Classification of semi-automatic devices
The division of semi-automatic welding devices is carried out according to various criteria.
Device type
This mainly applies to the body of the device. If all the components are in one body, then it will be a single-body type. In two-body models, one block contains a welding torch, a wire feeder, and a control panel. In the second block there is a current source having equipment for regulating the start.
Type of wire
The semi-automatic machine can use two types of wire: aluminum or steel. There are universal devices that can work with any of these types.
Seam protection
This happens in three ways: with a layer of flux, in protective gases, and using flux-cored wire. The most common method is to use shielding gases. The caveat is that cored wire can also be used in a gas environment.
Nature of movement
For mass production, stationary devices are used. In everyday life and for field work, portable semi-automatic devices will be more convenient. Mobile devices move on a chassis with wheels.
Electrical connection
Single-phase semi-automatic devices with low power can be plugged into a regular outlet. Three-phase require special connectors.
Wire feeding
With the push type, the drive pushes the wire into the welding torch. In the pull-type design, the drive is located in the torch handle and pulls the wire from the spool on which it is wound. The hybrid is a pulling-pushing type.
Polarity when welding semi-automatically
h26,0,0,0,0—>
Before welding, you need to decide which polarity you will use.
- Carbon dioxide pressure reducer. Adjusting the shielding gas supply
p, blockquote11,0,0,0,0—>
Plain copper-clad wire that is used with shielding gas should be used with reverse polarity when positive is applied to the wire. Straight polarity is used when the semi-automatic machine has flux wire installed, which is used without gas. In this case, a minus is applied to the wire, and a plus is applied to the metal being welded through the terminal. Thus, maximum heat generation is generated on the wire. This is necessary so that the flux in it can work properly.
p, blockquote12,0,0,0,0—>
If you use the wrong polarity for a certain electrode (in the case of a semi-automatic wire), then the strength of the weld will be poor. If the wrong polarity is used, there will be a lot of spatter, poor welding penetration and the welding arc will be difficult to control.
p, blockquote13,1,0,0,0—>
To change the polarity, you need to open the cover of the semiautomatic device and swap the terminals. Next to the terminals there is a table specifying the order of the terminals.
p, blockquote14,0,0,0,0—>
Welding wire
p, blockquote15,0,0,0,0—>
The semi-automatic machine can use two types of wires: plain copper-coated wire and flux-coated wire.
p, blockquote16,0,0,0,0—>
- Simple wire for semi-automatic welding is used with shielding gas and does not have any additives that can “resist” corrosion and contamination. Therefore, the surface must be prepared carefully.
- The second type of wire has a flux in the center, which, when burned, forms a protective gas. Thus, you can do without a gas cylinder. This wire creates deeper penetration when welding than conventional wire with gas. Flux-cored wire creates a lot of spatter and slag in the welding area, which must be cleaned up after welding is complete. When welding with such wire, minimal surface preparation is required, minor contamination is forgiven. This wire also works well when it's windy outside. For flux-cored welding, the machine must be set to straight polarity (see above).
- The greater the thickness of the metal being welded, the larger the diameter of the wire you need to use, since larger diameter wire conducts more electricity and gives more heat and better penetration.
Semi-automatic device
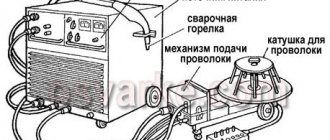
To better understand how to weld with a semi-automatic machine, you need to study its structure.
Main components of the device:
- Frame.
- Power supply.
- Control block.
- Burner.
- Bobbin with wire.
- Wire feed mechanism.
- The cable used to connect to ground.
- A hose designed to supply gas.
- Inert gas in container.
You can purchase additional accessories, such as a protective screen or a sleeve stand. Power sources for semi-automatic devices, usually operating on direct current, are inverters or rectifiers. Inverters are preferred, but their cost is much higher.
A welding hose is a hose that supplies gas, wire and cooling liquid to the work site. One end of it is connected to the apparatus, and the other to the gas burner. Inside the welding sleeve, in the center, there is a unit through which the wire is fed. Coolant is only available on some models. The longer the hose, the greater the possibility of welding in places where access is difficult. To connect the hose, a unified connector according to the Euro standard is used.
The large fitting in the center is used for the wire exit. The small one next to it is for supplying gas. The two contacts at the top are needed to switch modes. There are wires connected at the bottom that supply current.
A burner is connected to the hose, where all the wires and tubes are led out. The main components of the burner are the handle and the guide tube coming out of it.
There is a mode switch on the handle. A gas diffuser, a contact tip, and a nozzle are attached to the tube. The contact tip is a replaceable part because it is different for each wire diameter. The nozzle depends on the size of the tip.
The welding wire is wound on a spool, which can have different sizes. The wire feeding device includes a roller feed mechanism. The rollers have grooves for different wire diameters. The role of the electric motor is to perform rotation. The wire tension is adjusted manually.
Rollers are used for cored wires. There may be two or four. That's basically all you need for semi-automatic welding.
Pros and cons of a semi-automatic machine (wire machine)
The semi-automatic machine has many advantages that make it so popular among amateurs and professionals. We will list the main ones.
The most important advantage of a semi-automatic machine is the decent quality of welded joints. The device is so easy to use that even a beginner or amateur can handle the job. The welds are of high quality because the arc is easy to ignite, burns steadily throughout the entire welding process, and the metal itself is protected by gas or flux.
We also note that semi-automatic welding is quite productive, despite the fact that it is a little more complicated than RDS welding. During the process, you do not need to constantly change electrodes and be distracted. All you have to do is place the spool of wire in the feed mechanism and you can cook. That is why a semi-automatic machine can be found not only in a country house or garage, but also in a private workshop or service station.
The next plus is versatility. Using a semi-automatic machine, you can weld all types of metals, including those that cause difficulties in manual arc welding. The same aluminum or stainless steel. They are not so easy to weld due to the oxide film that forms on the surface of the metal. But a semi-automatic machine copes with this problem. You can also weld very thick and very thin parts without worrying about undercooking or burns.
Note that even a budget semi-automatic machine is often equipped with a large number of settings, so you can adjust each parameter to suit you. You can experiment with the wire feed or the shape of the torch flame. And despite the many adjustments, the device remains easy to use and largely intuitive. Anyone can handle it.
Let's move on to the cons. There are few of them, and in our opinion they are not so significant, but still.
The first thing you will encounter is the need to purchase many components. Buy a gas cylinder, buy wire, buy a torch, buy a sleeve for a semi-automatic machine, buy a reducer for a cylinder... Will you be able to spend the money or is it easier for you to buy coated electrodes and continue cooking with your inverter or an old transformer? Think about it.
The second thing you need to pay attention to is the difficulty of transporting the entire kit listed above. The semi-automatic device itself can weigh 15-20 kg, which is not that much. But all the components for it + the gas cylinder weigh many times more. The problem is solved if you install everything on a special cart.
Principle of operation
The theory of semi-automatic welding is as follows. The main feature is that instead of electrodes, welding wire is used, which enters the welding zone continuously.
Semi-automatic welding can be carried out in carbon dioxide (MAG) or inert gas (MIG). The technology of semi-automatic welding with carbon dioxide and inert gases involves setting the wire consumption value on the machine. At the exit, the wire has to pass through a hole in the contact tip. An arc occurs between the wire and the part being welded, and the metal begins to melt due to the high temperature, which leads to the formation of a weld pool. It begins to move after the burner. A weld remains behind, which gradually begins to cool.
A nozzle is used to form a gas cloud of a specific shape and density. Gas enters it through a diffuser, which is located at the point where the contact tip is attached. It is clear how a semi-automatic gas welding machine works. However, there is an option without using it. In this case, a special wire is used, which is a thin tube with flux inside.
Since the flux has a powder structure, the wire is also called flux-cored wire. When welding, flux, when burned, releases a gas that creates a protective environment. For beginners, semi-automatic welding without gas is a good and easier way to gain general information about the features of the process. For critical structures, gas welding is preferable.
Recommendations for selection
It is advisable to select a semi-automatic wire welding machine based on assessment factors:
- Mains voltage. For the household series, 220V is preferable.
- Power. For household tasks or small workshops, 10 kWt is enough.
- Maximum current up to 200-250 A.
- PV at maximum mode within 10-20%. For locksmith workshops - up to 40-60%.
- Welding thin-sheet material (1-2 mm), for example, automotive sheet, at home is more convenient with an inverter. Daily work is a welding rectifier or a powerful inverter-type semi-automatic welding machine.
- Purchase for a car repair shop or with an eye to future extended use - a unit with maximum functionality: operation in MMA, MIG/MAG, TIG modes and point contact connection.
A wire unit with the ability to work with or without gas is more complex than a conventional transformer or rectifier. The price is higher. But the advanced capabilities of the device more than pay for themselves with periodic part-time jobs or use in small businesses.
We invite you to share your experience in the “comments” block.
Welding wire
Following the widespread demand for semi-welding machines, the industry began to create various types of wires for them. Its correct choice increases the productivity of the welding process and improves the quality of the seam. An important aspect is increasing security. GOST 2246 contains requirements for the composition and quality of wire. Among the large number of types of brands, only a few of them are constantly used. The rest are narrow-profile.
The type, diameter and grade of wire depend on the chemical composition and thickness of the metals being welded. The composition of the wire must correspond to the same characteristics of the material. Therefore, wires are divided into three large types: low-carbon, alloyed and high-alloyed.
The type of brand is indicated on the label. Letters and numbers indicate the composition and percentage of the included elements. Wire, in which the content of harmful substances such as sulfur and phosphorus is reduced, has the letter “A” at the end of the marking. Two letters “AA” indicate highly purified metal.
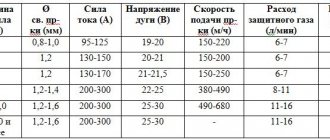
Wire diameters for semi-automatic welding range from 0.3 to 12 mm. The choice of diameter depends on the thickness of the parts. So, for example, if you are welding parts with a thickness of 3-5 mm, then the wire diameter should be no more than 2 mm. The choice of wire is also influenced by the selected amperage. To save money during the welding process, the consumption of filler material is controlled. It is influenced by the composition of the metal being welded, the diameter of the wire, and its quality.
What is MIG/MAG
The wire has such qualities as flexibility and thinness. And its use allows you to reduce the spattering of molten metal, increase the size of the weld pool and the depth of welding. Using semi-automatic wire machines, you can weld different grades of steel, non-ferrous metals, and other materials.
Modern wire welding machines use MIG/MAG technology. What do these English abbreviations mean? MIG is Metal Inert Gas and MAG is Metal Action Gas.
That is, what kind of gas is used in the welding process is of key importance here. If it is inert helium, then the technology should be called MIG, and if welding is carried out with CO2 gas, which is classified as active, then MAG.
The welding process with machines that support MIG/MAG technology is quite simple. Even craftsmen without serious experience in the profession can achieve decent seam quality and a good level of productivity.
With a semi-automatic welding machine it is possible to work spotwise and create continuous seams up to 40 meters long. Anyone today can purchase one of these devices in specialized stores, and it will definitely come in handy in the household.
In the design of a semi-automatic wire welding machine, three main elements can be distinguished: a transformer (or inverter) that generates an electric arc; a conveyor responsible for feeding the wire electrode; and a control unit, whose main task is to synchronize all processes.
Preparation
Before welding with a semi-automatic welding machine, it is necessary to carry out preparatory work. They begin with adjusting the semi-automatic welding machine. To do this, select the correct current value and set it on the device.
Then the wire feed speed and gas flow are adjusted, which is set using a valve on the cylinder reducer. You can evaluate the correctness of the settings on a small piece of metal. With proper adjustment, you should get a tight, even seam.
After this, the optimal gas flow rate is set. If it is insufficient, pores will appear in the weld seam. There is no limit to the upper value, but if it is unreasonably large, the gas will escape into the atmosphere uselessly, which will increase costs. If the seam is of insufficient quality, readjustment should be done.
Then you need to check whether there is a sufficient amount of gas in the cylinder to create working pressure. Working - pressure that allows for reliable protection of the bath in the work area. Then you need to decide on the polarity.
After selecting the polarity, you must connect to the appropriate terminal. Straight polarity will be ensured by connecting the welding cable to the positive terminal. Reverse polarity is used for very precise work.
Refueling and consumption
In order for the welding operation to proceed quickly and without errors, you need to correctly thread the wire into the machine. This is done as follows:
- Usually welders buy one or more wire spools at a time. After unwinding a small piece, straighten the outermost 10 centimeters using wire cutters;
- then you should examine whether there are any traces of corrosion or contamination on the wire surface. If everything is fine, then you need to advance the wire thread a few centimeters into the so-called liner (this is a tube in the area of the device sleeve);
- Now you need to turn on the semi-automatic welding machine and start working, not forgetting to make sure that the bends of the sleeve are not too strong and sharp. Because of this, the wire may well get stuck and break in it.
It is equally important during welding or in advance to find out at least the approximate consumption of welding wire. N
and the consumption rate is influenced by such parameters as the chemical composition of the metal, the thickness of the wire itself, and the technical characteristics of the welding machine.
In many cases, it is believed that the weight of the wire should be equal to 1.5% of the weight of the parts being welded. And the weight of the deposited material is always 6-10% less than the weight of the wire (this 6-10% “eats” the waste).
Open sources also indicate that the consumption of flux-cored wire per second during semi-automatic welding can range from 3 to 25 cm. Obviously, much will depend on the speed of the master welder.
Process technology
The peculiarities of semi-automatic welding are that wire is used instead of electrodes and the process occurs under gas protection. The semi-automatic welding technique involves maintaining a constant temperature. If the heating is insufficient, the edges will not melt normally and will not mix well with the filler material. If the temperature rises too high, the metal will begin to boil and evaporate.
There are two types of semi-automatic welding techniques. The first is that a continuous seam is made from start to finish. The second method uses spot welding. Welding points are placed at regular intervals.
Welding technology has features depending on the thickness of the metal parts, types of joints and their location in space. Thin parts are easier to weld semi-automatically if they are located in a vertical plane. If the thickness of the metal parts does not exceed 4 mm, then you do not need to cut the edges. It is better to weld thick parts in helium or argon. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the burner axis does not deviate from the vertical.
When welding corner and T-joints with a semi-automatic device, the parts should be installed “in a boat”. Thin lap joints are made in one pass using a copper or steel backing. Parts whose thickness exceeds 1.5 mm can be welded in weight, making several passes.
Semi-automatic welding rules:
- Welding should be carried out in such a way that the weld pool is visible to the performer. This is possible when the wire is held straight or at a slight angle.
- The gap between the welded elements with a thickness of 1 cm must be at least 1 mm. Then it is calculated based on the formula - 10% of their thickness. The gap must remain constant throughout the welding process.
- If a backing is used, it is placed from below on the parts to be welded, ensuring density.
- It is necessary to control the current value and arc size. This will reduce the splashing of hot metal.
- A thin wire should be guided along the seam. With a large diameter, it is advisable to perform oscillatory movements, which contribute to heating the edges.
The setting depends on the specific equipment model. Before starting work, you should carefully read the operating instructions.
Welding in general and semi-automatic welding in particular is a complex art that requires patience. You should not immediately strive to set a record. The semi-automatic welding technique for beginners is to practice first on simple parts.
Recommendations in the instructions
Before starting work, it is necessary to reliably ground the welding machine and only then begin setting up.
The semi-automatic welding machine must be connected to a gas cylinder system with protective gas. It is necessary to check the presence of welding wire in the spool, if you need to reload it and stretch it to the torch handle. The gas supply speed is of great importance in the welding process.
Therefore, it also needs to be installed. Gas equipment has gearboxes indicating gas consumption in liters. This is very convenient; you just need to set the required flow rate within 6-16 liters.
The operating instructions for the device provide recommendations on how to properly set up a semi-automatic welding machine, what current to use to weld a specific metal, and at what speed to feed the wire.
The instructions should contain special tables in which everything is described. If you set all the parameters in accordance with them, then everything should work out.
In practice there may be difficulties. The quality of semi-automatic welding is influenced by many parameters. If the supply network does not meet the standards, then the power source will produce voltage and current that is not what is needed, the parameters will be unstable.
The temperature of the medium, the thickness of the metal, its type, the condition of the surfaces being welded, the type of seam, the diameter of the wire, the volume of gas supply and many other factors affect the quality of semi-automatic welding.
Tables of recommended welding conditions are given for certain conditions, which cannot always be achieved. Therefore, when welding semi-automatically, many adjustments are made experimentally.
Of course, the recommended values are initially set, then the welding parameters are fine-tuned.
Advantages
The advantages of semi-automatic welding include:
- ease of use;
- high performance;
- possibility of welding in all spatial positions;
- seam deformations are minimal;
- possibility of welding thin joints;
- slight sensitivity to dirt and rust;
- zinc coatings are not damaged when welding with copper wire;
- obtaining a high quality seam.
The disadvantage is that the gas protection evaporates in a draft. The relative ease of controlling the process makes semi-automatic welding possible for beginners.
Difference from automatic welding
Automatic and semi-automatic welding have much in common and are very different from the manual method. The main difference between automatic welding and semi-automatic welding is that the semi-automatic machine mechanically feeds the wire, which acts as an electrode, to the work site, but then it is moved manually. This allows you to correctly form the seam and monitor its quality.
It is advisable to use automatic welding in mass or large-scale production. On welding forums the question is sometimes asked: how to weld semi-automatically with electrodes. Experienced welders answer that for this they will have to radically redo the machine, but this does not guarantee a high-quality weld.
Possible welding problems
h211,0,0,0,0—>
- The wire is welded to the metal without forming an arc. Cause: Wire feed speed is too high for the set voltage.
- When spatter (small balls of metal) fly out during welding. Brown and green colors on the seam and porosity also appear. Reason: there is no gas or not enough shielding gas is supplied from the torch to the welding zone.
- The seam does not penetrate deep enough. Such a seam will not be strong. You need to add voltage and increase the wire feed speed.
- Burning metal. This happens if the voltage is too high for a given thickness of metal.
- Poor penetration, haphazard seam, jerky welding. It may seem as if there is not enough voltage or wire feed speed. Check the ground clamp and the cleanliness of the metal it is clamped to.
- The burner “spits” and does not produce a continuous seam. This can happen if the torch is too far from the welding site. You need to keep the torch tip about 0.6 - 1.2 cm from the welding area.
- The wire rarely (occasionally) touches the metal, but once contact occurs, the wire melts and the residue remains at the tip of the tip. Cause: Wire feed speed too slow.
[adsp-pro‑4]
p, blockquote25,0,0,0,0—> p, blockquote26,0,0,0,1—>
Print article
h31,0,0,0,0—>after—>
The saturation of home workshops with complex professional-level power tools is impressive. But not all of the equipment's rated capabilities are used. How to set up a semi-automatic welding machine for metal of different sections, change it to aluminum, stainless steel - dry information in the instructions is not enough. Let's turn to the knowledge of production workers.
Education
Training in semi-automatic welding can be completed at special courses. The program includes theoretical and practical classes. You can choose individual training according to a schedule convenient for the student and also learn everything about semi-automatic welding. After graduation, you must pass an exam and prove that all knowledge has been acquired.
A certificate of the established form is issued, which lists the subjects taken, practical classes and indicates that the title “Electric and gas welder” has been awarded. It is possible to obtain an international diploma, which makes it possible to apply the acquired knowledge in other countries.
Training in semi-automatic welding gives an idea of the types of semi-automatic machines, the choice of welding mode and wire diameter, and the technology of the welding process. The lessons learned on the theory of “semi-automatic welding machines” will allow you to understand the designations of the materials used and the markings of the wire. The basics of semi-automatic welding include information about the design of semi-automatic devices, the principle of their operation, ensuring the safety of the welder, carrying out preparatory work, and choosing welding modes.
At the courses you can not only learn everything about semi-automatic welding, but also apply the acquired knowledge in practice. They are conducted under the guidance of a mentor, who will point out errors and explain how to eliminate them. Group classes have the advantage of being able to hear other students' questions and learn the correct answers. During practical classes, you should listen to the analysis of all situations, from which you can learn a lot of useful things.
Semi-automatic welding lessons are taught by professionals with extensive experience. The acquired profession is in demand and highly paid. Those who already have a welding profession, but who want to improve their skills, can also enroll in the courses. Training in a specialized course will help you understand what semi-automatic welding is. The knowledge gained will help you easily read drawings and understand technological materials.
Welding workpieces of considerable thickness
When joining workpieces with a thickness of more than 4 mm, preparation should be taken more carefully. In addition to cleaning the surface from dirt, paint and rust, the edges of the elements along which the welding seam will be carried out should be chamfered. How to properly remove a chamfer, at what angles, is regulated by GOSTs; information is also available on the Internet.
To ensure reliable connection of thick workpieces, it is necessary not only to conduct an arc along the edges being welded, but to make oscillatory movements with the torch. There are many types and methods of these movements, but most often the usual zigzag or reciprocating movements are used. The width of the molten weld metal approaching the surface of the part should be equal to the thickness of the workpiece.
Before starting work, you need to set the gap between the parts to be welded. Without a gap, the metal will not be welded to its full thickness, the seam will remain superficial and the necessary strength will not be provided. To strengthen T-joints made of thick metal, two more are placed on top of the finished seam - along the upper edge of the seam, extending onto the workpiece, and in the same way along the lower edge. This allows you to strengthen the seam, which can be important for parts with a thickness of 8 mm or more.
Despite the mistakes and some subtleties during training, semi-automatic welding is widely used; a video for beginners helps to visually distinguish the features, find out why certain errors appear and how to eliminate them. The importance of clarity is difficult to overestimate at the initial stages of using a welding machine, especially when independently mastering the equipment.