The sewer pipe market today is represented by a large selection of materials and their modifications - there is traditional cast iron, ductile iron, modern polymers, reinforced concrete, asbestos cement, and ceramics. Each material has its own pros and cons that determine the scope of application. To make the right choice, you need to know how the types of sewer pipes differ depending on the material.
Cast iron
The traditional material for making sewers; in old houses, the drainage system is made of cast iron. Its advantages include high strength, heat resistance, and less corrosion than steel pipes.
The main disadvantages of sewer pipes made of cast iron are heavy weight, difficult installation, and high price. The inner surface is rough and eventually becomes overgrown and clogged.
Cast iron pipes are further divided into:
- Bell-shaped cast iron pipes ChK;
- Cast iron pipes SML - socketless, connected with clamps;
- VChShG cast iron pipes (high-strength cast iron with nodular graphite).
The latter are distinguished by greater strength, comparable to steel; in addition, to protect against corrosion, the pipes are coated on the outside with varnish or zinc, and on the inside with a cement-sand coating. In addition to corrosion resistance, CPP increases the smoothness of the walls, reducing fouling and increasing throughput.
The price of ductile iron pipes is correspondingly higher than that of conventional cast iron pipes. In turn, they are divided into:
Tyton type - socket connection with a special Tyton O-ring.
Type RJS - with socket-lock connection for Tyton O-ring;
Type RJ - with a socket-lock connection, additionally fixed with a locking wire.
Installation features
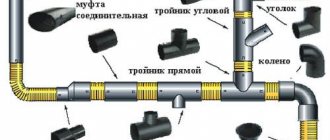
The main condition when installing sewerage from any material is the tightness of the connections. For joining pipes and bends, use:
- socket connection;
- glue installation;
- use of special configuration locks;
- argon or gas welding for steel and stainless steel pipes.
At home, the most common type is a socket connection.
To facilitate the work, select bends and pipes of the required diameter that are suitable in configuration. Take into account the angle of rotation, exit from the right or left. In this case, the parts are connected by joining the socket with a smooth end.
Plastic pipes and fittings are equipped on one side with a special chamfer, in which a sealing elastic band with a triangular shape in cross-section is installed. This makes the connection easier.
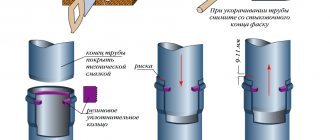
If the size of the room or the availability of parts for sale make it necessary to cut the pipes, file the smooth end into a cone. The cut part of the part is taken as a sample. Trying to insert a cut and untreated pipe into the socket will most likely lead to damage to the rubber seal. To facilitate docking, especially when purchasing products from different brands, it is recommended to lubricate the O-ring with any liquid product, such as soap solution.
For cast iron pipes, the socket joint is sealed with packing and covered with cement mortar.
Installation of sewer pipes and bends with glue is used for pipes without sockets. Such systems are chosen when there is confidence that no modifications will be required. Otherwise, dismantling is possible only with the destruction of parts and their subsequent replacement with new ones.
Low-pressure propylene pipes are connected with fittings with a tightening nut or special bends using electrical soldering, as described above. In private homes, such pipes are rarely used due to the unpresentable appearance of the connections.
Polymers
Although sewer pipes made of polymers have been produced for almost half a century, these materials appeared on the Russian market relatively recently. And they are rapidly gaining popularity, because they have significant advantages:
- Smooth internal walls, eliminating overgrowth and blockages;
- Light weight and easy installation;
- Low price of pipes and fittings;
- Chemical resistance, no corrosion, long service life.
Polymer pipes also have their disadvantages, the main ones being low strength and insufficient heat resistance. Hot waste cannot be drained; when laid at great depths, under roads, pipes may become deformed. The latter problem is solved by double-layer corrugated pipes; their metal frame provides sufficient rigidity for installation at depths of 15 m.
Three materials are used to produce polymer pipes.
Polyethylene PE
The cheapest polymer, not subject to corrosion, tolerates low temperatures well, but softens at high temperatures. For drains hotter than 40°C, polyethylene pipes cannot be used.
PE pipes are rarely used for ordinary sewerage, but the material is often used for the manufacture of two-layer corrugated pipes, the most well-known brands being Korsis and FD Plast.
Polypropylene PP
Somewhat more expensive, but tolerates high temperatures much better. The permissible wastewater temperature is 60° C, withstands short-term increases up to 95° C. It tolerates low temperatures worse, and becomes brittle even at -5° C. The problem is solved by choosing pipes made of block copolymer polypropylene, which is comparable in frost resistance to polyethylene.
The latter is a frequently used material for the manufacture of double-layer corrugated pipes with a large selection of brands:
- Pragma;
- Corex;
- Polytron Procan;
- Ikaplast;
- Wavin.
The Italian company Magnum produces corrugated pipes from both polyethylene and polypropylene.
Polyvinyl chloride PVC
In terms of temperature resistance, it is in the middle between PE and PP, and surpasses both materials in terms of chemical resistance. The most commonly used material is unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (UPVC). PVC-U pipes for internal sewerage are painted grey, they have a small diameter (up to 110 mm), length from 0.5 to 3 m. PVC-U pipes for external sewerage are orange, the diameter can reach 500 mm, the length is 12.3 m.
Purpose of PVC pipes for different operations
Wastewater is divided into two types: gray and black. Gray water is soapy water that drains from sinks, showers, bathtubs, bidets, washing machines and dishwashers. Black ones include organic remains in the form of feces, napkins, rags. Industrial waste is also characterized by an aggressive environment due to chemical reagents and other production waste.
Different pipe diameters are suitable for different functions. The further operation of the entire system depends on the correct choice. Diameter information is printed on the outer side wall of the pipe. The outer size and wall thickness are indicated here. The difference between these indicators is equal to the internal clearance.
To avoid mistakes, let’s figure out which sizes will fit where.
Diameter and purpose for internal sewerage
- For installing a bathtub, shower stall, washbasin, the recommended diameter is 50 mm. The dimensions are determined by the density of the drains, and just soapy water without solid objects flows out of the bathroom;
- For installation of a bidet – 50 mm;
- For toilet installation – 110 mm. This size is due to the strong pressure of the jet that washes away from the bowl; at this speed, denser inclusions in the form of toilet paper, napkins, and organic residues can get stuck and cause an emergency. Therefore, a wide diameter is recommended;
- For washing machine and dishwasher – 50 mm. Automatic devices have filters for entry and exit, so a small gap will be enough;
- Loungers for transporting liquid to the riser – 75 mm;
- The diameter of the riser is 110 mm. If many devices are connected to the system, the diameter should be increased accordingly. They also pay attention to the number of floors of the house: up to five floors, a diameter of 110 mm is suitable, and taller houses are equipped with risers with a large clearance of 150 mm.
Diameter and purpose for external sewerage
- The collector that removes wastewater from the house is 110-160 mm;
- Outlet pipeline from a bathhouse or sauna - 150-200. This clearance is provided on the basis that small solid objects remain in the bathhouse, for example, leaves from brooms, bunches of aromatic herbs, soap residues, etc., which can clog a narrower passage;
- Pool drains - it is recommended to choose a diameter of 200 mm or higher. A large volume of drained water should immediately go into the route and not overflow;
- In horizontal sections connecting several collectors into one riser, the pipe diameter is preferably from 200 mm;
- Industrial drains – 300 mm and above.
Rules for the design of waste mains
The first rule says: make a minimum number of turns, do not clutter the direction with unnecessary details, this will affect further operation. A properly installed highway will initially require less time and money for further maintenance.
Important! Too sharp turns on the highways cause traffic jams and stop the transport of wastewater. When cleaning the collector, it is very difficult to get the cable into a 90° angle.
When installing sewer systems, you should adhere to the following basic rules:
- To avoid stagnation in the sunbeds, you need to make a slight slope;
- 90° turns should be avoided; if you need to turn the pipe, it is better to split it into two 45° angles, this way it is easier to avoid frequent blockages and stops for cleaning and repairs;
- Narrowing of the lumen in the direction of fluid movement towards the risers is unacceptable. The diameter should remain constant or gradually expand towards the outlet;
- In the area of branches, inspection fittings with holes for cleaning are installed, making it easy to carry out cleaning measures in case of blockages. If the connected devices are easily disconnected from the general system, then the fittings are not installed;
- When designing a common line, the toilet is placed directly to the riser. The remaining devices are placed after it so that organic particles entering the sewer do not remain at the bends and cause an unpleasant odor in the room;
- The pipes are placed in special boxes or lined with foam plastic so that the vibration of the line that occurs during draining does not cause noise or cause inconvenience;
- Latch holders and plastic clamps are used to fix drain structures in the correct position. The necks of the pipes are fixed, and the horizontal sections are treated with fastening elements every 50 cm. Multiply the diameter of the pipe by 10 - the result obtained will be the ideal distance for the location of the fasteners.
When installing sewer systems, situations sometimes arise when you need to connect pipes of different diameters. For this purpose, adapters are provided that accept smaller sockets, and with another socket they fit into a hole of a larger diameter. The joints are treated with liquid soap. For docking toilets, straight and eccentric cuffs are produced.
Using the tips presented, the master will be able to ideally design a complete layout and installation of the sewer line.
On a note! When repairing old mains and replacing cast iron pipes with modern PVC, the diameter of the pipe is taken to be 10 mm less than the old cast iron. This is due to the fact that organic and other residues settle less in smooth plastic pipes, and the fluid permeability is higher.
Slope Calculation Table
Gravity sewerage assumes that wastewater will spontaneously flow through pipes, flowing to processing sites at treatment facilities. To do this, the calculations take into account, in addition to the diameter, the slope and volume of flow or the degree of filling of the collector. Usually the system operates in medium mode, half full, except for force majeure situations. The constantly decreasing slope prevents the liquid from stagnating, so the flow rate is stable.
Calculations are made subject to maintaining cleanliness of pipelines or partial, slight siltation.
Flow rate and degree of filling of the outer manifold
| Pipe size in mm | Filling level | Flow speed m/sec | Minimum slope |
| 110 | 0,5 | 0,7 | 0,0046 |
| 150 | 0,5 | 0,7 | 0,0046 |
| 200 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 0,0046 |
| 300 | 0,7 | 0,8 | 0,0033 |
The slope is calculated taking into account the terrain along which the line will pass. Storm drainage is calculated based on the maximum precipitation that falls in a given area, and the diameter of the lumen is selected accordingly.
The flow rate is important due to the particles of sand, pebbles and others that have abrasive properties contained in the drained liquid. Constantly affecting the walls, they gradually thin them, leading to leaks. Therefore, the optimal speed is calculated at which damage to the internal surface will be minimal.
With pressure sewerage, the indicators will be different.
Which sewer pipes are best for your home?
Today, the most common choice is PVC pipes. They can withstand the temperature of domestic wastewater, are lightweight, cheap, and easy to install. The industry produces a huge range of diameters, lengths, and all types of fittings.
In cases where you need to periodically drain very hot waste, you should choose a polypropylene sewer. And if the temperature is always low, polyethylene will do.
External sewerage of residential buildings is made from PVC pipes if it runs at a shallow depth and does not cross roads with heavy traffic. Otherwise, you need to use corrugated PE or PP pipes.
Dimensions of plastic pipes for sewerage
The size of the sewer pipe (internal and external diameter) is selected based on the design documentation and requirements for a specific facility. There are external and internal distribution of sewer pipes in residential buildings. So, for the installation of sewerage inside the building, pipes with a diameter of 16-50 mm are used, for the outside - up to 110 mm.
Depending on the pipe material, most manufacturers offer the following sizes:
- Polyethylene – 10-1000 mm.
- PVC – 16-500 mm.
- Propylene – 16-110 mm.
- PEX – 16-63 mm.
When choosing the size of sewer pipes, you can be guided by sanitary standards, which indicate the permissible diameter for various drains:
- Kitchen drain – 32–50 mm.
- The drainage from the bathroom from each point is 50 mm.
- Drain from washing equipment – 25 mm.
- Pipe supply to the riser – 50–75 mm.
- Fecal drainage – 110 mm.
- Central riser – 110–160 mm.
- Output to external drain – 110–160 mm.
- External drain with outlet from the bath – 160–200 mm.
- With outlet from the pool – 20–30 cm.
- City sewer lines – 30–50 cm.
Which sewer pipes are best suited for industry?
The main part of the sewer system of industrial enterprises is also installed from PVC pipes. In underground areas, corrugated pipes made of PP can be used.
Cast iron drainage is preferable in case of heavy load, as well as for draining hot liquid waste. In particularly critical areas it is worth using ductile iron pipes.
Ceramic pipes are used in the chemical industry where high-temperature aggressive liquids need to be drained.
Reinforced concrete and asbestos-cement pipes were often used for external sewerage in the past, but are now being replaced by double-layer corrugated pipes made of PE and PP. The use of reinforced concrete pipes is justified in areas with high loads if the organization has equipment for unloading and installation.
Pipe classification
In this matter, everything depends on what criterion is used for the classification. For example, according to operating conditions, it is possible to distinguish between pressure and non-pressure systems.
But it makes more sense to classify them according to material; the following types of pipes are distinguished:
- Plastic , for sewerage, in most cases, PVC is used, and polypropylene (PP) is used when installing heating systems. The question of how to connect sewer plastic pipes is discussed in more detail below,
- Iron . Steel pipelines are popular when installing water supply systems, cast iron is used for drainage systems, and bronze and brass pipes are also seen,
- Metal-plastic - between the layers of plastic there is an aluminum layer,
- Asbestos-cement , actually not used for sewerage,
- Fiberglass.