House with independent sewerage and water supply
Today we have to figure out how the sewerage and water supply of a private home can be organized in the absence of centralized networks. We will discuss possible sources of drinking and household water, methods of waste disposal and materials that are best used for installing water supply and sewerage systems.
Where are you from and where are you going?
First, let's get acquainted with the general concept and find out how autonomous water supply and sewerage systems for private houses work.
Water
Where to get water in the absence of a main water supply?
From underground. Literally. Groundwater is found almost everywhere; the only difference is the depth of the aquifers. Thus, in Sevastopol, where the author lives, the depth of water wells varies from 8-10 meters (Cossack Bay) to 60-70 (Cape Fiolent).
How exactly do you get water from the ground? Here are two possible solutions:
| Image | Description |
| The well is constructed at a shallow depth of the aquifer. The walls are reinforced with reinforced concrete rings, less often with brick or stone masonry. |
| The well allows the use of water from aquifer levels at depths of tens and even hundreds of meters. Drilling is possible not only in soft soil, but also in sedimentary and even rock formations (see Drilling a water well with your own hands: all the details of the work). The wellbore is strengthened with steel or plastic casing. |
Reference: the price of drilling one meter of well at the time of writing (mid-2021) is about 2,000 rubles. Typical diameters of a wellbore with casing installed are 125 and 160 mm.
It’s not enough to find water; it still needs to be raised from a considerable depth. This function is performed by electric pumps - surface and submersible.
The former are capable of serving only shallow wells: the vacuum created by the impeller can raise the water column by no more than 7-8 meters; but the latter, thanks to the sequential connection of several working chambers with their own impellers, provide a pressure of tens of meters, and do an excellent job of transporting water from wells of any depth.
Multistage submersible pump: several working chambers connected in series provide maximum output pressure
Drains
Where should household and household waste go?
Here are three solutions that differ in costs during construction and operation:
- Cesspool (aka storage septic tank). Liquid waste accumulates in an underground tank and is periodically pumped out by a sewage disposal machine. The obvious advantage of a cesspool is its low cost. An equally obvious drawback is high operating costs: pumping 4 cubic meters of liquid sewage costs 2000 - 2500 rubles;
Cesspool - cheap to build, but expensive to operate
Please note: in order to increase the frequency of pumping, storage septic tanks are often intentionally built to be leaky. As a result, untreated wastewater contaminates surface groundwater. In addition, the soil bottom of a leaky cesspool quickly (within 2-3 years) silts up, and the absorbency of the soil drops sharply.
- A deep biological treatment station is a local treatment facility that provides 98% wastewater treatment. Suspensions are screened out when sewage settles; The organic matter is then processed by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria into odorless sludge that can be used as fertilizer.
Eurobion deep cleaning station
Purified water can be used for irrigation, or simply dumped onto the terrain. The advantage of the solution is minimal costs at the operation stage, the disadvantage is the relative high cost: prices for treatment plants that can meet the needs of a small family start at about 70,000 rubles;
- An intermediate position is occupied by one- and two-chamber septic tanks. Wastewater treatment in them is carried out only due to gravitational separation (in other words, heavy suspended matter settles to the bottom of the settling tank, and light organic matter floats up and forms a crust on the surface).
Selected below the surface level, but above the bottom, the settled water flows through an overflow into a filter well or onto a filtration field, where it is safely absorbed into the soil. Siltation in this case occurs many times slower than in an unsealed cesspool: almost all the sludge remains in the sump and is periodically (usually once a year) pumped out from there by a sewage disposal machine.
Construction of a two-chamber septic tank: solid fractions of wastewater remain in the sump, purified water is absorbed into the soil
A septic tank combines modest operating costs (that is, the annual cleaning of the septic tank) with low cost. In particular, the transformation of a leaky cesspool into a full-fledged septic tank cost the author of the article a modest 9,000 rubles in 2013 prices.
A single-chamber septic tank with a filter well is built of concrete rings
Useful: the more chambers of the septic tank are connected in series by overflows, the higher the quality of wastewater treatment, the slower the filtration field or filter well silts up.
How everything works
Let's stipulate that in the future we will discuss the water supply and sewage system of a country house in relation to a very specific configuration - with water supply from a well and wastewater disposal through a single-chamber septic tank. Simply because these are the most universal and popular solutions. Let's get started.
Autonomous water supply system
So, the well is drilled and cleaned after installing the casing. What is needed to organize uninterrupted water supply to a private home?
| Image | Water supply system element |
| Submersible well pump. It must create a pressure equal to the sum of the depth of the well, the height of the highest point of the water supply system above ground level and 3-5 meters of excess pressure to ensure the operation of plumbing fixtures. The pump performance should ideally be slightly less than the well flow rate. The pump is lowered into it to such a depth that there is at least a meter between its water intake grid and the bottom: then it will not lift silt and sand from the bottom. |
| Check valve. It is installed in front of the pump and prevents water from the water supply from flowing back into the well when it is turned off. |
| Water supply input. Typically, a pressure polyethylene pipe with connections made by compression fittings is used in this capacity (see Fittings for water supply to a private house). The inlet is laid in the ground below the freezing level; where this requirement cannot be met, the pipe is insulated and supplied with cable heating. |
| Hydraulic accumulator. It ensures stable pressure in the water supply when the pump is turned off and increases the downtime of the latter. The larger the volume of the hydraulic accumulator, the less often the pump turns on and the greater the supply of water the home owner has during power outages. |
| Automatic pump control. A pressure sensor is responsible for controlling its switching on and off: when the pressure in the water supply drops to a critical level, the pump turns on and supplies water to the accumulator; When the upper preset level is reached, the power is turned off. |
In houses with a high, warm attic, the hydraulic accumulator is often replaced with a storage tank with a volume of 500 liters or more. Water flows from it into the water supply system by gravity.
A regular fill valve is responsible for the dosed supply of water into the container - the same as those found in the toilet flush cistern; the pump is controlled by a level sensor.
Scheme for connecting a storage tank to an autonomous water supply system
To prepare hot water use:
- Storage and instantaneous electric water heaters;
Please note: the disadvantage of ducts is their high power consumption and, accordingly, a large load on the wiring. Outside the city, where modest power limits are often set for a single house, in most cases it is better to use storage heaters.
- Indirect heating boilers that use the heat of the heating system to heat water. They work with any type of boiler. In the summer, when the heating is turned off, the coolant circulates through a small circuit - between the boiler and the boiler;
Connection diagram for an indirect heating boiler
- Gas water heaters and double-circuit boilers (gas and diesel).
Septic tank
A single-chamber septic tank is a settling tank in which wastewater is separated into water itself, light and heavy fractions. Water creates 98-99% of the volume of domestic wastewater, so the amount of solid waste accumulating in the sump is small.
For the disposal of treated wastewater, the following are used:
- On soils with high absorbency (sand, sandy loam) - a filter (drainage) well with a soil bottom and leaky walls;
Brick filter well: soil bottom and masonry walls with gaps
Useful: it is better to backfill the well not with previously removed soil, but with pebbles, crushed stone or boulders. Drainage will increase the absorption area of the pit walls. The bottom of the well is covered with a layer of boulders or large pebbles: in this case, the settling silt will remain on the surface of the stones and will not reduce the absorbency of the soil.
Filling the filter well with crushed stone
- A filtration field is constructed on loam and clayey soils: drainage pipes are laid in trenches or a pit on top of a layer of crushed stone and successively covered with 20 - 30 centimeters of crushed stone, a layer of geotextile and soil. The location of the pipes below the freezing level will ensure year-round operation of the filtration field. The soil surface above the drainage pipes can be used as a flower bed.
Septic tank with purified water discharge to the filtration field
How to calculate the size of a septic tank?
Instructions for calculating the volume of a sump are contained in SNiP 2.04.09-85 “Sewerage and water supply of a residential building.” With a daily wastewater volume of less than 5 cubic meters, the settling tank should exceed this daily volume three times, with a higher wastewater flow rate - 2.5 times.
Design and dimensions of a septic tank for different volumes of daily wastewater
How to estimate the daily volume of wastewater in your home? If you have a water meter, everything is very simple: wastewater flow with a minimum error is equal to the change in its readings. 98% of household waste is water, remember?
If there is no meter, or if a significant part of the water does not end up in the sewer (for example, when washing a car or watering a garden), focus on sanitary standards - 200 liters per family member per day. So, a family of three uses an average of 600 liters of water per day, so the minimum volume of a septic tank for it is 1800 liters (1.8 m3).
Water consumption rates for different water supply systems
In the case of a filter well or filtration field, the absorbent surface area and the absorbency of the soil are important to us.
Here are the values of the last parameter for different types of soil:
| Soil type | Absorption, liters per day per square meter |
| Sand | 90-100 |
| Sandy loam | 40-60 |
| Loam | 20-30 |
| Clay | 10 or less |
For example, on sandy loam soil with an absorption capacity of 50 liters per square meter per day, with a daily wastewater flow of 600 liters, the minimum wetted area of the walls of the filter well should be equal to 12 square meters. Such a wetting area will be provided, for example, by a filled cubic pit with a wall size of 1.55 meters.
Sandy loam soil: water absorption - up to 60 liters per day per square meter
When installing a septic tank, you will encounter two technical problems:
- Mixing settling wastewater with an influx of water. To minimize it, install a sewer straight tee on the supply pipe;
- Difficulty can also be caused by drawing water from the settling tank below the crust on the surface. And in this case, the problem is solved by installing a sewer tee on the overflow: its lower outlet is used to actually draw water, and the upper one is used to clear the overflow in case of blockages.
The supply pipe and overflow are equipped with tees
By the way: the diameter of the septic tank supply pipe is always made equal to 100-110 mm, but the overflow diameter can be reduced to 50 millimeters. According to the author’s experience, this size is quite sufficient for transporting settled water that has been purified from large contaminants.
To install the overflow, you can use a 50 mm pipe
Modern water treatment
Modern septic tanks use a number of wastewater treatment methods: mechanical, chemical and biological. Biological treatment is recognized as the optimal method. This method uses microorganisms that themselves destroy organic contaminants. .
In practice, several methods of waste disposal are possible:
- diversion to the terrain,
- drainage of water through a perforated pipe by gravity,
- drainage of water by gravity into a drainage well,
- discharge to the storage system.
In addition, follow these guidelines:
- Discharge of wastewater from a septic tank into the ground is used for subsurface irrigation of agricultural crops. The sludge that is then removed from the septic tank serves as fertilizer.
- A system for draining water directly into the ground is possible for sandy or sandy loam and loamy soils.
- To drain wastewater into heavy loams, a special engineering solution will be required.
Materials
What materials are used to install water supply and sewerage in a house with your own hands?
Water
For plumbing throughout the house, polypropylene pipes are most often used.
Water supply distribution is made with polypropylene pipes
Their advantages are very convincing:
- Cheapness;
- Long service life (from 50 years in cold water and from 25 years in hot water);
- Minimum hydraulic resistance due to smooth walls;
- No deposits;
- Quick and easy installation using low-temperature soldering;
Installation of a single water outlet on a polypropylene water supply
- Maintenance-free connections as strong as solid pipes.
A couple of subtleties:
- When installing a water supply system, use pipes with an outer diameter of at least 20 millimeters, otherwise you will experience a drop in pressure at the water collection points farthest from the input;
- Hot water distribution is carried out using reinforced pipes. Reinforcement reduces the elongation of polypropylene when heated.
Sewerage
For the installation of internal sewerage, gray sewer pipes made of PVC or more heat-resistant polypropylene are used.
Pipes and fittings for internal sewerage
The sewerage outlet to the septic tank in the ground should be laid with an external (orange) pipe: it has greater annular rigidity and can withstand significant deforming loads.
What should be the diameter of the sewer:
- Toilets are connected with a diameter of 110 mm. The same diameter is used to install the outlet on the septic tank;
- All other plumbing fixtures are connected with a diameter of 50 mm.
Sewer comb: the toilet is connected with a diameter of 110 mm, other devices - with a diameter of 50 mm
Features of the design of water supply systems for private houses
In small private buildings, the source of cold water supply may be a separate well. Its diameter ranges from 1 to 1.5 m. A prerequisite for drilling an individual well is the presence of a water measuring unit, consisting of a meter and a filter. In some node designs, data transmission to a common control center is carried out remotely.
The choice of the optimal option for supplying hot or cold water to an industrial or residential facility should be carried out taking into account its technical characteristics and the expected volume of work. Qualified specialists will answer in detail all questions related to the choice of a water supply system, calculate its approximate cost, tell you where to start, and help with the preparation of the documentary and design base.
Installation rules
Finally, a few words about how to properly install sewerage and water supply at home:
- The hot water supply line is always laid above the cold water pipes. Otherwise, the flow of warm air rising from the hot water supply pipes will heat the water in the cold water system;
- Long straight sections of polypropylene water pipes in the hot water supply system are equipped with U-shaped or annular bends - compensators. Clamps near expansion joints must allow pipes to slide freely. These measures will help you avoid deformation of eyeliners and spills when heated;
Installation of a compensator on a polypropylene hot water supply system
- The diameter of the sewer in the direction of movement of the wastewater can only increase. Reducing the diameter will cause constant blockages;
- The sewerage system is installed with a constant slope along the entire length of the horizontal branch of 3-3.5 cm per linear meter with a pipe diameter of 50 mm and 2 cm per linear meter with a diameter of 110 mm. Counterclones are strictly prohibited: fat and suspended matter will settle in them, which over time will again lead to blockages;
The sewer comb section is installed with a negative slope. Blockages guaranteed
- Plastic sewerage should be fixed in increments of no more than 10 diameters. Pipes fixed with a large pitch will sag over time, forming areas with a negative slope;
- To attach sewer pipes to smooth walls, use plastic clips; to those with significant unevenness, use adjustable clamps;
- Connections between siphons and sewers are sealed with cuffs or any sealing material. Otherwise, sewer odors will penetrate into living spaces;
Sealing connections between plumbing fixtures and sewerage systems
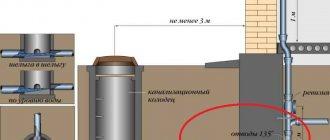
- Sewerage with a septic tank absolutely requires ventilation. The sewer pipe is discharged from the top point of the sewerage system through the roof or, less commonly, through the gable of the house.
Advice: it is advisable to equip the fan pipe with a deflector, which increases draft in windy weather.
In the photo - fan pipes with deflectors to increase traction
Types of autonomous sewage systems
Autonomous sewer systems are in great demand and popularity today. Their demand is associated with the growing number of residential and industrial buildings isolated from external sewer networks. Another factor explaining the demand for such systems is their convenience and speed of installation work. There are the following types of autonomous local sewer systems:
- Dry toilets are an ideal option for a country house or summer cottage. The main expense item is related to the purchase of consumables and waste disposal. The design of such a system does not require the development of design documentation.
- Drainage pits are outdated, but still often used sewerage systems in private buildings. Their operation is associated with the need for constant pumping of waste products. However, this option is still in demand in some regions, since by definition it is the most affordable.
- Septic tank - provides a high degree of waste treatment, has minimal operating costs, and is suitable for small country houses.
- Biological treatment systems. Expensive, but multifunctional and efficient local sewer networks.
When choosing an autonomous sewer system, the main criterion is the mechanism for the movement of wastewater; this can happen by gravity or using special pumps. Each of these mechanisms has its own advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when giving preference to one or another system.
The principle of gravity sewerage ensures that wastewater drains naturally, and it is important to correctly calculate the slope angle. This must be done at the design and installation stage. Also an important factor influencing the functionality of a gravity sewer system is the diameter of the pipeline intended for drainage. It is important to find the optimal balance between the angle of inclination and the width of the pipes. If they do not comply, users will face constant blockages and the need to clean the sewer.
Sewage systems designed on the principle of gravity flow have a number of advantages, the main ones being affordable cost, independence from the availability of electricity sources, and ease of operation. The disadvantage of such a system is the impossibility of its installation in the absence of a sump tank in close proximity to the object.
Local sewer networks, where wastewater is pumped using a pressure principle using pumps and pumping stations, are distinguished by their ability to transport waste over long distances. Such a network can be laid over any terrain. Its functionality will not be reduced, since the power of the pumps is sufficient for the effective operation of the structure in places where the bends change the direction of the pipes. The main disadvantage of such a pressure system is the dependence on the availability of a power source for uninterrupted operation of the pumps.