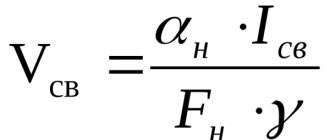Direct and reverse polarity of DC welding units allows you to adjust the temperature on the electrodes and workpieces. If a plus is connected, the anode thermal spot will heat up to 3900 °C. When connecting a minus, this indicator with the cathode point will be equal to 3200 °C. For welding different metals, this difference is significant.
When welding, direct or reverse polarity is used.
What does welding polarity affect?
Working with rutile electrodes is possible in both types of polarity. The manufacturer recommends cooking analogues of the UONI type at minus. The heating of the part depends on the welding polarity.
With direct feeding, the workpiece heats up more, allowing the seam section to be made deeper.
With reverse polarity, the element being processed heats up less, and the temperature is concentrated at the end of the electrode. The second mode is focused on processing thin metal and products sensitive to overheating.
Features of forward and reverse welding
The direct polar method is designed for:
- rolling installation from special steels using fusion method;
- non-consumable tungsten welding using surfacing wire;
- working with fluid materials;
- cutting workpieces using welding fixtures.
The thermal balance of the arc determines the nature of the distribution of thermal power.
If you accidentally change the pole, the working process with direct current will be delayed, the seam will become wide, and the rate of burning of consumables will increase.
Reverse polarity is appropriate for carefully welding the workpiece, without allowing burns. This method is used for processing non-ferrous metals during flux welding.
Connection differences
The difference in connection is due to the polar redistribution of the workpiece and the electrode holder. With the direct method, electrons move to the workpiece, and a minus tends to the electrode end. The arc is characterized by increased compactness and density. On the “return” the plus goes to the holder, the place of contact of the thermal spot with the metal is scattered.
The method of connecting the poles is determined by the physical parameters and thickness of the part.
Dependence on the type of voltage
If you cook on alternating current, the arc goes out and flares up when the sine wave passes zero. At high-frequency voltage this change is visually invisible. The type of current determines arc constancy. On a machine with a constant indicator, welding capabilities are expanded, since you can change the direction of electron movement and arc density. This will affect the connecting force.
We recommend reading: How to weld a car with your own hands
The influence of the type and polarity of the current is explained by the release of different amounts of heat.
On alternating voltage generators, the cable is connected in any configuration. The type of current should be taken into account when selecting electrodes. The recommended parameters are indicated on the box or in the instructions for consumables. It is more practical to work with universal elements designed for the possibility of changing poles.
Let's start cooking
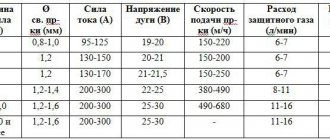
First we set the correct current strength on the inverter. We remember that in inverter technologies, alternating current welding is the main type. The strength of the welding current depends on the composition of the electrode and the diameter of its tip, the position of the workpieces during welding and the type of seam in the planned joint.
All these dependencies can be found in the comprehensive instructions for the device itself and in the inserts in packs of electrodes. Theoretically, the welding current can be selected according to the diameter of the electrode rod: for each millimeter of diameter there should be about 30 A.
We find a comfortable and stable position, put on a mask and begin work with the elbow abducted. It is better to wrap the forearm with a cable. If this is not done, your hand may get tired during welding, and the cable will begin to dangle, which will negatively affect the quality of the weld.
Direction of electrode movement for a novice welder.
For debut work, it is better to choose metal blanks that are not the smallest size - more than 20 cm, this will be more convenient. As beginners usually do: put on a mask, ignite an electric arc and immediately, with one breath, pass the workpiece along the entire length of the seam.
If your part is short and you weld it in one breath, you may develop the unnecessary habit of welding the seam in one breath. Therefore, train on long parts with proper breathing.
Now about the arrangement of objects during work. It is better to place the workpieces on a work table - a horizontal surface. The electrode in the holder should be at right angles to the table plane, then the angle of inclination should be approximately 30°.
Now you need to ignite the arc to move along the planned weld.
Welding can be done at a backward angle, in which case a 30° tilt goes in the direction of the seam. If the angle is forward, the electrode tilts in the opposite direction from the seam. The electrode should be held approximately like a pencil - at a height of 2 mm from the surface of the workpiece.
It must be remembered that when burning, the electrode shortens, so the distance above the surface must be constantly monitored.
Differences when working with an inverter and a semi-automatic device
The thermal regime of the electrode tip during welding (direct current) is affected by polarity. With a positive connection the figure reaches almost 4,000 g, with a negative connection it is 1000 g less. Using direct and reverse polarity when welding with an inverter, you can more accurately adjust the work process. In the second case, consumables burn out faster.
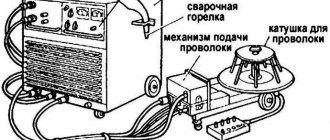
A feature of semi-automatic welding is the presence of a wire additive that is fed evenly. The seams are even and neat due to the uniform heating of the metals. The work process is facilitated by the built-in electronic type converter. Direct terminal aggregation is suitable for standard cored wire.
Direct current of reverse polarity on a semi-automatic device is used to ionize shielding gas and flux additives.
Why are electrodes calcined?
This is done for only one purpose, to remove moisture. When welding with a raw electrode, welding seam defects may occur. Such an electrode will stick to the part all the time.
Every construction company must install equipment that pierces electrodes. This operation is not available to amateur welders.
If you started working with a new pack, but were unable to use it up completely, the remaining number of electrodes should be hidden in a dry and warm place. Never store electrodes in the basement or attic. They will quickly become damp and unusable.
Features of welding work
When welding with direct current of reverse polarity, good heating of the part is achieved, obtaining a kind of melting bath. Its quality is influenced by the type of polarity. If the current is too high, the heating will be greater, the product will heat up to the point of repulsion from the electric arc, which will prevent the connection. An underestimated indicator is also ineffective, since there will not be the required thermal regime.
When performing welding work, the main attention is paid to connecting the parts being joined.
With straight polarity
Nuances of welding equipment operation:
- Metal flows into the bathtub from consumables drop by drop. This creates spattering of the product and increases the melting coefficient.
- An unstable electric arc occurs.
- There is a decrease in welding on one part, and on the other, the carbon content decreases.
- Proper heating of the part is ensured.
- The additive heats up less.
- When processing flux materials, deposition efficiency increases.
When welded with straight polarity, ferrous metal in the weld cavity contains almost no carbon and is saturated with silicon and manganese.
With reverse polarity
The difference between a negative connection is that the electrode is exposed to increased temperature.
We recommend reading Features of welding mixtures and their use
To level out the likelihood of burnout and improve the quality of welding, you need to remember the following features:
- Reducing the current potential if it is necessary to reduce the thermal regime on the workpiece.
- Initial application of a partial seam with short sections moving to the center, further returning to joining on the other side, final processing of intermediate zones. This causes a reduction in material warping.
- Welding thin parts with regular interruption of the arc.
- The interlocking of materials by pressing them tightly together. Clamps or additional weight are suitable for this purpose.
- Butt welding with minimal gap.
- Connecting thin material with uneven edges using a copper or steel plate that serves to absorb heat.
Reverse polarity is selected when working with thin-walled parts.
How butt seams are welded
If the edges are not beveled, the bead applied should have a slight flare on each side of the joint. To prevent lack of penetration, it is necessary to create a uniform distribution of molten metal.
Only the correct setting of the current and the competent selection of electrodes will allow for good welding of 6 mm metal if the parts do not have beveled edges. The current value is selected experimentally. Why are several test strips welded?
If the parts have V-shaped bevels, the butt weld can be a single layer or have multiple layers. The main role in this issue is played by the thickness of the metal.
When one layer is welded, the arc should be excited at point “A”, at the bevel boundary, according to Figure 67a. After which the electrode is lowered down. The root of the seam is completely boiled, then the arc is sent to the next edge.
When the electrode moves along the bevels, its movement is specially slowed down to ensure good penetration. At the root of the seam, on the contrary, they speed up the movement to prevent a through burn.
On the reverse side of the welding joint, professionals advise applying an additional weld seam.
In some cases, a 2-3 mm steel lining is mounted on the opposite side of the seam. To do this, increase the welding current by about 20–30% relative to the standard value. In this case, through penetration is completely excluded.
When the weld bead is created, the steel backing is also welded. If it does not interfere with the design of the product, it is left. When welding very important structures, the opposite side of the root of the weld is welded.
If you need to weld a multilayer butt seam, the root of the seam is welded first. For this purpose, electrodes with a diameter of 4–5 millimeters are used. Then the next layers are surfaced with expanded beads, for which large-sized electrodes are used (See Figures 67, b, c).
Advantages and disadvantages of different methods
Knowing what direct and reverse polarity are when welding, you need to take into account the advantages and disadvantages of both methods. This will allow you to change the connection of the terminals and achieve better results.
Advantages of direct polarity over the reverse method:
- obtaining a narrow seam bead;
- deep welding of the part;
- presence of a stable electric arc;
- a wide range of consumables with different types of coatings.
Flaws:
- metal splashing;
- increased risk of burning through workpieces;
- the appearance of residual stress in places of heat treatment.
The advantage of direct polarity is deep welding of the part.
The advantage of negative polarity is that the circuit is suitable for accurate processing of thin and special alloys.
The disadvantages include:
- the need to use electrodes that are resistant to overheating;
- shallow depth of the suture bead;
- maintaining a short arc.
How rollers are made
The electrode is inserted into the holder. To cause a current to appear in the melting area, it is enough to scratch the surface of the metal with the tip of the electrode, or simply knock several times on the workpiece.
When an electric arc appears, the electrode is directed to the workpiece, maintaining a constant gap between the metal surface and the electric arc. The gap should have a constant value and be in the range of 3–5 millimeters.
Important! To obtain a high-quality seam, it is necessary to maintain the same arc length at all times. If you change this value, the arc may be interrupted and the seam will have many defects.
The direction of the electrode is made at a certain angle relative to the plane of the workpiece. The most optimal angle is considered to be 70 degrees. The inclination does not have a specific value, the main thing is that the welder is comfortable. During the work process, the welder himself finds the optimal position for himself, depending on the specificity of the work being performed.
During such practical exercises, you need to learn how to correctly select the current strength so that the supply remains stable all the time. If there is not enough current, the arc will constantly go out. With a very powerful flow, metal penetration will begin. Only through experimentation can you learn how to correctly set the welding mode.
What criteria should you use to choose polarity?
When choosing the type of connection for a welding machine, you need to pay attention to a number of important criteria. This will prevent defects or excessive consumption of materials and ensure the required strength of the connection.
Sheet metal thickness
Parts whose thickness does not exceed 3 mm are often burned through. To weld such workpieces, a reverse-polar scheme is used, providing an anode thermal spot at the edge of the electrode. This approach is appropriate when processing non-ferrous, alloyed materials.
We recommend reading What is GOST 16037-80
Types of metals
The positive terminal is responsible for the final heating of the products and the holder. The cathode generates less heat than the anode. When machining refractory steels, it is better to use direct connection when the temperature reaches 4000 °C. For metals that change characteristics when overheated, connect the negative terminal. With direct-polar processing, the seam deepens; with “reverse” processing, it concentrates on the surface.
Types of electrodes
When choosing the brand of electrodes, take into account the type of current. Any variety is suitable for alternating voltage, since polarity does not play any role in this case. For varieties OK, OZS, MR, reverse connection is recommended. UONII and similar modifications are designed for a direct circuit. Manufacturers' recommendations are indicated on the packaging. Many welders prefer universal analogs to other options.