Brands of electrodes for steel welding
Since there are dozens of types of steels, it means that the same number of electrodes have been developed for them. To weld steel with electrodes, you must have manual arc welding skills, select suitable electrodes and know the characteristics of the metal itself. We will talk about all this further.
Most often on store shelves you can find electrodes for welding carbon steels. And all because this metal is used most often. Therefore, any more or less large manufacturer produces electrodes for welding carbon steel. The most common brands are MR, UONI, OZS and ANO. Let's take a closer look at exactly what types of these grades are used for steel.
Brands of welding wire and its purpose
| Welding wire grades | GOST | For welding |
| Sv-08G2S Sv-08GS | GOST 2246-70 as amended. 1987 | Carbon and low alloy steels in carbon dioxide |
| Sv-08 Sv-08A Sv-08GA | Submerged carbon and low alloy steels | |
| Sv-05Х20Н9ФБС Sv-08Х25Н13БТУ | Corrosion-resistant steels in carbon dioxide | |
| Sv-07Х19Н10Б Sv-06Х19Н9Т | For argon-arc welding of corrosion-resistant steels | |
| SvAK5 | GOST 7871 75 harm. 1989 | Aluminum grades AD1 and AD1M |
| SvAMg5 SvAMg6 | Aluminum-magnesium alloy AMg5, AMg6 |
17a. Welding materials used in welding general purpose pipelines
| Steel parts to be welded | Submerged arc welding | Welding and flux-cored wire for open arc and carbon dioxide welding | Electrode for manual arc welding | ||
| flux | welding wire | type | brand | ||
| St3kp, St3ps | AN-348A, OSTS-45 | Sv-08 | Sv-08G2S, PP-AN1, PP-AN8, PP-2DSK | E42, E46 | MR-3 ANO-4, ANO-6 |
| St3sp, VSt3ps, St3Gps | AN-348A, OSTS-45, AN-348AM, OSTS-45M | Sv-08AA, Sv-08A | Sv-08G2S, PP-AN3, PP-AN7, PP-AN11, PP-2DSK | E42A, E46A | UONI-13/45, SM-11 |
| 09G2S, 10G2S1, 10HSND, 14G2, 15HSND | Sv-08GA, Sv-10G2 | Sv-08G2S, PP-AN7, PP-AN9, PP-2DSK, PP-3DSK | E46A, E50A | UONI-13/55, UONI-13/45, ANO-7, TMU-21 | |
| 17G1S, 17G1S-U | Same | SV-08G2S, PP-AN7, PP-2DSK | E50A | UONI-13/55, TMU-21 | |
Welding Features
To ensure decent quality of seams, you need to know some of the nuances of welding steels. Of course, we can't list them all, but you'll learn the basics that will make your job easier.
When welding high-carbon steel, it is recommended to preheat the metal to a temperature of no more than 650 degrees. For welding, use contact, gas or arc technology. It is advisable to use fluxes and filler wire. The composition of the wire must be identical to the composition of steel.
To weld austenitic steels, use resistance welding technology using a reduced welding current density.
Dissimilar steels
As for welding dissimilar steels, this too has its own characteristics. Those metals that belong to different classes are considered dissimilar. For example, austenitic steel and pearlitic steel are dissimilar. High-alloy and low-alloy steels are also considered dissimilar. For such work during RDS welding, it is necessary to use special electrodes for welding dissimilar steels. But RDS welding is still not recommended. It is advisable to weld such metals not by electric arc welding, but by laser or plasma. Such technologies require a shallow melting depth of the metal. Therefore, the quality of the seams is much better than with arc welding.
A separate technology was invented specifically for welding pearlitic and austenitic steel. The essence of this technology is simple. A small layer of austenitic steel is fused onto the pearlitic steel part. Then the edges are heated and both parts are welded together. In this case, you need to choose the welding mode that is suitable for the austenitic part.
Use low hydrogen electrodes when welding dissimilar steels. Indeed, with an excess amount of hydrogen, parts begin to form cracks in their initial stages. Also, with an excess of hydrogen, the likelihood of pore formation increases.
Which electrodes are best for cooking: choosing the right electrodes
A welding electrode is a relatively small rod that is made from various metals and has electrically conductive properties. Its main purpose is to supply current during welding. The quality of the seam depends largely on the chosen electrode. Considering that there are quite a large number of varieties, the question arises: “which electrodes are best for solving a particular problem?”
Key selection criteria
When choosing which electrode to weld metal with, you need to consider the following parameters:
- Rod diameter.
Selected depending on the thickness of the structure being welded. The thinnest rods have a diameter of 1.6 mm. They are intended for joining sheets no thicker than 2 mm, while rods with a diameter of 5-6 mm allow you to weld sheets up to 13 mm thick.
- Welding current strength.
This parameter is calculated in such a way that for each millimeter of the rod there is about 30-40 Amperes of current. If welding is performed in a vertical position, the current strength is reduced by 15%. - Metal grade.
Each of them has its own unique chemical composition and physical properties. For example, to work with heat-resistant steels, you need to use electrodes that provide a temperature of about 1100°C.
Please note that the welding current should not be too low, as this will cause the tip to stick. If the values are excessively high, the arc will burn well, but in this way the surface of the material can be burned. In this mode, rods with a small diameter burn out very quickly, unable to cope with their task.
It is also important what components the rod coating consists of. As a rule, there are 6-12 of them. In this case, each component is responsible for creating the environment necessary for the formation of strong seams with stable characteristics.
The main ones:
- cellulose layer - creates a cloud of gas with a reducing agent;
- calcium fluoride – makes iron oxides more fusible, and the released gas stabilizes the combustion process;
- carbonates - responsible for the formation of slags;
- ferromaterials (Mg and Si) – deoxidize the seam after welding;
- titanium dioxide - allows the slag to harden, which improves the fluidity of the melt;
- gum with clay elements - makes the coating more durable;
- iron powder – improves the quality of the weld by equalizing the temperature.
It is necessary that the material of the electrodes and the type of metals being welded match their characteristics.
Welding carbon and low alloy steels
In this case, the main role is played by the electrode coating material. So, for welding boiling grades of steel (has a low carbon content and is slightly deoxidized), any coating is suitable. To weld semi-quiet steels, which have large sheet thicknesses, a base or rutile coating is required. When welding structures made of mild steel at low temperatures or under dynamic loads, electrodes with a basic coating are also used.
Unstable arc combustion can deteriorate the quality of the seam and will not allow normal welding of metal structures using alternating current. The arc burns best in the presence of cellulose, acid and rutile coatings. In this case, you can use welding transformers. In addition, you need to thoroughly clean the welded edges from rust, oil and dirt in order to avoid the formation of steam.
How to weld and surfacing cast iron
The procedure allows you to eliminate defects in cast iron castings, as well as restore damaged parts that have exhausted their service life. The result is steel, various alloys based on copper, nickel, etc. Models of the TsCh-4, OZCH-2, OZCH-6 and similar brands cope best with the above task. In some cases, for example, during the repair of cast iron tubes with heavy contamination and high humidity, it is advisable to use the OZL-25B, OZL-27 and OZL-28 grades.
Welding of non-ferrous metals
Each of these metals has its own melting threshold and physical and chemical properties. For example, intense oxidation does not allow welding of titanium and its alloys. In the case of aluminum, the process is complicated by the oxide film, which melts at a temperature of 2060°C, and in order to melt the aluminum itself, 660°C is enough. The film formed due to the oxide can lead to disruption of the integrity of the seams and a decrease in their strength. It is removed by adding chloride and fluoride salts of alkali and alkaline earth metals.
Copper also has its own problems when welding - pores form in the weld under the influence of gas bubbles (especially oxygen and hydrogen). To avoid this, the copper must be well deoxidized, and the edges must be thoroughly cleaned before welding begins. In turn, bronze is highly brittle, and nickel and its alloys are sensitive to gases dissolved in the weld pool - nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen. As a result of this process, hot cracks and pores appear in the metal structure.
Metal cutting
Arc cutting of metal structures is used for installation and repair of various metal structures. It is not very efficient; you should not expect a “beautiful” seam from it, or an accurate cut.
However, this cutting method does not require additional equipment or highly qualified workers. It is easy to learn for a beginner. Cutting by electric arc welding is often used in training, in particular in mastering the principles of working with an inverter. This method is often used by home craftsmen for inexpensive metal cutting.
Welding alloy steels with increased heat resistance
Alloyed heat-resistant steels are welded with special electrodes that provide a certain heat resistance of the welded joints.
The resulting structure must withstand significant mechanical loads and high temperatures. The likelihood of cracks forming due to temperature changes is also minimized. Thus, at temperatures up to 475°C, models made of molybdenum like E-09M are used, and at temperatures up to 540°C, models with a high content of chromium and molybdenum (E-09MH, E-09X1M, E-09X2M1 and E-05X2M) are used. . E-10Kh5MF has a high chromium content, which makes it possible to weld steel structures with the appropriate chemical composition.
What electrodes should be used to cook high-alloy steel?
Such steels contain 13% chromium and have anti-corrosion properties. In this case, the metal seam must be resistant to atmospheric precipitation in slightly aggressive environments, heat-resistant (maximum temperature 650°C) and heat-resistant (maximum temperature 550°C).
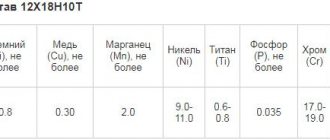
Models of type E-12Х13 of brands LMZ-1, ANV-1, etc. have such properties. If the steel has a low carbon content and there is nickel alloying, preference is better to give to products under the index E-06Х13Н. If you need to weld steel sheets containing 25% chromium, options like E-08X24N6TAFM are best, making the finished weld ductile, impact-resistant and corrosion-resistant.
Welding of dissimilar steels and alloys
We are talking about steels and alloys that have unique physical and mechanical properties, chemical composition, and weldability. Such steels can be carbon and alloyed, high-strength, heat-resistant, and also high-alloy.
Welding steels and alloys with dissimilar structures also has a number of characteristic features. To avoid the formation of cracks, areas with an inhomogeneous structure at the melting site, as well as excessive growth of residual stresses, models like ANZHR-1, OZL-27, NIAT-5, EA-395/9, OZL-25B, IMET-10 and TsT- are used 28 with special properties.
Welding machine compatibility
When choosing which electrodes to weld steel with, it is necessary to take into account not only the type of material for which they are intended, but also the features of the welding machine.
Of course, in theory and in practice, the owner of an electric arc machine can use any electrode. However, in reality there are devices that are better suited for use with rods of a certain type of coating (for example, IN226 CEL - excellent for cellulose-coated electrodes).
In addition, welding machines have a current limitation. This range imposes its own limits on the use of diameter electrodes. How to determine if consumables are suitable? Just look at the table below:
Now you are more familiar with electric arc welding and some of the nuances of choosing welding electrodes. We advise you to read other articles in this section to gain useful knowledge about welding processes, materials and important nuances for improving the quality of welding work.
Recommendations for beginners
As you can see, welding steel comes with many nuances that you need to be aware of. Beginners are often afraid to take on steel welding, thinking that they will not be able to complete such a complex job. But, believe me, the more experience you have, the higher your professional skills. This means the work itself is easier.
You can avoid complex welding work as much as you like, but you will never learn the main thing. And having a solid base of theory and skills, you can already perform complex welding. Even without enough experience.
Your work will be simplified by the correct selection of electrodes. Are you welding heat-resistant steel? Come to the store and clearly explain to the seller that you need electrodes for heat-resistant steels. This is where you can start. In the future, you will already gain enough experience to choose electrodes yourself without outside help.