Steel 70G Steel 60S2KhFA Steel 60KhFA (60KhF) Steel 65 Steel 65G (65G1) Steel 65GA Steel 65S2VA Steel 68A Steel 68GA Steel 70 Steel 60S2KhG Steel 70G2 Steel 70S2KhA (EI142) Steel 70S3A Steel 70KhGFA Steel 75 Steel 80 Steel 85 Steel KT-2 Steel KT-3 Steel 55S2A Steel 3K-7 Steel 40R Steel 50RA (50R) Steel 50KhG Steel 50KhGA Steel 50KhGFA Steel 50KhFA (50KhF) Steel 51KhFA Steel 55S2 Steel 60S2Х (60S2ХА; 60С2ХА) Steel 55S2ГФ Steel 55 HGR Steel 55HFA (55ХФ) Steel 60G Steel 60S2 Steel 60S2A Steel 60S2G Steel 60S2N2A
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Sheets and strips | B23 | GOST 103-2006 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B22 | GOST 1133-71, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006 |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | B72 | GOST 26366-84 |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | GOST 4405-75, TU 14-1-1409-75 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | GOST 7417-75, GOST 7419-90, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14959-79, TU 14-1-2118-77, TU 14-1-2265-77, TU 14-1-4343- 89, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-136-367-2008 |
60S2HFA
Download the full price list of ProfProkat LLC
Brand
| Steel 60S2HFA | |
| Classification | Structural spring steel |
| Substitute | Steel 60S2A, Steel 60S2ХА, Steel 9ХС, Steel 19Х20Н4АМ3Д2С |
| Other designations | Steel 60S2HFA; Art. 60S2HFA; 60S2HFA |
| Foreign analogues | — |
| Application | Steel 60S2HFA is used: for the production of hot-rolled plates; responsible and highly loaded springs and springs |
| Notes | Spring alloy high quality steel |
| Type of delivery | |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 14959-79 |
| Long and shaped rolled products: | GOST 1133-71, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 7417-75, GOST 2879-2006, GOST 7419-90, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78, GOST 14955-77, TU 14-1- 2118-77, TU 14-1-2265-77, TU 14-1-4343-89, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-136-367-2008 |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 103-2006, GOST 4405-75, TU 14-1-1409-75 |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 26366-84 |
Chemical composition in % of material 60S2HFA
| Chemical element | GOST 14959-79, in% |
| Carbon (C) | 0,56 — 0,64 |
| Silicon (Si) | 1,40 — 1,80 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 0,90 — 1,20 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0,10 — 0,20 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0,40 — 0,70 |
| Nickel (Ni), no more | 0,25 |
| Sulfur (S), no more | 0,025 |
| Phosphorus (P), no more | 0,025 |
| Copper (Cu), no more | 0,20 |
| Iron (Fe) | the basis |
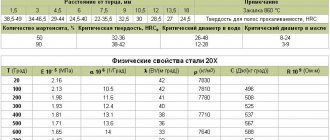
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of material 60S2HFA
| Delivery status | Section, mm | σt, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, kJ/m2 | H.R.C. |
| Sheet metal. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering at 450-550 °C | ≤80 | ≥1540 | ≥1640 | ≥10 | ≥35 | ≥432 | 45-49 |
| Sheet metal. Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C | ≤60 | ≥1780 | ≥1960 | ≥11 | ≥39 | ≥736 | |
| Sheet metal. Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C (1 hour) + Tempering at 325 °C | ≤60 | ≥1810 | ≥1960 | ≥8 | ≥38 | ≥657 | 45-51 |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 850 °C + Tempering at 410 °C, cooling in oil | 10-20 | ≥1670 | ≥1860 | ≥5 | |||
| Long products. Steel categories: 3, 3A, 3B, 3B, 3G, 4, 4A, 4B. Quenching in oil from 870 °C + tempering at 470 °C | Sample | ≥1470 | ≥1670 | ≥6 | ≥25 |
Mechanical properties of steel 60S2KhFA depending on tempering temperature
| Delivery status | holiday t(°C) | σt, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, kJ/m2 | H.R.C. |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | 200 | ≥294 | ≥59 | ||||
| 250 | ≥2190 | ≥2340 | ≥6 | ≥20 | ≥294 | ≥58 | |
| 300 | ≥2180 | ≥2340 | ≥6 | ≥22 | ≥314 | ≥58 | |
| 350 | ≥2160 | ≥2240 | ≥6 | ≥24 | ≥324 | ≥57 | |
| 400 | ≥1870 | ≥1930 | ≥7 | ≥29 | ≥363 | ≥53 | |
| 450 | ≥1690 | ≥1810 | ≥8 | ≥35 | ≥383 | ≥49 | |
| 500 | ≥1540 | ≥1640 | ≥10 | ≥35 | ≥432 | ≥46 | |
| 550 | ≥1440 | ≥1530 | ≥10 | ≥37 | ≥461 | ≥43 |
Technological properties of steel grade 60S2HFA
| Weldability | Not applicable for welded structures. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | Less inclined. |
| Forging temperature | Start - 1200 °C, end - 800 °C. Cooling is slow, subsequent heat treatment is annealing. |
Hardness
of material 60S2HFA
| Delivery status | HB |
| GOST 14959-79. Rental categories 1A, 2A, 3A, 3B, 4A t/o | ≤285 |
| GOST 14959-79. Rental categories 1B, 2B, 3B, 4B, 3G without t/o | ≤321 |
Fatigue limit of steel 60S2HFA
| Heat treatment, steel condition | s -1 (MPa) | t -1 (MPa) | σ B (MPa) | σ 0,2 (MPa) |
| Oil quenching 85-860 °C + tempering at 415 °C | 549 | 294 | 1900 | 1810 |
| Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C | 588 | 309 | 1960 | 1780 |
| Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C + tempering at 325 °C | 613 | 328 | 1960 | 1780 |
Physical properties of structural spring steel 60S2HFA
| Test temperature, °C | 20 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity, E, GPa | 191 |
| Modulus of elasticity under torsional shear (G, GPa) | 77 |
| Steel density, pn, kg/m3 | 7850 |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties : | ||
| σв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] | |
| σT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] | |
| δ5 | — Elongation at break, [%] | |
| ψ | — Relative narrowing, [%] | |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] | |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] | |
| Physical properties: | ||
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] | |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] | |
| | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] | |
| | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] | |
| | — Material density, [kg/m3] | |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] | |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] | |
| Weldability: | ||
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment | |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment | |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing | |
Buy high-quality structural spring steel 60S2HFA
with an average carbon content of 0.60%, chromium 1.1%, silicon 1.6%, manganese 0.55% and vanadium 0.15%.
Pipe
Angle Channel Strip Circle Hexagon Reinforcement Square Beam Sheet Regulatory
documentation
GOST 103-2006. Hot-rolled long-rolled steel strip. Assortment.
GOST 1133-71. Forged steel round and square. Assortment.
GOST 2590-2006. Hot-rolled round steel products. Assortment.
GOST 2591-2006. Hot-rolled square steel products. Assortment.
GOST 2879-2006. Hot-rolled hexagonal long steel. Assortment.
GOST 4405-75. Hot-rolled and forged strips made of tool steel. Assortment.
GOST 7417-75. Calibrated round steel. Assortment.
GOST 7419-90. Hot rolled steel for springs. Assortment.
GOST 8559-75. Calibrated square steel. Assortment.
GOST 8560-78. Rolled calibrated hexagonal. Assortment.
GOST 14955-77. High-quality round steel with special surface finishing. Technical conditions.
GOST 14959-79. Rolled products from spring carbon and alloy steel. Technical conditions.
GOST 26366-84. Brass-plated steel wire for tire bead rings. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-1409-75. Alloy thick sheet steel, hot rolled. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-2118-77. Hot-rolled bars in profiles measuring 250 mm or more from structural carbon and alloy steel. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-2265-77. Hot rolled grade steel. Brand 60S2HFA. Technical conditions.
TU 14-1-4343-89. Hot rolled rods made of spring steel grade 60S2HFA. Technical conditions.
TU 14-11-245-88. High precision shaped steel profiles. Technical conditions.
TU 14-136-367-2008. Rolled hot-rolled, turned, round sections with a size of more than 200 mm. Technical conditions.
Additional Information.
Correspondence between Soviet and Russian steel grades.
International analogues of steels
Correspondence table HB - HRC.
Tool materials.
The influence of the main alloying elements on the properties of steel.
Mechanical characteristics
| Section, mm | holiday t, °C | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | y, % | kJ/m2, kJ/m2 | H.R.C. |
| Sheet metal. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering at 450-550 °C | |||||||
| ≤80 | — | ≥1540 | ≥1640 | ≥10 | ≥35 | ≥432 | 45-49 |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | |||||||
| — | 200 | — | — | — | — | ≥294 | ≥59 |
| Sheet metal. Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C | |||||||
| ≤60 | — | ≥1780 | ≥1960 | ≥11 | ≥39 | ≥736 | — |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | |||||||
| — | 250 | ≥2190 | ≥2340 | ≥6 | ≥20 | ≥294 | ≥58 |
| Sheet metal. Isothermal hardening with holding at 290 °C (1 hour) + Tempering at 325 °C | |||||||
| ≤60 | — | ≥1810 | ≥1960 | ≥8 | ≥38 | ≥657 | 45-51 |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | |||||||
| — | 300 | ≥2180 | ≥2340 | ≥6 | ≥22 | ≥314 | ≥58 |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 850 °C + Tempering at 410 °C, cooling in oil | |||||||
| 10-20 | — | ≥1670 | ≥1860 | ≥5 | — | — | — |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | |||||||
| — | 350 | ≥2160 | ≥2240 | ≥6 | ≥24 | ≥324 | ≥57 |
| Long products. Steel categories: 3, 3A, 3B, 3B, 3G, 4, 4A, 4B. Quenching in oil from 870 °C + tempering at 470 °C | |||||||
| — | ≥1470 | ≥1670 | ≥6 | ≥25 | — | — | |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880-890 °C + Tempering | |||||||
| — | 400 | ≥1870 | ≥1930 | ≥7 | ≥29 | ≥363 | ≥53 |
| — | 450 | ≥1690 | ≥1810 | ≥8 | ≥35 | ≥383 | ≥49 |
| — | 500 | ≥1540 | ≥1640 | ≥10 | ≥35 | ≥432 | ≥46 |
| — | 550 | ≥1440 | ≥1530 | ≥10 | ≥37 | ≥461 | ≥43 |
Steel 60S2A spring-spring
Decoding
According to GOST 14959-2016, the number 60 before the letter designation indicates the average mass fraction of carbon in steel in hundredths of a percent, i.e. the average mass fraction of carbon in steel is 0.60%. The letter C means that the steel is alloyed with silicon (Si), and the number 2 indicates the approximate mass fraction of silicon in whole units, i.e. silicon in steel is approximately 2%. The letter A at the end of the steel name means that the steel is high quality, i.e. steel with increased requirements for the chemical composition and macrostructure of metal products made from it compared to high-quality steel.
Substitutes and analogues
60S2N2A, 60S2G, 50HFA.
Foreign analogues
| Germany DIN (EN) | 60Si7 (1.5027) [1] |
| USA (AISI, ASTM) | 9260 |
| UK (BS) | 251A60 |
| Japan JIS | SUP 6 |
| Poland PN/H | 60S2A |
Type of delivery
- long products, including shaped steel, GOST 14959-79, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 2879-88, GOST 7419.0-90 - GOST 7419.8-90;
- Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78;
- Tape GOST 2283-79, GOST 21997-76. Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 4405-75;
- Wire GOST 14963-78. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71, GOST 14959-79;
- Polished rod and silver GOST 7419.0-90 - GOST 7419.8-90, GOST 14955-77;
Characteristics and Application
Steel 60C2A is an alloyed special steel used for the manufacture of the following products:
- heavily loaded springs,
- torsion shafts,
- spring rings,
- collet,
- friction discs,
- Grover washers,
- springs made of strip steel 3-16 mm thick,
- springs made of strip steel with a thickness of 3-18 mm and spring strips with a thickness of 0.08-3 mm,
- twisted springs made of wire with a diameter of 3-12 mm.
Steel is prone to decarburization, is resistant to grain growth, and has deep hardenability. The maximum operating temperature is +250 °C [2], in aircraft construction it is recommended to use steel no higher than a temperature of +200 °C [3].
Conditions for using steel 60S2A for disc springs (GOST 33260-2015)
| ND for supply | Spring standard | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use |
| Assortment GOST 2283, GOST 7419. Technical requirements GOST 14959 | GOST 3057 | -60 to 120 | Used for work in conditions of atmospheric corrosion with anti-corrosion coatings* |
*After electrochemical coatings, heat treatment (tempering) is required to remove hydrogen embrittlement, as indicated in the design documentation.
Conditions for using steel 60S2A for helical coil springs (GOST 33260-2015)
| ND for supply | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use |
| Wire GOST 14963. Rolled products GOST 2590 | -60 to 250 | Safety and pressure relief valves, bypass and shut-off valves, etc. |
NOTE. For class II springs, it is allowed to replace rolled grade 60C2A with grade 60C2.
Maximum permissible dimensions of metal products made from steel 60S2A for the manufacture of springs and springs (GOST 14959-2016)
| strip thickness | diameter or side of a square |
| 14 | 20 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 14959-79)
| C | Mn | Si | Cr | Cu | Ni | S | P |
| no more | |||||||
| 0,58-0,63 | 0,60-0,90 | 1,6-2,0 | 0,30 | 0,20 | 0,25 | 0,025 | 0,025 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 14959-2016)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % | ||||||||
| WITH | Si | Mn | Sk | V | W | Ni | B | Cu, no more | |
| 60С2А | 0,58-0,63 | 1,60-2,00 | 0,60-0,90 | No more than 0.30 | — | — | No more than 0.25 | — | 0,20 |
Temperature of critical points, °C [4]
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Arc3 | Arc1 | Mn[5] |
| 770 | 820 | 770 | 700 | 305 |
Recommended processing modes for springs made of steel 60S2A [2]
| Temperature, °C | Hardness HB of finished springs | |
| oil hardening | vacations | |
| 850-870* | 460-480 | 418-387 |
*When bending sheets and hardening with one heating, the temperature rises to 900-950 °C.
Recommended heat treatment [3]
Low annealing at 650-700 °C; hardening from 870±10 °C in oil, tempering at 430-490 °C (HRC 44-48, σв = 155-180 kgf/mm2)
Hardness of metal products made from steel 60S2A as delivered (GOST 14595-2016)
| Hardness of metal products, HB, no more | |
| without heat treatment (categories 1 B, 2B, ZB, 4B, ZG, ZD and ZE) | heat-treated (categories 1A, 2A, ZA, ZB and 4A) |
| 302 | 269 |
Mechanical properties of metal products during tensile testing (GOST 14595-2016)
| Recommended mode of thermal treatment of samples | Mechanical properties, no less | ||||||
| Hardening | Vacation | ||||||
| Heating temperature, °C | Cooling medium | Heating temperature, °C | Cooling medium | Yield strength σt, N/mm2 | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 | Relative elongation δ5,% | Relative narrowing ψ, % |
| 870 | Oil | 420 | Air | 1375 | 1570 | 6 | 20 |
NOTE:
- The mechanical properties of metal products during tensile testing are determined on longitudinal heat-treated samples.
- During the recommended heat treatment, temperature deviations are allowed:
- hardening — ±15 °С;
- hardening — ±50 °С;
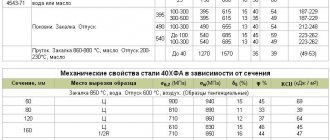
Mechanical properties of steel of various heats [3]
| Workpiece diameter, mm | σпц | σ0.2 | σв | δ5 | ψ | NV kgf/mm2 |
| kgf/mm2 | % | |||||
| 14 | — | 144 | 160 | 10 | 40 | 460 |
| — | 150 | 163 | 10 | 44 | 460 | |
| 15 | 136 | 143 | 162 | 10 | 40 | 445 |
| 135 | 142 | 162 | 11 | 45 | 445 | |
| — | 155 | 160 | 10 | 44 | 445 | |
| — | 152 | 155 | 10 | 42 | 445 | |
| 21 | 133 | 147 | 163 | 10 | 43 | 445 |
| 135 | 146 | 161 | 10 | 47 | 445 | |
| — | 155 | 163 | 11 | 53 | 460 | |
| — | 154 | 159 | 11 | 56 | 460 | |
Mechanical properties of annealed and cold-worked strip made of steel 60S2A (GOST 2283-79)
| Nominal thickness, mm | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), no more | Relative elongation δ4, %, not less | Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) |
| Annealed tape | Cold-worked tape | ||
| From 0.10 to 4.00 incl. | 880 (90) | 8 | 780-1180 (80-120) |
Mechanical properties
| Source | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB, no more |
| no less | ||||||||
| GOST 14959-79 | Steel categories
Hardening at 870 °C in oil; tempering at 420 °C | — | 1375 | 1570 | 6 | 20 | — | — |
| [6] | Isothermal hardening from 860-880 “C, cooling. in molten salt at 310-330 °C; holiday at 310-330 °C, cool. on air | 10 | 1570 | 1770 | 12 | 50 | 62 | HRCе 47-50 |
| [7] | Springs. Winding at 850-950 °C; hardening from 850-870 °C in oil; holiday at 430-460 °C, cool. on air | Not defined | 388-477 | |||||
| Springs. Quenching from 850-870 °C in oil; holiday at 400-450 °C, cool. on air | Same | 387-418 | ||||||
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature [5]
| tref., °C | σ0.2, MPa | σ0.2, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HRCе |
| 300 | 1960 | 2160 | 2 | 36 | 10 | 462 |
| 400 | 1470 | 1670 | 7 | 39 | 18 | 425 |
| 500 | 1080 | 1290 | 10 | 42 | 29 | 340 |
| 600 | 730 | 1030 | 17 | 48 | — | 298 |
NOTE. Hardening at 850 °C in oil; vacation.
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp., °C | σ0.2, MPa | σ0.2, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Rod with a diameter of 17 mm. Hardening at 860 °C in oil; tempering at 550 °C, 3 hours, hardness HB 340-364 [8] | |||||
| 20 | 1090 | 1270 | 11-13 | 33 | 24 |
| 300 | 930 | 1220 | 15 | 44 | 43 |
| 400 | 820 | 950 | 19 | 71 | 44 |
| 500 | 510 | 590 | 23 | 87 | 43 |
| Sunset with 860 °C in oil; tempering at 425 °C [9] | |||||
| 20 | 1570 | 1710 | 10 | 46 | 32 |
| 200 | 1370 | 1670 | 13 | 40 | 34 |
| 300 | 1270 | 1570 | 20 | 58 | — |
| 400 | 1080 | 1220 | 22 | 71 | — |
Endurance Limit [6]
| Heat treatment | σ-1, MPa | n |
| Isothermal hardening, holding at 330 °C, 1 hour + tempering at 300 °C, 1 hour; σв = 1680 MPa | 686 | 106 |
| Quenching + tempering at 420 °C; σв = 1810 MPa | 637 | 106 |
| Oil hardening; tempering at 400 °C; σ0.2 = 1760 MPa, σв = 1900 MPa | 500 | — |
Impact strength KCU [10]
| Heat treatment | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C | |
| +20 | -70 | |
| Hardening at 850 °C in oil; holiday at 460 °C, 1 hour, cool. on air | 39 | 34 |
Technological properties
- Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1200, end 800. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, sections 251-350 mm are cooled in a pit.
- Weldability - not applicable to welded structures.
- Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 0.70 and Kv b.st = 0.27 in the hot-rolled state at HB 270-320 σw = 1080 MPa.
- Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
- Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
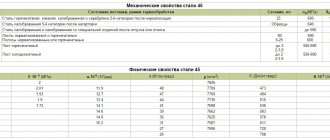
Hardenability (GOST 14959-2016)
| Hardness HRCe at a distance from the end, mm (hardening from 850 °C) | |||||||||
| 1,5 | 3 | 4,5 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 27 | 39 |
| 60-67 | 59-67 | 57-66 | 54-65 | 44,5-63 | 38,5-60 | 35,5-56 | 34-52,5 | 30-43,5 | 27-39,5 |
Critical diameter d
| Critical hardness, HRCе | Amount of martensite, % | d, mm, after hardening at 850 °C | |
| in water | In oil | ||
| 51-53 | 50 | 47-82 | 24-53 |
| 58-60 | 90 | 60 | 36 |
Density ρп kg/cm3 at test temperature, °С
| Steel | 20° | 100° | 200° | 300° | 400° | 500° |
| 60С2А | 7680 | 7660 | 7630 | 7590 | 7570 | 7520 |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | α*106, K-1 at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | |
| 60С2А | 11,8 | 12,7 | 13,3 | 13,7 | 14,1 | 14,5 | 14,4 | 12,2 |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C | ||||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | |
| 60С2А | 28 | 29 | 29 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 28 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C | ||||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | |
| 60С2А | 212 | 206 | 198 | 192 | 181 | 178 | 158 | 144 | 134 |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa
| steel grade | At test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 600 | 700 | 800 | |
| 60С2 | 82 | 80 | 77 | 74 | 69 | 54 | 54 | 50 |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K)
| steel grade | s, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C | |||||||
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | |
| 60С2А | 510 | 510 | 520 | 535 | 565 | 585 | 620 | 700 |
Bibliography
- GOST 33260-2015. Pipeline fittings. Metals used in valve making. Basic requirements for the selection of materials
- Tylkin M.A. Thermist Repair Service Handbook. 1981
- Sklyarov N.M. Aviation materials. 1975 Volume 1
- Brand of steels and alloys. Ed. Sorokina V.G. 1989
- Brand of steels. CBTI. 1961
- Rakhstadt A.G. Spring steels and alloys. 1971
- Brand of steel and alloys. TsNIITmash. 1977
- Properties of steels and alloys used in boiler and turbine manufacturing. Part 1. TsKTI. 1966
- Metals and alloys: Reference data on physical and mechanical properties at various temperatures and loading conditions. 1975
- Solntsev Yu.P., Stepanov G.A. Materials in cryogenic technology. 1982
Find out more
Steel X12MF tool stamping...
Structural alloy steel 40X2H2MA…
Steel 45X structural alloy…
Steel 4ХМФС tool stamping…
Description of mechanical symbols
| Name | Description |
| Section | Section |
| sT|s0.2 | Yield strength or proportional limit with tolerance for permanent deformation - 0.2% |
| σB | Short-term strength limit |
| d5 | Elongation after break |
| y | Relative narrowing |
| kJ/m2 | Impact strength |
| H.R.C. | Rockwell hardness (diamond indenter, spheroconic) |