Why should you contact Ecology 24?
- Affordable price for cleaning sewerage in Moscow;
- We work using proven technologies and use special equipment (washing and sludge removal machines, fecal pumps);
- We clean drainage systems.
How we are working?
Which of the four sewer cleaning methods we use depends on the blockage and the material of the pipes. If the pipes are heavily clogged, we clean the pipes using several methods in succession.
- Hydrodynamic method: flushing the sewer using a special machine. Its electric drive supplies water into the pipeline under high pressure (≈ 200 atmospheres). In addition, the hose has nozzles, so the water flows move so reactively that they clear fecal matter and other blockages from the walls of the main pipe. By periodically cleaning the sewer using the hydrodynamic method, emergency situations can be avoided, and its trouble-free service life is significantly increased. The use of the hydrodynamic method does not destroy the pipe material. In addition, the method does not harm the environment, since no chemicals are used;
- Chemical method: cleaning fecal sewage using chemical reagents: surfactants, corrosion inhibitors, chemically active substances. The method is often used in conjunction with hydrodynamic flushing of the pipeline. After using the reagents, we flush the pipes. This prevents destruction of the pipeline and sealing elements by chemicals.
- Mechanical sewer cleaning. To do this, we use special equipment - pneumatic, root cutting or drilling. The design of the cleaning heads does not damage the inner surface of the pipes. Thanks to the flexible shaft, all turns of sewerage pipes are cleaned.
- Thermal cleaning method. This is a combined method in which sewer cleaning is carried out using jets of water heated to +120 °C.
Cleaning the sewer system restores the functioning of the drainage system and eliminates blockages in hard-to-reach areas of the sewer system. The drainage system is completely cleaned and wear and tear of the sewerage pipes of country houses and process pipelines of industrial enterprises is prevented. And with proper prevention of blockages, the sewer system will work smoothly.
There are three ways to order sewer cleaning:
- Call +7-499-130-5562
- Send a letter to the email address indicated on the site
- Leave an online application on the website.
We will clean the fecal sewer within 2 hours, taking into account ALL the features of the pipeline!
Application in everyday life
Most people do not encounter topographical surveys in everyday life. Most often, the task of reading, deciphering and drawing up such maps falls to cartographers and builders, and topographic surveys of utility lines are considered the most popular.
Symbols of utility networks on topographic surveys are a prerequisite for their objectivity. This includes telephone networks, water supply, power lines, gas pipelines and other communications.
Symbols on topographic surveys of utilities are carried out in a linear way - straight solid or dashed lines:
- all above-ground operating pipelines and communications are indicated by a straight solid line 0.3 mm thick;
- all project, damaged or inoperative overhead communications are indicated by a dotted line 0.2 mm thick;
- all underground communications are indicated by a dotted line.
At intersections with other objects or communications, near the frame (at least every 5 cm), a letter designation that characterizes the transported material (product) is integrated into the line indicating the utility communications.
The letter determines the nature of communications:
- The letter G implies that the utility network transports gas; the designation of the gas pipeline on a topographic survey can be carried out with continuous (for above-ground) and intermittent (for underground installation) lines;
- B - water supply, whether the line will be continuous or intermittent, also depends on the method of communication;
- T - heating main;
- N - oil pipeline;
- K - sewerage.
Often, such information in topographical terms is presented as informatively as possible, indicating the pressure in the mains (gas), the material and thickness of the pipes, the number of wires and voltage in the power lines.
For this reason, an explanatory letter of lower case or numbers are often added to the first capital letter in designations.
For example, the designation Kl on a topographic survey means: storm sewer, in turn, a similar designation kb on a topographic survey will mean domestic sewerage.
Story
Paris sewer
The earliest structures that acted as sewers were discovered in the cities of the Indus civilization: in Mohenjo-Daro, which arose around 2598 BC. e., perhaps the first public toilets known to archaeologists were discovered, as well as the city sewerage system.
Sewerage structures were also found in ancient Babylon, the second oldest.
In Ancient Rome, a grandiose sewerage engineering project - the Great Cloaca - was created under the fifth king of Ancient Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Prisca.
In ancient China, sewers existed in several cities, such as Linzi.
Types of sewer systems used in the arrangement of a country house or cottage
Most often, in country and cottage villages there is no centralized sewer system, which leads to the need to organize.
There are several types of such sewer systems:
- The cheapest, but also the least convenient option to use is a cesspool
; - Dry toilets
do not require installation work, but they force you to regularly purchase various materials used for recycling waste, after which the problem of their disposal also arises; - A septic tank
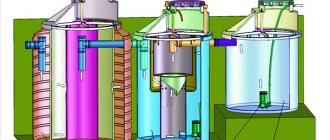
is a fairly popular device because, without requiring frequent waste removal, it cleans wastewater by approximately 75%. In addition, it is enough to clean the septic tank itself once every 1-2 years; - Filters
and devices in which deep wastewater treatment is carried out using biological material. The high quality of cleaning is balanced by the high cost of these devices.
When installing an autonomous sewer system, the method of transporting wastewater is also important: will it move by gravity or using pumps.
Design of utility networks in topographic survey
Often the question “how are sewers indicated on a topographic survey” implies an interest in the color of the lines. There is a lot of controversy regarding the color of communications on topographic surveys. On the one hand, there is a special manual: “Rules for drawing symbols on topographic plans of underground communications on scales 1:5000 ... 1:500” Moscow, “NEDRA” 1989.
The handbook states that all signs are painted in black, and even prescribes the recommended thickness of these lines. At the same time, the reference book allows “for greater clarity” to convey the lines in a different color.
Household network K1
The entire sewerage complex of a residential building is called a utility-fecal, or utility-household, and is designated in design and regulatory literature as sewerage K1.
This network unites plumbing receivers, such as bathtubs, sinks, sinks, toilets, bidets, etc., used for sanitary and hygienic purposes. Receiving devices are used, such as funnels, trays, ladders, and sewer pipes connecting them.
A mandatory part of plumbing fittings is a hydraulic valve. This is a U-shaped siphon half filled with water. This simple technique creates a water barrier that prevents gases from flowing back into the room. Toilets and drains are structurally made with valves; they are connected to other appliances after the drain holes.
Plumbing receivers are connected to outlets through which household wastewater enters the sewer network.
Sewage scheme K1
The pipeline part includes horizontal sections laid with a slope. They flow into risers - vertical sections that combine drains and lead them to the collector. The connection of various sections is made using shaped parts that ensure a change in the direction of the pipelines and their deflection.
A collector is a pipeline laid horizontally with a large slope, connecting the sewage system of a building with the complex of a populated area.
Ventilation piping is an essential part of the plumbing system. They run vertically and are connected to the drainage system. Ventilation helps stabilize the pressure in the sewer system. When designing drainage in small areas, drainage ventilation is provided by air draft, which is a consequence of heating the risers by the internal heat of the premises.
For the installation of a household drainage network, different types of pipe products can be used, the use of which is regulated by SNiP. In the case of waste disposal by gravity, cast iron, asbestos-cement, concrete, reinforced concrete, plastic, and glass pipes are recommended.
When implementing pressure discharge, cast iron, reinforced concrete, plastic or asbestos-cement pipes can be used. For the ventilation part, in addition to cast iron, SNiP allows the use of asbestos-cement pipes, polypropylene, and PVC pipes.
Sections of Ø 50 mm are used as outlets from appliances other than the toilet. Toilet outlets are made with Ø 110 mm. The dimensions of the elements of the entire network are determined by calculations carried out during the design of the sewer system.
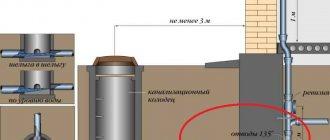
Sewer K1 has its own outlet, which is arranged at an angle of 90⁰ to the outer walls, buried to a level slightly higher than the base of the foundation. If there is a basement, the release is performed above the basement floor.
The building's sewerage system is connected to the public sewer system. In the case of a country cottage, it is possible to organize a shambo sewer system, when waste is discharged into a receiving pit on the site and is periodically pumped out and removed. In this case, you should organize vehicle access to the drainage pit.
Compliance with all standards and high-quality installation of household wastewater disposal is a guarantee of reliable operation of the entire wastewater disposal unit.
Materials used in city sewerage
The highest demands are placed on the materials used in urban sewerage, since they are constantly in contact with the highly aggressive environment of the transported wastewater. Typically, sewer pipes are made from the following materials: • Polypropylene; • Cast iron; • Polyethylene; • Polyvinyl chloride; • Reinforced concrete (used for external networks with a diameter of more than 150 mm and large-section collectors). Sometimes asbestos-cement, ceramic, and glass pipes are used. Sewage wells with various functions are made of durable plastics, precast or monolithic reinforced concrete.
Classification of wastewater and sewerage systems
A necessary form of cleaning populated areas from wastewater is sewerage. Its task is to remove water and liquid waste generated as a result of household activities of the population of cities, towns and the work of industrial enterprises. Together with surface waters (irrigation, atmospheric, groundwater) that appear on the surface of urban and rural areas, liquid waste is a contaminated liquid and is called wastewater. They contain chemical, biological and organic components. They must be removed, cleaned, disinfected and sent to the nearest water bodies. The sewer system and drains serve this purpose.
Wastewater is divided into the following categories:
- * household or household - from houses, industrial buildings, formed as a result of human activity. Contain organic, mineral, bacterial contaminants;
- * production - from industrial enterprises, resulting from technological processes. Contain organic, mineral, toxic contaminants;
- * atmospheric - from city areas, roofs of houses, rainwater, melt water. Contains mineral and chemical contaminants.
Drainage systems depend on the composition of wastewater. The degree of pollution is characterized by the amount of pollution per unit volume. The concentration of pollutants depends on the rate of water consumption in a populated area, the nature of the production site for collecting sedimentary water, and its quantity. The wastewater sewerage system ensures the reception, transportation, purification, disinfection, and disposal of useful substances into the reservoir. There are two types of sewerage: export and floating.
Export sewerage is based on the removal of individual volumes of liquid to aeration fields.
A floating sewer consists of a system of underground pipelines and devices that transport wastewater to treatment facilities. This system is most common in large populated areas. To install it, you must have an internal water supply with a consumption rate of at least 60 l/day per person
The floating sewerage system consists of internal devices, external networks, pumping stations, treatment facilities and wastewater discharge devices.
Floating sewerage, depending on how the issue of wastewater disposal is resolved, is divided into storm sewer, fecal (domestic) sewerage, general alloy sewerage, separate (complete, incomplete), semi-separate and combined.
The all-alloy sewer system carries out the removal of storm wastewater by one pipeline system, which comes after rain from urban areas through storm-intake grates, and household wastewater, coming from residential buildings and industrial buildings. With separate sewerage, two independent wastewater disposal systems are used: storm sewerage (drainage) and domestic and fecal sewerage. Wastewater from industrial enterprises is discharged by a separate system to purify it from specific contaminants. Currently, a separate sewerage system is most applicable.
Norms, rules and symbols on water supply and sewerage drawings
The main components of pipeline systems are: straight pipes that are tightly connected to each other; suspensions and supports; control and measuring equipment; shut-off and control devices; fasteners; seals and gaskets; automation means.
In addition, the elements of pipeline systems also include the materials necessary to provide effective protection of all the above components from the harmful effects of low and high temperatures, as well as from electrochemical corrosion.
The locations of the elements of pipeline systems are their branches, turns, as well as transitions to another diameter. They serve to ensure a long service life of the system as a whole, as well as the tightness of the entire structure. Practice shows that without such elements as bends, tees and transitions, practically no pipeline system is currently implemented.
Liquid properties
Liquids are those substances that are in a liquid aggregate state. It, in turn, is intermediate between the solid and gaseous states of aggregation. The liquid also has a property that is not found in any other state of aggregation: it is capable of changing its shape under the influence of tangential mechanical stresses within almost unlimited limits. In this case, mechanical stresses can be very small, and the volume of liquid remains unchanged.
Another important property inherent in all liquids is surface tension. Neither gases nor solids have it, but it is explained by the following reasons: due to the fact that the balance of forces acting on the surface molecules is disrupted, a certain new resultant force appears, directed into the substance. This is precisely what explains the fact that the surface of a liquid is always “tensioned”. If we consider this situation from the point of view of physics, then it can be argued that surface tension is nothing more than the force due to which the molecules of a liquid do not move from its surface to the deep layers. It is the force of surface tension that explains the shape of falling drops of any liquid.
Industrial treatment and wastewater disposal K3
Sewerage K3, used for the removal of industrial waste, is called industrial. Unlike household water, it also contains the necessary treatment facilities. All process wastewater can be divided into two groups: lightly contaminated, which does not require treatment, and contaminated, which cannot be discharged into water bodies without preliminary treatment.
Sewage diagram k3
Since technological waste can have various inclusions, depending on the type of production, they may contain salts of heavy metals, phenols, toxic substances, etc. The presence of such inclusions determines the use of different structures of engineering communications. Such a structure may consist of:
- Plumbing receivers for drains.
- Diversion structures of industrial buildings.
- Treatment facilities.
- Transfer pumping unit.
- Release to the utility network.
When organizing this type of wastewater disposal, special attention is paid to treatment facilities. Depending on the degree and type of contamination, whole blocks or individual elements can be used
Wastewater treatment is regulated by regulatory technical documents.
Testing wastewater for the content of harmful substances and determining the permissible concentration is regulated by GOST requirements.
The sewerage system is a complex set of engineering equipment, including, in addition to plumbing fixtures, powerful pumping units and modern cleaning devices. Properly arranged water supply and wastewater disposal improve the environmental situation of populated areas.
Not only wastewater from industrial enterprises, but even domestic sewage from an ordinary country house must be thoroughly cleaned. Wastewater from even such a small facility can seriously harm the surrounding environment if it is not properly treated before being discharged into open water bodies or ground. Not so long ago, cesspools were built to collect sewage from a private house or cottage. But recently they are practically not used due to non-compliance with sanitary standards. Now wastewater is collected in special facilities, where, after careful processing, it is 95-99% purified and can be freely discharged into water bodies or soil. In our article we will look at how domestic wastewater is treated.
To begin with, it is worth understanding the composition and characteristics of domestic sewage wastewater. This is the name of the water that was used in households. needs or in production. In addition, wastewater includes atmospheric waters that are collected from the surface of the earth.
For the correct selection of household cleaning technology. and industrial wastewater, you need to know the nature of the pollution. Thus, there are three types of wastewater pollution:
- Pollutants of mineral origin. This includes all inorganic impurities, for example, soil particles, salts of various origins, as well as various inorganic chemical elements and compounds. Such pollutants can be present both in domestic wastewater and in wastewater received from industrial enterprises.
- Organic pollutants are present in large quantities in households. drains. This includes complex elements of animal and plant origin. Also included in this group of pollutants are various chemical and polymeric organic compounds. As for household sewage wastewater, 80-90 percent of it consists of impurities of organic origin. As part of the household In wastewater, such pollutants are present in the form of fecal matter, food debris, and peelings from vegetables and fruits.
- Biological pollutants are various microorganisms that live in wastewater and feed on the elements contained in the effluent. So, bacteria, fungi, viruses live in large quantities in sewage, there are helminth eggs and other protozoa.
Literature
- Sewerage // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
- Sewerage // : / ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969-1978.
- Water Dictionary. - M., 1974
- SNiP 2.04.01-85* - Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings;
- SNiP 2.04.02-84 - Water supply. External networks and structures;
- SNiP 2.04.03-85 - Sewerage. External networks and structures;
- STO 02494733 5.2-01-2006 - Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings;
- S. V. Yakovlev, Yu. M. Laskov.
Sewerage (water disposal and wastewater treatment). 7th ed. - M.: Stroyizdat, 1987. - G. S. Safarov, V. F. Veklich, A. P. Medved, I. D. Yudovsky
New technology in housing and communal services - Kiev: Budivelnik, 1988. - 128, p. : il; 17 cm. - Bibliography: p. 124-129 (68 titles). — 3000 copies. — ISBN 5-7705-0097-2
Gravity sewer systems
The most popular type of sewer system for self-organization is gravity sewerage, in which wastewater, under the influence of gravity, moves into a sump through pipes laid at a certain slope.
The advantages of such a sewerage system are its low cost, ease of maintenance and independence from external energy sources, and the only disadvantage is that the sump must be located at a limited distance from the drains.
Owners of houses connected to a centralized sewer system do not need to independently maintain the sewer systems, but they should pay their bills for sewer use up-to-date, otherwise they may face such a problem as turning off the sewer system for non-payers.
When creating an autonomous sewer system, everything is much more complicated.
The first step is to decide on the type of sewer system, wisely weighing all the pros and cons of various systems.
For example, when choosing the type of autonomous sewage system, many people prefer a cheaper and easier-to-equip cesspool, rejecting the option of installing a modern system with wastewater treatment as expensive and difficult to install, without taking into account that the service life of the cesspool is noticeably shorter.
The construction of a system with treatment facilities requires at the initial stage certain costs for the hydraulic calculation of the sewer network, materials for installing the system, and wages for specialists installing the sewer system, but much less trouble arises during the operation phase.
The undoubted advantages of modern sewer systems over the same cesspools also include the absence of an unpleasant odor and a negative impact on the environmental installation,
In addition, simpler sewer systems require more financial investment in maintenance and repair.
Just to remove waste from the cesspool, you will have to call sewer trucks at least twice a month, whereas a conventional septic tank only requires annual cleaning of the chambers, and installations that carry out complete biological treatment of wastewater require even lower maintenance costs, since only replacement of the filter membrane is required once every 2-3 years.
All this allows modern sewer systems to recoup installation costs during the operation phase due to low maintenance costs.
Before you start building a country house, country house or cottage, you should study in detail the various types of sewage systems in order to have an idea of their advantages and disadvantages, and then choose the most suitable option, taking into account all sorts of factors, from the area in which construction is taking place to the amount , which can be spent on sewerage installations.
The internal sewer network (Fig. 10.1) includes waste liquid collection devices installed in apartments (baths, washbasins, toilets, sinks), outlet pipelines, sewer risers, outlets to external networks located in the basement or underground. In industrial-type buildings of prefabricated housing construction, sanitary-technical cabins of separate and combined types of factory production are used to place sanitary facilities. Schemes for the location of sanitary fixtures, water supply, gas and ventilation devices have been developed.
The internal system includes devices for cleaning the network and sewerage. All receiving devices in bathrooms and kitchens are equipped with hydraulic valves, which are called siphons. The siphon is a curved channel filled with water to a height of 60 mm, closing the outlet of gases. Outlet pipes from appliances are connected to risers, so it is advisable to place all wastewater receivers under each other, connecting them to one riser. The diameter of the riser is assumed to be the same over the entire height, equal to the maximum diameter of the connected outlet pipes. The risers will be placed openly near the walls or hidden in the walls or shafts. Pipes used are cast iron, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene (PVP).
On the risers on the first and last floors, as well as three floors in height, cleaning devices are provided - inspections at a height of 1 m from the floor level. To clean horizontal sections of pipes, cleaning valves are also installed. The internal sewerage system is gravity flowing with incomplete filling of the pipes. The speed of movement of wastewater through pipes must be no less than the self-cleaning speed - 0.7 m/s.
Features of the designations used
To correctly place a sewerage system in a building, it is worth, first of all, taking into account all possible nuances in the preliminary drawing. It is worth remembering that a different project should be used for each type of room. In addition, the designer must take into account other factors, including:
- building features;
- geographical location;
- number of residential and non-residential rooms;
- number of terminals for connecting drains.
Even at the design stage, a large number of nuances arise. It is to take them into account that a diagram will be required, which includes the designation of the sewerage system, and according to which subsequent installation work will be carried out.
During the design process, generally accepted symbols on water supply and sewerage drawings should be used. Such symbols are easy to understand for a master who really understands his work.
The designation of sewerage in the drawings, which is used during the design of the project, is regulated by the relevant GOSTs and SNiP rules. GOST 21.205-93 SPDS . Symbols for elements of sanitary systems. The use of any other types of images is considered unacceptable.
According to localization, domestic sewerage is divided into 2 types
- internal sewerage - includes all plumbing and pipelines installed in the building;
- external sewerage - ensures the removal of wastewater from buildings, for which a pipeline, sewage pumping stations, treatment plants and other devices are used.
The internal sewerage system receives wastewater at the point of its generation and discharges it outside the building into the external sewerage network.
Domestic wastewater includes water from toilets, showers, baths, kitchens, as well as water from washing premises. Pollution can be fecal - contaminated with organic waste and household - contaminated with household chemicals.
External sewerage is designed to transport wastewater outside populated areas or enterprises to treatment facilities. There, wastewater is neutralized and purified to the levels established by regulatory documents, after which the water is released into the reservoir without disturbing its natural state.
The sludge formed as a result of wastewater treatment is disposed of or used in the national economy, for example in the production of building materials, road surfaces or fertilizers for agricultural needs.
In a separate row there is a domestic sewage system, installed in places where there is no centralized drainage system or the inability to connect to one. As a rule, this is a suburban building or an old, non-sewered foundation in cities. The following types of domestic sewerage are used here.
1. A cesspool or drainage pit is the simplest structure, which is a pit, the walls of which are made of brick, stone or reinforced with concrete. Probably the only advantage of this type is its low cost. The main disadvantages of cesspools are: a fetid odor, which is especially noticeable when removing wastewater from the pit, as well as the penetration of potentially dangerous bacteria from wastewater into the environment and contamination of groundwater. Accumulated waste is removed using sewage disposal equipment.
2. Storage tank - a plastic, fiberglass, iron or concrete tank connected to the building’s sewer system. It receives contaminated wastewater, which is then pumped out by special machines. Unlike a cesspool, this storage tank is completely sealed and does not harm the environment.
3. A septic tank is a closed settling tank, usually consisting of three communicating sections. In each of them, wastewater is purified from certain wastes: in the first - suspended particles, in the second - organic waste. The third section is made leaky in order to remove purified water by infiltration through the ground. The deposited sediment is also removed using special equipment or manually.
4. A deep treatment station (local treatment facilities) is a complex system where water purification is carried out not only mechanically (filtration) and physical laws (separation of heavy and light fractions of pollution), but also with the help of special microorganisms, for which a favorable environment is created. . It is, without a doubt, the best option for autonomous sewerage on the site, but requires significant financial costs. Therefore, this type of domestic sewage system is used to service several buildings or even an entire settlement.
For the high-quality functioning of any type of domestic sewage system, periodic cleaning of its elements is required: pipes and valves, pumps and tanks, checking automated control systems, replacing filter materials, etc. In order to prevent emergency situations and save material resources, it is necessary to carry out regular preventive maintenance - the only effective method of maintaining the working condition of the domestic sewage system.
offers a full range of sewer system maintenance services. Prices for the services offered can be viewed in our basic Price List.
General provisions
In high-volume manufacturing, each part is manufactured to a predetermined degree of precision. It is almost impossible to make them with completely identical characteristics. Therefore, a harmonious system of permitted changes in real accuracy classes is provided.
In metalworking technology, tolerance is the value established by the standard by which it is allowed to change the processing accuracy.
Each parameter is indicated on the drawing. The specified tolerance size reflects the numerical characteristics of the permitted gap and its location on the product. According to the rules, the placement of the area to which the tolerance relates is oriented relative to the so-called zero line. For this indicator, tolerances are:
- symmetrical and asymmetrical (allowed deviation is allowed on one or both sides relative to the selected zero line);
- above or below a given normal;
- with a given amount of displacement in the required direction.
Fit is a parameter that indicates the acceptable accuracy when connecting individual parts into a single unit. It is set by the established gaps or interference.
They are divided into three approved types:
- a predetermined gap;
- permissible interference;
- transitional type.
In all cases, the fit tolerance is considered to be the value that is calculated as the difference between the largest and smallest value of the permissible gap. The entire existing system is classified according to the following criteria:
- the bases of the system are the tolerances of holes and shafts;
- accuracy classes (they are divided into 19 qualifications);
- the magnitude of the prescribed interference.
Tolerances for holes are understood as a set of permitted values with the same qualifications. For them, maximum permissible hole sizes are established. Variation in the size of the landings is achieved by changing the maximum dimensions of the shaft. In the shaft system, the listed parameters change in the reverse order. The maximum shaft size remains constant for different fits, but the maximum hole dimensions change.
In the system of tolerances and landings, qualification numbers are indicators of processing accuracy. As the serial number increases, the size tolerance increases. All sizes are divided into a certain number of intervals. The size of each interval is three millimeters. The ruler of these intervals starts with a size from 1 to 3 mm, then from 3 to 6 mm and so on. Each interval has its own average geometric size and designation. It is determined by the boundaries of the interval. Qualifications from fifth to seventeenth are defined for them. The lower the quality number, the more accurate the processing is.
All calculated parameters are summarized in tables. The main documents that systematize these indicators and the rules for their designation are:
- ESDP stands for a unified system of admissions and landings - established by GOST 25347-82;
- NDCs are enshrined in standard 25346-89 (the basic standards of interchangeability establish the possibility of replacing some products with similar ones);
- ESKD unified system of design documentation combines all requirements for the design of documents and markings - it is set out in detail in standard 2.001-2013;
- Standards of various levels and purposes: government departmental, industry;
- Technical specifications (used as standards for the manufacture of highly specialized parts).
Download GOST 25346-89
Download GOST 25347-82
Download GOST 2.001-2013
ESDP is used to regulate all parameters. ONV allows you to accurately determine gaps in parts of complex configurations. For example, keyed or splined connections, threads, gears, and so on.
Each size must be indicated in each of the documentation:
- on all types of drawings;
- design sketches;
- technological maps;
- additional graphic images (explanatory notes, sketches).
Correctly selected deviation parameters form the basis of technological processes. Constant adherence to approved standards allows us to develop and manufacture a reliable and durable unit.
Check out our coated interior gutters
The internal drainage system is designed to drain atmospheric precipitation through a network of pipelines through the building into a storm drain (city drain). The internal drain consists of drainage funnels, pipelines, outlets, devices for cleaning and inspecting the network through audits.
Drainage funnels are installed in low areas of roofs, one or two per section of a residential building, in tray roofing panels. The number of funnels on the roofs of other buildings is calculated from the condition that there is one funnel per 250...500 m2 of roof area. A minimum slope of 0.025 is provided to the funnels due to a constructive solution or a screed made of cement-sand mortar.
Internal drainage risers are installed from cast iron free-flow pipes in buildings up to three floors high, from cast iron pressure pipes - in buildings over three floors. Drainage risers can also be made of steel, asbestos-cement and plastic pipes with appropriate justification. The minimum diameter of drainage pipes is 50 mm. They are laid along building structures, hidden or open.
Life is impossible without water. Water supply systems for settlements and individual buildings can be called methods of ensuring life support. And drainage is an integral part of them.
All plumbing fixtures and pipes that are used to remove human waste and recycled water form an internal sewer system. According to the network, it is limited by the walls of buildings, exits up to the first inspection well. Typically, wastewater is discharged by gravity, but, if necessary, pumps are used for transfer.
Building sewerage includes the following types:
- Household – K1.
- Industrial - K3.
- Stormwater (includes drains from the roofs of houses) - K2.
- United – K1+K3.
Shape tolerances
This type of permitted deviation is caused by processing inaccuracies that occur due to the actual capabilities of the processing equipment.
These include:
- straightforwardness;
- planes;
- mismatch of the circle shape (these include: roundness; ovality tolerance);
- change in the shape of a cylinder - cylindricity tolerance.
The first category includes the following deviations:
- the shape of the processed surface (the planar pattern is disrupted, the radius of the machined shaft changes, the geometry of figures with flat edges is disrupted);
- the parallelism and perpendicular arrangement of surfaces between each other or adjacent parts is disrupted;
- different roughness appears along the length, cross-section, and circumference.
The parameter values are assessed by comparing the nominal surface (indicated in the drawing) and the real one (obtained on machines of a given accuracy class). The resulting deviations allow us to calculate the required tolerance.
A change in the radius of the finished product relative to that specified in the drawing is called a violation of roundness. To prevent possible negative consequences during operation, a roundness tolerance is introduced. When examining a part in one of the planes, the required tolerance of the longitudinal section profile is determined.
The nature of the mutual curvature of the arrangement of planes is divided into the following types:
- general parallelism (compared to a line directed along the surface);
- perpendicularity and intersection of axes (the preservation of a right angle throughout the entire surface is checked);
- tilt;
- symmetry (relative to the selected axis).
The flatness tolerance determines the amount of permitted deviation from the designated level. The main characteristic is the so-called tolerance zone. It is designated in a selected area, which is located between planes for which strict parallelism parameters must be observed. The distance to the surface is determined by existing standards. Monitoring the deviation of these parameters from those specified in the drawing is indicated on the profilogram.
Storm sewer K2
To remove rainwater, a storm drainage system is installed - K2. It represents a plumbing system of funnels, gutters, pipes, filters for purifying wastewater from sand. Open type structures are most often used. Drainage is carried out using open gutters or channels.
Sewage scheme K2
They transport water flows to the underground part of the complex. For drainage, PVC pipes are used, including corrugated pipes with a smooth inner surface, and asbestos-cement pipes.
Properly arranged and designed in accordance with technical regulations, K2 sewerage will protect the building from subsidence and cracking of walls. Upon completion of installation, the system must be tested by an organization that has the appropriate license.
Additional signs and explanations
With the help of topographical surveys, all the nuances of the area are displayed on paper: from natural caves to completely man-made gas stations, so to complete the picture, graphic elements are combined with letter ones. Decoding a topographic survey is considered objective only if all the elements “signs plus letters” are taken into account. Some elements, such as the designation of wells on a topographic survey, can be presented in several versions.
Letter symbols on topographic surveys often give schematic images a new meaning, for example, an ordinary rectangle will simply indicate non-scale residential buildings - only complete with letter explanations does the map make sense. So, the designation on the topographic survey TP inside this rectangle will mean that the building is a transformer substation.