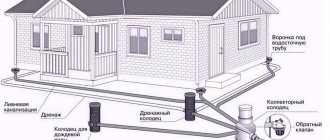
Drainage system around the house
Land owners in spring and autumn, as well as owners of excessively moist soils, face the problem of draining excess water. In this case, it is necessary to equip a drainage system, because excess water causes diseases of garden and vegetable crops, erosion of the foundations of courtyard buildings, and flooding of cellars and basements. Classic drainage systems are pipes lined with crushed stone and wrapped in geotextiles. But this option is characterized by high costs of labor and money. This system has alternative solutions. In some cases, it is possible to create drainage without crushed stone - an economical method of draining water from a land plot.
Video review of the Softrock drainage system. What it is?
Softrock is not just drainage pipes, but systems that are completely ready for installation, allowing you to reduce the volume and complexity of work when installing drainage. What is included in the drainage and distribution system:
✔ flexible perforated pipes surrounded by polystyrene foam filler;
✔woven geotextile mesh in which this filler is wrapped;
✔connecting couplings and clamps, which are purchased additionally, are used for fastening drainage pipes.
Three-meter blocks consist of pipes with different internal diameters. The result is a structure that is 20–50% more efficient than analogs that use ordinary crushed stone.
SoftRock drainage has the following characteristics:
- pipe diameter – 110, 160, 200 mm;
- outer diameter of the pipe (surrounded by filler) – 300 mm;
- hardness class – 4 SN;
- pipe length – 3 m.
The foam tubules are designed in such a way that they improve the flow of fluids in the drainage system. Siltation is excluded due to the use of geotextile mesh.
Advantages
Currently, on the building materials market you can easily select ready-made drainage pipes prepared for direct installation in trenches. They do not need to be wrapped in filter material and covered with loose rocks such as crushed stone and sand. This pipe is a multilayer structure. The body of the workpiece is made of plastic. There are perforations in the walls. The outside of the product is wrapped in foam and protected with geotextile.
The advantages of drainage systems made from drainage pipes include:
- Possibility of installation without the use of equipment;
- reliability of the design and guarantee of drainage efficiency;
- absence of siltation during operation;
- flexibility of pipes, simplifying their installation in non-straight sections;
- system resistance to low temperatures;
- high strength manufacturing material that can withstand heavy mechanical loads.
The fact that after their installation the area remains clean, without traces of sand and rubble, can also motivate the use of drainage pipes. Also, their use of ready-made pipes makes it possible to save on the purchase of bulk materials. In this case, there is no need to waste time on wrapping pipes and their thermal insulation.
What benefits will you get if you buy Softrock rather than a traditional crushed stone system?
Install it yourself - quickly and inexpensively!
Due to the low weight and flexibility of the product, installation is simple, straightforward and can be done by one person. The main thing is to provide a place where the water will drain. It is advisable to lay sand outside the drainage, especially if the soil is clayey. The fact is that such soil is waterproof and needs to be backfilled with sand or black soil, which in turn allows moisture to pass through well.
Increase your drainage efficiency by 40%!
There will be no standing water on your site! Thanks to the geosynthetic filler, it will flow freely into the drainage pipes.
Use drainage with outstanding performance!
The softrock can withstand the weight of 2.5 meters of earth and will not collapse if a car weighing up to 25 tons passes on top. The system lasts up to 100 years, is resistant to cold and freezing, and is perfectly adapted to the climatic conditions of Russia. The closed design is extremely reliable - it resists blockages, siltation and can be reused.
Save on the use of expensive special equipment!
For installation you do not need to use special equipment, because you can do the work yourself. You can transport pipes using a GAZelle, which can accommodate 120–140 linear meters of pipe, or a truck, which can accommodate 1,000 linear meters at once.
Keep your property looking impeccable!
During installation, there will be no dirt, rubble or heavy equipment on the site, which means that the lawn or landscape will not be damaged.
Get the best quality at an affordable price!
The price of pipes with a diameter of 110 mm (they are in greatest demand) and Russian-made filler is from 330 rubles per meter. Make sure that high quality and uninterrupted functionality don't have to be expensive!
Buying Softrock is a much more profitable solution than purchasing conventional pipes. You save on hiring a team of craftsmen, installation and delivery of equipment. In addition, there is no need to buy crushed stone, and its cost can reach 1/3 of the price of the entire system.
Comparison of installation costs for a classic scheme using gravel and sand and the SoftRock drainage system
| Materials | Cost of materials for installation of 1 linear meter with classic drainage | Cost of 1 linear meter of SoftRock |
| Crushed stone | 374 rub. (1 m3 = 1870 rub.) | 450 rub. |
| Sand | 270 rub. (1 m3 = 1350 rub.) | |
| Drain pipe | 80 rub. (1 m = 80 rub.) | |
| Geotectile | 30 rub. (1 m = 30 rub.) | |
| Total: | 754 rub. | 450 rub. |
| Add. expenses (special equipment - installation) | 12,000 rub. | Not required |
| Add. expenses (special equipment - delivery of crushed stone) | from 3500 rub. | Not required |
| Add. expenses (special equipment - sand delivery) | from 3,500 rub. | Not required |
| Taking into account all expenses: | more than 20,000 rub. | 450 rub. linear m. |
Selection of geotextiles
When creating drainage without crushed stone, to increase the efficiency of drainage, it is necessary to use high-quality geotextiles, which will prevent the system from prematurely silting, thus extending its service life. Geotextiles are a polymer filter material that is resistant to chemicals dissolved in water and temperature changes. In addition, it has sufficient elasticity and resilience, allowing the fabric to withstand significant mechanical loads.
The main types of geotextiles include:
- Needle-punched. In this case, the material is stitched with special threads using serrated needles.
- Thermally bonded. During its manufacture, the base of the material is heated, thus fastening the fibers that form it.
Important! Certain types of geotextiles are made from natural materials. This fabric cannot be used in drainage systems. All you need is synthetic fiber material.
The cost of geotextiles depends on its density, strength and filtering ability. For high-quality drainage, material with a density of 100 to 150 g/m2 or 200 to 300 g/m2 is suitable. The optimal filtration coefficient has a fabric with a density of 100 g/m2. It can handle a load of up to 140 m3 of water per day. When choosing geotextiles, you need to pay attention to its strength. For drainage, choose a material with a tensile strength of up to 250 kg.
Types and features of filler
Filler "Russia"
Styrofoam:
- Cheap. Save about 40%!
- Short-lived. Polystyrene foam is a porous material; moisture is retained in the pores, which freezes at sub-zero temperatures, which leads to the destruction of the filler.
Filler "Import"
Special polystyrene:
- Reliable. Service life up to 100 years!
- It is successfully used in Canada - in climatic conditions similar to Russian ones.
How to make drainage in an area without pipes
Ditch preparation
Before making drainage without the use of pipes, it is necessary to draw up a geodetic plan of the site with marked areas of high ground and low ground. These sections will determine the direction of the trench lines, since drainage without pipes should begin at the highest point of the relief and end at the lowest. The drainage system layout should consist of: a central conductor with a depth of at least 50 cm, drainage drains at a distance of 7-10 meters from each other, as well as a water storage tank if it is not discharged by the system outside the site.
A trench is dug at an angle that coincides with the direction of the drainage. The bottom of the recess should be made semicircular, like a gutter.
The ditches are cleared of debris and dirt, after which the bottom is lined with tecton. Geotextiles are laid on top inside the ditch so that the bottom and side walls are completely covered with a margin of at least 20-30 cm. After this, crushed stone is poured and covered with geotextile fabric with an overlap of at least 30 cm. Sand is poured on top of the crushed stone and thoroughly compacted. You can lay turf on a sandy surface or use a geogrid or geogrid if the trench site is located in an area with a high load on the soil.
Soil drainage without the use of waterproofing materials is done in a similar way, but has fewer advantages. Soft drainage with the laying of geotextiles and tecton not only removes water from the site, but also filters it, allowing it to be used in the future as process water or for watering plantings.
SoftRock demonstrates excellent functionality in many areas
✔ For the foundation The task of the drainage and distribution system is to prevent water from entering the base of the object. Drainage is installed at a distance of 0.45 m from the ground surface, along the outer wall of the foundation. In this case, the water is “intercepted” and discharged into the sewer, which is located below and equipped with an internal pipe.
✔ For basements Drainage is carried out to a discharge point or well, after which the moisture is removed by a pump. As a rule, such systems are installed in trenches whose width is about 30 cm.
✔ As a septic tank As one of the elements of a septic tank, Softrock is a set of pipelines with drain holes, which is laid at a depth of no more than 2 m.
✔ For roof drains Melt water is drained away from the foundation or retaining walls of the building. There are two options for removing moisture - underground and surface.
You can learn more about prices and delivery conditions from the managers if you call us at one of the phone numbers listed at the top of each page of the site or in the Contacts section.
- Related products
- Additional products
Types of drainage systems
The drainage system is designed to drain water from a plot of land with a house and outbuildings. Excess moisture rapidly destroys the foundations of buildings, causes various diseases in cultivated plants, and floods basements and cellars. In addition to eliminating these problems, a properly created drainage system prevents the establishment and spread of mosquitoes and midges, and tree roots do not rot.
Drainage around the house consists of the following elements:
- water collectors (equipped ditches);
- wells (water intakes).
In any case, the work of digging trenches cannot be avoided. If you plan to drain only rainfall, then a ditch depth of 0.5–0.6 m is sufficient. When it is still necessary to keep the level of melt and groundwater under control, then you need to go deeper by about 1.5 m. This depth is also necessary if you have a garden with fruit trees on the site.
In order for the created system to function for a long time, they make a slope on the sides of the trenches and strengthen their bottom.
Water drainage from a site can be done in several ways. They differ in the level of monetary and labor costs. There are 2 main types of drainage systems:
- closed;
- open.
Open type system for draining excess water
The latter type is used to remove water formed after heavy rains or spring melting of snow. The usual open drainage device is a trench dug throughout the entire area with an average depth of 0.7 m and a width of 0.5 m, the side walls of which have a slope. Quite often, trays made of plastic or concrete are placed in ditches, which are covered with a grating (mesh) on top. The bottom of the excavations is covered with a 10 cm layer of sand, which is compacted firmly.
A closed type of drainage is used to drain soil water. In this case, ditches are dug with a side slope, with a depth below the freezing mark of the soil in the region. Pipes are laid at their bottom to drain water into the water intake, around which crushed stone, gravel, broken brick or stone are poured. This budget method is ineffective because the backfill quickly silts up.
An alternative and effective drainage option is to create a drainage system with crushed stone without pipes, or without such backfill at all.
Installation examples: Retaining walls
Retaining walls serve to hold soil masses. Hydrostatic pressure from groundwater can destroy even a low retaining wall, so drainage is critical to the longevity of the wall. Additionally, groundwater seepage through brick or wood retaining walls can cause unsightly staining and discoloration. Just like foundation drainage applications, rubble-free drainage systems trap and drain groundwater from the back of a retaining wall, relieving hydrostatic pressure and preventing seepage.
Laying
Depending on the design of the retaining wall and groundwater conditions, drainage pipes without crushed stone can be placed either at the base or stacked on top of each other at the back of the wall.
Product
The choice of the diameter of the drainage pipe without crushed stone for most retaining walls should correspond to the diameter of the pipe and the location of the drainage material, according to the technical documentation.
Installation instructions
Below is a typical process for installing retaining wall drainage, which may vary depending on site conditions.
Attention: It is not recommended to replace brick with drainage systems without crushed stone when the brick is used to support a wall, such as when backfilling a floor, anchoring a wall, or consisting of reinforced soil. It is not recommended to use drainage pipes without crushed stone in retaining walls whose visible front part exceeds 1.5 meters without preliminary technical calculations. The design engineer can use drainage pipes without crushed stone in such walls after making the necessary calculations, taking into account the lightweight structure of our products.
Installation examples: Site drainage
Site drainage/garden drainage is designed to prevent excessive soil moisture in garden beds and flower beds, which can harm garden plants.
Location
In the case of garden beds, drainage pipes without crushed stone can be laid along the perimeter of the flowerbed, touching other elements of the garden decor (lawn or path), or in a non-standard way for the purpose of draining identified problem areas (for example, due to the location of plants in the flowerbed). In the case of stone partitions or tree plantings, drainage pipes without crushed stone are in most cases installed along the inner edge of the flower bed at least 45 cm below the planning level, and up to 60 cm below the planting level of trees and other surface garden plants with a deep root system. The pipes can extend beyond the flowerbed if necessary. Drainage pipes without crushed stone should discharge moisture into a drainage hole or other discharge area through the flowerbed wall. In tree beds located in areas of poor drainage, drainage pipes without crushed stone should be used to create a circular bend at least 2 times wider than their root ball. Trenches should be dug to a depth of 45 to 60 cm for flower beds and below the depth of the root ball for tree plantings. The pipes must carry water from the planting area to the discharge point below.
Product
Drainage systems without crushed stone with a diameter of 25 cm with a built-in pipe with a diameter of 11 cm (DT-110) can be used in larger planting areas, as well as in areas that receive additional drainage from other sources.
Installation instructions
Below is a standard process for installing garden drains, which may vary depending on site conditions.
beds
Follow the basic drainage ditch installation instructions on page 7 to install gravel-free drainage in beds.
Flowerbeds
- 1. Connect a drainage pipe without crushed stone to the flowerbed drainage hole or other extension through the wall of the flowerbed. Lay pipes without crushed stone along the inner perimeter of the flower bed, the walls of the flower bed at least 18 cm below the ground level for most flower beds, deeper for trees and other plants with deep root systems. Additional pipes can be connected in larger flower beds.
- 2. Place suitable soil on top of the pipes and plant plants and turf as desired. Sand backfill is not required, as the garden soil mixture acts as a good drying agent while maintaining the required level of soil moisture.