To ensure the normal and long-term functioning of pipelines, it is necessary to take care of several important details in advance:
- Firstly , in a pipeline system, all pipes must be properly connected to each other;
- Secondly , it is necessary to ensure the same high-quality connection of pipes with connecting parts, fittings, fittings, compensators, etc.;
- Thirdly , the correct choice of pipeline design plays an important role.
There are special requirements for pipe connections, the most important of which are:
- Strength so that the pipeline can be operated under pressure;
- Density;
- Resistance to external factors and aggressive environments;
- Simplicity and speed of installation.
Types of pipe connections
Pipe connection option
Pipe connections can be detachable or permanent.
Detachable type connections include:
- Threaded,
- Bell-shaped,
- Flanged, etc.
Permanent type connections include:
- Connections formed by soldering;
- Joints formed by welding;
- Joints formed by gluing;
- Compounds formed by pressing;
- Connections formed by concreting.
The connection principle is selected taking into account many factors:
- The material from which the connection parts are made;
- Operating conditions of the future pipeline;
- The temperature of the substance that will be transported through the pipes;
- Pressure inside the pipeline;
- Physical and chemical characteristics of the product that will be transported.
Connection methods
There are many types of connections. Their choice depends on various factors:
- material of manufacture;
- characteristics of liquids;
- operating conditions.
The methods of connecting pipes into a single system are different in each case. Copper products are most often soldered, plastic ones are welded, metal-plastic ones are joined using compression fittings, and steel ones are joined using threads.
The system must be reliable
Types of connections can be detachable or permanent:
- Detachable threaded connections of water pipes and other networks allow, if necessary, to disassemble the system without violating its integrity. Typically, this type of joint is used when arranging internal communications.
- The most popular types of permanent pipe connections are welding. This method also includes gluing, which is used less frequently, since many consider it less reliable.
Types of steel pipe connections
The following methods are most often used to connect steel pipes:
- Welding;
- Thread;
- Flanges.
Welding of process pipes usually occurs butt welding. The nature of the welds in connections can be different.
The most common seams are the following:
- One-sided. They are used when welding pipes with a diameter not exceeding 53 cm;
- Double-sided. Used for pipes with a diameter of more than 53 cm of group A.
- Double-sided with spacer ring.
Spacer rings are designed to reduce the flow area of the pipe. With the help of rings, the movement of the product transported through pipes is slowed down.
It is very important to use officially approved regulatory and technical documents (GOSTs) when choosing types, sizes and parts of pipes, fittings and welded joints.
Flange connection
Features of connecting profile pipes
Profile pipes have good strength and relatively low weight, so they are often used for the installation of frame structures, as well as for other construction purposes.
The shape of profile pipes can be:
- rectangular (the most common shape);
- square;
- ovoid (oval);
- others (more complex forms).
The most reliable way to create structures from profile pipes is to fasten them by welding
Electric arc welding is usually used to connect square pipes. There are also special connections that are made using bolts and rivets. Square and rectangular pipes are joined using the same methods.
In addition, various parts can be joined to such pipes. This joining is carried out using self-tapping screws. These elements do not require preliminary holes.
Welded joints of steel pipes
It is very important that in a pipeline the strength of the welded joints of the pipe parts is identical to the strength of the pipes themselves. Not so often, but it is still possible to use welded joints whose strength is lower than the strength of the base metal. This is possible when the technical specifications confirm the strength of the welded joint used.
Sometimes during the welding process of steel pipes, deposits of molten metal form on their inner surface. This is not very good, since due to such formations the permeability of the pipe is reduced, and the resistance to the movement of the substance transported through the pipes increases.
This problem especially often arises when welding pipes of small diameter - from 1 to 3.2 cm. To avoid such a drawback on pipes that are operated under high pressure, they are welded into a socket.
Fittings connecting parts of pipeline
17.04.2018
Introduction
Fittings are the connecting parts of a pipeline installed for branching, turning, transitions to another diameter, as well as when frequent assembly and disassembly of pipes is necessary. Without such products, it will be difficult to assemble a communication system for heating, gas equipment, sewerage or water supply. Fittings are also used for hermetically sealing pipelines and for other auxiliary purposes.
Fittings connecting the ends of pipes of the same diameter are called straight, fittings connecting the ends of pipes of different diameters are called transition fittings.
Areas of use
Fittings have a very wide range of applications; they are necessary when installing almost any pipeline:
- gas station
- Housing and communal services use water pipes in areas;
- Filling and loading systems
- instrumentation
- Oil and gas valves
- Metallurgy
- Oil and gas industry on oil pipeline sections;
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Heat and Energy on heating mains
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Chemical industry
- Refrigeration units
- Food industry
Types of fittings
1) Coupling – an element for fastening parts of a pipeline. They are simple (straight) and transitional. The first resemble a piece of cut pipe with any type of connection and connect two identical pipes. Transition pipes are used to connect pipes of different diameters to each other. Such a coupling has different diameters at different ends;
Figure 1. Crimp fitting.
2) Barrel - completely has the appearance of a coupling. The only difference is that there is a thread cut on the upper surface of the edges. Barrels are used to transfer from a pipe, for example, to a faucet. The simplest one also looks like a piece of threaded water pipe;
Figure 2. Male barrel fitting.
3) Squeegee - at first glance, this is a copy of a barrel. But if you look closely, the difference is immediately visible: on one side the thread is much longer than on the other. They are mainly used to repair ruptures in pipelines. They are mainly attached in pairs with couplings;
Figure 3. Connection fitting with external thread.
4) Angle – used to change the direction of the pipeline. Angles are couplings and barrels, bent at an angle of 90, 30, 45 degrees. Fittings at other angles are very rarely found on sale;
Figure 4. Angle fitting with internal thread.
5) Tee - used in cases where it is necessary to separate the pipeline into several branches. Such fittings allow you to make a new branch without interrupting the main one. Usually the pipe is diverted from the main one at an angle of 90 or 45 degrees. To do this, you need to select a suitable tee;
Figure 5. Male Tee fitting.
6) Crosspiece - used for the same purposes as a tee, only with its help you can make two new pipeline branches at once or connect four pipes. Its branches are located at angles of 90 degrees among themselves;
Figure 6. Female cross fitting.
7) Fitting - a connecting element (fitting) with an internal thread, necessary for connecting a flexible hose or soft pipe with a metal pipe (tube) having an external thread of the appropriate diameter.
A female threaded fitting is also called a nut fitting.
Figure 7. Fitting fitting.
 Plugs - used to close a pipeline branch. This may be a temporary closure until work is completed, or it may be permanent (if necessary). They serve as auxiliary elements;
Plugs - used to close a pipeline branch. This may be a temporary closure until work is completed, or it may be permanent (if necessary). They serve as auxiliary elements;
Figure 8. Male plug fitting.
9) Futorka - a type of threaded fitting. It is a nut or bushing that has an external thread for a connection of a larger diameter and an internal thread for a connection of a smaller diameter, or vice versa.
Figure 9. Ferrule fitting.
10) Union nut (American) - connecting pipes using a fitting, which is a coupling with a union nut. The American allows you to connect the main line without rotating the pipes. You join two parts, for example, a pipe and a coupling, and twist the nut. In this case, the parts themselves do not rotate. An American detachable connection with a union nut is used to connect two sections of pipes of small diameter. This connection has small dimensions and is designed for quick assembly and disconnection of pipes for repair or replacement without the need to rotate the entire section of pipe or one of the pipes.
Figure 10. American fitting.
Figure 11. American fitting. Drawing.
Methods of fastening fittings
1) Adhesive. The name speaks for itself. All joints are connected using polymer glue. It is very convenient and does not require the use of special tools; This fastening method is used for PVC pipes - these are products made of a plastic polymer with the unpronounceable name polyvinyl chloride. This material finds its application in many areas of modern life, including the creation of pipelines for various purposes.
Installation of a pipeline using glue is called cold or chemical welding, due to the strength and integrity of the resulting connection. PVC adhesive has a common base with the material from which PVC pipes are made. It acts on the top layer of the parts being joined, softening it. After the glue hardens, a durable monolithic structure is obtained.
Figure 12. Bonding polymer pipes.
2) Threaded. The threaded fitting is quite easy to install, and then it can be disassembled. When disassembled, it is a combination of a fitting, a union nut and sealing rings. The design may vary depending on the type of thread, but these changes are minor and relate only to the practical use of the parts. Threaded steel or brass pipe fittings can be installed in a short period of time. This process is quite simple and does not require special tools. The fitting is screwed onto the pipe and tightened with a wrench. However, simplicity lies the main problem with working with such connections. No matter how well you tighten the nut, over time it will loosen and leak. The thread does not make it possible to really seal the joint properly. The situation can be corrected by wrapping sealing tape around the thread, but these are only half measures. In any case, you will have to constantly check the connections for strength and tighten the nuts if necessary.
Figure 13. Threaded fittings.
3) According to the type of thread, fittings are divided into three groups:
a) Metric thread (DIN/GOST) - European thread standard. It has a wide range of sizes and different thread pitches. Threads of this type are parallel (cylindrical), but there are also conical threads.
b) Inch pipe thread (BSP) - English thread standard. The English inch system is used, one inch is equal to approximately 25.4 mm. Widely used in the pipe industry, and in plumbing in particular. Thread pitch is measured in threads per inch.
c) Inch thread (SAE) - American thread standard. The American inch system is used, one inch is equal to approximately 25.4 mm. It is used on almost all equipment of American companies, regardless of the country in which this equipment was produced. Thread pitch is measured in threads per inch.
4) Self-fixing. Inside this fitting there is a special spring-clamping mechanism with teeth. During installation, the self-locking fitting is pushed onto the pipe all the way, and then, using a special wrench, the fasteners are snapped onto it. At this moment, the teeth in the fitting mechanism snap into place and fit into each other's groove. Tightness is achieved using a special seal between the teeth. This fact must be taken into account if the pipe is part of the grounding. After all, such fastening, thanks to the dielectric gasket, disrupts electrical conductivity.
The convenience and practicality of this type of connection is also due to the fact that using the same key that is used for clamping, the fitting can be disconnected in a matter of seconds.
Figure 14. Self-locking fitting design.
Figure 15. Self-locking fitting.
5) Capillary soldering fittings. When connecting copper pipes by capillary soldering, a telescopic (coaxial) overlap connection is used, in which a capillary effect occurs in the installation gap (only 0.02-0.40 mm thick) when heated (molten solder is evenly sucked into the gap and, cooling, provides a strong connection ).
Figure 16. Capillary solder fittings.
They are the simplest in design and the cheapest of copper fittings. Pipes and fittings for soldering are made from one grade of copper - Cu-DHP, and they can be used for high-temperature and low-temperature welding. When soldering using fittings, installation time is reduced, and the strength and reliability of connections increases, since the metal of the pipes is not deformed.
For low-temperature capillary soldering, there is a specific type of copper fittings with a special groove around the circumference inside the fitting, into which solder has already been inserted; all that remains is to put it on a pipe whose edge is coated with flux (usually borax), and heat the joint with a torch. The use of such fittings speeds up installation several times.
High-temperature soldering is widely used in the installation of water supply and heating systems due to the high strength of the resulting connections. Special shortened shaped fittings are also produced for it with the dimensions specified in EN 1254-5. Short fittings are prohibited from being used in gas supply systems due to the narrow junction band.
6) Compression. They connect pipes of different diameters and from different materials. Compression fittings consist of components such as a fitting, a split ring and a union nut, while providing a reliable connection of the elements using an ordinary wrench.
By tightening the union nut of the fitting, we thereby compress the press sleeve (split O-ring) on the pipe, thereby achieving the required density between the inner wall of the pipe and the fitting fitting.
Figure 17. Compression fittings.
The advantage of this is that installation does not require the use of special tools and equipment, while it remains possible to dismantle the connection if necessary.
7) Press fittings. They are very durable, but to install them you need a special tool - a press. Mainly used for connecting pipes made of plastic and metal-plastic. Used for radiators, boilers, boilers. After their installation, a sealed connection is obtained. Suitable for all types of pipes. It cannot be disassembled in the future and does not require any tightening.
Press fittings for metal-plastic pipes, the price of which always corresponds to the quality, have the following design:
- body, most often brass, varying depending on the type of model (coupling, adapter, angle);
- a stainless steel sleeve is the main element of the fitting, which is compressed and is not able to restore its shape after installation;
- the ring clip required to connect the body and sleeve is made of elastic material and also plays the role of a protective gasket that prevents the flow of galvanic currents to the connection made.
Figure 18. Press fitting design.
 Slip-on fittings
Slip-on fittings
Pipe connections using push-on fittings are performed as follows:
- Prepare the pipe for connection and put a coupling on it.
- The cleaned edge of the pipe is treated with an expander and flared.
- Place the pipe on the fitting fitting, clamp the sleeve in a manual or hydraulic press, press it onto the fitting, and the connection is ready.
The principle of operation of a push-on fitting is simple: by directly pushing the coupling onto the fitting, the pipe is pressed as tightly as possible, thereby ensuring a reliable connection.
Figure 19. Connecting pipes with a slip fitting.
9) Welded fittings. Metal fittings are welded “butt” or “overlapping”, resulting in a permanent connection. This type of pipe connection requires the use of special equipment and high specialization of the worker.
Figure 20. Stainless steel butt weld fitting.
Welded fittings are designed for installing water pipes from polypropylene pipes and some types of metal-plastic pipes; they themselves are also made of polypropylene/plastic.
Welding (if you can call it that) occurs using a special soldering iron, which simultaneously melts the inside of the fitting and the outside of the pipe, after which they are joined, forming a monolithic (solid) connection.
Such connections can be used for the installation of a water supply system in a closed manner, and do not require maintenance at all.
Figure 21. Polypropylene butt weld fitting.
Fittings with embedded heaters are a subdivision of welded fittings, but their advantage is that a welding machine is not needed, since the heating element, which melts both the fitting and the pipe, is located inside it.
The installation process looks like this: the pipes are inserted into the fitting, the fitting is connected to a special transformer using contacts located on it, the pipe is melted and soldered inside the fitting.
Figure 22. Fittings with embedded heaters.
10) Flanges - flange fittings that have a flange as a connecting part. Produced with bend angles of 45° and 90°. Depending on the flange diameter, several standards are distinguished:
- 3000psi - according to SAE J516/J518, light series.
- 6000psi - according to SAE J516/J518, heavy series.
- Komatsu - a flange developed by the Japanese company Komatsu with a flange diameter of 34 mm.
- Supercat is a reinforced version of the 6000psi flange, differs from it in the thickness of the plate, it is always 14.3 mm.
To ensure the tightness of the connection, when using flanges, they have a special groove into which an O-ring is inserted. Rings are made from different materials and, as a rule, are not included in the delivery set of flanges; they are purchased separately. To select a flange, you need to know three parameters: the diameter of the shank, the diameter of the flange plate and the thickness of the plate. The flanges are fastened using special clamps, which can be split (consist of 2 halves) or continuous (put on the flange before crimping).
As a rule, these products are selected for the cross-section of the pipeline. Also, sometimes the flange parts for joining are welded directly to the pipes, but in this case the reliability of the unit is greatly reduced.
The advantage of flange fittings is the fact that with their help, shut-off valves, various sensors, valves, etc. can be installed on large-diameter pipelines.
Figure 23. Flange fitting.
Tips for choosing fittings
The main selection criterion is the diameter of the connected pipeline. This is the main factor to consider when choosing. If you get the diameter wrong, you won't be able to make the connection. You should also take into account the purpose of the product - depending on where exactly and for what exactly you will use it. If the pipeline system is designed independently, then it is necessary to draw up a diagram of the future design. On it, in addition to the length of the runs, nodes and supply points should be indicated. It is recommended to use fittings from the same manufacturer.
Advantages of fittings
The fitting, despite its small size, is one of the most important parts in pipelines. The use of fittings greatly simplifies the installation of the pipeline; they are produced in standardized sizes. Most systems using fittings can be quickly disassembled and assembled. Fittings allow you to create and implement the most complex projects and structures. For example, in areas where there is very little space or the object has a complex configuration.
Thanks to such a mass of advantages, today fittings are used for laying any pipeline: heating, water supply, gas supply and other systems. Author of the article: Elena Petrovna Domashnikh, specialist in working with corporate clients at Cryonics LLC
Flanged connections for steel pipes
Flange connections are most often used in places where pipes are connected to various devices or equipment of different types, on which mating flanges are located. You can also find flange-type connections on sections of pipes that need to be regularly repaired or replaced during use. For example, when installing sewer pipes.
A flange connection consists of two flanges complemented for sealing purposes by a gasket or ring, connecting nuts and bolts.
Threaded steel pipe connections
Threaded connections are most often used in pipelines when connecting them to instrumentation and pre-threaded fittings. Threaded connections are also used when installing sewer pipes in heating, water supply or sewerage networks.
The threaded connection is made by cutting or rolling threads from the outside of the pipe. Subsequently, a coupling with a similar internal thread is screwed onto this thread.
As a rule, when connecting steel pipes, conical or cylindrical threads are used.
To avoid leaks from the pipeline, a sealing material is placed between the coupling and the pipe, which can be used as a variety of substances (rubber, sealant, asbestos fiber, etc.). The choice of sealant mainly depends on the temperature of the substance transported by the pipeline.
The most commonly used seals include:
- Linen strand. This substance is pre-impregnated with red lead or white lead and operated at a temperature not exceeding 105 degrees.
- Asbestos cord with flax strands. Impregnated with granite and used at temperatures exceeding 105 degrees.
- Cord and FUM tape. It is fashionable to use at operating temperatures up to 200 degrees.
It should be remembered that flanged and threaded connections must be checked for damage from time to time, so their use in hard-to-reach or inaccessible places is not recommended.
Popular types of pipeline connections
In addition to practicality, when choosing the type of connection, you also need to take into account the properties of the material, as well as the operating mode of the pipeline. For example, the sewer system in a private house operates in a free-flow mode, so a regular socket connection is suitable.
But in the case of installing a heating system, you will need something more reliable. The following are the most common methods.
Threaded connection
It can be considered a classic method that was used decades ago.
The instructions have not changed at all since then; you need to act in the following sequence:
- The fitting is tried on and a mark is made on the pipe to which the thread will need to be cut;
Set of nozzles for thread cutting
- Actually, the thread is cut. For convenience, the pipeline must be secured in a vice; the slightest misalignment of the die when cutting threads can cause leaks in the future;
- winding is performed - linen thread or any synthetic seal is simply wound onto the thread. Its price is minimal, and the tightness of the joint increases significantly;
It is recommended to wrap tow on the threads for greater tightness of the joint.
- a fitting is screwed onto the thread. The threaded connection of pipes belongs to the detachable category, which facilitates dismantling and cleaning of the pipeline.
Note! Threading weakens the section slightly. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid, if possible, mechanical impacts on the joint.
Using a collet (clamp) fitting
The use of such a fitting allows you to connect even pipes from different materials. The connection is detachable, which can also be attributed to the advantages of using collet fittings.
Collet connection diagram
When a collet connection of pipes is used to join different materials, the tightness of the joint is achieved on one side by a union nut and a ferrule ring, and on the other by a collet.
Docking is performed in the following sequence:
- a union nut and a ferrule ring are put on the pipe (in that order);
- then the nut is tightened, the ring is deformed and tightly presses the end of the pipeline to the end of the fitting;
- on the other hand, a pipe is simply inserted into the collet and pushed in until it stops. The design creates sufficient pressure on it, so that the strength of the joint is guaranteed.
Steel teeth hold the pipe firmly in place
Movable connection
Sometimes standard fittings do not allow pipes to be joined at the desired angle. In this case, you can use a swivel pipe connection. This joining method will also be useful in that the angle of inclination can be easily changed without dismantling part of the pipeline.
In the photo - a swivel joint
Such connecting parts are sold already assembled, and mobility is achieved due to the unusual design of the socket. The bell itself is quite wide, and the part of the pipe that is placed in it has a spherical shape. The space between the end of the pipeline and the inner surface of the socket is filled with rubber inserts and a layer of lubricant.
This is what the hinge joint looks like in cross section
Note! The resource of this type of connection is limited (the manufacturer indicates a guaranteed number of turns), so you should not bend or unbend the pipeline unnecessarily.
As for the rotation angle, it is usually in the range of 40-50ᵒ. Large rotation angles complicate the design of the rotating part and jeopardize the tightness of the joint. Transporting aggressive liquids greatly reduces the service life of the joint.
High pressure pipeline
It is unlikely that you will have to work with high pressure at home (the pressure in the water supply cannot be considered as such). But in industry, quite often liquids are transported under significant pressure, which puts forward more stringent requirements for joints.
High pressure hoses of different diameters
High pressure pipe connections with a large number of turns and fittings installed in these places will have a low degree of reliability compared to a pipeline with a minimum number of turns.
To solve this problem, high-pressure hoses are often used. Externally, such a hose looks like a regular rubber hose with metal fittings on both sides.
Despite its appearance, the design of the RVD is complex. The sleeve consists of an inner layer of special rubber, and strength is achieved through a power frame made of metal threads. There are often several such power frames.
RVD structure
The main advantage of such hoses is that the rotation is smooth and the resistance to fluid flow is minimal. The ends of the hose are connected to the pipeline using metal fittings.
American - simplicity and reliability
Any type of pipe connection must be reliable and, if possible, allow the pipeline section to be dismantled as quickly as possible without dismantling the rest of it. According to these parameters, the American is unrivaled.
Brass elements for American connection
To connect 2 sections of the pipeline in this way, you will need 2 threaded fittings (one of them with a restrictive collar), a rubber gasket and a union nut. The ends of the pipeline must have internal threads.
The American pipe connection is performed in the following sequence:
- the part with external thread is screwed onto a section of the pipeline with internal thread;
- after this comes the turn of the part with the collar, you need to put a seal and a union nut on it, after which the fitting is also screwed onto the pipe;
- After this, all that remains is to screw the union nut onto the external thread of the mating fitting.
Note! Unlike most other types of connections, dismantling part of the pipeline does not require disassembling the entire pipeline. The entire assembly/disassembly process is accomplished with just one nut.
T-joint
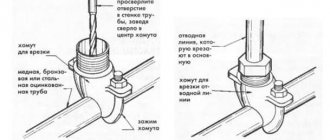
A T-joint of pipes can be at a right angle or at an acute angle; it is necessary when another pipe needs to be inserted into an existing pipeline. An example would be the insertion of a sewer pipe coming from an apartment into a riser. There are two ways to ensure insertion - using special fittings or welding (if the pipes are metal).
As for fittings, tees and crosses are used for this; these elements allow you to create a complex assembly. Such connections to a tee can be made by any of the described methods. A compression fitting, PP welding (in the case of a polypropylene pipeline), a socket connection (if we are talking about sewerage), etc. can be used.
Tees allow you to connect without welding at any angle
Inserting metal pipes by welding is rarely done and is quite difficult for a novice plumber. The main problem here is to correctly mark the cutout on the pipe that needs to be cut into and on the end of the pipeline that will be connected.
When cutting into a pipe, correct marking is important
To solve this problem, you can use special templates, which, depending on the diameter, show curves that mark the contour of the cutout; you can also use special programs for marking.
Pipe tapping template
Note! If the cutouts do not match perfectly, then the cracks will have to be welded with pieces of metal, and this will negatively affect the tightness. Therefore, you need to pay special attention to the markup.
Union connection
The pipe fitting belongs to the detachable class and consists of the fitting itself (a regular bushing with a thread and a restrictive collar), an O-ring and a union nut.
The procedure for joining pipeline sections in this way is somewhat reminiscent of the American one:
- you need to put an o-ring and a union nut on the fitting (threaded bushing);
- after this, the fitting is screwed onto the threaded pipe;
- To complete the connection, all that remains is to screw the union nut onto the coupling or the end of another pipeline.
Scheme of fitting connection with external thread
This method is often used when some kind of measuring device needs to be embedded into an existing system. The fitting is convenient because there are almost no restrictions on the diameters of the elements to be connected; to ensure tightness, it is enough to simply select the desired diameter of the fitting fitting.
Groove connection
This type of connection can be considered one of the simplest. The groove connection of pipes belongs to the category of weldless detachable types of pipeline joining.
Grovelok is a regular clamp that allows you to quickly combine 2 pipes into one. The design of this element is quite simple - a plastic case inside of which there is a rubber seal and bolts on both sides. By tightening the bolts, the necessary pressure is created, the rubber cuff is deformed, fitting tightly to the surface of the pipeline, thereby ensuring the tightness of the joint.
Groove connection diagram
Weldless pipe connection is the best option from the point of view of pipeline maintenance. At any time, the bolts can be loosened, the clamp removed, and the damaged section of the pipe can be cleaned or replaced.
The design of some groovelocks is a little more complicated and has a protrusion along the entire circumference at the bottom. There must be a groove in the pipeline at a certain distance from the joint; when joining, the protrusion on the groovelock fits into this groove, providing additional strength to the joint.
Connecting plastic pipes by welding and gluing
Welding and gluing methods are used in cases where it is necessary to ensure permanent connections of plastic pipes. Welding is a physical process of joining two substances, when heated, the molecules of one substance join with the molecules of another substance (diffusion), as a result of which the boundaries between the two substances disappear and their physical separation becomes impossible.
When heated, plastic melts, becomes fluid and takes on a viscous form, as a result of which almost any substance can be attached to it.
Under pressure, the molten plastic and another element are combined. Typically, the surfaces to be joined are heated only in the area of the future seam. This uses a tool heated by filler material or gas.
How to connect two plastic pipes
When welding with heated gas, the elements being welded and the filler material are simultaneously heated. In this case, the heater is a stream of hot gas, which is preheated in the burner.
Important! If a heated tool is used during welding, then during the heating process the surfaces of the parts being welded are melted through contact with the heating tool.
The tool is usually heated over an open fire. Electric current or other substances may also be used. Welding with this method is usually carried out butt and socket.
When welding with a filler material, the heat that the filler material transfers to the elements being welded is used. As a result of such heating, the elements melt, become soft and are firmly connected to each other.
Welded connection of plastic pipes
Detachable connections for plastic pipes
There are three main types of detachable connections for plastic pipes:
- Flanged;
- Bell-shaped;
- Connections using union nuts.
Flange connections are made on flanged pipes made of PVC, polyethylene and polypropylene. Connections with union nuts are not used very often.
It is mainly used when installing or repairing pipes in a water supply system if their diameter exceeds 6.3 cm. If the pipe size is less than the specified value, then the connection with union nuts is not used. This is explained by the increased sensitivity of plastic to stress, cuts and damage, as well as to weakening of the pipe cross-section.
The socket type of connection is usually used on pipes of sanitary systems. In this case, it is optimal to use rubber sealing rings and a combination of polyethylene pipes inside the pipeline structures and PVC outside.
With any of the listed types of connection, movement of parts that occurs due to deformation due to certain temperature conditions is possible.
Connecting flexible pipes without welding
Often, in order to install a pipeline without the use of welding equipment, special connecting elements - fittings - are used. Fittings for flexible pipes must have a large reach to make a reliable and airtight joint.
Compression fittings allow you to create a tight connection without welding or threading
As a rule, fittings are used in flexible pipelines that have small or medium cross-sections (from 20 to 315 mm). For parts with a diameter above 315 mm, a fitting joint is not practical. This is due to the fact that the reliability of such a connection is quite low.
For joining low-pressure polyethylene (HDPE) products, special compression fittings are mainly used. The joining of individual elements in a pipeline structure using compression products allows for quick installation, which is also inexpensive and simple.
However, compression products are most often used to connect small diameter pipes. Medium-diameter pipes are connected using couplings. The coupling is perhaps the most common fitting option.
Glass pipe connection
A glass pipeline has one main difference from pipelines made of other materials. The glass pipeline is assembled only from detachable connections. Small lengths of pipe with smooth ends are joined using a radial compaction process.
A plastic or rubber coupling is placed on the end of each pipe, which is then pressed against the outside of the pipe using metal clamps.
One of the main disadvantages of this type of glass pipe connection is the risk of pipe failure due to increased radial stress on a small section of the pipeline.
Basically, this type of connection is used on pipelines where the pressure is minimal or absent at all. And on pipelines where pressure is constantly present or the probability of its occurrence is quite high, connections using rubber tension rings are used.
Important! If the pressure in the pipeline is high, then it is customary to use coupling, flange and coupling-threaded connections with tension rings in the amount of two. If the pressure exceeds 0.1 MPa, then flanged, boltless aluminum and locking coupling connections are used, the number of rings in which is three.
Over time, in glass pipelines, the fastening strength of the tension rings weakens and the strength of the connection, accordingly, also decreases. If you want to avoid this, it is better to use a connection without the use of tension rings. For this purpose, special thickenings (collars) are made at the ends of the pipes.
Tools
19 votes
+
Vote for!
—
Vote against!
Pipeline installation involves connecting pipes according to the overall design of the pipeline system. There are a large number of pipes made from different materials, and according to this criterion they have individual connection methods. Let's look at how to connect pipes correctly below.
Table of contents:
- Methods of connecting pipes - brief description
- General recommendations for connecting pipes using a socket
- Pipe welding technology
- Connecting polypropylene pipes using gluing
- Methods for connecting pipes made of different materials
- Connecting pipes with fittings: features and technology
- Additional sealing of the threaded connection
Methods of connecting pipes - brief description
There are two main types of pipe connections:
- sectional;
- one-piece.
Before deciding which one should be preferred, it is necessary to find out what material the pipes that are being connected are made of.
There are two types of detachable connections:
- flanged;
- coupling
A flange connection of pipes is appropriate if the material for the manufacture of the pipe is polyvinyl chloride. In this case, it is recommended to use flanged cast iron fasteners, in the lower part of which there is a rubber gasket.
To carry out this connection method, follow these steps:
1. Place a sample of the pipe at the place of its connection, achieve a perfectly even cut.
2. Place one end of the flange onto the cut surface.
3. Insert the rubber gasket until there is a 10cm overhang.
4. Slide the flange onto the gasket and connect them using bolts and mating flanges.
5. Use a special tool to secure the bolts.
Threaded pipe connections are used both when working with pressure and non-pressure pipes. To install the coupling, follow these instructions:
1. Cut the two ends of the pipes at right angles.
2. At the point where they join, install a coupling, which should be located in the middle between the pipes.
3. Place marks on the surface of the pipes to indicate the location of the coupling.
4. Using a special lubricant, treat the internal surfaces of the pipes and couplings.
5. Install one of the pipes into the coupling.
6. Install the second pipe in such a way as to obtain a single longitudinal axis, join the pipes and put on the second pipe according to the markings specified in advance.
In addition, there is a classification of methods for connecting pipes according to the material from which the pipes are made; a distinction is made between connecting parts from:
- plastic;
- metal;
- cast iron;
- polypropylene.
Each of these materials has individual connection characteristics and requires a special approach to carrying out this process.
General recommendations for connecting pipes using a socket
If we consider the connection procedure from a practical point of view, then installation work should be carried out manually. A crowbar is used as a lever to establish the position of the pipes; a wooden spacer is placed between it and the pipe. If it is impossible to use a crowbar, it is recommended to use a jack.
When the pipeline is constructed, it is necessary to check the evenness of the installation of sealing gaskets. They look like thin metal plates that are located at the socket and smooth end of the pipe. The plate must come into contact with the rubber ring. Further movement of the plate is associated with the circumferential part of the pipe.
When connecting metal pipes in this way, be especially careful and use silicone lubricant.
Tip: When making a connection using the socket method in a residential building at above-zero temperatures, silicone is replaced with liquid soap.
This connection method is permanent and involves the complete merging of two pipes. To separate such a pipeline will require a lot of effort, and in the end the integrity of the entire pipeline will be compromised.
Instructions for using the socket method of connecting pipes:
1. Two parts are connected, one of which is a socket with a rubber ring, and the second is a pipe with a smooth end.
2. Two areas should be pre-cleaned of dirt. Inspect for any defects or minor damage.
3. Make sure the rubber gasket is positioned correctly.
4. Remove the chamfer on the smooth end of the pipe.
5. Lubricate the two areas to be joined with silicone grease. Do not allow dirt or dust to come into contact with their surface.
6. Adjust the evenness of the installation of the pipes and connect them so that the smooth section is inserted into the socket.
7. The installation depth should be marked on the surface of the pipe in advance.
Pipe welding technology
Among the welding methods for connecting pipes, two options should be distinguished:
- docking;
- bell-shaped
The second option involves melting the outer part of one of the pipes and the inside of the second pipe. After this, a quick connection of the two elements occurs.
The butt connection is made by melting two identical sections of pipes and then connecting them, which is carried out with the application of certain forces.
The procedure for welding pipes is a very complex job, which requires special skills in working with a welding machine. There are certain types of welding that involve this process. The most popular are arc and electric options.
Before starting work, preparatory work should be carried out, which consists of washing the contaminated sections of pipes with caustic soda and warm water, trimming the joint with a file and treating it with special mixtures in the form of solvents.
Gas welding is based on the combustion of gas, the formation of a flame, which contributes to the melting of the filler material and the formation of the welded joint. The wire is a filler material that fills the gap between two pipes. The connection of steel pipes and the connection of plastic pipes is carried out using gas welding.
Electric arc welding facilitates joining using consumable or non-consumable electrodes. When choosing the second option, filler material is required.
When pipe welding is carried out in a qualified manner, there are no fistulas or other defects, and the connection is almost invisible.
Tip: When connecting a pipeline that is under constant pressure, it is better to use the welding method, as it is of higher quality and more efficient than gluing.
Connecting polypropylene pipes using gluing
This method is permanent, so the pipes after such a connection cannot be dismantled without damaging their integrity. To implement this, you will need a special glue that is applied to the specially treated edges of the pipes.
There are several types of glue suitable for different pipe surfaces:
- Epoxy type glue is used when gluing parts made of metal or polymers;
- glue B F2 - used when connecting metal pipes;
- glue called 88 N - connects rubber pipes to each other and to metal ones.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the instructions for connecting polyvinyl chloride pipes to each other:
1. Pre-prepare the surface of the pipes by sanding and degreasing using special compounds containing methylene chloride.
2. In addition, it is possible to apply a special glue when gluing sewer pipes. Its main function is degreasing and delamination of the pipe section that can be glued. The use of this composition significantly increases the strength of the connection.
3. Using a cotton swab or brush, cover the surface of the pipes with glue, and then insert them into each other. If the connection is made correctly, small drops of glue will appear on the surface.
4. Already connected pipes should be coated with another layer of adhesive solution. This procedure will make the connection more durable and airtight.
Advice: The use of glue for pipes should be characterized by minimal contact of the glue with oxygen, since it negatively affects its quality.
This connection method has the advantage that almost immediately after applying the glue, further operation of the pipeline is possible.
Methods for connecting pipes made of different materials
To connect polyvinyl chloride pipes with other types of pipes, it is necessary to use special adapters, fittings or seals.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the options for connecting plastic pipes:
- to connect a plastic pipe with a socket located on a cast iron pipe, double sealing equipment is required;
- to connect a socket on a metal pipe to a PVC pipe, a standard seal is sufficient;
- using a connecting pipe, the connection of plastic pipes with ceramic ones is ensured;
- the procedure for connecting a smooth fiberglass section to a plastic pipe requires a connector and a section made of rubber;
- in order to connect the fiberglass pipe on which the socket is located, it is necessary to use a rubber hose and a threaded ring;
- Special connectors are made for cast iron pipes.
Connecting pipes with fittings: features and technology
Before moving on to the direct connection of metal pipes, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the advantages of their use:
- high level of strength is the most important advantage of using steel pipes; such pipes can withstand the highest pressure and temperature;
- cost - affordable, when comparing prices for plastic or alternative types of pipes and metal ones, their cost is approximately the same;
- the service life of steel pipes reaches half a century;
- when using galvanized pipes, they are practically not subject to corrosion;
- can withstand temperatures above 210 degrees Celsius;
- resistant to mechanical damage and heavy loads.
There are two ways to install metal lines:
- sectional;
- one-piece.
The first option is based on the use of fittings, and the second on welding or gluing pipes together.
There are a large number of fittings, among them the following parts are distinguished:
- crosses;
- corners;
- couplings;
- tees;
- locknuts;
- adapters;
- plugs;
- fittings.
The connection of metal pipes with fittings is carried out using a threaded method. If it is missing on the pipe, a special tool or lathe is used to equip it.
Fittings are:
- metal;
- brass;
- copper;
- cast iron;
- steel;
- chrome plated;
- made of stainless steel.
These parts allow not only to connect pipes with their further separation, but also involve the connection of pipes of various sizes and shapes.
The use of threaded fittings is common on pipelines with a diameter of no more than 5 cm.
Using the welding method is a rather labor-intensive process that requires qualified equipment and a specialist to carry it out. The use of fittings allows you to obtain a connection of excellent strength, faster and easier.
In relation to the method of connecting the fitting to the steel pipe, they are divided into parts:
- welded type;
- threaded type;
- flange type;
- crimp type.
The presence of a smooth end distinguishes parts of the first type. Screw threads are used to connect threaded fittings.
The most popular are crimp or threaded type parts, as they require repeated use and a simplified installation procedure.
When making a threaded connection, it is recommended to use flax tape, which is wound on the surface of the pipe, while covering it with oil paint or drying oil. The advantage of this connection is high quality for a minimal fee.
Compression type fittings include a ferrule, nut and body. Recommended for use on plastic or metal-plastic pipes. Also suitable for metal pipes as a temporary connection.
This type of fitting implies repeated use in everyday life. The process of connecting with a compression fitting is based on pressing the rubber gasket and clamping ring to the surface of the pipe using a nut. Thus, it is possible to create a tight connection.
This method is less powerful than the above. Its disadvantages include a low level of resistance to mechanical stress. In addition, the connection is leaky and can allow hot water to pass through. Since the operating temperature of the rubber ring should not exceed one hundred degrees, and with constant exposure to high temperatures it stretches and the tightness decreases.
Flange type fittings are either welded or threaded. With their help, quick installation and dismantling of the pipeline is carried out.
Additional sealing of the threaded connection
If the pipeline is assembled using a detachable threaded method, then additional sealing will be provided by the use of a special FUM tape. It is recommended for use when installing pipelines for heating, gas or sewer systems.
The temperature range for using sealing tape is from -40 to +200 degrees. Fluoroplastics are the basis of this material. The substances included in its composition are resistant to alkali, acid and other substances that have an aggressive effect.
To seal threaded connections, the use of tape is required, the thickness of which is from 0.07 to 0.1 mm. Its surface should be smooth and elastic.
Video pipe connection: