Their owners have to deal with the problem of flooding on personal plots and dachas often or with a certain frequency. This depends on the abundance of precipitation, the amount of melt water, especially if the soil does not have sufficient carrying capacity. And this can cause many negative consequences:
- flooding of houses and buildings;
- destruction of their foundation;
- swamping of the area.
Excess moisture can also cause rotting of plant roots in any soil.
Laying depth of drainage pipes
The minimum level of drains is calculated taking into account their resistance to physical and temperature loads.
When laying the drainage ditch as deep as possible, high-strength pipes are used.
In unstable soils, pipes are laid on a specially laid base.
The deeper the drains and wells are laid, the more effort and money required for installation. Drainage systems come in two types:
- Superficial, with a channel depth of 0.3-0.4 meters.
- Deep, sewer trenches are dug up to 3 meters.
To determine at what depth to bury drainage, you need to know the structure of the soil. It all depends on its density.
It is necessary to take into account the amount of soil freezing in your region so that the pipes are laid at a level exceeding its value.
When installing a drainage system near a building, drains are laid below its base. The optimal depth of the drainage ditch is 1.1-1.3 meters. In the garden plot, the pipes are lowered no more than 150 centimeters. Ditches are dug at a distance of 5-10 meters from each other.
Experts advise digging trenches deeper than the calculated value, a couple of tens of centimeters, so that there is room for laying a “cushion” at the bottom of the canal. We should not forget about the slope in the direction of the collector.
Linear drainage
As for linear drainage, depending on the location it differs into wall and remote from the structure. This drainage is covered with lattice overlays and collects that part of the precipitation that does not fall into the point storm inlets. Linear drainage is used in the following cases: 1. Prevention of washout of the top fertile soil layer, which is important for areas with landscape differences. If the horizon tilt exceeds 3 degrees, then this outcome is most likely. 2. If the landscape on the site is fairly flat, but the site itself is located in a lowland, then during precipitation, streams of water flowing from the heights also threaten the fertile layer, as well as plants and houses. 3. Draining of sidewalks and paths - the pedestrian area is located on a slight elevation, while moisture flows down a small slope into the drainage channels. 4. Road drainage - is an ordinary ditch along the road surface.
Site analysis
A method for diagnosing soil moisture absorption. Dig a small hole, up to half a meter deep, and fill it with water. If all the moisture goes into the ground within a day, then natural drainage will be quite enough. If the water remains at the same level or decreases slightly, additional drainage is required.
Before starting work on installing a drainage system, you should draw a plan for the drainage system and calculate its slope. This can be done using a map, using the altitude points marked on it. If there is none, watch the rainwater: where it flows, that’s where the drainage system should be directed.
With a flat surface of the site, the depth of laying the drainage of the site should be gradually increased towards the final section of the drainage. If the building is located on a hill, then ditches of equal depth are dug towards the natural slope.
The depth of drainage structures is set in accordance with the intended tasks. Namely:
- To drain rainwater from the site, shallow grooves of 10-15 cm are suitable.
- To dehydrate the soil surface to improve the growth of flowers and shrubs, you need to choose a backfill or closed type method, in which the drainage depth is provided from 40 to 60 cm.
- If we are talking about the well-being of fruit trees growing in an excessively wet area, then it is necessary to arrange the drainage in such a way that it removes excess water from the roots of the plants. For small trees, the drainage depth is up to 1.2 meters.
- Only a closed drainage system can protect the foundation and the building itself from the negative effects of moisture. In this case, the depth directly correlates with the thickness of the foundation: the minimum occurrence of the drainage pipe is half a meter from its base.
Drains need to be laid along the entire perimeter of the territory. The drainage depth on the site is calculated based on the level of soil freezing in winter and the depth of the building foundation. The data is presented in the tables below.
Forms of underground system design
Underground drainage can have different designs:
- 1.Ring structure. The drains form a ring around the building. This design is used to reduce the height of groundwater so that it does not flood the basements of buildings. Perforated pipes are laid below the soil freezing layer and the depth of the foundation, the distance from the walls of the building is five to eight meters. Ring underground communication is suitable in areas with sandy soil, in areas with a slope, if groundwater flows above the base of the foundation.
2. Wall structure. If the groundwater is located half a meter from the base or closer, the site has predominantly clay soil, there is a high probability of flooding with high water. The drainage system pipes are buried under the foundation around the building at a two-degree slope. Collectors collect water that drains itself; sometimes they use a pump to collect water. The collected water can be irrigated, or it can be further drained into the sewer.- 3.Plast structure. Installation of a drainage system is considered one of the most difficult. The system drains soils from water flowing between layers of water-resistant rocks and promotes groundwater backup when other drainage methods fail to cope with their task. A pond is created under the base of the foundation, filled with drainage materials such as gravel, crushed stone or stone. The artificial reservoir goes no less than thirty centimeters deep.
Parts of underground drainage structures must be combined and can be combined well with each other.
What is the depth for different types of drainage
The drainage system, laid below the soil freezing level, will ensure the removal of melt and groundwater throughout the year. In this case, the correct slope of the system in the direction of drainage (per linear meter) must be observed:
- for clay soil – 2 cm;
- for sandy soil – 3 cm.
Deep drainage protects the foundation of the house. Usually two methods of underground drainage are used:
- Ring system. A flexible pipe is laid in a ring shape along the perimeter of the building. The depth of the drainage pipe is 500 mm below the base of the foundation. There are no corners in this design and no drainage wells are required. Ring drainage is considered low-cost. However, it is ineffective and is suitable for buildings without basements built on clay soil.
- Wall drainage . Maximum removes excess moisture from the base of the foundation, keeps the basement dry for a long time. Requires significant financial costs due to more complex installation and the need to install drainage wells.
Drainage wells protect pipes from blockages, facilitate system maintenance, and perform collector functions. The depth of drainage should be measured starting from 30 cm from the base of the foundation.
When carrying out work on arranging a drainage trench, they are guided by SNiP regulations. The rules prohibit the drainage of storm water to areas inhabited by animals, rivers, and swampy lowlands.
At turns and every 20 meters of the drainage route, wells are installed for its maintenance. The depth of the drainage well is the same as the depth of the drainage ditch. The bottom of the well should be 10-15 centimeters below the perforated pipe.
In addition to the shallowly buried surface and deep wall drainage methods, a banal storm drain from the roof is used, which is drained into the ground.
How to drain a summer cottage without drainage
The reasons for water stagnation in a site are not necessarily related to high groundwater levels.
For example, during heavy spring rains, when the ground is still frozen, water will stagnate at the surface.
There are ways to reduce soil moisture without installing a drainage system, here are some of them:
- Adding sand to the soil. For clay or peat, at least 30 kg per 1 m3. This will improve the soil's hydropermeability, which also increases productivity.
- Open, shallow trenches to quickly drain floodwater into a drainage ditch.
- Replacing the fertile layer with a special composition tailored to your conditions.
- Planting trees, usually around the perimeter of the site. Some tree species develop well in moist soils and, thanks to their powerful root system, dry out the area. Such properties are possessed, for example, by willow or birch.
We calculate by freezing depth
To determine the correct drainage depth in an area, you need to subtract the diameter of the pipe from the freezing depth of the soil in a particular area:
- 300 mm – the pipe size does not exceed half a meter;
- 500 mm – drains with a diameter of more than 50 centimeters.
The result will show the minimum depth of the drainage ditch. For example, let’s make calculations in the city of Irkutsk, for a clayey area:
| Freezing level | Pipe diameter | Subtract from freezing level | Ditch depth |
| 1.8 meters | 200 mm. | 300 mm. | 1.5 meters |
Consequently, in Irkutsk, the minimum depth of the drainage system is 1.6 meters.
You can find out the level of freezing for your region from the Internet or in directories from design companies.
The central zone of the Russian Federation freezes to 1.5 meters. This is an average, which drops to 1 meter 15 centimeters in areas of heavy snowfall.
The main climatic indicator influencing the depth of freezing is temperature: the higher it is, the lower the level of soil freezing. When installing drainage, you also need to take into account the composition of the soil. For example:
| City | Soil composition | Soil composition |
| Irkutsk | Clay, loam | 180 centimeters |
| – | Sandy loam, sand | 219 centimeters |
| – | gravelly sand | 234 centimeters |
| – | Coarse soil | 266 centimeters |
| Slyudyanka | Clay, loam | 184 centimeters |
| – | Sandy loam, sand | 224 centimeters |
| – | gravelly sand | 240 centimeters |
| – | Coarse soil | 272 centimeters |
based on tabular data from reference manual 131.13330.2018
When installing a drainage system in conditions of excess moisture in the soil, it is necessary to lay pipes deeper than the freezing level of the soil.
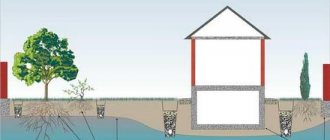
Drainage systems
An example of a drainage system design for a summer cottage.
Surface drainage is the least labor-intensive and uncomplicated system. Its task is to remove water that falls in precipitation and formed when snow melts.
Surface drainage is necessarily organized around buildings, and is divided into 2 types:
- Point - consists of separate water receivers (points) and a system of shallowly buried water pipes;
- Linear - a system of drainage trays.
Both point and linear drainage are usually protected by debris gratings. To effectively drain water, drainage trays and tubes must be sloped (1-2 cm per 1 m).
Deep drainage is needed to drain the soil and lower the groundwater level.
Drainage is collected either from perforated pipes or in the form of crushed stone channels. If the slope is maintained, water is discharged through drains outside the site.
To lower the groundwater level throughout the entire area, drainage is laid at a level of 0.8-1.5 m. But near the house, the drainage depth should be 50 cm below the plane of the foundation support.
The distance between drains is recommended 9-11 m (for loam - 7-9 m, for clay - 4-5.5 m). More details in the table:
| Depth of drains, m | Sandy soil | Loamy soil | Clay soil |
| 0,45 | 4,5-5,5 | 4-5 | 2-3 |
| 0,6 | 6,5-7,5 | 6,5-7,5 | 3-4 |
| 0,9 | 9-11 | 7-9 | 4-5,5 |
| 1,2 | 12-15 | 10-12 | 4,5-7 |
| 1,5 | 15,5-18 | 12-15 | 6,5-9 |
| 1,8 | 18-22 | 15-18 | 7-11 |
The drainage is laid starting from the highest point of the site, and from the lowest point it is discharged outside. It is important to maintain a slope for water pipes: 1-2 cm per 1 m (for sandy soils - 3 cm per 1 m).
The slope may be greater, but not less. A larger slope improves drainage.
We calculate based on the thickness of the foundation
In this case, a simple arithmetic operation will also help. Add another half meter to the depth of the foundation of the house. This is enough to prevent the foundation from being washed away. For example:
| Foundation depth | Add | Ditch depth |
| 1 meter | 0.5 meters | 1.5 meters |
The calculation will help create a drainage system at the correct depth. Remove moisture in advance and prevent dampness in the basements and erosion of the foundation of the building.
It is important to consider the season of construction work. In spring, groundwater comes as close as possible to the surface of the earth, and in summer it moves deeper. Their lowest level is observed in winter.
When calculating the depth of drains on a site, you can pay attention to the average thickness of the snow cover in a particular area. Snow is a good natural insulator.
Professionals advise combining both methods of calculating the laying depth of a drainage system in order to select the optimal parameters - those that are larger, with a margin.
A correctly calculated drainage system scheme will ensure its uninterrupted operation and will allow for a more efficient use of forces and resources.
Point drainage
Point drainage involves the use of: ⊗ storm funnels; ⊗ storm water inlets; ⊗ ladders; ⊗ door grilles. Such structures are installed in door pits and other areas where water collection is required - this can be either draining a roof storm drain or a watering tap. Through a point water collector, water enters underground pipes, and then into the storm sewer collector.
Drainage of water from the roof
The roof drain material is varied: steel, copper, polymer-coated steel, aluminum, etc. Plastic is especially popular. It is economical, resistant to damage, is a sound-insulating material, airtight, and light in weight and installation.
To properly design a roof drain you will need:
- Metal bracket;
- Hairpin with a special nut;
- Adjustable mount;
- Gutter bracket;
- Tip;
- Connecting coupling;
- Knee;
- Funnel plug;
- Gutter plug;
- Corner element;
- Funnel;
- Gutter connector;
- Gutter;
- Drain pipe.
The quantity and type of each element depends on the perimeter of the roof and the amount of pumped liquid, because too powerful a drainage system is irrational from the point of view of financial costs, and a weak one will not cope with the task. It is necessary to find the best option. The figure shows the required dimensions typical for central Russia.
On a note! To reduce the cost of purchasing consumables, you can make gutters yourself. You can make concrete elements at home using special pouring molds.
Filtration and storage wells
In the absence of the possibility of discharging water into natural reservoirs: ditches, rivers, ponds, there is nothing left but to equip a well. There are two options: a well with a drainage bottom and a storage tank.
Drainage of a summer cottage
Option 1. With drainage wells
The essence of constructing a drainage well is that the water entering it is filtered and seeps into deeper soil layers. There may be several of them in a pipe drainage system. They are located at the beginning of the line, in places of turns, intersections, changes in slope or pipe diameter.
Circular drainage on the site with drainage into drainage wells
Homemade pipe well
Factory-made well
The well can be built from factory-made concrete rings with perforations, purchase a ready-made plastic product, or cut a piece of large-diameter pipe, make holes in its walls and install it in a cylindrical hole 1.8-2 m deep on a prepared crushed stone base.
Prices for popular models of drainage wells
Drainage well
Option 2. With storage
The water that is collected from the site can be used in some way on the farm: for washing cars, breeding fish or crayfish, watering greenhouse crops. In any case, if groundwater on a site already reaches a high level, it is irrational to add surface runoff to it.
- Water can be discharged into a street storm drain, a ditch, or simply into a forest or river. For this purpose, not a drainage well, but a storage well is introduced into the system. The difference between them is that the first has permeable walls and bottom, while the second must be airtight.
- A pump with a float sensor is installed in it. As soon as the container is filled above a predetermined level, it begins to work, discharging excess water into a drainage channel or a drainage well located further from the site. The rest is always in stock, and if necessary, you can use the accumulated water.
Storm water tank with submerged pump
- It can be very helpful if you need to extinguish a fire. Or when you start some kind of construction in the yard that will require water - for example, to moisten a compacted sand cushion.
- During the summer drought, the water supply, for which you don’t have to pay a penny, will also be useful for watering beds that suffer from excess moisture in other seasons. After all, at dachas there is often no water except what its inhabitants bring for themselves to drink.
Electric submersible pumps
Stages of drainage
1
. It is necessary to dig a trench around the perimeter of the building. The shape of the trench should be inclined, and its lower part should be half a meter deeper than the lowest point of the foundation. Effective drainage is only possible with a slope of at least 2 cm per 1 linear meter. In the pit at the corners of the building, it is necessary to additionally select soil - 400-500 mm, this is necessary for trouble-free placement of the sludge collection part of the drainage well. In most cases, the vertical walls of the trench are made at an angle of 45-60°, this way you can ensure the safety of the work and prevent sudden collapse of the soil. In cramped conditions, it is possible to strengthen slopes using sheets of plywood or boards knocked together from boards.
2
. After cleaning the foundation from soil residues, it is necessary to treat the concrete with a bitumen-kerosene primer, after which a layer of waterproofing rubber-bitumen mastic is applied. It is a soft resin; before the mastic hardens, it is necessary to press a reinforced mesh with a cell width of 2x2 mm into it - this is exactly what is used for plastering work. Next, you need to take a break and wait for the concrete to dry, and then repeat the layer of sealant.
3
. We lay a layer of geotextile and a layer of gravel at the bottom of the ditch, level the slope - before laying out the drainage pipes, we form semicircular grooves in the gravel layer. The geofabric must completely separate the crushed stone from the sand and clay; very often it is not possible to purchase a fabric of the required width; in these cases, the geofabric is laid with an overlap of 15-20 cm, the edges can be fixed with a stapler or pieces of double-sided tape. Geotextiles are not laid along the foundation wall, but in some cases, when it is necessary to ensure maximum protection of the waterproofing layer, a special polymer membrane is installed that separates the crushed stone layer from the bitumen. The membrane, as such, does not provide absolutely any waterproofing; its main purpose is to protect the foundation from the point pressure of crushed stone, and to drain groundwater down to the drainage pipe - which in turn will drain the water from the building. The upper part of the polymer membrane is brought out under the blind area of the building and is protected by a special plastic or metal profile.
4
. We lay out drains, which can be bought with ready-made perforated holes. Alternatively, you can purchase regular PVC sewer pipes and punch the holes yourself. In this case, the hole size should be smaller than the average grain of gravel on the bed. But before you engage in such amateur activities, evaluate the labor costs and the final effect of the work performed; in most cases, it is easier and more reliable to opt for a specialized pipe from reliable manufacturers. How not to make a mistake when choosing when the market offers flexible pipes with the ability to install at incredible depths, and drainage systems without crushed stone, flat pipes, and sometimes just “stockings” filled with foam plastic, which, according to manufacturers, should replace both crushed stone and pipe. Basic advice: for foundation drainage, only rigid double-wall pipelines, supplied in lengths, with a stiffness class of SN4 and SN8 are suitable. For lawns and lawns, with a drainage ditch depth of up to 1-1.2 m, a flexible pipe supplied in coils is ideal. It is advisable to use pipes with running outer diameters: 110 and 160 mm. This way, there will be no problems with purchasing expensive tees and turns of non-standard diameters.
5
. We connect the drains into a single system using crosses and tees - the system should go to the collector located at the lowest point of the drainage system. The slope is controlled using a level; you can also pull a cord along the highway.
6
. If the drainage system has turns, then each of them must be provided with an inspection well. It is a piece of pipe, the upper part of which we cover with a lid. Such elements allow the owner to control the operation of the drainage system and rid it of blockages. Before buying a well, you need to think about how the blind area will be designed, and what appearance of the drainage hatch is best for you. Currently, there are hatches made of plastic, cast iron (round and square) and special products for planting lawns in them - hidden hatches.
7
. We fill the drains with crushed stone and cover them with geotextile. In drainage work, only granite crushed stone and pebbles are used, since these materials do not cake and their throughput does not change over time.
8
. If a storm sewer is laid on top of the drainage system, then its pipes are laid out on top of a layer of crushed stone. This solution will significantly improve the operation of the drainage system, reduce the cost of construction and installation work, and most importantly, will lead to the discharge of water from the roof to a complete and competent solution.
9
. Pour a layer of river sand on top of the crushed stone layer to a height of 15 cm, then cover the drainage system with soil - it is better to pour it with a mound, which will allow you to get a flat surface after all the layers have settled. All bulk materials must be separated from each other by geotextile fabric; when installing the blind area, it is advisable to lay a layer of plastic film in order to protect sand and crushed stone from cement particles.
Tools and materials
Before starting installation work, make sure that you have all the necessary construction tools and materials:
- Wheelbarrow.
- Shovel.
- Level.
- Hacksaw for metal.
- Tamping.
- Drainage pipes and all components, fittings, couplings, etc.
- Rotating plastic wells designed for drainage.
- Gravel or crushed stone.
- Geotextiles.
Special mention should be made about drainage pipes. They have two types: perforated and corrugated plastic. To prevent clogging, it is recommended to use geotextiles. It will act as a kind of filter. Its use is especially effective if the predominant soil is clay. Geotextiles will protect the system from silting. The filler of this material is rye straw and peat. Thanks to this, geotextiles are environmentally friendly and harmless to the environment. Filtration using this method will increase the productivity of the drainage system. But despite this, after some time, it will need washing.