SNiPs
| Document's name | Link for review |
| Internal sanitary systems | SNiP 3.05.01-85 |
| Main pipelines | SNiP 2.05.06-86 |
| External networks and structures of water supply and sewerage | SNiP 3.05.04-85 |
| Sewerage. External networks and structures | SNiP 2.04.03-85 |
| Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings | SNiP 2.04.01-85 |
| Water supply. External networks and structures | SNiP 2.04.02-84 |
| Concrete and reinforced concrete structures | SNiP 2.03.01-84 |
| Planning and development of the territory where citizens conduct gardening. | SNiP 30-02-97 |
Stages of designing external and internal networks
Solutions for internal and external networks of a new or reconstructed building are described in a separate section of the project. It is filled out in accordance with Resolution No. 87 and will be submitted for approval and examination. Design is carried out in accordance with the customer’s technical specifications, using information from surveys and surveys.
Dear Clients!
The information in this article contains general information, but each case is unique. You can get a free consultation from our engineers using one of our telephone numbers - call:
8 Moscow (our address)
8 St. Petersburg (our address)
All consultations are free.
Design of external and internal networks for construction
When designing external and internal engineering networks of a new building, the architectural, space-planning and structural solutions chosen by the designers are taken into account. Also, to determine the characteristics of the equipment, pipe diameter and other parameters of engineering systems, technical conditions for connection are studied. Specifications must be obtained through resource supply organizations. The permissible load of the object is determined based on the content of the technical specifications.
When developing and justifying external and internal engineering networks, specialists indicate the following data:
- information about climatic and meteorological conditions at the construction site, average ambient temperatures;
- information about sources of resources from public networks;
- justification and description of decisions on laying pipelines inside and outside the building, pipe diameters, thermal insulation measures, emergency shutdown points;
- measures to protect networks from aggressive environments and influences, from soil erosion by groundwater;
- calculated data on loads on the designed networks;
- information about automation and control systems;
- information on energy efficiency measures;
- other data, depending on the type and purpose of the building, network characteristics.
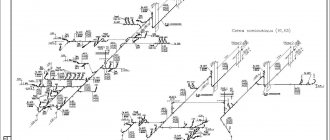
The project will be accompanied by diagrams, drawings, plans and sections for all utility networks. To preliminary check the performance of systems, an information model of the building and networks is made. Detailed documentation for the contractor must be prepared, specifications, estimates and calculations for construction materials must be drawn up.
Design of utility networks during reconstruction and repair
For design during reconstruction or major repairs, the parameters of existing utility networks are taken into account. The planned work may consist of increasing or decreasing the length of networks, changing the layout and amount of resource supply, and installing additional equipment. Also, specialists of the design organization must provide:
- ensuring safety during construction, installation and commissioning work, especially if during the repair period part of the facility will be connected to resource supply systems;
- optimal and efficient placement of connection points and connections of new communication elements, metering devices and equipment;
- options for replacing or restoring worn and damaged network elements;
- compliance with load standards and limits specified in the technical specifications.
The project for organizing construction work must include measures to disconnect the building and its existing systems. This requires prior agreement with resource supply organizations.
Expert commentary. For any design option, utility networks must comply with architectural, planning and other decisions. Otherwise, the internal or external engineering system will fail ahead of time, work with reduced loads, and require constant repairs.
When designing, diagrams of the location of networks on the site are drawn up
GOSTs and TU
| Document's name | Link for review |
| System of design documents for construction. External networks. Water supply and sewerage. Working drawings. | GOST 21.604-82 |
| Cast iron hatches for inspection wells. Specifications | GOST 3634—89 |
| Concrete and reinforced concrete structures for sewer, water and gas pipeline wells. Specifications | GOST 8020—90 |
| Ceramic sewer pipes. Specifications | GOST 286—82 |
| Water purification devices. General requirements for efficiency and methods for determining it | GOST R 51871-2002 |
| Cast iron sewer pipes and fittings for them | GOST 6942-98 |
| Polymer pipes with a structured wall and fittings for them for external sewerage systems. Specifications | GOST R 54475-2011 |
| Polymer sewer wells | GOST 32972-2014 |
| Compact units for treating domestic wastewater. Types, parameters and sizes | GOST 25298-82 |
| Sewerage. Terms and Definitions | GOST 25150-82 |
| Sanitary drainage fittings. Specifications | GOST 23289-94 |
| Manholes for inspection wells and stormwater inlets. Specifications | GOST 3634-99 |
| Pipes and fittings made of polyethylene for internal sewerage systems. Specifications | GOST 22689-2014 |
| Pressure pipes made of polyethylene. Specifications | GOST 18599-2001 |
| Dynamic pumps. Test methods | GOST 6134-2007 |
| Soils. Permeability Field Test Methods | GOST 23278-78 |
Sewage installation
What does the SNiP we are interested in - internal water supply and sewerage networks - say about the installation of waste systems inside buildings? In order not to overload the reader with information, we will select only those requirements that are relevant when installing a sewer system in a residential building with your own hands.
- For drainage of wastewater, closed gravity pipelines should be used;
- Sewer branches assembled from straight pipes are laid in a straight line. For turns, shaped fittings are used (corners, half-bends, tees, etc.);
- To connect horizontal sewer branches under the ceiling of rooms (including in technical basements and subfloors) to the risers, you need to use oblique crosses and tees;
Author's comment: the upward-directed oblique outlet does not leak even when the connection is depressurized.
The connection to the riser is made with an oblique tee
- Connecting two bathtubs or any other devices that require a volley discharge of water to the riser is done with an oblique cross. It prevents overflow of the comb (indoor sewage system) while simultaneously draining water from two devices.
The sewer riser must be ventilated. Ventilation solves two problems at once:
- Transportation of vapors to living quarters by natural draft;
- Breakdown of water seals on plumbing fixtures during a salvo discharge.
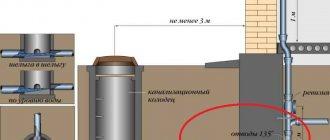
The ventilation outlet (fan pipe) is discharged through the roof.
The height of the vent pipe above its level depends on the type of roof:
| Image | Roof type and vent height |
| Flat non-operational - 30 cm |
| Pitched - 50 cm |
| Operated - 3 m |
Please note: the horizontal distance from the drain pipe to the nearest openable window or balcony must be equal to or exceed 4 meters.
Each riser must have inspection points to clear blockages. In apartment buildings, audits are located:
- In apartments on the top floors;
- In the basement;
- In houses with a height of five or more floors - every three floors.
Sewer inspection in the apartment
In addition to risers, revisions or oblique tees are installed at all turns of drainage pipes (horizontal sewer branches) and on long straight sections.
The maximum distance between revisions is determined by the diameter of the waste pipe:
| Pipe diameter, mm | Maximum distance between revisions, m |
| 50 | 8 |
| 100-150 | 15 |
| 200 | 20 |
Inspection of the corner of the bed in the basement
Main regulatory documents in the field of water supply and sanitation
List of main regulatory documents that are used in the design, construction and operation of water supply and sanitation systems in Russia
References to standards in this article are divided into categories, but it must be remembered that all documents refer to each other and complement each other. The process of finding the right technical solution is not simplified by the fact that there is a so-called List of mandatory regulatory standards (and individual items from these standards).
Here and below are links to the Tekhekspert portal; it is always better to look at the standards for such databases, because That's where they update the fastest.
- INTERNAL WATER PIPELINE AND SEWERAGE
When designing internal water supply and sewerage systems for buildings, the specialist first uses the set of regulatory documentation given below.
1.1 To determine water flow rates, pipeline diameters, places where they pass, requirements for water meters, etc. These documents are used:
30.13330.2016 Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings"
SP 73.13330.2012 “SNiP 3.05.01-85 Internal sanitary systems of buildings”
1.2 Internal fire extinguishing (from fire hydrants) is regulated primarily by this standard:
SP 10.13130.2009 “Fire protection systems. Internal fire water supply. Fire safety requirements"
1.3 And if there are automatic fire extinguishing systems (sprinkler, deluge, etc.), this document is also used:
SP 5.13130.2009 Fire protection systems. Fire alarm and fire extinguishing installations are automatic. Design standards and rules
- EXTERNAL WATER PIPELINE AND SEWERAGE
When designing external water supply and sewerage networks, both inside the yard and citywide, as well as wastewater treatment plants, experts refer to the following standards.
2.1 Determination of water consumption, pipeline diameters, installation of structures on the network, etc. regulated by the SP data:
SP 31.13330.2012 “SNiP 2.04.02-84* Water supply. External networks and structures"
SP 32.13330.2018 “SNiP 2.04.03-85 Sewerage. External networks and structures"
2.2 Water consumption for fire extinguishing is dictated by:
SP 8.13130.2020 “Fire protection systems. Sources of external fire-fighting water supply. Fire safety requirements"
2.3 The relative position of the pipelines relative to each other, both in plan and in profile, is looked at according to this document:
SP 18.13330.2011 Master plans for industrial enterprises
- RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE SUBSCRIBER AND THE SUPPLYING ORGANIZATION
3.1 Relations (for example, the composition of wastewater discharged into the municipal sewer) between the subscriber (primarily a certain object) and the supplying organization (most often all the local Vodokanal are regulated by these laws:
416-FZ Federal Law on Water Supply and Sanitation
And
RF GOVERNMENT DECREE N 644 Rules for cold water supply and sanitation
! It is also necessary to take into account that each region may have its own additional requirements, which, as a rule, tighten certain requirements for the composition of wastewater!
3.2 The quality of services provided to a specific user (for example, you in your apartment) must meet the requirements specified in the following law:
RF GOVERNMENT DECREE N 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings”
3.3 The quality of drinking water in any system must meet the Sanitary Standards and Rules:
SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems…"
- BEST TECHNOLOGY AVAILABLE
Also in Russia, the creation of technical reference books on the most accessible technologies that should be used when designing various systems is actively underway. Currently, the following documents are used in the field of water supply and sanitation:
ITS 8-2015 Wastewater treatment in the production of products (goods), performance of work and provision of services at large enterprises
ITS 10-2015 Wastewater treatment using centralized wastewater systems for settlements in urban districts
- OLD SNIPs
Unfortunately, the new joint ventures are significantly inferior to the classic Soviet SNiPs in terms of completeness and information richness. Some applications or sections that are fundamentally important for specialists are simply missing in the new documents. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to refer to the original versions.
You can download these documents from our website using the links below:
SNiP 2.04.01-85* Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings
SNiP 2.04.02-84* Water supply. External networks and structures"
SNiP 2.04.03-85 Sewerage. External networks and structures"