Scheme of hot water supply with instantaneous water heater
The following can be used as an instantaneous water heater:
- DHW gas water heater;
- DHW heating circuit of a double-circuit heating boiler;
- electric instantaneous water heater.
- plate heat exchanger connected to the heating circuit.
The instantaneous water heater begins to heat the water at the moment the water is drawn
when the hot water tap is opened.
All energy spent on heating passes from the heater to the water almost instantly , in a very short time of water movement through the heater. In order to obtain water at the required temperature in a short period of time, the design of an instantaneous water heater provides for limiting the speed of water flow. The water temperature at the outlet of the flow-through heater very much depends on the water flow -
the size of the stream of hot water flowing from the tap.
To properly supply hot water to only one shower head, the power of the instantaneous water heater must be at least 10 kW. You can fill a bathroom in a reasonable time using a heater with a power of more than 18 kW
.
And if, when filling the bath or running the shower, you also open the hot water tap in the kitchen, then for comfortable use of hot water you will need a flow heater power of at least 28
kW. To heat an economy class home, a lower power boiler is usually sufficient. Therefore, the power of a double-circuit boiler is chosen
based on the need for hot water.
A DHW circuit with an instantaneous water heater cannot provide comfortable and economical use of hot water in the house for the following reasons:
- The temperature and pressure of water in the pipes very much depend on the amount of water flow. For this reason When you open another tap, the water temperature and pressure in the hot water system changes greatly.
It is very uncomfortable to use water even in two places at the same time.
- When the flow of hot water is low, the instantaneous water heater does not turn on at all and does not heat the water.
To obtain water at the required temperature, it is often necessary to use more water than necessary. - Each time the water tap is opened, the instantaneous water heater starts again. It constantly turns on and off, which reduces its service life . Each time, hot water appears with a delay, only after the heating mode has stabilized. Frequently restarting the heater reduces efficiency and increases energy consumption. Some of the water goes down the drain uselessly.
- It is impossible to recirculate water in the distribution pipes throughout the house. Hot water from the tap appears with some delay.
The waiting time increases as the length of the pipes from the water heater to the water collection point increases.
Some of the water at the very beginning has to be drained uselessly into the sewer.
Moreover, this is water that has already been heated, but has managed to cool down in the pipes. - Scale deposits quickly accumulate
on a small surface inside the heating chamber of an instantaneous water heater. Hard water will require frequent descaling.
Ultimately, the use of an instantaneous water heater in a domestic hot water system leads to an unreasonable increase in water consumption and the volume of sewerage , to an increase in energy consumption for heating, as well as to insufficiently comfortable use of hot water in the house.
The DHW system with instantaneous water heater is used, despite its disadvantages, due to the relatively low cost and small size of the equipment
.
The system works better if a separate individual instantaneous water heater is installed near each water collection point.
In this case, it is convenient to install electric flow heaters. However, such heaters, when drawing water simultaneously in several places, can consume significant power from the electrical network (up to 20 - 30 kW). Typically, the electrical network of a private home is not designed for this, and the cost of electricity is high.
Useful tips
When constructing a new building, it makes sense to immediately install a storage boiler with a capacity of over 100 liters. It will provide comfortable living without the need for alterations in the future.
If the house is used infrequently, for example a summer house, then there is no point in installing a storage system; a flow-through heater is sufficient. At the same time, the compact arrangement of flow points in such buildings will ensure convenience during operation.
If you have a large family, you can install additional capacity in the storage water supply system. A 30-liter tank with additional electric heating, which serves to compensate for heat loss, will allow you to compensate for changes in water consumption with a large number of household members.
When purchasing a gas boiler, preference should be given to ready-made boiler-boiler kits. Their parameters have already been selected for each other, such a combination will optimally consume heat.
When heating a house with solid fuel, it makes sense to use a heat storage tank to create a secondary hot water supply circuit. This will significantly reduce energy costs.
At temperatures of 55 degrees and above, salts begin to actively precipitate from the water. They clog the pipes and impair the flow of water. This is especially important for flow-through heaters that heat large volumes over a short length of pipe. If the water contains more than 140 mg of impurities per liter of water, then instantaneous water heaters cannot be used - they break down too quickly and stop heating the water.
How to choose an instantaneous water heater
The main parameter for choosing an instantaneous water heater is the amount of water flow that it can heat.
For comfortable use, it is recommended to focus on the following volumes of hot water consumption at a temperature of 55 ° C at the points of analysis:
- from the sink faucet or washbasin 4.2 l/min (0.07 l/sec);
- from the bath or shower tap 9 l/min (0.15 l/sec).
For example.
Three points of disassembly are connected to one instantaneous water heater - a sink in the kitchen, a washbasin and a bathtub (shower). To fill only the bathtub, you must select a heater that is capable of delivering at least 9 l/min. water with a temperature of 55 oC. Such a water heater will also provide the use of hot water simultaneously from two taps - in the sink and washbasin.
It will be comfortable to use hot water in the shower and washbasin at the same time if the heater capacity is no less than 9 l/min + 4.2 l/min = 13.2 l/min.
Manufacturers in the technical specifications usually indicate the maximum performance of an instantaneous water heater, based on heating water at a certain temperature difference, dT, for example, 25 °C, 35 °C or 45 °C. This means that if the water temperature in the water supply is +10 °C, then at maximum performance, water with a temperature of +35 °C, 45 °C or +55 °C will flow from the tap.
Be careful. Some sellers in advertising indicate the maximum performance of the device, but “forget” to write for what temperature difference it is determined . You can buy a geyser with a capacity of 10 l/min, but it turns out that at this flow rate it will only heat the water by 25 °C, i.e. up to 35 oC. Using hot water with such a column may not be very comfortable.
For our example, a gas water heater or a double-circuit boiler with a maximum productivity of at least 13.2 l/min at dT=45 °C is suitable. The power of the gas appliance with these hot water parameters will be about 32 kW.
When choosing an instantaneous water heater, pay attention to one more parameter - the minimum performance, the flow rate l/min at which heating is turned on.
If the water flow in the pipe is less than the value specified in the technical characteristics of the device, the water heater will not turn on. For this reason, it is often necessary to use more water than necessary. Try to choose a device with the minimum minimum capacity as low as possible, for example, no more than 1.1 l/min.
Electric instantaneous water heaters intended for domestic use have a maximum heater power of about 5.5 - 6.5 kW. At a maximum productivity of 3.1 - 3.7 l/min, water is heated at dT = 25 °C. One such water heater is installed to serve one water point - a shower, washbasin or sink.
Wiring
Installation of heating and water supply in a house begins with the selection of a wiring diagram for engineering systems.
HVS
Cold water is distributed according to a dead-end scheme (that is, it moves through the water supply system only when drawing water).
The wiring can be:
| Image | Description |
| Troinikovoy: water collection points are connected in series to a common supply line for all. The advantage of tee wiring is low material consumption, the disadvantage is a drop in pressure throughout the entire water supply system when water flows through any connected device. |
| Manifold: each device is equipped with its own supply line, starting in the manifold cabinet and equipped with a shut-off valve. There is no drop in pressure, but the consumption of pipes is several times greater and, willy-nilly, they have to be installed only hidden. |
DHW
In addition to dead-end wiring, recirculation schemes are used for hot water supply systems. The circulation pump continuously pumps water between the boiler taps. This ensures instant supply of hot water to any tap and continuous heating of heated towel rails mounted in the gap.
DHW supply with recirculation from an indirect heating boiler
Heating
Like water supply, heating can be collector or sequential (tee). The first type of wiring is more often used with water-heated floors: the high hydraulic resistance of small-diameter pipes laid in a screed limits the length of one circuit to 100-120 meters.
In addition, the heating distribution can be:
| Image | Description |
| Single-pipe. The so-called Leningradka is a heating dispensing ring with radiators connected parallel to it. The advantage of the Leningrad machine is its absolute fault tolerance: as long as there is at least some difference at the ends of the bottling, circulation in it continues. The disadvantage is a significant temperature difference between heating devices. |
| Two-pipe dead-end: radiators are connected as jumpers between supply and return bottlings; in this case, at the moment of flow from bottling to bottling, the direction of movement of the coolant changes to the opposite. This wiring allows you to bypass any obstacles and form several parallel branches of the heating system. However, jumpers between bottlings cause the difference between them to drop as they move away from the boiler. The result is cooling of distant heating devices until defrosting in extreme cold. The problem can be solved by balancing - limiting the passage of the connections of the batteries closest to the boiler. |
| Two-pipe associated (Tichelman loop). Several small circuits with the same length and, accordingly, the same hydraulic resistance are formed in it. As a result, all batteries are heated to the same temperature. |
Radiator connection diagrams
Installation of heating and water supply in a country house includes, among other things, the installation of heating devices. If panel radiators and convectors are mounted only in the manner prescribed by the manufacturer, then sectional radiators can be connected to the bottling or riser according to one of three schemes.
| Image | Description |
| Lateral one-way connection is effective when the battery length is no more than 10 sections. If it is longer, the outer sections will be noticeably colder than those closest to the liners. |
| Diagonal connection is effective for any length of the device and ensures uniform heating of all sections. |
| The lower two-way connection is advantageous in that it guarantees circulation even when the circuit is aired (air is forced into the upper collector, and circulation goes through the lower one). In addition, with a lower two-way connection, the battery will never need to be flushed: all the sludge is carried away by the coolant circulating through the lower collector. |
DHW circuit with storage heater (boiler) and water circulation
A storage water heater (boiler) is a heat-insulated metal tank of a fairly large volume.
Most often, two heaters are built into the lower part of the water heater tank at once - an electric heating element and a tubular heat exchanger connected to the heating boiler (diagram for connecting the boiler to the boiler). The water in the tank is heated by the boiler most of the time.
The electric heater is turned on as needed when the boiler is stopped. Such a boiler is often called an indirect heating boiler.
Hot water in an indirect heating boiler is consumed from the top of the tank. In its place, cold water from the water supply immediately enters the lower part of the tank, is heated by a heat exchanger and rises upward.
In the European Union, hot water systems in new houses are required to be equipped with a solar heater - a collector. To connect the solar collector, another heat exchanger is installed in the lower part of the indirect heating boiler .
The water in the boiler is heated by a solar collector. If there is not enough heat from the collector, then the boiler or electric heater is switched on. Read: “DHW system with solar collector” .
System with recuperator and solar collector
To reduce the cost of heating a home and heating water in Europe, various energy-saving technologies have long been used. These include a recuperator and solar collector system.
Since hot water does not have time to cool down during its use and flows down the drain hot, this is an unjustified loss of heat. To reduce them, a recovery system is installed at water consumption points. It is a heat exchanger, often made in the form of a coil, installed on a sewer pipe. The flowing hot water heats the environment and, as a result, the heat exchanger. Cold water from the water supply is connected to this heat exchanger, which then enters the boiler.
Thanks to this operating scheme, the hot water taken from the hot water supply system partially heats the cold water that replaces it and thereby offsets the costs.
Additional savings will be achieved by using a solar collector. Despite the apparent low efficiency, it provides significant savings in the long term. In the solar collector, the water is heated by 5-7 degrees, then heated by 5-7 degrees in the recuperator. Having a water temperature of 10 degrees in the water supply, at the entrance to the boiler it will already be 20 - 25 degrees. That is, it is necessary to heat not by 45, but only by 30 - 35 degrees, which gives up to 25% energy savings on heating. In the future, such savings allow not only to recoup the costs of installing additional equipment, but also to reduce costs in general.
DHW diagram with layer-by-layer heating boiler
| DHW diagram with layer-by-layer heating boiler and instantaneous water heater |
Recently, a hot water supply system with a layer-by-layer heating boiler has been gaining popularity,
the water in which is heated by a flow-through water heater. This boiler does not have a heat exchanger, which reduces its cost.
Hot water is drawn from the top of the tank. In its place, cold water from the water supply immediately flows into the lower part of the tank. The pump drives water from the tank through a flow-through heater and supplies it directly to the top of the tank. Due to this, the consumer gets hot water very quickly
— you don’t need to wait until almost the entire volume of water warms up, as happens in an indirect heating boiler.
Rapid heating of the top layer of water allows you to install a smaller boiler in the house, as well as reduce the power of the flow-through heater,
without sacrificing comfort.
The Galmet SG (S) Fusion 100 L layer-by-layer heating boiler is connected to the DHW circuit of a double-circuit boiler or to a gas water heater.
The boiler has a built-in three-speed circulation pump. Boiler height 90 cm, diameter 60 cm. Manufacturers produce double-circuit boilers with a built-in or remote layer-by-layer heating boiler. As a result, the cost and dimensions of the DHW system equipment are somewhat smaller,
than with an indirect heating boiler.
The water in the boiler is heated in advance,
regardless of whether it is spent or not. The hot water reserve in the tank allows you to use hot water in the house for several hours.
Thanks to this, the water in the tank can be heated for quite a long time, gradually accumulating thermal energy in the hot water. Hence another name for the boiler - storage water heater.
The long duration of water heating allows the use of a relatively low power heater.
Where does hot water supply to a private home begin?
Before you begin installing hot water supply in a private home, you need to decide on some parameters of this system.
First of all, you need to figure out what kind of plumbing fixtures you will use, in what quantity and where you will place the equipment. As a rule, this is a sink, bathtub, shower cabin, washbasin, jacuzzi, bidet, etc.
After you have decided where you will place the plumbing, you need to allocate a place in a private house for installing water heating equipment. To do this, it is necessary to take into account the technical capabilities of the device. Experts recommend placing it at the same distance from hot water consumers.
Then the pipes and all related fittings are selected. As a rule, pipes with a diameter of 15 or 20 mm are suitable for internal wiring. For these purposes, galvanized or non-galvanized pipes are used, as well as products made of metal-plastic, polyethylene or polypropylene. Polypropylene pipes are the most popular. You will need a certain number of fittings, couplings and other elements that must be purchased in the required quantities in accordance with the wiring plan for the hot water supply system of a private home.
Next, you should select equipment for preparing hot water.
Today, there are a large number of companies that will quickly help solve the problem of providing hot water supply to a private home, and will also provide the equipment necessary for water purification. These procedures are mandatory, since in private houses, as a rule, the water sources are wells, artesian wells, etc., and the water in them, as a rule, has a composition that is far from ideal. Therefore, such water cannot be used not only for cooking, but also in hot water supply systems. This is due to the fact that it contains salts of calcium, magnesium and other elements, due to which the water becomes harder.
Read material on the topic: Communications in a private home
Storage gas water heater - boiler
Storage boilers, the water in which is heated by a gas burner, are less popular in domestic hot water systems. Installing heating and hot water systems in a house with two gas appliances - a gas boiler and a gas boiler - turns out to be noticeably more expensive.
Storage gas water heater - boiler
It can be advantageous to install gas boilers in apartments with central heating or in private houses with heating by a solid fuel boiler and heating of water in the hot water system with liquefied gas.
Gas water heaters, like boilers, are available with an open combustion chamber and a closed one, with forced removal of flue gases and with natural draft in the chimney.
There are storage gas boilers on sale that do not require connection to a chimney . (Household gas stoves also operate without a chimney.) The power of the gas burners of such devices is small.
Gas boilers with a capacity of up to 100 liters are designed for wall mounting. Large volume water heaters are installed on the floor.
Water heaters use different methods of gas ignition - with a pilot wick, electronic with batteries or hydrodynamic ignition.
In devices with a pilot wick, a small flame is constantly burning, which is first ignited manually. A certain amount of gas burns uselessly in this torch.
Electronic ignition operates from the mains or a battery.
Hydrodynamic ignition is started by rotating a turbine, which is driven by the flow of water when the tap is opened.
What to consider when organizing hot water supply for a private home
As a rule, the installation of any water heating device in a private home is carried out by a professional, since this requires preparing a suitable diagram, obtaining permission, and installing ventilation or a chimney if such a need arises.
If you use plastic pipes, the installation process is greatly simplified due to their durability and strength, and these products do not require the use of a welding machine. You should purchase fittings, silicone, tow, spare fasteners for pipes and batteries. You also need a set of tools, consisting of a special soldering iron, scissors, a hammer drill, a screwdriver, a level and a hammer, several types of keys, pliers, metal snips, etc.
The hanging boiler should be located at a distance of at least 50 cm from the ceiling. Reliable fasteners are used for it and radiators. When you set up a boiler room, it is recommended to cover the walls and floor with fire-resistant tiles and do not forget to provide free access to the water heater for periodic maintenance.
It is also necessary to install a chimney and ventilation system. You will also need a circulation pump; it is quite compact and capable of providing constant pressure, as a result of which the water quickly heats up.
If you are working with plastic pipes, you will need an assistant, since the connection is instantaneous and distortions must be avoided. Radiators are installed at the very last moment.
Make sure they are at the same level. The distance to the floor should be from 10 to 15 cm, from the wall - from 2 to 5 cm. By installing shut-off valves and temperature sensors, you can control the water temperature and shut it off if necessary.
If you do not have the necessary installation skills, it is better to turn to professionals. It is important to perform the correct calculations. The first thing you will need to do to properly install the hot water supply of a private house with your own hands is a diagram.
Read material on the topic: How to choose water supply pipes so that they last a long time
How to choose the volume of a storage water heater - boiler
The larger the volume of the storage water heater, the higher the comfort of using hot water in the house. But on the other hand, the larger the boiler, the more expensive it is, the higher the costs of its repair and maintenance, and the more space it takes up.
The size of the boiler is selected based on the following considerations.
It is generally accepted that the boiler volume, selected at the rate of 20-30 liters per person, will provide the minimum necessary comfort for using hot water in the house.
Increased comfort will be provided by a boiler, the volume of which is selected at the rate of 30 - 60 liters per user of water.
A high level of comfort will be provided by a water heater with a volume of 60-100 liters per person living in the house.
To fill the bathtub, it is necessary to use up almost all the water from the boiler with a volume of 80 - 100 liters.
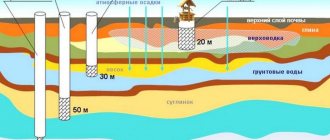
Water source
As a rule, only cold water is supplied to a private house. It is heated for household needs by a local heat source. What can become a source of water?
The video in this article will help you learn more about the design of the cottage's engineering systems.
Water main
If there is a main water supply near your house, the problem can be solved by concluding an agreement with the local Vodokanal. After drawing up and approving the project, a water metering well is built, a connection is made into the main line and a water metering unit is installed - a water meter with a coarse filter and shut-off valves.
Water metering unit in a well
Country water supply
In order to ensure uninterrupted water supply, a storage tank is installed in a house connected to a country water supply with water supply according to a schedule. The simplest solution is to install it in the attic: water will be drawn into the container when it is supplied to the water supply system through a float valve, which prevents overflow, and will move to the water collection points by gravity.
Water is supplied by gravity to the water supply from a tank installed in the attic
Alas, it is difficult to organize water supply and heating of a wooden house in this way: for wooden beams, the weight of a storage tank of several tons will be an excessive load. In this case, you can resort to plan “B”: the tank is installed in an insulated basement or subfloor and is supplied with a pumping station with a hydraulic accumulator.
Water supply from a tank in the basement with water supply from a pumping station
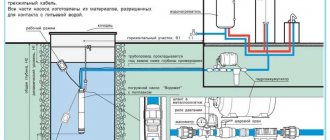
Well, borehole
How to implement water supply from a well or well?
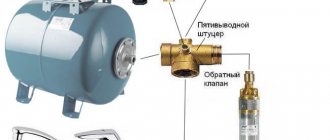
- The borehole pump is equipped with a check valve, which will prevent water from draining from the water supply when the pump is turned off (see Belamos borehole pump);
- The pump is controlled by a pressure sensor and an automatic relay;
- A hydraulic accumulator is installed in the water supply circuit. Its task is to stabilize pressure and save pump life.
Water supply from a well with a submersible pump
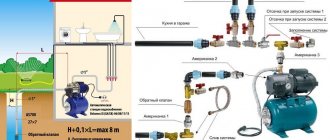
Useful: if the distance from the ground level to the water intake level is less than 8 meters, the pump can be surface-mounted. In this case, a check valve is placed on its suction pipe.
Scheme of autonomous water supply with a surface pump
How to choose boiler power for a DHW boiler
When choosing a boiler, you need to pay attention to the power of the heating element that is installed in it. For example, to heat 100 liters of water to a temperature of 55 oC in 15 minutes, a heater (heat exchanger for the boiler, built-in gas burner or heating element) with a power of about 20 kW must be installed in the boiler.
In real operating conditions, the temperature of the water in the boiler is equal to the temperature of the water in the water supply only when the heating is first turned on. In the future, the boiler almost always contains water that has already been heated to a certain temperature. To heat water to the required temperature in an acceptable time, heating devices of lower power are used.
But it’s still better to check how long it will take to heat the water in the boiler. This can be done using the formula:
t = m•cw•(t2 – t1)/Q , in which: t – water heating time, seconds (s); m – mass of water in the boiler, kg (mass of water in kilograms equals the volume of the boiler in liters); cw is the specific heat capacity of water, equal to 4.2 kJ/(kg•K); t2 – temperature to which the water should be heated; t1 – initial water temperature in the boiler; Q – boiler power, kW.
Example: The time for heating water by a 15 kW boiler in a 200-liter boiler from a temperature of 10°C (we assume that the water entering the boiler has this temperature) to 50°C will be: 200 x 4.2 x (50 – 10) /15 = 2240 s, that is, about 37 minutes.
DHW scheme with water recirculation in the system
The use of a storage water heater in a domestic hot water system allows for the recirculation of hot water in pipelines. All hot water collection points are connected to a ring pipeline through which hot water constantly circulates.
The length of the pipe section from each point of hot water consumption to the ring pipeline should not be more than 2 meters.
The circulation pump of the DHW hot water recirculation system is small in size and has low power.
Water recirculation in the DHW system is ensured by a circulation pump. The pump power is small, several tens of watts.
Pumps for DHW, unlike heating pumps, must have a maximum operating pressure of at least 10 bar. Heating pumps are often designed for a maximum pressure of no more than 6 bar. Another difference is that the DHW pump must have a hygienic certificate allowing use in drinking water supply systems.
The water in hot water supply systems is constantly renewed and the oxygen content in it remains quite high. Hot water is highly corrosive. In addition, hot water must meet sanitary requirements for drinking water. Therefore, for the manufacture of DHW pumps, corrosion-resistant non-ferrous metals or stainless steel are used. For these reasons, circulation pumps for hot water supply are noticeably more expensive than similar pumps for heating systems.
In some DHW pipeline designs, it is possible to create natural water recirculation, without a pump.
As a result of water circulation in the hot water supply system, hot water is constantly supplied to the sampling points.
In a DHW system with a storage heater and water recirculation, the water supply mode is more stable:
- Hot water is always present at the sampling points.
- Water can be collected simultaneously in several places. The temperature and pressure of water change slightly when the flow rate changes.
- You can take any, no matter how small, amount of hot water from the tap.
The recirculation circuit allows not only to increase the comfort of water supply in remote points of the house, but also makes it possible to connect heated floor circuits to it in individual rooms. For example, in a bathroom, a water-heated floor will be comfortable all year round.
A DHW system with water recirculation constantly consumes energy
for the operation of the circulation pump, as well as to compensate for heat losses in the boiler itself and in the pipes with circulating water. To reduce energy consumption, it is recommended to install a circulation pump with a built-in programmable timer that turns off water circulation during hours when it is not needed. The boiler and hot water pipes are insulated.
Circulation system
With a large house, the length of pipes from the boiler to the point of consumption can be more than 10 meters. In this case, it is not very convenient to wait until the cold water drains and the hot water starts flowing, so a system with hot water circulation is used.
To do this, a closed hot water circuit is installed, which provides access to it from anywhere in the house. All flow points are connected to it and are located no more than 1.5 - 2 meters from the pipeline.
A circulation pump is inserted into the ring circuit, which ensures the movement of hot water. Having passed the entire circle, the water cools down and returns back to the boiler, where it is heated again. This allows you to reduce the waiting time for hot water to one or two seconds and reduces losses in water pressure.
The disadvantage of such a system is the presence of additional costs for the operation of the pump and compensation for heat loss. But they can be reduced by additionally insulating the boiler and pipes of the ring circuit and using automation to regulate the operation of the pump.
Disadvantages of a hot water supply system with a double-circuit gas boiler or water heater
Clocking of a double-circuit boiler in heating mode
As you know, a double-circuit gas boiler can provide a house with hot water and be a source of heat in the heating system. Hot water is prepared in a flow-through heat exchanger of the boiler. Read about the general disadvantages of a DHW system with a flow-through heater at the beginning of this article. But gas appliances with a flow-through heater have another problem - the difficulty of choosing the maximum power of a double-circuit boiler or hot water heater.
Most often it turns out that the required boiler power for preparing hot water is significantly greater than the power required to heat all rooms in the house.
As already mentioned in the article above, in order to obtain hot water at the required temperature and its maximum consumption, double-circuit gas boilers and water heating geysers have a fairly large maximum power, about 24 kW . or more. Boilers and heaters are equipped with automatic equipment, which can, by modulating the burner flame, reduce their power to a minimum, equal to approximately 30% of the maximum. The minimum power of a double-circuit gas boiler or water heater is usually about 8 kW. or more. This is the minimum boiler power, both in DHW and heating modes.
Due to design features, the gas burner of a double-circuit boiler or water heater cannot operate stably with a power less than the minimum (less than 8 kW). At the same time, to work with the heating system of a private house or autonomous heating of an apartment, the boiler in heating mode very often must produce a power of less than 8 kW.
For example, power 8 kW. enough to provide heat to the premises of a house or apartment with an area of 80 - 110 m2, and during the coldest five-day period of the heating season. In warmer periods, the productivity and power of the boiler should be significantly less.
Due to the fact that the boiler cannot operate with power below the minimum, problems arise with the adaptation (coordination) of the double-circuit boiler and the heating system.
In small facilities with low heat consumption for heating, the boiler produces more heat than the heating system can accept. As a result of inconsistency between the parameters of the boiler and the system, the double-circuit boiler begins to operate in pulse mode, “clocking” - as people say.
Operating in the “clocking” mode significantly reduces the service life of boiler parts and significantly reduces efficiency.
Read more: “Setting the power of a double-circuit gas boiler”
Clocking a gas boiler or water heater in DHW mode
Diagram of heating tap water with a double-circuit gas boiler or hot water column, depending on the temperature ( T oC) and flow rate ( Q l/min) of hot water. The thick line shows the boundaries of the Working Area. Gray zone, position 1 - clock zone of the boiler or dispenser (switching between ON/OFF).
For normal heating of water by a boiler or column, in the diagram the point of intersection of the temperature and hot water flow lines (operating point) must always be located inside the working zone, the boundaries of which are shown in the diagram with a thick line. If the hot water consumption mode is selected so that the operating point is in the gray zone, pos. 1 on the diagram, then the boiler and column will clock. In this zone, with a small water flow, the power of the boiler or dispenser turns out to be excessive, the boiler, dispenser turns off due to overheating, and then turns on again. Either hot or cold water comes out of the tap.
Read more: “Alternately cold and then hot water comes from the boiler.”
Low efficiency of double-circuit gas boilers and water heaters
Double-circuit gas boilers, when operating at maximum power, have an efficiency of more than 93%, and less than 80% when operating at minimum power. Imagine how the efficiency will further decrease if such a boiler has to operate in pulse mode, with the gas burner constantly re-igniting.
Please note that a double-circuit boiler operates at minimum power most of the time throughout the year. At least 1/4 of the spent gas will literally fly uselessly down the pipe. Add to this the cost of replacing prematurely worn-out boiler parts. This will be the price to pay for installing cheap heating and hot water equipment in your home.
What do you want - choose
If the power of a double-circuit gas boiler is more than 20 kW. , is selected based on heating the maximum required flow of hot water, then the boiler cannot provide economical and comfortable operation in low heating power mode and when heating water at low flow rates. The same can be said about the operation of a hot water column.
Most often, there is no need to prepare large flows of hot water in the house. For many people, it is much more important to ensure comfortable and economical use of hot water with low consumption.
For such economical owners, many manufacturers produce double-circuit gas boilers and water heaters with a maximum power of about 12 kW. and the minimum is less than 4 kW. Such boilers and heaters will provide more economical and comfortable heating and the use of hot water in quantities sufficient for taking a shower or washing dishes.
Before purchasing a double-circuit boiler or water heater, owners need to decide which mode of hot water consumption is more profitable and comfortable - with a large water flow or with a small one. Based on this decision, choose the power of the boiler or dispenser. If you want both, you will have to choose a hot water system with a boiler.
For shower lovers, for preparing hot water and heating houses and apartments with a heated area of up to 140 m2, with one bathroom , I recommend installing double-circuit gas boilers with a maximum power of 12 kW. They best suit the needs of heating and hot water systems of small private houses and apartments.
For those who like to take a bath, as well as for large houses and apartments with an area of more than 140 m2, I highly recommend using a hot water system with a stratified heating boiler and a double-circuit boiler, or with an indirect heating boiler and a single-circuit boiler.
Many manufacturers of heating equipment produce special kits, a boiler plus a built-in or remote boiler, just for such cases. Such a set of equipment will be more expensive, but will provide an increased service life of the equipment, gas savings and more comfortable use of hot water.
Materials
The hot water supply system for Soviet-built residential buildings was installed with steel pipes (black and galvanized) using welding and threaded fittings. However, now, excuse me, it’s the twenty-first century, and steel (at least black) in no way meets the regulatory requirements for the durability of water pipes.
What materials are in use now?
| Image | Description |
| A copper pipe is incomparably more durable than a steel pipe (copper water pipes from a century ago still work perfectly) and is not inferior to it in strength (the breaking pressure for a 15 mm pipe with a millimeter wall is 240 atmospheres). Not only that: copper helps disinfect water due to its bactericidal properties. To connect pipes, socket soldering, crimp and compression fittings are used. |
| Hot water supply in the house, installed with a corrugated stainless pipe, will be resistant to water hammer and significant overheating. With a wall thickness of only 0.3 mm, stainless steel is almost as strong as a copper pipe, outperforming it in terms of flexibility and manufacturability of installation on compression fittings. |
| Polypropylene pipes are designed for pressures up to 25 atmospheres and temperatures up to 90 degrees. The advantage of this material is the minimal cost of the pipes themselves (from 20 rubles/m) and welding fittings (from 3 rubles). To connect them, a soldering iron with Teflon tips is used. |
| Heat-resistant and cross-linked polyethylene is used mainly for hidden collector distribution of hot water supply. Heat resistance is from 70 to 110 degrees, it is determined by the amount of copolymers and PERT and the degree of cross-linking of PEX. Installation - on compression fittings, fittings and (for PERT) coupling fittings for welding. |
| A metal-polymer pipe with compression fittings is ideal if you want to install a hot water supply for your dacha yourself with a minimum set of tools. To install the fitting, you only need two wrenches (open-end or adjustable), an inexpensive calibrator and a pipe cutter. The inner lining of the pipe is made of PEX or PERT and provides quite acceptable temperature resistance. |
DHW circuit with sewerage heat recuperator
In Western Europe and around the world, various ways to save energy when operating a private home are popular.
After use, hot water from the house flows into the sewer and takes with it a significant part of the thermal energy that was spent on heating it.
Scheme for the recovery of thermal energy from sewerage wastewater into the hot water supply system
To reduce energy losses in the house, a scheme is used to recover (return) heat from sewage into the domestic hot water system of a private house.
Cold water passes through a heat exchanger before entering the DHW boiler. The wastewater from sanitary equipment is sent to the heat exchanger.
In the heat exchanger, two streams, cold water from the water supply and hot water from the wastewater, meet but do not mix. Some of the heat from hot water is transferred to cold water. The hot water boiler receives already heated water.
In the diagram shown in the figure, only those sanitary fixtures that operate with hot water flow are sent to the heat exchanger. This recovery scheme is advantageous to use with any method of heating water - both with a boiler and with a flow-through heater.
To recover heat from the drains of sanitary appliances, which first accumulate hot water and then discharge it into the sewer system (bathtub, swimming pool, washing machine and dishwasher), a more complex scheme is used with water circulation between the boiler and the heat exchanger while these devices are emptying.
Tips for the developer
For houses and apartments with permanent residence, I highly recommend using a hot water system with a stratified heating boiler and a double-circuit boiler, or with an indirect heating boiler and a single-circuit boiler. The boiler volume is at least 100 liters. The system will provide good comfort in using hot water, economical consumption of gas and water, as well as a smaller volume of waste into the sewer. The only disadvantage of such a system is the higher cost of the equipment.
With a limited construction budget, in small country houses for seasonal living, you can install a hot water system with a flow-through heater.
It is advisable to use a DHW circuit with a flow-through heater in houses with a kitchen and one bathroom, where the heating source and hot water collection points are located compactly , at a short distance from each other. It is recommended to connect no more than three water taps to one instantaneous water heater.
The cost of such a system is relatively low,
and the disadvantages of operation in this case are less pronounced. A double-circuit gas boiler or gas water heater takes up little space. Almost all the necessary equipment is mounted in the device body. To install a boiler with a power of up to 30 kW or a gas water heater, a separate room is not required.
To prepare hot water and heat houses and apartments with a heated area of up to 140 m2, with one shower in the bathroom , I recommend installing double-circuit gas boilers with a maximum power of 12 kW.
In a DHW system with a gas water heater or a double-circuit boiler
The stability of the water supply mode will increase significantly if
a buffer tank is installed in the circuit between the heater and the water collection points
- a conventional storage electric water heater. It is especially recommended to install such a buffer storage electric water heater near distribution points remote from the gas appliance.
Read more: Connecting an electric hot water boiler to a double-circuit gas boiler or water heater
In a scheme with a buffer tank, hot water from a gas water heater or double-circuit boiler first enters the tank of the electric boiler - water heater
. Thus, the tank always contains a supply of hot water. The electric heater in the tank only compensates for heat loss and maintains the required temperature of hot water during the period when there is no water supply. An electric water heater with a small capacity tank is enough - even 30 liters, and using hot water will become much more comfortable.
DHW system with instantaneous water heater and built-in boiler or remote stratified heating boiler
will be somewhat more expensive. But here you will not need to spend expensive electricity to maintain the water temperature, and the comfort of using water will be the same as with an indirect heating boiler.
In houses with an extensive DHW network, implement a scheme with a storage water heater (boiler) and water recirculation. Only such a scheme will provide the necessary comfort and economical operation of the hot water system. True, the initial costs of its creation are the highest. It is recommended to buy boilers that are sold complete with a boiler.
In this case, the parameters of the boiler and boiler have already been correctly selected by the manufacturer, and most of the additional equipment is built into the boiler body.
If the heating in the house is carried out with a solid fuel boiler , then it is beneficial to install a buffer tank - a heat accumulator, to which you can connect a hot water supply system with water circulation.
Otherwise, to heat water in the house, an indirect heating boiler, additionally equipped with an electric heater, is connected to the solid fuel boiler.
It is beneficial to use an electric hot water boiler in a house with a solid fuel boiler
Often, only electricity is used to heat water in a house with a solid fuel boiler. For hot water supply in the house, near the water collection points, an electric storage boiler - a water heater - is installed. There is no hot water circulation system in this option. It is more profitable to install your own separate storage heater near remote water collection points. In this case, electricity is spent more economically on heating water.
When water is heated above 54 °C, hardness salts are released from the water. To reduce scale formation
If possible, heat the water to a temperature lower than specified.
Instantaneous water heaters are especially sensitive to scale formation. If the water is hard, contains more than 140 mg
CaCO3 in 1 liter, then
the use of instantaneous water heaters, including those with stratified heating boilers, for heating water is not recommended.
Even small scale deposits clog the channels in the instantaneous heater, which leads to the cessation of water flow through it.
It is recommended to supply water to the instantaneous water heater through an anti-scale filter, which reduces water hardness. The filter has a replaceable cartridge that will have to be changed regularly.
To heat hard water, it is better to choose a hot water storage system with an indirect heating boiler.
Salt deposits on the heating element of the boiler do not impede the flow of water, but only reduce the performance of the boiler. The boiler is easier to clean from scale.
It should be remembered that prolonged heating of water to a temperature of less than 60 ° C can lead to the appearance of Legionella bacteria harmful to human health in the storage tank (boiler) with hot water. It is recommended to periodically perform thermal disinfection of the hot water supply system , increasing the water temperature to 70 ° C for some time.
More articles on this topic:
⇒ Connecting a layer-by-layer heating boiler to a double-circuit boiler ⇒ Why there is either cold or hot water from the boiler ⇒ Descaling the DHW heat exchanger of a boiler or column ⇒ Solar collector - water heater for a home, pool
⇆
More articles on this topic
- Review of heating equipment "Teplodar"
- Liquid thermal insulation as home insulation is a hoax
- Cheap shallow foundation for a house in a swamp
- Warm lightweight masonry mortar for laying block walls
- How to make the right concrete floor in a wooden or frame house
- Choosing a soft roof for the roof of a private house
- Installing a boiler in a private house in the attic
- How to make an entrance vestibule in a private house
How to organize hot water supply for a private house through a heat exchanger
In Western European countries, as well as throughout the world, various energy saving methods are very popular.
Used hot water goes down the drain, taking with it a large portion of the energy spent heating it.
In order to reduce energy losses in a private home, an energy recovery scheme from sewage should be used.
Cold water, before entering the heater, flows through a heat exchanger, which, in turn, is discharged into drains from plumbing equipment.
In the heat exchanger, two streams are distinguished - cold tap water and waste hot water, which collide, but do not mix. A certain amount of heat from hot water is transferred to cold water, and warm water enters the heater.
The diagram shown above shows that only the drains of plumbing equipment that operate on hot water are directed to the heat exchanger. This scheme is very beneficial for all methods of heating water in a private home.
Read material on the topic: How to make heating in a private house: options and schemes