Material 35HGSA Chelyabinsk
Not a single production can operate without steel, be it heavy engineering or the manufacture of household electrical appliances. There are many brands of this product, as well as a large number of dispensing forms. Our company sells material 35KhGSA in large quantities and with a minimal margin. To clarify the properties and characteristics of a particular brand, you can contact the company’s managers.
Like all products, material 35ХГСА is purchased from leading manufacturers. Therefore, we are ready to provide a quality guarantee with full responsibility. The minimum number of intermediaries determines the low cost. Coupled with fast delivery, this enables our business partners to conduct stable and mutually beneficial cooperation.
In addition to tempering, in the form of one or another part (blank), our company carries out metal processing. All events undergo strict control for compliance with GOST and rules. The specialists of our company carry out such work as galvanizing, creating parts according to customer drawings, producing castings, manufacturing various profiles and much more.
Having the latest equipment and vast experience in our arsenal, we can offer product testing for a number of parameters, such as strength characteristics, chemical composition, alloy purity, and so on.
Each buyer is offered a huge range of products in various formats, as well as current services and works. To quickly understand and choose a product that meets your needs, you need to contact the company manager and receive detailed information on all issues of interest.
35ХГСА
- Products made of steel 35HGSA in stock:
Circle - Band
- Square
- Forging
to make a request
High-quality structural alloy steel 35KhGSA
Substitutes: Steel 30KhGT, Steel 30KhGS, Steel 30KhGSA, Steel 35KhM
Steel 35KhGSA is used: for the production of hot-rolled plates; flanges, cams, pins, rollers, levers, axles, parts of welded structures and other upgradeable parts of complex configuration operating under alternating loads.
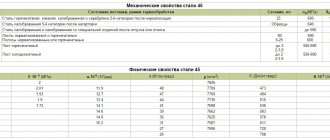
Specifications
| Chemical composition in% |
| NTD | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | W | V | Ti | Si | Ni | Mo | Cu |
| TU 14-1-4118-86, GOST 4543-71 | 0,32-0,39 | ≤0,025 | ≤0,025 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,10-1,40 | ≤0,20 | ≤0,050 | ≤0,030 | 1,10-1,40 | ≤0,30 | ≤0,15 | ≤0,30 |
According to GOST 4543-71, the content in especially high-quality steel is regulated: P≤0.025%; S≤0.015%; Сu≤0.25%.
| Mechanical properties |
| Mechanical properties at 20°C |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Samples for mechanical testing. Isothermal hardening at 880 °C in a mixture of potassium and sodium nitrate having a temperature of 280-310 °C, cooling in air | ||||||||||||||||
| ≥1270 | ≥1620 | ≥9 | ≥40 | ≥383 | ||||||||||||
| Forgings. Quenching in air from 880 °C + Tempering at 500 °C, cooling in air | ||||||||||||||||
| 100-300 | ≥490 | ≥660 | ≥13 | ≥40 | ≥530 | |||||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on the section |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering at 500 °C, cooling in water (longitudinal samples) | ||||||||||||||||
| 10-20 | ≥1000 | ≥1110 | ≥12 | ≥54 | ≥322 | |||||||||||
| 20-40 | ≥940 | ≥1080 | ≥11 | ≥50 | ≥310 | |||||||||||
| 40-60 | ≥860 | ≥960 | ≥11 | ≥46 | ≥270 | |||||||||||
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering at 600 °C, cooling in water (longitudinal samples) | ||||||||||||||||
| 20-40 | ≥810 | ≥970 | ≥14 | ≥58 | ≥280 | |||||||||||
| 40-60 | ≥780 | ≥880 | ≥13 | ≥58 | ≥250 | |||||||||||
| Mechanical properties of the rod |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Steel, calibrated and calibrated with special surface finishing, hot-rolled and hot-rolled with special surface finishing | ||||||||||||||||
| Heat treated (annealed) | ≤241 | |||||||||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on the forging cross-section and heat treatment mode |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Forgings. Quenching + Tempering | ||||||||||||||||
| KP 490 | 100-300 | ≥490 | ≥660 | ≥13 | ≥40 | ≥530 | 212-248 | |||||||||
| KP 540 | 100-300 | ≥540 | ≥690 | ≥13 | ≥40 | ≥481 | 223-262 | |||||||||
| KP 590 | ≤100 | ≥590 | ≥730 | ≥14 | ≥45 | ≥579 | 235-277 | |||||||||
| KP 640 | ≤100 | ≥640 | ≥780 | ≥13 | ≥42 | ≥579 | 248-293 | |||||||||
| Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering | ||||||||||||||||
| 200 | ≥1570 | ≥1910 | ≥12 | ≥48 | ≥481 | ≥52 | ||||||||||
| 300 | ≥1550 | ≥1760 | ≥12 | ≥50 | ≥579 | ≥50 | ||||||||||
| 400 | ≥1420 | ≥1620 | ≥12 | ≥51 | ≥432 | ≥47 | ||||||||||
| 500 | ≥1180 | ≥1300 | ≥14 | ≥52 | ≥432 | ≥42 | ||||||||||
| Long products. Isothermal hardening from 880 °C to saltpeter having a temperature of 300 °C | ||||||||||||||||
| Without departure | ≥1460 | ≥1670 | ≥12 | ≥52 | ≥687 | ≥50 | ||||||||||
| 300 | ≥1450 | ≥1670 | ≥12 | ≥55 | ≥697 | ≥50 | ||||||||||
| 400 | ≥1410 | ≥1570 | ≥14 | ≥54 | ≥520 | ≥48 | ||||||||||
| 500 | ≥1220 | ≥1330 | ≥14 | ≥53 | ≥383 | ≥43 | ||||||||||
| Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Long products. Quenching in oil from 880 °C + Tempering at 500 °C, cooling in water or oil | ||||||||||||||||
| 20 | ≥1200 | ≥1300 | ≥11 | ≥52 | ||||||||||||
| 250 | ≥1260 | ≥12 | ≥57 | |||||||||||||
| 400 | ≥1000 | ≥14 | ≥72 | |||||||||||||
| 500 | ≥540 | ≥31 | ≥70 | |||||||||||||
| Technological properties |
| Machinability | In the hot-rolled state at HB 207-217 sB = 710 MPa Kn solid alloy = 0.85 Kn b.st. = 0.75. |
| Weldability | Limited weldability. Welding methods: RDS, ADS submerged arc and gas shield, ArDS. Heating is recommended and subsequent heat treatment is required, CTS without restrictions. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | Prone. |
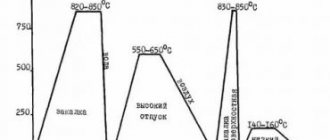
| Forging temperature | Start - 1250 °C, end - 860-880 °C. Sections up to 100 mm are cooled in air, 101-200 mm - in a mold, 201-300 mm - with a furnace. |
| Flock sensitivity | Sensitive. |
| Critical point temperature |
| Critical point | Temperature °C |
| AC1 | 760 |
| AC3 | 830 |
| AR3 | 705 |
| AR1 | 670 |
| MN | 352 |
| Impact strength |
| Delivery condition temperature | -40 | -60 |
| Quenching in oil from 880 °C + tempering at 200 °C, air cooling | ≥481 | ≥383 |
| Quenching in oil from 880 °C + tempering at 300 °C, air cooling | ≥481 | ≥383 |
| Quenching in oil from 880 °C + tempering at 400 °C, air cooling | ≥383 | ≥285 |
| Isothermal hardening from 880 °C (in saltpeter 300 °C) + tempering at 300 °C (holding 1 hour), air cooling | ≥608 | ≥520 |
| Isothermal hardening from 880 °C (in nitrate 300 °C) + tempering at 400 °C (holding 1 hour), air cooling | ≥471 | ≥363 |
| Hardenability |
Distance from the end, mm/HRCе
| 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 24 | 30 |
| 50.5-50 | 49-54 | 47.5-53 | 46-52.5 | 41.5-52 | 38-51 | 36.5-48.5 | 35-46.5 | 30-43 | 25-40.5 |
| Heat treatment | Amount of martensite, % | Crete. dia. in water | Crete. dia. In oil | Crete. hardness, HRCе | Dist. from the cooled end, mm |
| 60 | 40 | 47 | |||
| 60 | 20 | 51 |
| Physical properties |
| Test temperature, °C | 0 | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity (E, GPa) | 215 | 215 | 211 | 203 | 195 | 185 | 175 | 165 | 144 | 125 |
| Modulus of elasticity under torsional shear (G, GPa) | 84 | 83 | 82 | 79 | 75 | 71 | 66 | 62 | 54 | 47 |
| Density (r, kg/m3) | 7850 | 7850 | 7830 | 7800 | 7760 | 7730 | 7700 | 7670 | ||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (l, W/(m °C)) | 38 | 38 | 38 | 37 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 30 |
| Ud. electrical resistance (R, NΩ m) | 210 | 210 | ||||||||
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | 11,7 | 12,3 | 12,9 | 13,4 | 13,7 | 14,0 | 14,3 | 14,3 | ||
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | 496 | 504 | 512 | 535 | 585 | 620 | 625 | 695 |
| Designations |
Mechanical properties:
|
Standards for quality characteristics of brand 35hgsa
The fundamental standards for 35xgsa steel are laid down in GOST 4543-71. Explanation of the marking shows the content of alloying additives in it (in%):
- carbon – 0.35 (can reach up to 0.39)
- chrome – 1.1-1.4
- manganese – 0.8-1.0
- silicon – 1-1.4
- nitrogen – about 1.0
GOST allows the presence of other alloying elements in the chemical composition of this brand: silicon, nickel, copper, as well as small amounts of sulfur and phosphorus. Depending on the presence of a substance superior to other additives, steel of group 35 is divided into chromium (35x) or manganese without chromium, chrome-molybdenum-vanadium, etc. Chrome-silicon-manganese steel 35KhGSA can be replaced with medium-alloy structural grades 30KhGS, 30KhGSA, 30KhGT, 35KhM. Among the foreign analogues there are the Bulgarian brand 35ChGSA and the Polish ones - 35HGS, 35HGSA.
Data on the mechanical properties of this metal, obtained at a temperature of 20oC, indicate the strength of steel, since its hardness, impact strength, and short-term strength allow, according to GOST, the grade to be used in the manufacture of parts of complex configurations, in structures with high temperatures, abrasive elements, i.e. e. where the endurance and durability of the metal are needed.
Steel 30KhGSA - structural alloy
Analogs, Substitutes
Substitute steels 40KhFA, 35KhM, 40KhN, 25KhGSA, 35KhGSA.
Interpretation of steel 30KhGSA
The number 30 indicates the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent, i.e. The carbon content in steel is about 0.3%. The letter X indicates the presence of chromium in the steel; the absence of a number after the letter means that the chromium content does not exceed 1.5%. The letter G indicates the presence of manganese in the steel; the absence of a number after the letter means that the manganese content does not exceed 1.5%. The letter C indicates the presence of silicon in the steel; the absence of a number after the letter means that the silicon content does not exceed 1.5%. The letter A at the end of the steel marking means that the steel is high quality.
Application of 30HGSA
Steel 30KhGSA is used for the manufacture of shafts, axles, gears, flanges, casings, blades of compressor machines operating at temperatures up to 200 ° C, levers, pushers, critical welded structures, parts operating under alternating loads, fasteners, parts operating at low temperatures. temperatures.
Weldability
Steel 30KhGSA is weldable to a limited extent. Welding methods: RDS, ADS under submerged arc and gas shield, ArDS, EShS. Preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. KTS (Contact Spot Welding) without restrictions
Characteristics
Electrical resistivity ρ, at 20 °C - 210 nOhm*m
Density ρ kg/cm3 at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 30ХГСА | 7850 | 7830 | 7800 | 7760 | 7730 | 7700 | 7670 | — | — | — |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ W/(m*K) at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 30ХГСА | 38 | 38 | 37 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 30 | — |
Specific heat capacity c, J/(kg*K), at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 496 | 504 | 512 | 533 | 554 | 584 | 622 | 693 | — | — |
Thermal conductivity coefficient λ, W/(m*K), at test temperature, °C
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 46 | 46 | — | 41 | — | — | 33 | — | — | 29 |
Linear expansion coefficient α*106, K-1, at test temperature, °C
| 20-100 | 20-200 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| 11,7 | 12,3 | 12,9 | 13,4 | 13,7 | 14,0 | 14,3 | 12,9 | — | — |
Modulus of normal elasticity E, GPa, at test temperature, °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 30ХГСА | 215 | 211 | 203 | 196 | 184 | 173 | 164 | 143 | 125 | — |
Modulus of elasticity in torsional shear G, GPa, at test temperature °C
| Steel | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| 30ХГСА | 84 | 82 | 79 | 75 | 71 | 66 | 62 | 54 | 47 | — |
Critical point temperature
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 | Mn |
| 760 | 830 | 705 | 670 | 352 |
Chemical composition, % (GOST 4345-2016)
| Steel | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Al | Ti | V | B |
| 30ХГСА | 0,28-0,34 | 0,90-1,20 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,80-1,10 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
According to GOST 4345-2016, the mass fraction of nitrogen (N) should not exceed: in open hearth steel - 0.005%; in oxygen-converter steel: - without extra-furnace treatment: 0.006% - for thin sheet metal products and strip; 0.008% - for other types of metal products; — with out-of-furnace processing: 0.010% — for thin-sheet metal products and strips; 0.012% - for other types of metal products; in steel smelted in electric furnaces - 0.012%. The mass fraction of nitrogen in steel is not standardized or controlled in the following cases: - if the mass fraction of total aluminum in the steel is at least 0.020% or acid-soluble aluminum - at least 0.015%, or - nitrogen-binding elements (titanium) are introduced, individually or in any combination - no more than 0.040%, vanadium - no more than 0.05%, niobium - no more than 0.05%), while the total mass fraction of aluminum, titanium, vanadium and niobium should be from 0.02% to 0.15%. The mass fraction of the listed elements must be indicated in the quality document.
The mass fraction of residual elements is allowed, no more than: tungsten - 0.20%, molybdenum - 0.11%, vanadium - 0.05% and residual or intentionally introduced titanium (except for steel grades listed in Note 1 of this table) - not more than 0.03%.
According to GOST 4345-2016, the mass fraction of phosphorus, sulfur and residual elements (copper, nickel and chromium) according to the analysis of the ladle sample and in the finished metal products must comply with the requirements of Table 2.
Mechanical properties
| Source | Delivery status | Section, mm | KP | σ0.2 MPa | σin MPa | δ5, % | ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB, no more |
| no less | |||||||||
| GOST 4543-71 | Bar. Hardening at 880 °C in oil; holiday at 540 °C, cool. in water or oil | 25 | — | 830 | 1080 | 10 | 45 | 49 | — |
| GOST 8479-70 | Forging. Hardening + tempering | Up to 100 | 490 | 490 | 655 | 16 | 45 | 59 | 212-248 |
| 100-300 | 490 | 490 | 655 | 13 | 40 | 54 | 212-248 | ||
| Up to 100 | 540 | 540 | 685 | 15 | 45 | 59 | 223-262 | ||
| Up to 100 | 590 | 590 | 735 | 14 | 45 | 59 | 235-277 | ||
| 100-300 | 590 | 590 | 735 | 13 | 40 | 49 | 235-277 | ||
| Up to 100 | 640 | 640 | 785 | 13 | 42 | 59 | 248-293 | ||
| Up to 100 | 675 | 675 | 835 | 13 | 42 | 59 | 262-311 | ||
| Bar. Quenching from 860-880 °C in oil; holiday at 200-250 °C, cool. on air | 30 | — | 1270 | 1470 | 7 | 40 | — | HRCе 43-51 | |
| Bar. Quenching from 860-880 °C in oil; holiday at 540-560 °C, cool. in water or oil | 60 | — | 690 | 880 | 9 | 45 | 59 | 225 |
Mechanical properties depending on the section
| Section, mm | σ0.2 MPa | σin MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 30 | 880 | 1000 | 12 | 50 | 69 |
| 60 | 760 | 880 | 12 | 50 | 69 |
| 80 | 740 | 860 | 14 | 50 | 78 |
| 120 | 670 | 820 | 14 | 50 | 78 |
| 160 | 590 | 740 | 14 | 60 | 78 |
| 200 | 530 | 720 | 14 | 45 | 59 |
| 240 | 490 | 710 | 14 | 46 | 59 |
Note. Hardening at 880 °C in oil; tempering at 600 °C, cool. in water.
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature
| tref., °С | σ0.2 MPa | σin MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 | Hardness HB, no more |
| 200 | 1570 | 1700 | 11 | 44 | 88 | 487 |
| 300 | 1520 | 1630 | 11 | 54 | 69 | 470 |
| 400 | 1320 | 1420 | 12 | 56 | 49 | 412 |
| 500 | 1140 | 1220 | 15 | 56 | 78 | 362 |
| 600 | 940 | 1040 | 19 | 62 | 137 | 300 |
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
| tsp., °С | σ0.2 MPa | σin MPa | δ5, % | ψ% | KCU, J/cm2 |
| Bar. Hardening at 880 °C in oil; tempering at 560 °C | |||||
| 300 | 820 | 980 | 11 | 50 | 127 |
| 400 | 780 | 900 | 16 | 69 | 98 |
| 500 | 640 | 690 | 21 | 84 | 78 |
| 550 | 490 | 540 | 27 | 84 | 64 |
| Sample 5 mm in diameter, 25 mm long, rolled. Deformation speed 2 mm/min; strain rate 0.0013 1/s | |||||
| 700 | — | 175 | 59 | 51 | — |
| 800 | — | 85 | 62 | 75 | — |
| 900 | — | 53 | 84 | 90 | — |
| 1000 | — | 37 | 71 | 90 | — |
| 1100 | — | 21 | 59 | 90 | — |
| 1200 | — | 10 | 85 | 90 | — |
Endurance limit
| Strength characteristics | σ-1, MPa | τ-1, MPa | n |
| σв = 1670 MPa | 490 | 1666 | 107 |
| σв = 880 MPa | 372 | 882 | 107 |
| σв = 1080 MPa | 470 | — | 106 |
| Hardening from 870 °C; holiday at 200 °C | 696 | — | — |
| Quenching from 870 °C; tempering at 400 °C | 637 | — | — |
Impact strength of KSM
| Heat treatment | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C | ||||
| +20 | -20 | -40 | -60 | -80 | |
| Hardening at 880 °C in oil; tempering at 580-600 °C, σв = 1000 MPa | 69 | 55 | 41 | 35 | 23 |
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1240, end 800. Sections up to 50 mm are cooled in air, sections 51-100 mm are cooled in boxes.
Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 0.75 and Kv b.st = 0.85 in the hot-rolled state at HB 207-217 iov = 710 MPa. Flock sensitivity is sensitive.
Tendency to temper brittleness - prone.
Critical diameter d after quenching in various environments
| Amount of martensite, % | Critical hardness HRC3 | d, mm, after hardening | |
| in water | In oil | ||
| 50 | 38-43 | 60-91 | 34-60 |
| 90 | 43-48 | 40-68 | 18-40 |
Find out more
Steel 35 structural carbon quality…
Steel 95Х18 structural bearing…
Steel 18Х2Н4МА (18Х2Н4ВА) structural alloy…
Spring steel 75
Mechanical properties
| Heat treatment, delivery condition | Section, mm | s0.2, MPa | sB, MPa | d5, % | y, % | KCU, J/m2 | HB | HRСе |
| Bar. Quenching 880 °C, oil Tempering 540 °C, water or oil. | ||||||||
| 25 | 830 | 1080 | 10 | 45 | 49 | |||
| Forgings. Hardening. Vacation. | ||||||||
| KP 490 | <100 | 490 | 655 | 16 | 45 | 59 | 212-248 | |
| KP 490 | 100-300 | 490 | 655 | 13 | 40 | 54 | 212-248 | |
| KP 540 | <100 | 540 | 685 | 15 | 45 | 59 | 223-262 | |
| KP 590 | <100 | 590 | 735 | 14 | 45 | 59 | 235-277 | |
| KP 590 | 100-300 | 590 | 735 | 13 | 40 | 49 | 235-277 | |
| KP 640 | <100 | 640 | 785 | 13 | 42 | 59 | 248-293 | |
| KP 675 | <100 | 675 | 835 | 13 | 42 | 59 | 262-311 | |
| Quenching 860-880 °C, oil. Vacation 200-250 °C, air. | ||||||||
| 30 | 1270 | 1470 | 7 | 40 | 43-51 | |||
| Quenching 860-880 °C, oil. Vacation 540-560 °C, water or oil. | ||||||||
| 60 | 690 | 880 | 9 | 45 | 59 | 225 | ||
Steel 30KhGSA. Physical properties
| Test temperature, °C | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity, E, GPa | 215 | 211 | 203 | 196 | 184 | 173 | 164 | 143 | 125 | — |
| Density, pn, kg/cm3 | 7850 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m °C) | 38 | 38 | 37 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 31 | 30 | |
| Ud. electrical resistance (p, NΩ m) | 210 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Test temperature, °C | 20- 00 | 20-20 | 20-300 | 20-400 | 20-500 | 20-600 | 20-700 | 20-800 | 20-900 | 20-1000 |
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | 11.7 | 12.3 | 12.9 | 13.4 | 13.7 | 14.0 | 14.3 | 12.9 | — | — |
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | 496 | 504 | 512 | 533 | 554 | 584 | 622 | 693 | — | — |