- Geotextiles for drainage: types and features of the material
- What types of geotextiles are there?
- Geotextiles for drainage (geofabric): technical characteristics and scope of application
- How to choose the density of geotextiles for drainage
- What geotextile to use for drainage
- Drainage geofabric for arranging the foundation of a house
- Drainage system for garden plot
- Dornit: non-woven geotextile for wide applications
- Prices for woven geotextiles per m²
- Geofabric laying technology for drainage
- Laying geotextiles in drainage tanks
- Which side to lay geotextiles
- Video: what density to choose geofabric for drainage
Geotextiles for drainage: types and features of the material
Geofabric has long ceased to be something unusual. Now it is widely used both in construction and in the arrangement of various systems, including sewerage. Let's consider the main types and characteristics of this material, how to choose and use geofabric for drainage . What you should pay attention to before buying geotextiles for drainage , and what does not play a significant role.
Geotextiles are one of the most suitable materials for constructing various drainage systems.
What types of geotextiles are there?
Geotextiles come in different types and, depending on the operating requirements, are used in different conditions.
Therefore, the main criterion for classifying a geotextile is the material of its manufacture:
- polypropylene or polyester make it possible to produce geotextiles of the highest quality;
- from monofilament and staple raw materials, a product is obtained that has sufficient strength and quality suitable for use in most construction works;
The most popular are Dornit geotextiles and TechnoNIKOL non-woven geotextiles.
- geotextiles made by thermal bonding cannot boast of particular strength, since it is the thinnest of all the proposed options. However, it is he who has one of the best indicators when it comes to water resistance;
- the use of mixed yarns for the manufacture of geotextiles is not recommended, although such options are also commercially available. The thing is that cotton or wool threads that are included in the composition are very easy to rot. And this is a completely undesirable process when it comes to construction or arrangement of drainage.
Before choosing and buying geotextiles, you need to decide where and in what work it will be used. Depending on this, the type of material from which it is made is selected. You can figure out which geotextile is best for drainage by reading its main technical characteristics.
Geotextile Dornit for drainage.
Quality and properties of geotextiles
The best drainage geotextile is completely synthetic. Some types of geotextiles use natural fibers (textile production waste), but such material is of relatively low quality and is rarely used and not everywhere.
- Chemical resistance. Despite constant exposure to a humid environment, mold does not form on geotextiles. The processes of decay also do not affect it.
- The material is inedible for any insects and rodents.
- Highly environmentally friendly.
- Operating temperature – from -60 to +110 degrees Celsius.
- High coefficient of elasticity.
- Significant tensile strength.
Synthetic geotextiles are made from polyester or polypropylene monofilaments. The material can be needle-punched or thermally bonded.
- In the first case, the main layer of fibers is stitched with threads using serrated needles. In this way, very high quality fabric is obtained.
- In the second case, a solid fabric is created by significantly heating the warp fibers. The material made in this way is very durable and almost impermeable to liquid.
Geotextiles for drainage (geofabric): technical characteristics and scope of application
Geotextile for drainage or other systems is a material that has high performance:
- rigidity;
- elasticity;
- porosity.
It is these qualities that make it possible to use it for strengthening the soil, dividing the territory, filtering wastewater, protecting the slopes of the site, arranging drainage, etc.
Geofabric has gained particular popularity in Europe, where the construction of highways is indispensable without its use. The synthetic origin of the material allows it to retain its characteristics for a long time, and its high strength allows it to withstand severe loads. Some manufacturers produce geotextiles with a tensile density of up to 250 kg.
A characteristic feature of geotextiles is rigidity, elasticity and porosity.
When it comes to private or industrial construction, geofabric also has its place here. It is widely used for the arrangement of urban sewer systems, in the construction of houses, railways, highways, in gardening and for drainage. What density of geotextiles is required for use in a particular area? For example, for the construction of drainage systems, geofabric with a density of 200 g/m³ and higher is used, for landscaping work about 100 g/m³ is enough, and in the construction of runways for aircraft – 800 g/m³.
The principle of operation of this material is very simple: it is a layer that is used to separate two other layers from each other, while providing additional density. For example, it helps to significantly reduce the risk of sinkholes on the road, and also prevents erosion of the area by groundwater.
Advantages of geotextiles
The wide popularity of geosynthetics in the construction industry is associated with its superiority over classical fabric.
Benefit When creating drainage systems, the consumption of geotextiles is insignificant, so the cost of purchasing it is minimal. In addition, in combination with the canvas, less bulk material is required. As a result, the cost of the drainage system is reduced several times.
Environmental friendliness Products based on polymer threads do not contain volatile, toxic compounds. They do not pollute the environment during production and installation.
Service life (up to 30 years) Polymer fabrics do not decompose in acidic and alkaline environments. They do not rot under the influence of water and microorganisms. Their technical properties do not change at sub-zero temperatures, under the influence of chemically active substances. Cloths become unusable only due to clogging of micropores, but this is a slow process. High-quality geotextiles serve regularly for 2-3 decades.
Layout of drainage system elements with geotextiles
High strength Synthetic material stretches 45% without tearing. Due to its strong and elastic structure, the canvas reliably reinforces the soil.
Versatility Geotextiles are used in a wide variety of construction areas. It is part of drainage structures, highways, underground structures, and asphalt areas.
Temperature resistance The material can withstand sudden temperature changes. It retains elasticity and strength at -60 degrees. Does not melt and does not lose properties when heated to +100 degrees.
Ease of installation When installing the canvas, professional equipment is not required. The rolls are unrolled and cut with scissors right on the construction site.
If a geosynthetic material contains cotton and wool threads, it will deteriorate faster. In an aggressive soil environment, it decomposes into its constituent components and rots. Products made from polypropylene monofilament are more reliable. In the store they stand out from their analogues with their white color.
How to choose the density of geotextiles for drainage
In drainage systems, geofabric plays a very important role - it prevents subsidence of the soil layer in the drainage system, and also prevents the process of diffusion of crushed stone into the water. Geotextiles act as a filter that protects the drainage pipe and materials from flooding.
Drainage installation on the site.
When thinking about which geotextile to choose for drainage, it is best to give preference to material made from monofilament. It is easy to identify such a material among others - its snow-white color gives it away. It is better if the fabric is made by thermal bonding.
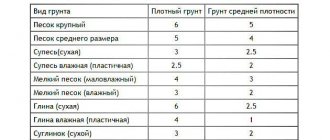
If crushed stone is used as drainage, small stones can pierce the material, causing damage to it. This is worth paying attention to when choosing a geofabric of the required density. The indicator for creating a drainage core will be at least 200 g/m³.
If you plan to wrap the drainage system, then geotextiles with minimal density and thickness are suitable for this. At the same time, its water-repellent and other technical characteristics must be at the highest level.
Laying geotextiles and preparing for installation of a drainage system.
Geotextiles: what is it and how is it used, how to choose for drainage, installation in photos
To answer this question, you need to understand the main types of material. This non-woven fabric is classified according to the following characteristics:
Basic properties and selection rules
How to choose geotextiles for drainage and which one is best to use to ensure that the system operates with maximum reliability? Here you need to take into account all the physical characteristics of the material, which will vary depending on the specific type of canvas. Among the main ones it is worth highlighting:
Once the answer to the question of how geotextiles are used and what they are is received, all that remains is to decide which fabric should be chosen for the drainage system.
Laying drainage pipes using geotextiles
Experts recommend material with the following characteristics:
Geotextile laying technology
Before laying geotextiles, it is necessary to clarify the basic technological requirements for installation. In particular, it is believed that geotextiles are too susceptible to sunlight, so they are not taken out of the packaging in advance, but before actual installation. It is also recommended to cover the material with soil as quickly as possible, without leaving it in direct sunlight. Proper preparation of the trenches is also important - each of them must have smooth slopes and no construction debris inside, because it can damage the coating.
The technology for laying geotextiles here involves the following steps:
The photo shows the laying of geotextiles - step by step technology
All work on laying drainage pipes using geotextiles is carried out at the highest possible speed. Thanks to the creation of such an effective system, it is possible to avoid silting of pipelines when discharging filtered liquid.
Manufacturers and cost of geotextiles
Now, knowing the answer to the question of what geotextile is and how it is installed, we will tell you how to choose geotextile for drainage and which one is better to use. To determine the economic feasibility of using geotextiles, you need to select the right material based on the cost factor. The price per square meter of geotextile will vary between 0.3-1 dollar and will depend on the brand, type of material and its performance characteristics.
Among the popular manufacturers are the Russian companies Dornit, Avantex, Geotex, Geopol, GronT, Montem, Nomotex. Foreign manufacturers are also widely represented on the market - the American company Typar, the Czech NETEX A, the English Terram, the Austrian Polifelt.
In general, the price of geotextiles suitable for use in drainage installations is low. You should not focus only on cost or country of origin. The advantages of geotextiles suitable for the installation of high-quality drainage systems are assessed comprehensively - density and strength, manufacturing method and type of raw materials are taken into account. The selected material must comply with the existing operating conditions and the functional purpose of the system, and the fame and popularity of the brand in this case fades into the background. Moreover, many domestic companies have successfully mastered the technology of low-cost production of high-quality geotextiles.
Review of Geotextiles: what is it and how is it used, how to choose for drainage, installation.
Geotextile is a waterproof fabric characterized by high strength. Numerous 100% polypropylene fibers are used as the base.
The use of geotextiles has found distribution in various fields of construction. This became possible due to the high performance properties of the material. Geotextiles are resistant to mold and fungi, they do not rot and are not damaged by rodents. The material does not lose its qualities when the temperature changes from -60 to +100 degrees. Geotextiles are characterized by high strength, resistance to chemicals and ultraviolet rays.
What geotextile to use for drainage
There is a huge selection of geotextile materials on the market, and if you do not have the proper experience in this field, you will almost certainly get confused. In order to make the right choice, it is necessary to carefully study all the requirements for drainage geotextiles. The price of the product also depends on these indicators.
The use of fabric made from mixed materials is not allowed, since cotton fibers tend to wash out over time, which significantly reduces the ability of geotextiles to filter liquid. Thus, the system will soon require repairs, which will entail additional costs. Monofilament is the only suitable option for this case.
It is worth paying attention to the filtration coefficient that the manufacturer indicates for this type of material. The optimal indicator is considered to be 125-140 m/day. A higher value is required only if the fabric is located in soil with high water inflow.
Laying geotextiles in the area around the house.
There are some requirements for the density of geotextiles for drainage, which are also related to the permissible load. So, for a longitudinal load the indicator should be 1.9-3 kN/m, and for a transverse load - 1.5-2.4 kN/m. In this case, the total bursting strength should be at least 400-500 N.
Other parameters, such as roll width, can be any and are selected depending on the cross-section of the filter layer. The cost of a roll largely depends on the manufacturer, as well as on the density of the material. You should not save on this, because low-quality geotextiles may subsequently become damaged and require replacement.
Unique properties of Texpol geotextiles
Geotextiles Texpol, depending on the surface density, are divided into types. Density varies from 150 to 600 g/m2. Breaking load (length/width) – from 3/3.4 to 9.6/12 kN/m2. Elongation at break (length/width) – from 200/220 to 250/230%. The material has excellent physical and mechanical characteristics, resists well the negative effects of the biological environment and UV radiation, and has fairly good resistance to aggressive chemical environments.
Physical and mechanical characteristics of Texpol geotextiles:
| The name of indicators | Texpol150 | Texpol200 | Texpol250 | Texpol300 | Texpol350 | Texpol400 | Texpol450 | Texpol500 | Texpol600 |
| Surface densityg/sq.m. | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/(m K), no more | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 | 0,08 |
| Relative elongation at break, % no more along the length along the width | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 125140 | 125140 | 125140 | 125140 |
| Breaking load, kN/m2, no less, lengthwise width | 3,03,4 | 5,06,0 | 6,06,5 | 6,77,6 | 7,28,6 | 7,69,2 | 8,09,6 | 8,410,6 | 9,612,0 |
| Filtration coefficient, m/day (with vertical load P = 0.01 MPa), not less, in the direction perpendicular to the plane of the canvas in the plane of the canvas | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 | 6030 |
| Unevenness by mass,%, no more | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 |
Download characteristics of geotextile Texpol
Drainage geofabric for arranging the foundation of a house
Its durability largely depends on how well the foundation of the house is laid. That is why it is worth paying special attention to the arrangement of the drainage system in order to avoid the house being washed away by groundwater. Before starting work, you need to understand exactly at what depth the waters lie, as well as what type of soil you are dealing with. This will help you navigate the choice of materials: pipes, geotextiles and crushed stone.
Based on production technology, a distinction is made between thermally bonded and needle-punched geotextiles.
First of all, you will need to dig a trench around the entire perimeter of the foundation. It should be dug with a slight slope towards the direction of water movement. In this case, the width of the recess is calculated based on the diameter of the pipes, as well as the required distance around the pipe. For example, if you are laying a pipe with a diameter of 11 cm, then the space allocated for crushed stone will be about 10 cm.
On a note! If there is a blind area, the trench must be located along it.
Then sand must be poured into the bottom of the trench. The thickness of the layer should not exceed 5 cm. Geotextiles are laid on top, which are immediately covered with crushed stone. Pipes are laid on top and crushed stone is poured back in.
The top and side layers of crushed stone must be at least 10 cm. All these components are covered with geotextiles, which are fastened with wire at intervals of about 30 cm. Then everything is covered with soil and the drainage system for the foundation can be considered ready.
Geotextiles in rolls.
What is geotextile?
Under the name “geotextiles” there is a group of materials of various purposes, composition, production method and even type. Most often they are laid “on” or “in” the ground. The main component is synthetic threads or fibers. These materials are durable and relatively inexpensive. In some cases, fiberglass is used in production, sometimes natural materials - cotton, wool - are added to synthetics. All this changes the properties and characteristics of the material and affects the area of use.
Geotextiles are sold in rolls ranging from 2 to 6 meters wide
Raw materials for the manufacture of geotextiles
The most common are polyester and polypropylene geosynthetics. Polypropylene has a denser structure, usually higher tensile strength, and is not as fleecy in appearance. The disadvantage of polypropylene is that it reacts poorly to ultraviolet light and becomes brittle. Therefore, it is better not to use it as a covering material.
Polypropylene geotextiles can have any color, since dyes can be added to the feedstock. The basic one is white, but more often the color changes due to additives that are added to obtain special properties. For example, in order for geosynthetics to better tolerate sunlight.
Materials that look and feel different
Polyester geotextiles can be made from recycled materials (plastic bottles, etc.), and therefore usually cost less. Polyester threads are not long, so the material is more “shaggy” and less tensile strength. Color - any, but most often gray (Dornit brand), black, beige or brown, very rarely - white. This is when it is made from primary raw materials.
Geotextile "Dornit" is a non-woven, needle-punched material with high strength. Made from synthetic fibers, the fabric is wound into rolls of 50 meters and goes on sale in this form. Due to its strength, wear resistance and fairly affordable cost, Dornit is actively used in the construction industry and landscape design
To summarize, polypropylene geotextiles should be used where high strength is needed - when constructing roads, paths, strengthening slopes, foundations, and fills. Polyester material - suitable for beds, flower beds, slides and other landscape features.
Production methods and main properties
There are three different ways to make geotextiles:
- Geotextile - woven fabric made of synthetic threads with different weaving methods. By changing the thickness of the threads and their density, materials with different physical properties are obtained. Woven geofabric always has high tensile strength, therefore it is used where there may be mechanical loads - as a reinforcing, separating material. In some types of geotextiles, the distance between the threads is rather large, which allows water to easily pass through, while at the same time preventing mixing of materials. Such grades are ideal for drainage and can be used as a fraction separator.
Geotextile has a weave
- Non-woven fabric - made from short or long fibers of polyester or polypropylene joined in various ways. The connection method can be: using needles, geotextiles are called needle-punched;
- when sintered at high temperatures - thermally bonded;
- using thin streams of water - hydraulically bonded.
The needle-punched manufacturing method can be distinguished by its greater hairiness
If the fibers are connected using needles or thin streams of water, the material resembles felt in appearance and has a fleecy surface. Thermally bonded - smoother. Different methods of connecting threads give geotextiles different properties, therefore, they are used in different areas.
Thermally bonded geotextile has one side that is smoother
If we compare all three types of non-woven geotextiles, hydro-bonded has the highest tensile strength, then thermally-bonded and the “weakest” is needle-punched (the needles still damage the fibers). Thermally bonded geotextiles are made from polypropylene, since polyester has too high a melting point, which dramatically increases its cost.
Impregnation and landscaping
There are geotextiles with impregnations - latex, plasticizers, plastic compounds. They give the material additional properties, but almost completely deprive it of filtering ability. This must be taken into account when choosing a material. For example, for constructing a pond the lack of filtering capacity is a plus, for drainage it is a minus.
Impregnations are not always necessary
Bonding is the re-binding of already finished fabric. The method of re-bonding is usually different from the primary one. This gives the geotextile increased strength.
Drainage system for garden plot
Too close a location of groundwater can have an extremely negative impact on the life of plants growing in the garden. However, a way to combat this phenomenon was invented long ago, and today it is quite easy to implement even with your own efforts.
In order to drain water from the site, it is necessary to dig narrow trenches in the form of a “herringbone” throughout its entire area. They will contain narrow pipes with a diameter of 6.3 cm. They are cut into pieces of the required length and connected at the turning points using special tees.
It is at this phase that it is necessary to pay attention to the role of geofabric. It is necessary to make a drainage pipe in the geotextile filter. Each section of pipe must be wrapped with geofabric at least three times, and the winding must be secured with wire.
After this, the layers are laid out in the following order: crushed stone, geotextiles, crushed stone, earth.
Drainage system laying diagram.
On a note! At this stage, the geotextiles must be overlapped to provide more reliable protection.
Types of drainage
Before installing a drainage system, it is necessary to decide which type of drainage is most suitable in a given situation. Drainage of a site can be classified according to the depth of installation of drainage structures, it can be:
- Surface;
- Deep;
- Vertical.
Surface drainage, another name is external storm drainage, is constructed to drain rain and melt water from the territory that forms on the ground and flows from the roofs. Water collection in such a system is carried out using point and linear drainage systems.
Deep drainage is necessary to lower the groundwater level in low-lying areas with clay soils. At the calculated depth, drainage pipes of the required diameter are laid, discharging excess water into a drainage well or collector pipe.
Vertical drainage is a complex structure consisting of several wells equipped with drainage pumps. Pumps remove excess water from the site that accumulates in wells. Typically, vertical systems are designed and installed by specialists, since without special training it is very easy to make mistakes in the calculations.
Often, a water drainage system combines elements of surface, deep and vertical drainage. When designing, the type of soil, topography of the area, depth of groundwater and other indicators that affect the intensity of accumulation or outflow of moisture are taken into account. Only after drawing up the project can you begin to select and purchase the components necessary for installing the drainage system.
Dornit: non-woven geotextile for wide applications
One of the geofabric options that is widely represented on the market today is dornite. This is the name given to a fabric made from polymer raw materials and used in the construction industry for filtration, reinforcement and as drainage. At first glance, dornite is not much different from ordinary geotextiles, however, this is not so.
The technical characteristics of Dornit geotextiles are in many ways superior to other similar materials, primarily due to the method used in the process of its production. Needle-punched heat-treated geotextiles are capable of withstanding loads that significantly exceed those permissible for conventional materials.
Synthetic geotextiles.
Non-woven needle-punched geotextiles are produced using a special technology, which improves the quality characteristics of the material. This made it possible to use it in many areas. For example:
- in the construction of railways and roads;
- for laying pipelines;
- as a base for laying paving slabs;
- for equipping flat areas for parking.
Having found its place in many areas, dornite helps to successfully solve the following problems: increasing the strength of structures, separating layers of soil and drainage, filtration and prevention of soil leaching processes, protecting drainage systems from pollution.
Geotextiles are a common material used in the construction of industrial and residential facilities, including when laying roads.
Types of geotextile materials ↑
By production method ↑
Depending on the method of production of non-woven fabrics, geotextiles are of two types:
- Thermally bonded - produced by heating interwoven fibers, which are soldered together, creating a continuous web. Due to heat treatment, the material is thin, but at the same time durable. Thermally bonded geofabric is used as a filter layer for gravel or crushed stone backfill.
- Needle-punched - by “stitching” a compressed fabric formed from the finest threads, which are arranged in a chaotic manner. The finest needles, piercing the material with their hooks, entangle the threads, thus tightening them into a denser structure. Needle-punched geofabric is suitable for drainage systems with laying of geocomposite mats.
The material, created using the needle-punching method, allows water and air to pass through well, but does not decompose for two or more decades.
By fabric strength ↑
If you focus on strength, then non-woven fabric can be reinforced or non-reinforced. The reinforced material is additionally equipped with a mesh of durable threads. Thanks to this, it is able to withstand a tensile load of up to 250 kg. This property of the material allows it to be used during excavation work when processing areas experiencing significant stress:
- when organizing drainage systems;
- when repairing road surfaces;
- for the formation of landscape terraces and strengthening of slopes.
Reinforced geotextiles are able to distribute point loads over a large area
Acting as a strong separating layer between technological layers, geotextiles prevent subsidence of crushed stone into the ground, thereby extending the service life of the drainage structure.
Brands of non-woven fabric ↑
To construct drainage, product brands from both domestic and foreign manufacturers are used. Products produced by domestic enterprises have proven themselves well in this regard: Comtex, Dornit, Nomotex, Avantex, Polyzon, Kanvalan, Geocom.
The scope of application of geotextiles produced by domestic manufacturers is determined by its density and moisture permeability
Among foreign manufacturers, the following are very popular: Terram (Great Britain), Polifelt (Austria), Typar (Holland), NETEX A (Czech Republic), Typar (USA).
Product cost ↑
The cost of geofabric ranges from 10 to 20 rubles per square meter. As experts note, the cost and quality of fabrics used for drainage are not always proportional. Therefore, there is no point in purchasing expensive materials from foreign manufacturers.
Sometimes domestically produced products are not inferior in quality to imported analogues, and the price is an order of magnitude cheaper. Thermal fastening, excellent moisture permeability, but at the same time resistant to rapid clogging by large soil particles
If the price of the material is too low, it may indicate that you are dealing with a low-quality counterfeit product.
Prices for woven geotextiles per m²
Despite its excellent technical characteristics, geotextiles have a very affordable price. For example, the price of geotextiles for drainage per 1 m² is in the range of 10-20 rubles. Domestic material has a lower price per m². Geotextile for drainage from an imported manufacturer will cost a little more.
Shut up! Regardless of the price, you need to buy geotextiles for drainage that will meet all the requirements for geotextiles for this type of work.
The price of geofabric directly depends on the following indicators: density, strength, manufacturing method and material, and manufacturer. Before buying geofabric, be sure to read its technical characteristics.
Crushed stone enclosed in a geotextile wrap is used as drainage.
If you plan to entrust the installation of the drainage system to professionals, then you should familiarize yourself with the prices for laying geotextiles. On average, the price of laying geotextiles starts from 30 rubles per 1 sq.m. It’s easy to calculate that buying geotextiles for drainage yourself and laying it yourself will cost almost 2 times less.
Classification of geotextile products according to manufacturing methods
According to the production method, there are 2 types of products:
- woven;
- non-woven.
Woven geotextile
It is made by weaving fibers with a base. Manufacturers obtain modifications with different density indicators by changing the pore sizes. Woven fabrics can withstand intense tensile loads, so they are used to strengthen the soil. The purpose of woven geotextiles is to strengthen beds and improve the territory. It is not used in the manufacture of drainage systems.
Woven geotextile
Non-woven geotextile
It is made by thermal or mechanical joining of synthetic fibers. In the first case, the material is called thermally bonded, in the second – needle-punched.
To obtain needle-punched fabric, the finest fibers from polypropylene or polyester are used. The threads can be staple (in the form of short pieces) or continuous. When punched with needles, the process of felting the canvas is simulated. The products obtained by this method resemble artificial felt. They are characterized by high plasticity and the ability to stretch without damage. They pass liquid well in the longitudinal and transverse directions. Due to the peculiarities of the microstructure, they retain their filtering properties longer.
Needle-punched geotextiles have been successfully used to wrap drainage pipes and to prevent the accumulation of silt in drainage systems.
Thermally bonded geotextiles are made by heat treatment of threads that fuse when heated into a single fabric. Despite its small thickness, it is a highly durable material. This is a durable, biostable modification of geotextiles. Unlike its needle-punched counterpart, it provides filtration exclusively in the transverse direction. It becomes clogged with silt more quickly, so it is not used for wrapping pipes. The material is suitable for organizing a filter between gravel and sand, protecting drainage from weeds, and strengthening slopes. Its advantage is its resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
Microstructure of thermally bonded geotextiles
Additional strength to non-woven geotextiles is given by a reinforcing mesh made of durable synthetic fibers. Reinforced fabrics can withstand mechanical tensile forces of up to 250 kg.
Geofabric laying technology for drainage
In order to understand how to use geotextiles in the process of arranging a drainage system, we will consider why it is needed and what types there are.
Based on the existing topography, one of two drainage options is used:
- open;
- deep.
The first option is dug channels that are located on the surface of the earth. They are easy to install, but they have a rather unsightly appearance. If we are talking about arranging your own site, then this option can be called unsuitable.
Technology for laying geotextiles for drainage without crushed stone.
The deep system is not visible from the outside, as it is laid underground using special pipes and deeply dug trenches. It is to ensure the safety of pipes, as well as for arranging the inside of tanks, that geotextiles are used.
As mentioned earlier, geofabric is widely used for arranging drainage systems in private areas and local areas. Depending on the purpose and, accordingly, density, the price of geotextiles for drainage will vary.
Application of geotextiles
Geotextiles can be called a filter. By allowing moisture to pass through, but preventing the passage of solid particles, the fabric prevents heterogeneous layers of soil from mixing. Thanks to these properties, the canvas is widely used in the construction of drainage systems. They help drain rain and melt water from buildings, sidewalks and other structures.
In addition to the filtration function, geotextiles prevent the germination of weeds. If the canvas is placed under the decorative layer of a bulk garden path, then water will never accumulate on it and weeds will never grow. It is necessary to take into account that there are different types of drainage systems, therefore the choice of the type of geotextile occurs on an individual basis.
Laying geotextiles in drainage tanks
Another important condition that must be observed in order for the geofabric to fully fulfill its role is to correctly install it in the drainage system.
There are rules for this, following which you can achieve the desired result:
- The bottom of the trench must be completely cleared of construction debris. The walls should be as smooth as possible;
- It is recommended to unpack purchased geotextiles immediately before installation, since the material is sensitive to exposure to sunlight;
Scheme for laying attached and trench drainage.
- if necessary, the canvas can be cut to the desired size before installation;
- geofabric must be laid with an overlap;
- it is strictly forbidden to use those pieces of fabric that are damaged;
- laying should be done in such a way that the fabric is not stretched too tightly. At the same time, the formation of waves and folds is also unacceptable;
- if we are talking about laying geotextiles for drainage on large surfaces, then at this time it is necessary to fix the already laid sections to avoid their displacement;
- in order to maintain integrity, as well as minimize the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation, drainage material should be poured into the trench immediately after installation;
A layer of crushed stone is laid on top of the canvas, preferably granite, which is not subject to erosion.
- when the entire layer of drainage material is filled and compacted, the side edges of the geofabric should be turned inward. In this case, the free edges must have a length of at least 20 cm, this will help avoid the possibility of contamination of the filler;
- When all the edges are wrapped as expected, you can fill the trench with earth.
Which side to lay geotextiles
Another important question that arises during the work process is which side to lay geotextiles on? Even experts have divided opinions here. Some of them argue that there is no significant difference, and the fact that one side is rough and the other smooth is just a cost of production. Reviews claim that no matter which side the material is laid on, the characteristics of geotextiles remain unchanged.
Some manufacturers emphasize to consumers that geofabric should be laid with the smooth side down. In this case, recommendations on which side to lay geotextiles in the drainage will definitely be contained on the product packaging.
The use of geotextiles can increase the efficiency and durability of drainage systems.
Another opinion regarding the question of which side to lay geotextiles suggests using a rough surface for better adhesion to the ground.
In any case, when deciding which side to lay geotextiles on the ground, it is best to listen to the instructions of the manufacturer of the drainage geotextiles you decide to buy.