Characteristics of steel grade 60
Steel 60 is a structural high-quality carbon steel, not used for welded structures. CTS followed by heat treatment.
Not prone to flake sensitivity, no tendency to temper brittleness. Cutting machinability in a normalized state at HB 241 K υ solid. spl=0.70 and Kυ b.st=0.65. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1220 to 800 0C, with air cooling of workpieces with a cross-section of up to 300 mm. Steel 60 is used to make solid-rolled wagon wheels, working rolls of sheet mills for hot rolling of metals, eccentrics, spindles, bandages, clutch discs, spring rings of shock absorbers, lock washers, shims, shims and other parts that require high strength and wear resistance. . Work rolls of sheet mills for hot rolling of metal. Solid forged wheels for wagons and tires for rolling stock of broad gauge railways.
Steel 60 structural carbon steel
Substitutes
Foreign analogues
| Europe | USA | Japan |
| C60, Cm60 | 1060 | S58C |
Decoding
The number 60 means that the average carbon content in steel is 0.60%.
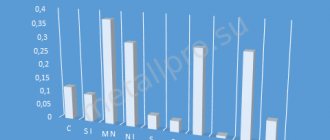
Chemical composition, % (GOST 1050-88)
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | S | R | Cu | Ni | As |
| no more |
| 0,57-0,65 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,25 | 0,04 | 0,035 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,08 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 1050-2013)
| steel grade | Mass fraction of elements, % |
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu |
| no more |
| 60 | 0,57-0,65 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,030 | 0,035 | 0,25 | 0,30 | 0,30 |
Characteristics and description
Steel 60 refers to structural unalloyed special quality steels with a high carbon content (0.60%) and normal manganese content, has high strength and high elastic properties.[1]
Steel is prone to cracks when quenched in water.
Purpose
Steel 60 is used for the manufacture of parts that require high strength and wear resistance, for example:
- Eccentrics,
- solid-rolled carriage wheels,
- tires for rolling stock of broad gauge railways,
- working rolls of sheet mills for hot rolling of metals,
- spindles,
- bandages,
- clutch discs,
- shock absorber spring rings,
- lock washers,
- adjusting washers,
- shims,
- work rolls of sheet mills for hot rolling of metal.
Temperature of critical points, °C [81]
Heat treatment
Small parts made of grade 60 steel (up to 10-12 mm in diameter) are hardened in oil at a temperature of 820-860 ° C, larger parts in water at a temperature of 800-820 ° C, tempering is carried out at different temperatures depending on the required mechanical properties.
Dependence of mechanical properties of steel 60 on tempering temperature
Hardness HB (GOST 1050-2013)
| steel grade | Hardness HB, no more |
| hot rolled and forged | calibrated and with special surface finishing |
| without heat treatment | after annealing or high tempering | hard-worked | after annealing or high tempering |
| 60 | 255 | 229 | 269 | 229 |
Mechanical properties of metal products for steel 60 (GOST 1050-2013)
| steel grade | Mechanical properties, no less |
| Yield strength σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Relative narrowing ψ, % |
| 60 | 400 | 680 | 12 | 35 |
NOTE. Mechanical properties for steel 60 were determined on normalized samples.
Mechanical properties of metal products made from steel 60 depending on size (GOST 105-2013)
| Mechanical properties of metal products size |
| Yield strength σ0.2, MPa not less | Tensile strength σв, MPa | Relative elongation δ5, % | Impact work KU, J |
| no less |
| up to 16 mm incl. |
| 580 | 850—1000 | 11 | + |
| St. 16 to 40 mm incl. |
| 520 | 800—950 | 13 | + |
| St. 40 to 100 mm incl. |
| 450 | 750-900 | 14 | + |
NOTE.
- Mechanical properties are determined on samples cut from heat-treated (hardening and tempering) workpieces.
- The “+” sign means that the tests are carried out to collect statistical data, and the test results are recorded in the quality document.
- The values of mechanical properties are given for metal products with a round cross-section.
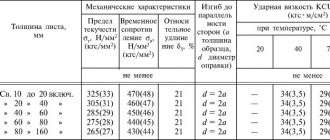
Mechanical properties depending on the section [140]
| Section, mm | Sample cutting location | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KSU, J/cm2 |
| no less |
| Quenching from 780-830 °C in oil; tempering at 560 °C |
| 30 | TO | 590 | 920 | 19 | 50 | 24 |
| 30 | C | 540 | 880 | — | — | 49 |
| Quenching from 780-830 °C in oil; tempering at 610 °C |
| 10 | C | 600 | 860 | 20 | 58 | 73 |
| 30 | TO | 540 | 880 | 20 | 50 | 49 |
| 60 | TO | 480 | 730 | 25 | 60 | 49 |
| 60 | C | 390 | 680 | 27 | 56 | 49 |
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature [140]
| tref., °С | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB |
| 400 | 1430 | 1690 | 2 | 3 | 4,9 | 450 |
| 450 | 1280 | 1430 | 5 | 10 | 19 | 410 |
| 500 | 1120 | 1210 | 7 | 16 | 23 | 375 |
| 550 | 1040 | 1150 | 7 | 20 | 24 | 370 |
NOTE. Hardening at 950 °C in oil.
Mechanical properties depending on test temperature [82]
| tsp., °С | σв, MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % |
| 20 | 700 | 17 | 60 |
| 200 | 680 | 14 | — |
| 300 | 560 | 27 | — |
| 500 | 460 | 30 | — |
| -25 | 760 | (21) | 61 |
| -40 | 790 | (23) | 61 |
NOTE. Hardening at 950 °C in oil.
Yield strength of steel 60 depending on test temperature
| tsp., °С | σ0.2, MPa |
| 20 | 510 |
| 200 | 530 |
| 300 | 450 |
| 500 | 320 |
| -25 | 540 |
| -40 | 540 |
NOTE. Hardening at 950 °C in oil.
Technological properties [81]
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1220, end 800. Sections up to 300 mm are cooled in air.
Weldability - not applicable for welded structures, welded steel with subsequent heat treatment.
Cutting machinability - Autvsp = 0.70 and A'y6st = 0.65 in the normalized state at HB 241.
Flock sensitivity is insensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Hardenability [50]
The hardenability range of steel 60 after hardening at 820°C is shown in the figure below.
Critical diameter d
| Amount of martensite, % | d, mm, after hardening |
| in water | In oil |
| 50 | 26-48 | 10-20 |
| 90 | 15-30 | 3-12 |
Density ρп kg/cm3 at test temperature, °С
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1
| steel grade | α*106, K-1 at test temperature, °C |
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 |
| 60 | 11,0 | 11,9 | — | 13,9 | 14,6 |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K)
| Steel grade | λ W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C |
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| 60 | — | 68 | 53 | — | 36 |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C |
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 |
| 60 | 204 | — | 208 | 189 | 174 |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K)
| steel grade | s, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C |
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 |
| 60 | 483 | 487 | — | 529 | — | 567 |
Type of delivery
- Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 1050-88, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 2879-88, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86.
- Calibrated rod GOST 7417-75, GOST 8559-75, GOST 8560-78.
- Polished rod and silver steel GOST 7419.0-90, GOST 7419.1-90, GOST 7419.3-90, GOST 7419.5-90, GOST 7419.8-90, GOST 14955-77.
- Thick sheet GOST 1577-93, GOST 19903-74.
- Tape GOST 2284-79, GOST 1530-78, GOST 21996-76, GOST 21997-76.
- Strip GOST 82-70, GOST 1577-93, GOST 103-76.
- Wire GOST 9389-75.
Find out more
Bearing steel ШХ15ГС
Steel 4ХМФС tool stamping…
Steel 45X structural alloy…
Structural alloy steel 34ХН3М…
Supply steel 60
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-88 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-88 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 8239-89 Hot-rolled steel I-beams , GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles, GOST 19772 -93 Bent steel angles, unequal flanges , GOST 8278-83 Bent steel channels, equal flanges , GOST 8281-80 , unequal , GOST 8283-93 steel trough equal flange profiles , GOST 380-94 Carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 85 09-93 Steel corners hot-rolled equal flange , GOST 8510-86 rolled steel angles unequal-flanged , GOST 8240-97 Hot-rolled steel channels , GOST 535-88 Rolled bars and shaped carbon steel of ordinary quality , GOST 2879-88 Rolled hot-rolled hexagonal steel, GOST 19903-2015 Hot rolled sheet products , GOST 19904-90 Cold-rolled sheets , GOST 16523-97 Rolled thin sheets of high-quality and ordinary quality carbon steel for general purpose, GOST 503-81 Cold-rolled low-carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot-rolled steel strip , GOST 82-70 Hot-rolled steel Wide-band universal, GOST 3282-74 Wire Steel low-carbon general purposes , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wires, GOST 10705-80 steel power steel pipes , GOST 10706-76 Pipes steel eight-dimensional , GOST 3262-75 Pipes steel water and gap-pipes .
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8510-86; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 8509-93; GOST 9234-74; GOST 11474-76; GOST 1133-71; GOST 2591-2006; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; GOST 82-70; GOST 6765-75; GOST 19903-74; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8559-75; GOST 1051-73; GOST 14955-77; GOST 7417-75; GOST 7419-90; GOST 1050-88; GOST 8560-78; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 1577-93; GOST 4405-75; |
| Ribbons | GOST 21996-76; GOST 21997-76; GOST 2284-79; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 20295-85; GOST 24950-81; GOST 3262-75; |
| Low carbon steel wire | GOST 792-67; |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 7372-79; GOST 9161-85; GOST 9850-72; GOST 9389-75; GOST 3920-70; GOST 26366-84; GOST 9124-85; |
Chemical composition in % of steel 60G and GOST standards for rental
The alloy of this grade has a relatively high carbon content, as well as manganese as the main alloying element:
- Fe – about 97%
- C – 0.57-0.65%
- Mn – 0.7-1%
- Si – 0.17-0.37%
- Ni – no more than 0.25%
- Cr – no more than 0.25%
- Cu – no more than 0.2%
- S – no more than 0.035%
- P – no more than 0.035%
60g steel enters the workshops of industrial enterprises in the form of shaped long products, manufactured in accordance with GOST standards:
- GOST 1051-73, 7417-75, 8559-75 and 8560-78 – calibrated rods
- GOST 14955-77, 7419.0-78 and 7419.8-78 – ground rods and silver
- GOST 1577-93 – thick sheets
- GOST 2283-79 – tapes
- GOST 4405-75 and 103-2006 – stripes
- GOST 1133-71 – forged blanks and forgings
Mechanical properties of steel 60 depending on the section
| Section, mm | Sample cutting location | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв(MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (J/cm2) |
| Quenching 780-830 °C, oil. Vacation 560 °C |
| 30 30 | K C | 590 540 | 920 880 | 19 — | 50 — | 24 49 |
| Quenching 780-830 °C, oil. Vacation 610 °C |
| 10 30 60 60 | Ts K K Ts | 600 540 480 390 | 860 880 730 680 | 20 20 25 27 | 58 50 60 56 | 73 49 49 49 |
Mechanical properties of steel 60 at normal temperature
| Type of delivery | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Rolled products, GOST 1050-88 | up to 80 | 680 | 400 | 12 | 35 | Normalization |
| Annealed tape, GOST 2284-79 | 440-740 | 10 |
| Cold-worked tape, GOST 2284-79 | 740-1130 |
| Steel | 700 | 510 | 17 | 60 | Hardening and high tempering |
| Steel | 30 | TO | 920 | 590 | 19 | 50 | 240 | Quenching 780 - 830oC, oil, Tempering 560oC |
Characteristics of material 60G
| Brand | 60G |
| Substitute: | 65G |
| Classification | Structural spring steel |
| Application | flat and round springs, springs, spring rings and other spring-type parts that require high elastic properties and wear resistance; tires, brake drums and bands, brackets, bushings and other parts of general and heavy engineering. |
Chemical composition in % of material 60G
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | Cu |
| 0.57 — 0.65 | 0.17 — 0.37 | 0.7 — 1 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.035 | up to 0.035 | up to 0.25 | up to 0.2 |
The temperature of the critical points of the material is 60G.
| Ac1 = 726, Ac3(Acm) = 765, Ar3(Arcm) = 741, Ar1 = 689, Mn = 270 |
Mechanical properties at T=20oC of 60G material.
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| 980 | 785 | 8 | 30 | Delivery status |
| The tape is annealed. | up to 1 | 650 | 15 |
| The hardness of the material is 60G after annealing, | HB 10 -1 = 241 MPa |
| Material hardness 60G without heat treatment, | HB 10 -1 = 285 MPa |
Physical properties of material 60G.
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.04 | 7810 |
| 100 | 11.6 | 483 |
| 200 | 11.9 | 487 |
| 300 | 12.9 |
| 400 | 13.8 | 529 |
| 500 |
| 600 | 14.6 | 575 |
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
Technological properties of material 60G.
| Weldability: | not applicable to welded structures. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | insensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | inclined. |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties : |
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] |
| HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: |
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
| Weldability: |
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
Source:
Physical properties of steel 60
| Temperature | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| 0C | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.04 | 7800 |
| 100 | 11 | 68 | 483 |
| 200 | 2.08 | 11.9 | 53 | 487 |
| 300 | 1.89 |
| 400 | 1.74 | 13.9 | 36 | 529 |
| 500 | 14.6 |
| 600 | 567 |
physical characteristics
| Temperature | E, GPa | G, GPa | r, kg/m3 | a, 10-6 1/°С | C, J/(kg °C) |
| 0 | 204 | 81 | 7810 | — | — |
| 20 | 204 | — | 7810 | — | — |
| 100 | — | — | — | 116 | 483 |
| 200 | — | — | — | 119 | 483 |
| 300 | — | — | — | 129 | — |
| 400 | — | — | — | 129 | 487 |
| 600 | — | — | — | 138 | 529 |
| 800 | — | — | — | 146 | 575 |
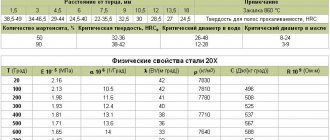
Hardenability of steel 60
| Distance from the end, mm | Note |
| 1,5 | 3 | 4,5 | 6 | 7,5 | 9 | 12 | 21 | 33 | 45 | Hardening 820 °C |
| 57,5-63,5 | 56-62 | 51-60,5 | 38,5-59 | 35-56 | 35,5-51,5 | 32-42 | 31,5-40 | 26-38 | 25-34 | Hardness for hardenability strips, HRC∂ |
| Amount of martensite, % | Critical diameter in water | Critical diameter in oil |
| 50 90 | 26-48 15-30 | 10-20 3-12 |
Foreign analogues steel 60
| USA | 1059, 1060, 1064, C1060, G10590, G10600, G10640 |
| Germany | 1.0601, 1.1221, C60, C60D, C60E, C60R, Ck60, Ck60N |
| Japan | S58C, S60C-CSP, S65C-CSP, SWR-7 |
| France | 1C60, 2C60, AF70, C60, C60E, C60RR, XC60, XC65 |
| England | 060A2, 060A62, 1449-CS, 1449-HS, 60CS, 60HS, C60, C60E, CS60 |
| European Union | 1CS60, 2C60, 2CS60, C60, C60E |
| Italy | 1C60, C60, C60E, C60R |
| Belgium | C60-1, C60-2 |
| Spain | C60, C60E |
| China | 60 |
| Sweden | 1665, 1678 |
| Bulgaria | 60, C60, C60E |
| Hungary | C60E |
| Poland | 60, 60rs, D55 |
| Romania | OLC60, OLC60AT, OLC60X |
| Czech | 12061 |
| Australia | 1060 |
| Switzerland | C60, Ck60 |
| South Korea | SM58C |
- Structural steel
- Tool steel