Repair work related to the complete or partial replacement of pipes in drainage systems in private houses and apartment complexes is a rather labor-intensive process. This is due to the location of communications and the need to dismantle plumbing equipment. Therefore, when designing and constructing sewer network installations, special attention is paid to the choice of sewer pipe material. The main selection criteria are the material itself and the strength class, according to the current GOST, corresponding to preliminary technical and economic calculations based on the operating conditions of sewer pipes.
Sewage pipe system
The most common types of sewer pipes are:
- polymer pipes (polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride);
- ceramic pipes;
- cast iron
Depending on the operating conditions, each of these types of products has a certain service life.
Scope of application of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene is an organic polymer that has supplanted polyvinyl chloride in the global plastic products market and is confidently catching up with polyethylene in terms of use. Polypropylene pipes are used for laying any pipelines.
Polypropylene pipes (certain types) can be used within the range of temperature fluctuations from + 95 to – 15 degrees Celsius.
Polypropylene pipes are used for transportation:
- Cold water. Water supply and sanitation in apartment buildings and private households. Watering, irrigation, fire extinguishing systems.
- Hot water (up to 95 degrees). Hot water supply, water (not steam!) heating.
- Food and technical liquids in production.
- Gas under pressure. Household gas - underground transportation, distribution to private households.
- Air. Ventilation and air conditioning systems.
- Aggressive inorganic substances.
The popularity of polypropylene pipes for use in private households, commercial construction and industry is explained not only by their low price compared to metal, but also by a number of other positive differences:
- polypropylene is resistant to contamination, which allows long-term operation without reducing the internal diameter and contamination;
- the material has low thermal conductivity, this allows significant heat savings when transporting hot water, and when cold water is supplied there is no condensation on the walls;
- Among the advantages are ease of installation and variety of possible wiring. The presence of a large number of fitting configurations (including adapters for metal threads) allows you to quickly and inexpensively assemble the required structure. If necessary, parts of the structure are easy to replace;
- The advantage over metal is the low weight of polypropylene. The products are easy to transport, carry during installation, and hold;
- does not rust, does not require painting, absorbs noise;
- The maximum service life of polypropylene pipes, as stated by the manufacturer, is 50 years.
We recommend that you read: Linear expansion when installing pipelines made of polypropylene pipes
Product classification
The service life of a product, both plastic and metal, is determined by the wall thickness and material parameters. Thus, plastic polypropylene water conduits are classified as follows:
- single-layer - the wall consists of one material;
- multilayer – is a composite material.
In addition, all product options are divided into the following 4 types:
- PPH is the simplest version of the product. It is used for supplying cold water and ventilation, as it is not resistant to heat;
- PPB – made from block polymer. This material is much stronger and can withstand the high heat of the transferred fluid. Used for the construction of hot and cold water supply and heating systems;
- PPR – the material serves as a random copolymer. Used for organizing water supply - cold and hot, as well as for underfloor heating systems;
- PPs is the option that is most resistant to high temperatures, allowing operating temperatures up to +95 C.
The service life of each option can be found in the corresponding tables.
Durability of polypropylene pipes and their connections
However, it should be understood that the pipeline will last for half a century with minimal load + ideal external conditions. The service life depends on three main factors:
- Quality of raw materials and production. For the production of pipes, several types of polymers are used, which differ in their spatial structure. The durability of the material is affected by the purity of the raw materials used and compliance with the production process. Deviation in the conditions of the polymerization reaction can significantly reduce the service life of the manufactured product. The pipes are not poured directly from polymer granules, but are made from sheet material. Here it is also important to adhere to the seam joining technology. Each production stage contributes to the quality of the final product and service life.
- The number of connections used in the system and the quality of installation of the components. The guaranteed service life of polypropylene pipes is 10 years, subject to compliance with the permitted operating parameters.
- Terms of Use. It is important to consider the level of permissible pressure in the system and temperature indicators.
Note! Violation of one of the recommended parameters over a long period of operation significantly reduces the service life of polypropylene pipelines. Instead of the expected 50 years of operation, the system becomes unusable after 2-3 years.
Dimensions and diameters
The diameter of plastic sewer pipes for a private house or apartment is chosen 110 or 50 mm.
For household appliances, showers, bathtubs and sinks, 50 mm is suitable. For a toilet – 110 mm. Large diameter pipes are used for laying industrial sewerage: 200 – 300 mm. Regardless of the type of pipes, their dimensions remain standard so that products from different materials can be used in one system.
Pressure pipes differ from non-pressure pipes in the thickness of their walls. In a free-flow system, where the liquid flows due to a slope, the thickness can be about 3 - 5 mm. If a pump is used that creates pressure, the wall thickness must be selected based on the expected pressure.
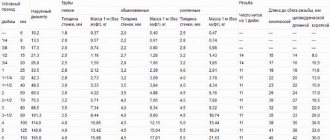
Size chart for PVC sewer pipes for a private home.
| External diameter | Wall thickness | Where is it used? |
| 50 mm | 1.3 mm | Shower, bath, bidet, washing machine |
| 90 mm | 2.2 mm | Dishwasher |
| 110 mm | 2.7 mm | Toilet |
| 200 mm | 4.9 mm | External sewerage if there is a sauna |
| 315 mm | 7.7 mm | Pool |
Dimensions are given for non-pressure sewer systems.
Durability options
Industrial production offers consumers polypropylene pipes of various diameters and wall thicknesses. These characteristics determine the scope of application of plastic products.
Each category of products has its own markings and corresponding technical characteristics. For polypropylene products, the letter marking PN and digital marking are used, indicating the maximum permissible pressure.
Categories of polypropylene pipes:
- PN 10. Polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 20 to 250 mm are produced under this marking. They are designed for transporting and supplying cold and warm liquids and gases under pressure. The maximum permitted temperature is 45°C, the optimum for the stated service life is 25°C. Pressure is indicated by the number 10 and means 1 MPa (1 MegaPascal, which is about 10 atmospheres).
- PN 16. The purpose of the products is similar to the first. Permitted temperature - 60°C, pressure 16 atmospheres.
- PN 20. This category of products allows their use for hot and cold water supply, water heating, and drainage. Maximum temperature 75°C, permissible pressure 2 MPa.
- PN 25. Products in this category are made with reinforced walls with aluminum foil or fiberglass. They have a more rigid structure and are less susceptible to thermal expansion and deformation. Used for installation of heating (water) and hot water supply systems. Withstands pressure of 24 atmospheres.
We recommend that you read: How to solder heating pipes correctly?
When choosing products, you should pay attention only to the labeling. The color of the pipes does not convey information, with the exception of black ones. Black polypropylene pipes are more resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
Durability of plastic pipes. Myths and reality
The very first thing that interests the buyer is the possible areas of application of the pipes and the main operating parameters.
Considering that plastic pipes have become widely used in Russia in domestic water supply and heating systems only over the past four years, these products are still a novelty for some, so the temptation is to offer the consumer plastic pipes that “can” work everywhere, even in systems heating with superheated steam, alas, is too high. So, having visited an exhibition or the office of such a company, you receive a booklet (or warm assurances), in which it is written in black and white - the operating temperature of “our pipes” (most often metal-polymer) is +95°C, pressure 0.1 MPa. The service life is 50 years! But that's not all. To completely defeat the client, a modest postscript follows: “a short-term increase in temperature up to +110°C is possible” (the record for such a “possible” increase, recorded by the author, is +135°C). Needless to say, such fantastic parameters have a magical effect on an inexperienced consumer. As a result, plastic pipes are installed in heating systems where superheated steam is used as a coolant. Accidents that occur as a result of an amateurish approach completely undeservedly form a negative attitude towards plastic pipes. It is doubly offensive that in Russia the same “rake” was already stepped on in the 60s, when polymer materials and the experience of their practical application were a novelty.
At the same time, industrialized countries have relied on improving the regulatory framework governing the use of plastic pipes. As a result, today more than 80% of pipelines are made of polymer materials. Low accident rates and a high degree of reliability and durability of plastic engineering communications are ensured, firstly, by strict adherence to the requirements contained in regulatory documents and, secondly, by qualified installation of pipelines, which must be carried out by specialists who have undergone special training and have the appropriate licenses to carry out such works
What does the existing regulatory documentation in Russia say about the durability of plastic pipes? First of all, SNiP 2.04.01-85* “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings” stipulates only the upper permissible temperature limit for the operation of hot water supply systems + 75 ° C with an estimated service life of 25-30 years, and SNiP 2.04.05-91* “Heating , ventilation and air conditioning" - +95°C with the same service life. As will be seen from the data below for specific types of pipes, the temperature value of +95°C is overestimated. The lack of information in SNiP 2.04.01-85*, which reveals the direct dependence of pipeline durability on operating temperature and pressure, often misleads inexperienced consumers of plastic pipes. The assurances of many suppliers that their pipes are designed for a temperature of +95°C and a pressure of 10 atm say absolutely nothing about their durability at such parameters. With such operating temperature and pressure values, any plastic pipe will last no more than 2-3 years. Where is the fantastic service life of 50 years?
Therefore, in order to avoid getting into trouble, it is necessary, in addition to SNiP, to use SP or TU, which contain much more necessary information.
So, back in 1996, NPO "Stroypolymer" developed and released SP 40-101 "Design and construction of pipelines from the polymer "Random copolymer", which clearly defines the operating parameters and, importantly, the dependence of durability on operating temperature and pressure, which clearly presented in table form (Table 1)
.
As for metal-polymer pipes, this is truly a “pig in a poke”. Despite the fact that SP 41-102-98 “Design and installation of pipelines for heating systems using metal-polymer pipes” was recently published, it is impossible to obtain any data on the dependence of pressure on temperature and durability in this joint venture or in the specifications of manufacturing companies. The only thing that is said in the joint venture is: “Metal-polymer pipes are used in the design and installation of heating systems, the design temperature of which does not exceed +90°C at a pressure in the pipes of no more than 1.0 MPa.” Some suppliers of metal-polymer pipes try to appeal to nomograms for the relationship between durability and reference stress. They may not realize that the reference stress, determined by Kessel's formula, is the tangential stress of the pipe wall caused by internal pressure. Fatigue strength, expressed as a reference stress, is independent of pipe dimensions and only indicates the behavior of the material. That is why these nomograms are used not for calculating pipelines, but for conducting bench tests of the materials from which the pipes are made. Nevertheless, it is interesting to observe how in the information of some companies the comparative curves of metal-polymer pipes seem to strive to transcendental heights, as if the water or coolant inside these pipes flows not through cross-linked polyethylene, but through an aluminum pipe.
Negative operational impacts
Negative impacts that reduce the service life of pipelines during operation are exceeding the permissible temperature and pressure parameters. Pressure surges are typical for centralized water and heat supply communications.
Water hammer in combination with high temperature reduces the service life of pipes, leads to failure of connections, and contributes to deformation of pipelines.
Sand, which is always sufficient in pipelines with process water, has an equally negative effect. Moving through the system, grains of sand, like sandpaper, erase the inner surface of the pipes. This effect is especially destructive at joints and welding beads.
In private households, the operational impact is more gentle, since there are no water hammers, the water is cleaner and the pressure in the system is lower. Here the service life can be greatly reduced under the influence of human factor.
Note! Atmospheric oxygen and sunlight are harmful to polypropylene products. The street part of the pipeline should be hidden in the ground. Where this is not possible, it is better to switch to metal pipes.
How long will the products last in the sewer system?
Increasingly, PVC plastic pipes are used when arranging sewerage models. They can be considered a high-tech development of our time, because such installations are reliable and have a number of advantages.
Among the main advantages of polyvinyl chloride products:
- Safety, non-toxic and non-flammable raw materials.
- Practicality in use and when laying highways.
- Light weight.
- Possibility of long-term operation without clearing blockages.
- Absolute neutrality to corrosion and aggressive substances.
- Resistance to various living microorganisms.
- High durability.
The service life of PVC sewer pipes, according to manufacturers, is more than 30 years. However, when purchasing such polyvinyl chloride products, it is necessary to take into account the conditions under which the pipeline model will be operated and what potential factors affecting it exist. For example, it is necessary to take into account the exposure of collectors to external environmental influences (weather conditions, ultraviolet light, etc.) and indoor humidity levels. It also doesn’t hurt to assess the likelihood of mechanical impact from outside and the risk of microorganisms multiplying inside the system. Typically, the durability of polyvinyl chloride collectors corresponds to the warranty period if the products are operated under optimal conditions and the media temperature does not exceed +75⁰C. At the same time, the pressure in the system should not exceed 4-6 atm.
If liquid with a temperature of about 70⁰C is constantly transported through the system, and the structure itself is regularly subjected to mechanical stress, its service life will be significantly reduced.
In this regard, PVC products are inferior to polypropylene, which, in turn, are more resistant to elevated temperatures and aggressive environments. The service life of plastic sewerage pipes made of polypropylene reaches 50 years in networks with a carrier at room, cold temperature and 30 years - if the carrier is supplied with a temperature of 80-90⁰C.
Linear extension of a polypropylene pipe after installation (temperature expansion)
The main problem with a polypropylene pipe is that when welding the pipe you have one temperature, but during operation it is different. When the temperature decreases, the pipe decreases in length, and when it increases, it lengthens accordingly. The change in pipeline length due to temperature changes is determined by the formula ΔL=ΔLΔt, where ΔL is the change in pipe length, mm; Δ – coefficient of linear expansion of the pipe; L – length of the design section, m; Δt – calculated temperature difference, °C. For unreinforced pipes, the coefficient of linear expansion is 0.15 mm/m° C, for reinforced pipes - 0.03 mm/m° C. Example: T1 = 20 ° C, t2 = 75 ° C, L = 6.5. Using the formula ΔL=ΔLΔt we get that, ΔL = 0.15 x 6.5 x (75 - 20) = 55 mm, Δt = 75 - 20 = 55 °C. According to the nomogram ΔL = 55 mm
it appears like this...
...and this is a very short section of pipe.
Polypropylene has a coefficient of thermal expansion 12.5 times greater than that of steel. This circumstance must be taken into account when installing polypropylene pipes. Because of this feature, internal stresses arise in the pipe, affecting primarily the welds. As a result, in many cases it can be said about polypropylene pipes that a system welded from polypropylene is beautiful before supplying water or heating through it.
Installation features
To avoid blockages along the wastewater route, pipe laying begins from the main riser in the direction of the well.
Pipes should initially be taken larger than the calculated diameter - this is for safety net - in case of installing new plumbing or building a bathhouse with a swimming pool. There are two connection options:
- Detachable when couplings or flanges are used. Tightness is ensured by rubber gaskets. The method is convenient because, if necessary, the water supply or sewerage system can be disassembled by simply removing the couplings.
- One-piece - in a socket, using welding or glue. The glue is selected depending on the materials. For polymers, this is epoxy resin.
Not all methods are available to beginners, so it is better to turn to professional workers, or choose the easiest connection method.
Advantages and disadvantages
The easiest way is to connect the pipes into a socket. It is important to place a rubber ring for tightness, and the socket itself should be directed in the direction from which the water flows. This reduces the risk of blockages. To make the pipes easily dock, use lubricant or regular detergent.
Welding is a complex method. Without skills, connecting pipes will not be easy. For non-pressure sewerage, welded seams are quite reliable.
The use of epoxy glue allows you to connect pipe parts at the molecular level. Before starting work, the joints are degreased. You need to act quickly, as the resin dries quickly in air.
The fittings are installed on O-rings to avoid leakage at the joints.
Rules for installing polypropylene pipes in an apartment (house)
It is unacceptable to brick polypropylene pipes into walls and floors according to SNiP 31-01-2003 if the building must have a service life of more than 20 years. According to SNiP 2.04.01-85*, clause 10.1*, the laying of plastic pipes should be primarily hidden: in baseboards, grooves, shafts and channels. This SNiP requirement is justified by the fact that pipes during operation must be protected from mechanical impact on them, protected from ultraviolet irradiation and must expand freely without the formation of excessive stresses in them. Even when laying a pipeline through a wall, it is recommended to use insulation.
What is the best material to make sewer pipes from?
Two types of pipes are used to install a sewerage system:
- cast iron,
- plastic.
Cast iron structures will last more than 80 years, but they have their disadvantages, including high cost, heavy weight and an uneven internal surface, which leads to waste retention and clogging.
Plastic pipes have maximum throughput due to the fact that they have smooth walls. In such systems, blockages almost never occur.
Service life of metal-plastic pipes
Metal-plastic pipes are more reliable and stronger than plastic ones, since they have a multi-layer structure - there is a reinforcing layer of aluminum inside. This product is treated with a polyethylene coating on the outside and inside.
We recommend: How to close pipes in the toilet and bathroom: 5 original ways
Communications made of metal-plastic combine the positive properties of all other structures, so they are more durable. The service life of structures made from this durable material reaches 50 years.
The service life of a water supply system in residential buildings, consisting of metal-plastic pipes, depends on the quality of the water and the correct installation.
Properties of steel pipes
The exact characteristics of steel water pipes depend on what type of steel it was made from. For example, non-galvanized water pipes are characterized by their low cost design and the widespread use of this substance, but on the other hand, their service life is quite low.
Steel pipes coated with a layer of galvanization do not have this disadvantage, however, they are much less suitable for repair and have several restrictions on the type of installation; they can only be assembled using threads. “Stainless steel” has almost no disadvantages. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to repair.
But there is a minus here too. It involves the incredibly labor-intensive process of installing stainless steel plumbing. This is due to a number of difficulties during welding of such pipes. Therefore, you will have to spend a lot of money on the services of a specialist welder.
Metal water pipes
The first metal water pipes appeared in the homes of wealthy citizens 3 centuries ago. Since then, the metal sewer system has undergone almost no changes.
In modern houses and apartments you can see sewer pipes made of the following types of metals:
- High-carbon, structural, unalloyed steel without corrosion protection, otherwise known as “black.”
- Copper of a high purity level with a minimum amount of impurities of antimony, lead and arsenic (less than 0.001 percent).
- High-carbon, structural steel with a zinc-based anti-corrosion coating, otherwise known as galvanized steel.
- Steel alloyed with chromium, or “stainless steel”.
What pipes are suitable for installing internal sewerage?
Sewage is the key to a favorable sanitary and hygienic situation in an apartment/house and the comfort of all residents. Properly selected pipes are a guarantee of long-term, uninterrupted operation of this utility network. They will prevent the occurrence of blockages, noise, and eliminate leaks. What pipes are suitable for installing internal sewerage?
The communications that drain wastewater from the building bear less load than the external ones. Their installation is carried out in an open or hidden way. But for any installation scheme, there are criteria for choosing internal sewer lines, these are:
- strength;
- temperature resistance;
- resistance to biological and chemical influences;
- good maneuverability;
- possibility of connecting plumbing fixtures;
- compatibility with external sewerage;
- simple installation;
- Possibility of repair and replacement.
For laying sewer systems in private houses and apartments, products from:
- cast iron;
- polymers (plastic).
Cast iron communications: pros and cons
This material is made from iron ore, which has high performance characteristics. Before the appearance of analogues, it was used for decades for laying external and internal drains. Products are distinguished from:
- gray cast iron (GC) - resistant to compression, suitable for arranging a riser, but fragile;
- malleable cast iron (ductile iron) - high-strength, ductile.
Based on functionality, cast iron products are classified into 2 types:
- SMU - with smooth ends;
- SME - one pipe outlet is smooth, and the other has a funnel-shaped extension (socket).
A cast iron socketless pipe is used to drain recycled water inside a building. Line elements are connected using clamps. Bell-shaped pipes are joined hermetically, therefore they are suitable for forming external drainage. The dimensions of cast iron sewer pipes include the wall thickness of the product, diameter, and weight. Communication throughput is determined by:
- nominal indicator. This is the internal diameter of a cast iron sewer pipe. It has the designation Dn;
- nominal diameter. It displays the rounded/conditional value of the internal hole of the product (DN);
- outer diameter - the distance between the outer walls of the communication (designation G).
The choice of pipes of a certain capacity is determined by the volume of waste. The diameter of cast iron products ranges from 50-150 mm. For laying internal sewerage systems, 50-100 mm communications are used, for external ones - 100-200 mm. The standard length of the product is 2 m. Taking into account GOST for cast iron sewer pipes, the weight of the product depends on its nominal diameter:
- The 50mm communication weighs 11kg;
- 100mm=25kg;
- 150 mm = 40 kg.
Note: the weight of the product is also affected by the thickness of the communication walls. It varies between 6.7-27 mm. Cast iron sewer pipe has a number of advantages:
- strength;
- long service life (up to 85 years);
- plasticity;
- resistance to loads.
Disadvantages of communication:
- large mass. The weight of the cast iron pipe complicates the transportation and installation of the product. This requires the use of special equipment;
- rough inner walls, which causes sediment accumulation;
- high cost due to the metal consumption of the product.
Plastic products: advantages and disadvantages
With the advent of polymers, which made it possible to produce lightweight and cheap products, the use of cast iron faded into the background. Communication data from complex plastics. Plastic sewer pipe - advantages:
- high strength;
- corrosion resistance;
- long service life (up to 60 years);
- lightweight design, facilitating its transportation and installation;
- high throughput of the product;
- low cost. Average prices for sewer plastic pipes 50 mm in diameter are 65 rubles/m.p., 100 mm = 155 rub./m.p. (for cast iron, 550 and 900 rubles/m.p., respectively).
The sizes of plastic sewer pipes are standard or individual (custom-made). They are selected depending on the expected load on the product. When installing an autonomous sewer system, the following diameters of sewer plastic pipes are used:
- 100-110-150 mm for risers and central lines, connecting a toilet, bidet;
- 40-50 mm - for distribution lines, connecting a sink/sink.
Plastic sewerage is laid from pipes:
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC);
- polypropylene (PP);
- polyethylene (PET).
PVC pipe
Communications made of unplasticized PVC are used to form external and internal drains (pressure/gravity). They are suitable for distributing sewerage throughout the house, when draining sewage by gravity. The diameter of PVC sewer pipes is established by GOST 51613-2000. According to it, the length of communications should be 4-12 m, the size of the internal opening should be 10-315 mm. In a private house, 110 mm PVC sewer pipes are used to form a riser and connect plumbing installations with a large drain volume. 40-50 mm communications are used for laying distribution lines and connecting sinks, and 25 mm for drainage from a washing machine/dishwasher. PVC pipe is durable and resistant to UV rays. The disadvantage of polyvinyl chloride communications is their susceptibility to temperature fluctuations. Constantly draining hot water softens and deforms the material. To avoid destruction of PVC communications, the temperature of the wastewater should not exceed 40˚. Compared to cast iron, plastic polyvinyl chloride pipeline makes more noise and is prone to burning. This releases toxic gas.
Polypropylene pipes
These are products made from synthetic, thermoplastic polymers. They are characterized by increased strength, temperature resistance, acid and alkaline agents. PP products are environmentally friendly and recyclable. Polypropylene pipes for sewerage last up to 100 years. Smooth internal walls provide good passage capacity for communications. This is a suitable option for laying internal sewerage. PP products are characterized by low noise/vibration levels and allow the creation of distribution lines of various configurations. Please note: when exposed to high temperatures, PP products elongate. This is compensated by the use of special designs during installation. Making sewer lines from plastic pipes is much easier and cheaper than from cast iron pipes.
Communications made of polyethylene
They are made from polymer that has undergone extrusion (high pressure processing). As a result, it acquires super strength. The properties of the line are affected by the density of the polyethylene pipe. There are PET communications:
- low density (high pressure lines) 0.910-0.925 g/cm3 - used for laying external sewerage, as they are resistant to mechanical damage;
- medium density - up to 0.940 g/cm3;
- high density (low pressure) up to 0.965 g/cm3 - products primarily for use inside the home.
Externally, products made from LDPE and HDPE are similar, but communications made from low-density material are harder. Compared to PVC structures, polyethylene products are more flexible and do not create noise. These communications are not afraid of acids, alkalis, are not subject to corrosion, have good elongation, and last up to 50 years. The disadvantage of these pipes is softening and deformation at a temperature of 80˚. GOST provides for an operating temperature of PET pipes of 40˚. The performance characteristics of polyethylene communications are reduced when exposed to UV rays.
Docking of sewer pipes
The laying of internal drainage networks involves the use of fittings. These are devices for joining line elements. Fittings are distinguished:
- threaded - used for joining cast iron products. The part is screwed onto the threads of the incoming and outgoing pipes, connecting them to each other. Provide a strong mechanical connection;
- flanged - paired steel disks connected with bolts are inserted at the junction of communications. One-piece flange connection of pipes is made by welding their ends. A special coupling is applied to the joint, connected to the electric heating elements;
- compression - the pipes are tightened with a nut having a silicone/rubber seal;
- self-locking - complex devices consisting of internal rings with teeth. They are installed at the joints of elements and secured with a special key. When pressed, the teeth penetrate deeply into the communications material, ensuring a strong connection. These fittings are reusable;
- welding - the ends of the pipes are degreased, fixed with clamps and processed by welding with a heated disk. The melted sections are joined to form a thin, strong edge;
- adhesive - a liquid polymer composition is applied to the joint, which quickly hardens. This method is also called “cold” welding.
It is important to choose the right sewer pipes and fittings for them
. Communication joints are the weak point of the system, the cause of leaks, blockages, and cracks. The cast iron pipeline is installed using caulking. The end of the communication with a chamfer is inserted into the fitting funnel. The connection is sealed with oil-impregnated fibers and additionally coated with cement mortar and fused sulfur. To ensure the tightness of the joints, the pipes are equipped with rubber gaskets. Cast iron products are also connected using clamps. A coupling is placed over the joint, which is tightened with bolts.
The ends of PET and PVC pipes are equipped with rubber seals. To connect the parts, cut off the pipe of the required size, remove the outer chamfer from it, coat it with sealant and insert it into the communication funnel. Docking of polymer products is also done using the flange method.
Sometimes it is necessary to connect communications from different materials. How is the transition from a cast iron pipe to a plastic one carried out? First, clear the socket of the metal communication (if it is old). The funnel expansion is treated with sealant and a transition from cast iron to plastic 110 mm (for a riser), or another suitable diameter (50 mm for a distribution line) is inserted. This cuff is made of rubber or polymer. The gaps between the elements are sealed. The joining of funnelless communications is carried out in the same way.
A strong and tight connection between cast iron pipes and polyethylene pipes will be ensured by the use of a self-unscrewing press fitting. It will allow you to avoid leaks that occur due to water hammer and temperature changes in the system. The end of the cast iron product is trimmed and cleaned, lubricated with grease and a thread is applied to it. Tow (sealing tape) is wound around this area, silicone sealant is applied and the press fitting is screwed on manually. This connecting element can be tightened at any time, preventing the formation of leaks
Characteristics of polymer pipes
Having examined the variety of different designs made from these materials, it is easy to understand that such pipelines have many advantages, including the following qualities:
- Complete independence from pumped substances. Plastic pipes not only do not change their properties under the influence of liquid passing through them, but also do not affect their chemical composition, which is especially important when constructing drinking water pipelines.
- Good level of ring stiffness. A pipeline made of polymer materials can withstand a pressure of 5 MPa. Of course, this is not much compared to systems made of copper and steel, but in most cases the pressure in domestic water supply systems does not exceed half of this figure, so the ring rigidity of polymer pipelines will be quite sufficient even to provide water to an apartment building.
- Long service life. With proper installation and careful use, a polymer pipe can last 100 years, which is several times longer than that of a non-galvanized steel pipe.
- The installation process is very simple, most operations can be completed without the help of specialists.
The negative properties of polymer materials common to all types include:
- High level of flammability. During a fire, plastic pipes not only burn, but also release a lot of toxic substances into the environment.
- Poor structural rigidity. Polymer pipes cannot resist either transverse or longitudinal deformations.
- Susceptibility to mechanical damage. The pipe can be damaged by any sharp or heavy object.