOUT | ABOUT | ABOUT | D | D |
| Zinc | D | N | N | N | D | N |
D - acceptable contacts (minimal risk of GC).
О - limited permissible contacts (average risk of GC).
N - unacceptable contacts (increased probability of GC).
Areas of use
Electroplating is necessary for:
- Protection. Metal coating protects the base material from rust and other destructive processes.
- Changes in external properties. Using galvanization, you can restore the beauty of the surface of a worn product and get rid of minor damage.
- Special purpose. The method is often used to improve the technical properties of the base.
Electroplating is necessary to protect the metal.
Electroplated surfaces are common in the automotive industry, jewelry and metal fabrication, building materials, cookware, fasteners and industrial equipment. In addition, the technology is also used to create CDs.
Types of galvanic coatings
Surfaces are galvanized using various metals. Depending on the coating used, the algorithm of actions and the result of the work differ.
Chrome plating
A common method of metal processing. Under the influence of chrome plating, the workpiece becomes resistant to wear. In addition, the method restores the original appearance of the product and eliminates traces of damage.
Copper plating
This is an intermediate processing cycle, since the finished product does not cope well with corrosion processes. Over time, the surface undergoes oxidation, so to avoid unpleasant phenomena, re-coating is performed. Acid and alkaline mixtures are used as electrolytes.
Copper plating is an intermediate processing cycle.
Galvanizing
The created galvanic couple withstands exposure to aggressive environments. The service life of parts is determined by the period of zinc destruction.
During this time, the metal will retain its external properties without rust.
Ironing
The method is intended to increase the strength properties of products that wear out quickly. Iron plating makes the metal resistant to various damages and rapid wear.
Iron plating increases the strength of products.
Nickel plating
The technological cycle is used when processing workpieces made of copper, steel and aluminum. The formed layer protects products from acidic environments, abrasion and mechanical stress.
Interesting: What is surface hardening
Brass plating
When processing, cyanide electrolytes of zinc, sodium, and potassium are used. The coating is distributed to maintain or improve the decorative properties of the samples. The method is in demand for steel blanks that will be covered with rubber inserts.
Brass plating is used to preserve the decorative properties of samples.
Rhodium plating
Allows you to increase the resistance of the product to the negative effects of acids, alkalis and chemicals. The chemical element makes the metal resistant to aggressive chemicals and mechanical stress.
Silvering and gilding
In demand in jewelry activities. The sample to be processed is immersed in a container with an electrolytic solution. Gold or silver ions dissolve in the mixture. After the cycle is completed, a thin layer of precious metal appears on the surface.
Silvering and gilding are in demand among jewelers.
Tinning
It is the application of a tin layer or an alloy of this metal to a metal surface. Processing by this method is in demand in mechanical engineering, radio engineering and the aviation industry.
Etching
This process using an acidic environment is performed in a glass, enamel or metal bath. The parts are kept in the solution for 1.5-2 minutes.
What are the benefits of using galvanic coating of parts?
The creation of galvanic coatings provides several serious advantages:
— stable and long-lasting anti-corrosion effect;
— increasing the resistance of surfaces to friction, wear and shock loads;
- change in electrical conductivity - depending on the coating, it can either increase or decrease;
— increases the ability to withstand high temperatures;
— increased protection from aggressive environments;
— the customer receives an excellent aesthetic effect.
Thanks to these capabilities, galvanizing of parts is used in such areas as:
— aircraft manufacturing;
— construction production;
— mechanical engineering;
— radio engineering and electronics;
— optics;
- design.
Properties of galvanic coatings
Electroplating coatings have several properties:
- Roughness. The degree of texture depends on the galvanization method used.
- Hardness of the outer layer. The parameter is measured using a special device PMT-3.
- Electrical properties. They are indispensable in the production of various conductive parts.
Electroplating coatings have the hardness of the outer layer.
Alternative to electroplating
To increase the strength properties and corrosion resistance of a metal workpiece, other methods are also used. Among them:
- Quenching the sample.
- Recrystallization.
- Coinage.
- Running in.
- Surfacing, etc.
To increase the strength properties, the sample is quenched.
The simplest and most effective options include the distribution of solid lubricant mixtures. They are similar to paints and varnishes, but with solid lubricating particles in the composition. This treatment promotes the formation of a thin film with high load-bearing properties and a low coefficient of friction.
Main types of galvanic coatings of metals
Currently, galvanic coating of products is carried out using various metals, forming a thin film that gives parts and structures reliable protection.
Among the main types of galvanic coatings of metals, the following can be distinguished:
- Electroplated copper coating.
This procedure is called mediation.
When applied to the surfaces of a wide variety of metals, copper forms a very strong protective film. In most cases, mediation is performed using copper sulfate.
- Electroplated silver plating.
Electroplating with silver – silver plating – is also often used. As a result, the surface of the products is covered with a silvery film, which imparts various useful properties to the metals. In addition, items processed in this way acquire a more attractive and expensive appearance.
Electroplating plays a special role in jewelry making. Its main task in this case is to improve the decorative characteristics of the processed products.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
- Electroplated gold plating.
Electroplating with precious metals, including gold – gilding – has also become increasingly used. The gold-plated surface of products acquires an attractive and expensive appearance; in addition, the gold film protects against corrosion.
We also note that gilding is used, including in relation to gold products, almost doubling the hardness of their surface layer. In addition, the gold film that covers the jewelry gives it greater brightness and attractiveness, as if illuminating it from within.
- Galvanic chrome coating.
Galvanic coating of metals with chromium gives them greater strength and resistance to aggressive environmental influences.
Chrome covers the surface with a thin film, giving the product protective and aesthetic characteristics.
- Nickel electroplated.
It is economical.
This method is optimal in cases where it is necessary to impart strength and resistance to various types of environmental influences to metal products and structures.
- Electroplated zinc coating.
Electroplating of ferrous metals with zinc – galvanizing – is common. As a result, a protective layer is formed on the surface of the products, which is characterized by high resistance to corrosion.
Metal products that have been processed using galvanizing can be used for a long time in conditions of high humidity, and even constant contact with fresh and salt water will not adversely affect their original characteristics. Galvanizing is used to coat pipe products, various containers, roofing elements, building and supporting structures. Thanks to this method of galvanic coating, metals receive, in addition to barrier protection, electrochemical protection.
- Galvanic tin coating.
Tin is used for electroplating aluminum, zinc, steel and copper. With its help, metals acquire characteristics such as hardness and strength.
Features of galvanic processing
Metal products are galvanized in several stages. To avoid mistakes, you need to strictly adhere to the algorithm of actions.
Preparation of electrolytic solution
Components are selected empirically, taking into account the following features:
- The type of coating that is formed.
- Thickness of the outer layer.
- Material for making the workpiece.
For each part that is subjected to galvanization, an individual composition with the appropriate recipe is needed.
Immersion of 2 anodes in the prepared solution
Contacts with a positive value are connected to the anodes. The voltage is supplied by a direct current source.
Contacts are connected to the anodes.
Immersion of the workpiece in the electrolyte
Before immersing the sample in the electrolytic mixture, it must be thoroughly treated with a brush and sandpaper. Then the anode plate is lowered into the bath, and the terminal with a positive value is closed using the anodes.
A workpiece is fixed between the anodes, and then a negative pole from the power supply is supplied to it.
The finished mixture is sent to the tank and filled above the level where the part is placed.
The period of time required to complete the tasks depends on the thickness of the layer.
What is galvanized steel?
Electroplating as a technology for processing metal products is an electrochemical process, the participants of which are the workpiece, an electrolyte, two electrodes and an electric current.
An electrolyte is a conductive liquid substance from which, as a result of the passage of an electric current through it, metal molecules are released, deposited on the surface of the workpiece and forming a thin film on it.
Galvanic coatings, which is what makes them remarkable, are formed not by simply applying a layer of metal to the surface being treated, but as a result of the penetration of its molecules into the surface layer of the part.
Electroplating is a reliable way to obtain a protective or decorative coating on metal products
What is the essence of the galvanic process?
To understand what electroplating is, it is important to understand the essence of such an electrochemical process. Galvanic processing of a product, during which a thin metal layer is formed on its surface, can be divided into several main stages:
- preparation of an electrolytic solution, the composition of which is selected in each specific case;
- immersion in an electrolytic solution of two anodes connected to the positive contact of a direct current source;
- immersion in a solution for galvanizing the workpiece, placing it between the anodes and connecting it to the negative contact of an electric current source (thus, the workpiece will act as a cathode);
- closing the formed electrical circuit.
Galvanic bath diagram
Galvanic processes that begin to occur in such an electrical circuit consist in the fact that positively charged particles of the applied metal contained in the electrolyte solution, under the influence of electric current, begin to tend to the negatively charged cathode-product, settling on its surface and forming a thin metal film on it .
Execution Goals
Electroplating can be applied to a metal surface for various purposes. For example, to perform galvanic chrome plating, the surface to be treated must be coated with a layer of nickel.
Basically, galvanic coatings are applied in order to improve the protective properties and decorative characteristics of products. Electroplating is also used to create exact copies of parts that even have a very high complexity of relief.
In such cases, the process is called galvanoplasty.
The method of galvanizing ferrous metals using galvanization is widely used. It allows you to form a layer of zinc on their surface, which is characterized by exceptionally high resistance to corrosion.
Metal products processed using this technology can be used for a very long time in conditions of high humidity, in constant contact with fresh and salt water, without losing their original characteristics.
Galvanizing is used, in particular, to process pipe products, various containers, and elements of roofing, building and supporting structures. Due to galvanizing, the metal receives not only barrier, but also electrochemical protection.
Galvanizing a car body in a galvanic bath
If with the help of galvanizing only the corrosion resistance of the metal is increased, then electroplating with chromium allows not only to solve this important problem, but also to make the surface of the workpiece harder and more wear-resistant, and also to increase its decorative appeal. Electroplated nickel coatings serve the same purposes.
Jewelry making is another area where electroplating plays a special role. Galvanization in this case is used to improve the decorative characteristics of the processed products.
The electroplating process is used to coat a piece of jewelry with a layer of gold or silver, restoring a surface that has lost its appeal over time.
It is noteworthy that even gold products are subjected to gilding using electroplating, which makes it possible to almost double the hardness of their surface layer. In addition, such a film applied to a gold product seems to illuminate it, making it brighter and more beautiful.
Equipment and materials
Electroplating of various metals requires the use of appropriate equipment and consumables.
For chrome plating, galvanizing, as well as for coating workpieces with other metals, the same type of galvanic equipment is used.
The differences when performing such processes will only be in the composition of the electrolyte used, its temperature and other processing modes.
Metal processing by galvanizing is performed using equipment such as:
- galvanic baths into which an electrolytic solution is poured, anodes and the workpiece are placed;
- DC source equipped with an output voltage regulator;
- a heating device with which the electrolytic solution is brought to the required operating temperature.
Galvanic bath with rocking mechanism
Electroplating also requires anode plates, which can be made from a variety of metals. The purpose of such plates is not only to supply electric current to the electrolyte, as well as to uniformly distribute the current over the surface of the workpiece, but also to replenish the loss of metal deposited on the part, which is actively consumed from the electrolyte.
Different types of electroplating are applied using electrolytic solutions with different chemical compositions.
To prepare such solutions, hazardous chemicals are used, so they must be stored in sealed glass containers with ground-in lids.
All chemical reagents from which the electrolytic solution is prepared for electroplating must be measured in precise quantities, so to perform this procedure it is necessary to use electronic scales.
Manual electroplating line for precious metals
Any line for metal electroplating or simple electroplating equipment must be installed in rooms equipped with an effective ventilation system. It is also necessary to take very seriously the personal safety of the specialist servicing the electroplating equipment.
All work related to electroplating must be performed in a respirator and safety glasses, thick rubber gloves, an oilcloth apron and shoes that can protect the skin of the feet from burns.
If this process is performed at home, and you still do not fully know what galvanization is, then you should carefully study special literature in advance or watch a training video on this topic.
Necessary materials and special equipment
To treat metals with a protective surface, you need to prepare:
- A constant current source for passing voltage through a closed circuit. You need to make sure that it has a regulator to change the output voltage parameters.
- Electrolyte reservoir. The workpiece to be processed will be immersed in the mixture.
To process metals, you need to prepare a direct current source.
As additional accessories, a device is used to heat the electrolyte to the required temperature.
Metal electroplating process
To carry out error-free galvanizing work, it is necessary to take into account the advice of experts. You should also follow the step-by-step guide.
Preparatory work
Galvanic metallization is carried out after several preparatory measures. First, you should clean the surface of rust, plaque, dust and dirt, and then sand it with sandpaper. After this, it is necessary to degrease the material to remove grease stains and oil stains.
Interesting: Guillotines for cutting metal
Having completed the preparation, you can move on to the main part of the work.
Galvanization
The flow diagram of this process is as follows:
- An electrolytic solution is lowered into the bath.
- Voltage is applied to the anode through the positive poles.
- The electrolyte mixture is heated to the required level.
- A negative contact is attached to the part. It is then slowly lowered into the tank.
Galvanization occurs according to the scheme.
Additional procedures
To make the part beautiful and improve its consumer qualities, you need to use a mixer that will interact with the outer surface. This will make the sample more marketable.
Evaluation of the final result
After completing processing, you should check the final result. If the actions were performed by specialists, there is no need to worry about quality. Using precision equipment, you can check the thickness of the applied layer, the uniformity of the coating and a number of other criteria.
Galvanic coating of metal according to GOST
All metals that are processed using the galvanic method must comply with the requirements of GOST 9.301–78, their surface roughness should not exceed the following values:
- Rz = 40 µm for protective coatings;
- Ra = 2.5 µm for protective and decorative;
- Rz ≤ 40 µm for special coatings in accordance with the functional purpose;
- Ra = 1.25 µm for hard and electrically insulating anodic oxide coatings.
Exceptions are allowed for non-working parts that are difficult to access for machining and non-working internal surfaces of parts, threaded surfaces, cut surfaces of stamped parts whose thickness does not exceed 4 mm, as well as for parts whose metal surface roughness requirements are specified in the standards.
The technical documentation must contain information about whether or not a change in roughness is required, as well as the need (or lack thereof) for additional protection of the product after coating with a layer of metal.
For processed parts, it is important to have no defects such as rolled inhomogeneity, rolled scale, burrs, delaminations and cracks from etching, polishing and grinding, pores and cavities.
The preparatory stage for galvanic coating of parts made of hot-rolled metal consists of cleaning them from pickling sludge, base metal corrosion products and other contaminants.
The surface of cast and forged products must be free of defects such as pores, gas and shrinkage cavities, slag inclusions, joints, underfills, and cracks. If products and structures have previously been subjected to such types of processing as tumbling, hydro- and metal sandblasting, they must be cleaned of sludge, slag, corrosion products and burrs. The surface of the part allowed for grinding must be free of various types of imperfections, including nicks, dents, burns, risks, burrs and defects from the straightening tool.
Electroplating is carried out for products that do not have sharp corners, which must be rounded and brought to a radius of 0.3 millimeters or more; the presence of chamfers is acceptable.
When using the galvanic treatment method for products with seams, it is necessary to ensure their continuity and protection, since electrolyte entering the gaps is unacceptable. If seams, especially discontinuous ones, raise doubts about their reliability, they should be sealed. Galvanic coating of metals is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 9.301–78.
In addition to clear requirements for appearance, galvanic coatings must have special properties required by the customer. There are also a number of conditions relating to thickness, porosity and bond strength. When using such protective layers for alloys, the requirements apply to the chemical composition; if for non-metallic inorganic surfaces - for protective properties.
As for the additional properties of galvanic metal coatings, it is important for them to comply with the requirements of design documentation.
Parameters such as thickness, chemical composition, protective properties and porosity must comply with GOST 9.301–78.
The type and thickness of coatings that are applied to parts (in accordance with the requirements of GOST 9.301–78, GOST 9.073–77, GOST 21 484–76) must be within the limits specified in the regulatory and technical documentation. Exceptions apply only to parts manufactured according to grades 7, 8 and 9 or having interference fits; threaded parts; springs
In the table below you can familiarize yourself with the methods of designating coatings defined in accordance with GOST 9.306-85
| Type of coverage | Coverage designation | |
| According to GOST 9.306-85 | Digital | |
| Zinc, chromated | Ts.khr | 01 |
| Cadmium, chromated | Kd.hr. | 02 |
| Multilayer: copper-nickel | M-N | 03 |
| Multilayer: copper-nickel-chrome | M-N-X | 04 |
| Oxidized, oil-impregnated | Oks. prm. | 05 |
| Phosphate, oil impregnated | Phos. prm | 06 |
| Tin | ABOUT | 07 |
| Copper | M | 08 |
| Zinc | C | 09 |
| Silver | Wed | 12 |
| Nickel | N | 13 |
To give the coating a higher quality, the surface of the product or structure is pre-etched and degreased, thus removing oxide and fatty contaminants from it.
Different types of coatings are characterized by special operational properties and mechanical parameters, each of them is designed to perform different functions.
Electroplating at home
With little time and effort, you can electroplate a metal surface at home. This is done in the following ways:
- Together with ionic electrolyte.
- With muric acid.
- With compatible metals.
With ionic electrolyte
When galvanizing at home, it is necessary to assess in advance what kind of reaction is expected to be obtained. This affects the type of anode material and the composition of the electrolyte solution.
It is necessary to evaluate the composition of the electrolyte solution.
Atoms that gradually attach to the sample must be present in the working mixture. Therefore, to obtain a beautiful silver or gold coating, you need to include appropriate impurities in the electrolyte.
With muric acid
This component is a salt substance with the formula HCI. Processing using this mixture looks like this:
- A piece of copper and a steel sample are connected to the power sources, observing polarity.
- An electrolyte based on water and hydrochloric acid mixed in a 5:1 ratio is immersed in the tank.
- 2 elements are lowered into the mixture, and the clamp on the sample is connected to the galvanization site.
- The composition is stirred periodically. This is necessary to maintain the uniformity of the layer.
With various metals
Different methods of processing one type of metal by another through an electrochemical reaction are implemented on one machine at home. To carry out such work, it is necessary to decide on the galvanization technology and the type of material for applying the protective layer.
Metal processing methods are implemented at home.
Precautionary measures
Since electrolyte is a toxic and dangerous substance, a number of precautions must be taken when working with it at home. The danger to the body is posed by harmful vapors released when the working mixture is heated and its chemical reactions. Additionally, there is a risk of electrical shock during galvanization, especially if the circuit is not grounded. When exposed to high temperatures, plastic bathtubs are damaged.
Designation of galvanic coatings
Galvanic layers have different designations:
- 00 - fasteners without a protective layer.
- 01 - zinc treatment with chromating.
- 02 - cadmium coating with chromate plating of fasteners.
- 03 - multi-layer processing with a copper-nickel alloy.
- 04 - multi-layer copper-nickel-chrome treatment.
- 05 - oxide coating.
- 06 - phosphate treatment with oiling.
- 07 - tin layer.
- 09 - copper layer.
- 10 - oxide anodizing coating.
Using various electroplating methods at home allows you to produce jewelry, apply protective layers, and perform a number of other useful operations with metal without outside help.
What properties do electroplated metal coatings have?
- Surface roughness.
Electroplating applied to metal slightly changes the roughness of its surface, most often increasing it.
- Hardness of electrolytically metalized surface.
To measure it, a PMT-3 device equipped with a diamond pyramid is used. It is pressed into the coating, applying different loads. And then, by analyzing the remaining traces (prints), the inherent microhardness of the coating, measured in Vickers megapascals, is calculated.
- Electrical properties.
In the process of manufacturing various parts of devices, contacts, etc., special importance is attached to the electrical properties of coatings, including contact (transition) resistance and electrical conductivity.
Galvanic coating of parts affects the physical and mechanical characteristics of the base (processed) metal, which is caused by both the properties of the protective layer and the process of hydrogenation of the coated metal.
The penetration of hydrogen into the treated surface (its hydrogenation) leads to a decrease in the ductility of steel. How significant an effect hydrogen will have on the mechanical properties of steels depends on their structure (martensitic, trostite, austenitic, etc.). Steels with a cane structure are more susceptible to embrittlement compared to steel products with a sorbitol structure.
The most noticeable hydrogenation can be observed when processing steels with a martensitic structure. Galvanic treatment of high-strength steels, which are characterized by high internal stress, can lead to the formation of cracks.