Welding methods
The classification of welding methods is regulated by GOST 19521 and provides for three main methods based on energy:
- Thermal.
- Thermomechanical.
- Mechanical.
The thermal method includes types of welding that involve joining parts by melting, which also involves the use of thermal types of energy, such as arc and gas. The thermomechanical method includes types of welding in which thermal energy is used in combination with pressure: electric contact, diffusion, gas press.
The mechanical method involves types of welding that are carried out using pressure and mechanical forces: cold welding, ultrasonic, explosion and friction welding. Cold welding is divided into spot, seam, and butt welding.
The degree of mechanization distinguishes between manual, semi-automatic, and automatic methods of the welding process. Each welding method has its own characteristics, so a special technological document is drawn up for a certain type of work.
Definition of the welding process
Various technologies are used to join parts in industry and construction. Welding holds the leading position. It is widely used in mechanical engineering and other industries, during construction and repair work. This popularity can be explained by the high reliability of the resulting structures and their strength. The technology is cost-effective and has high productivity.
Welding is a technological process that results in the formation of permanent joints of materials. Sometimes the concept is mistakenly attributed only to the technology of connecting metal elements. In fact, various types of welding make it possible to reliably fasten not only metal, but also glass, graphite, ceramics, and plastic. The connection occurs under the influence of temperature at the interatomic level, as a result of deformation, or by a combination of two methods.
At the physical level, during welding, the atoms and molecules of the surfaces being joined form strong bonds. For such connections to occur, certain conditions must be met:
- the surfaces to be welded must be cleaned of dirt, oxides, and foreign atoms;
- to facilitate the interaction of atoms with each other, their energy activation must occur;
- The workpieces to be welded must be placed at a distance that could be compared with the interatomic distance in the elements.
During the cooling process, a weld seam is formed at the joint.
What is a technological map
A welding flow chart is a design document, essentially a detailed step-by-step instruction manual for a welder tasked with joining metal parts using this method.
The welding map is drawn up by the process engineer, signed by him and subject to approval by the chief engineer.
The welder is issued a welding flow chart for the correct implementation of the work ahead of him. The technological map of welding works is a kind of collection of instructions on how, in what order and with the help of what equipment it is necessary to connect metal parts to each other and how to control the quality of the resulting connection.
There are many types of joining metal parts by welding. Each specific case has its own characteristics. Therefore, even the most experienced welder must understand the nuances of the work ahead of him before starting work. A technical map for welding metal structures, which is an integral document included in the general set of all necessary equipment, can provide invaluable assistance in this regard.
Only those welders who have passed certification can be allowed to work, having proven, among other things, the ability to competently understand technological maps and use them. The presence of this document is a kind of prevention of injuries and burns to the welder, since it describes in detail the safety rules that must be followed when carrying out such a complex process as welding.
A technological map for welding metal structures is drawn up and used when carrying out work at a professional level. The form and rules according to which the technological map for welding metal structures is filled out are regulated by GOST 3.1705-81.
Classification of welding types
Welding technology is constantly improving and becoming more diverse. Today there are about 20 types of metal welding, which are classified into three groups:
- Pressure welding is carried out by the application of mechanical energy, when bonds between crystals are obtained by plastic deformation of the material. As a result, the metal begins to flow, moving along the joining line of the parts, taking with it a layer of contaminated impurities. The process of deforming and joining surfaces without preheating is called cold welding for metal. In this case, interatomic bonds are formed, which leads to tight joining of parts.
- Fusion welding is carried out by joining products without applying pressure. Heat sources for such metal welding are gas flame, electric arc, and beam energy. When welding, the surfaces heat up and melt, forming interatomic bonds between the two metals and the electrode, combining into a common weld pool. After cooling and hardening of the composition, a continuous cast seam is formed.
- Thermo-mechanical welding of metal is carried out using heat and pressure. The joint of the material is first heated and then pressed. Heating the part gives it the necessary plasticity, and mechanical action combines the parts of the product into a monolithic connection.
Why do you need a technical map?
The welding process consists of many steps, which are not easy to remember even for an experienced welder. In addition, although there are general recommendations, each connection of metal parts made using the welding process has its own nuances.
A technological map for welding work provides significant assistance. Before starting the process, the welder must familiarize himself with the welding data sheet. The presence of this document is of particular importance during critical welding work. These types include, for example, a technological map for welding pipelines.
It is also of great importance to have such guidance material as a technological map of assembly and welding work when performing complex installation work of large structures and similar tasks.
At the same time, the welder will have a complete picture of the work ahead of him, the stages and transitions between them. He will have an idea of how to control the resulting welded joint and what equipment needs to be prepared for this. Having a welding process map will improve the quality of the work performed and get a good result.
In addition to the welder, the welding technical map can be used by workers whose responsibilities include monitoring the resulting welded joints.
The presence of a technical map for welding work allows you to increase the productivity and efficiency of the welder when assembling various metal parts in this way, so its importance cannot be overestimated.
Gas welding technology
This type of welding work allows you to connect various metal structures not only in industrial enterprises, but also in domestic conditions. The technology of metal welding is not very complicated; during combustion, the gas mixture melts the edges of the surface, which are filled with filler wire. When cooled, the seam crystallizes and creates a strong and reliable connection of materials.
Gas welding has many positive aspects:
- Ability to connect different parts offline. Moreover, this work does not require a powerful source of energy.
- Simple and reliable gas welding equipment is easy to transport.
- The ability to carry out an adjustable welding process, as it is easy to manually change the angle of the fire and the speed of heating the surface.
But there are also disadvantages to using such equipment:
- The heating area has a large area, which negatively affects neighboring elements of the part.
- Lack of ability to automate the welding process.
- The need to strictly adhere to safety measures. Working with a gas mixture has a high degree of explosion hazard.
- The thickness of the metal for a high-quality connection should be no more than 5 mm.
What data is indicated on the card?
The technological map describes in detail the technical process for welding metal structures.
The information indicated in the technological map includes:
- Information about the main materials that make up the parts being welded.
- Type of welding.
- Equipment used.
- Parameters that should be set on the equipment used.
- Temperature regime.
- Ways to prepare for the process.
- Fixation of products.
- The sequence in which the weld should be formed.
- Standards used.
- Safety regulations.
- Methods for monitoring the resulting connection.
In addition to the listed items, any additional items may be added to the welding chart at the discretion of the process engineer or customer.
When drawing up a contract, customers can put forward their requirements, for example, regarding the timing of the process or monitoring of the resulting connections.
The description of the material of the parts being welded is one of the most important points of the technological map for welding work on metal structures. It must contain information about the grade of metal of the parts being welded, their parameters and characteristics, the steel group, and information about how the edges of the parts should be cut.
The development of a technological map begins with an analysis of the parts to be welded and the selection of a welding method depending on the conditions under which it will be performed. According to calculations and instructions from regulatory materials, the welding mode, number of passes and other characteristics are selected.
Each card is assigned its own identification number. It is indicated in the technical documentation, as well as specifications. All technological maps are stored in the department of the chief technologist. They are given to the welder before starting work. Failure to comply with the recommendations specified in the card may result in a poor-quality connection of products, which can lead to destruction of the structure.
What items are present?
The technological map must contain the following information:
- Everything related to the base material of the surfaces: metal grade, parameters and chemical characteristics, steel group, data on cutting and cleaning of edges. This is the most important point of the TC. The main task of the master to minimize the risk of making a mistake is to correctly determine the type of working material. All other points of the instructions depend on this.
- Method and type of welding, parameters for installation.
- Welding equipment used.
- Temperature conditions.
- The sequence of formation of welding seams.
- Regulatory documentation for welding (NTD).
Any items can be included in the TC at the discretion of the organization or the customer.
Customer requirements
The organization or individual on whose order the work is being carried out puts forward demands for exact deadlines for completion. They are prescribed as a separate paragraph in the Labor Code after approval. The customer determines wishes for assessing the conformity of welded structures after quality control.
Work order
To optimize production, a standard algorithm of actions is provided:
- Check equipment and prepare materials. Parts are cleaned of foreign elements. The heat-affected area requires special attention so that small grains do not have a negative impact on the quality of the entire product. If necessary, grind the edges with a grinding machine or manually with a file. The groove is filled with electrode metal, the gap between the edges varies depending on the brand, thickness of the parts, type of welding, etc.
- If the gap is insignificant, the connection is made without filler material - with a non-consumable electrode. The consumable electrode welding option is provided for a wider gap. Its size is directly proportional to the depth of penetration of the edges involved. The optimal groove is the X shape, which ensures the durability of the weld and minimizes the risk of deformation of the finished weld product.
- The edges are dulled by tightly compressing the parts with a vice.
- It's time to assemble. Welding elements are fixed in different ways: with bolts, fasteners, tacks, so that the place for the future seam is as convenient as possible to work with an electrode or torch.
- After all the preparatory stages, they proceed directly to welding. This is done in different ways, for example:
- manual arc - coated electrodes or non-consumable electrode;
- mechanized - with self-protecting flux-cored wire or a consumable electrode in an environment of active gases and mixtures;
- automatic – submerged;
- gas;
- termite.
We recommend reading: Types of welding stations and information about them
Equipment and equipment for movements
Tools for installing and moving welding machines are various lifting and retractable platforms with remote control, columns and carts.
Most of the columns are rotatable, making it possible to manipulate the device to rearrange the product. Used to install 2 types of automatic welding machines:
- non-self-propelled (allows only circular and circular seams);
- self-propelled (designed for circular, circular and straight seams).
Carts are used for circular and longitudinal. Depending on the design there are:
- bicycle;
- verbal;
- portal.
Work crew
A working (production) team of welders is a group of people who jointly conduct specialized labor activities in an enterprise on the basis of common responsibility and interest in the result. The creation of work teams can significantly speed up the pace of production of homogeneous products on a large scale. All management tasks are resolved by a specially created brigade council.
Welding specialists must be certified in accordance with PB 03-273-99.
The welder's workplace is organized according to the technical process. Collective provision of special clothing, protective masks and necessary assembly and welding equipment is provided.
What types of welding stations are there?
Before admission to production welded joints, the worker welds samples to confirm his qualifications.
On-site safety and health measures
Requirements for welding are set out in GOST 12.3.003 and the rules for the safe conduct of gas welding and electric welding work.
The welder may be exposed to such hazards as:
- electric shock;
- inhalation of harmful fumes;
- burn;
- ultraviolet and infrared irradiation;
- exceeding the permissible degree of noise and vibration, etc.
General requirements:
- Persons over 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, received safety instructions, completed an internship and completed a verification test may be allowed to perform electric and gas welding work.
- The welder must have qualification group II in electrical safety.
- Workers are equipped with the necessary personal protective equipment, which includes:
- canvas welder's suit;
- shoes or boots;
- canvas mittens;
- safety glasses or face shield;
- workwear for winter work.
- If you discover a danger or suspect a technical malfunction of anything, you should immediately report it to management.
- Each participant in the process must perform only the work that was assigned to him.
- Hands, shoes and clothes must be dry.
- Flammable materials must be located at a distance of at least 5 m from the welding zone, and explosive materials - at least 10 m.
- If it is necessary to work at height, you should use scaffolding or ladders with special platforms covered with fire-resistant flooring and with guardrails for protection.
- Regular inspections of equipment are carried out for possible mechanical damage and negative effects of high temperatures.
- If you have to carry out welding outdoors in conditions of precipitation, then the power sources are placed in mobile sheds. Electric shock in a production environment occurs due to a worker touching live parts of equipment under dangerous voltage:
- up to 12 V – in wet conditions;
- up to 36 V – dry.
- After welding is completed, you should carefully clean the workplace and disconnect the equipment from power consumption, and hide the cylinders in a storage room.
Quality control of welded work
The welding inspection is designed to detect defects at all stages of production. Control is carried out in accordance with design, regulatory and technological documentation and consists of:
- input and operational control;
- assessment of the implementation of work done and structures created.
Through incoming inspection, the quality of materials, equipment, tools and devices is examined for compliance with all necessary standards. The results are entered into the inventory technical condition log.
With the help of an operational check, the quality of the assembly of the welded elements and the connection itself is revealed, the size and position of gaps, joints, overlaps, and tacks are taken into account.
Compliance assessment of the finished structure is carried out as the final stage upon delivery of the facility. The requirements for it are provided for by documents that stipulate:
- methods and scope of testing activities (non-destructive and destructive testing);
- testing of the finished product;
- compliance with the quality level.
Measurements and tests carried out during inspections using non-destructive or destructive methods are carried out in specialized laboratories. The methods, in turn, must be certified in accordance with GOST R 8.563.
Introductory sheet
At the end of studying the Labor Code, each worker signs a document confirming the completion of the job description: indicates the position, puts his name, date and signature. The document acts as evidence that all people involved in production will be guided in their work by the established rules and procedures, and in case of non-compliance with the regulations, sanctions will follow.
Melting method
There are several types of welding process using the fusion method, which must be indicated in technological charts for welding metal structures:
- Manual arc.
- Gas.
- Semi-automatic.
- Automatic.
- TIG welding.
The most common is arc welding. It finds wide application both in everyday life and in industry. This type of welding process can join parts and structures made of different materials. The set of the apparatus for carrying out this process includes electrode holders, as well as a mass holder mounted on the part to be welded.
Manual arc welding is performed using electrodes consisting of a metal rod and coating, the function of which is to protect the rod and ensure the stability of the electric arc.
The assembly and manual arc welding operation sheet contains information about which electrodes can be used. There is a large selection of electrodes. With the right choice, this method can be used to weld parts made of various materials. This method allows welding in all spatial positions, as well as in hard-to-reach places. Negative aspects include low efficiency of work, low productivity, and harmful conditions. To obtain a high-quality result, this type of work can only be carried out by a welder with experience and high qualifications.
Although there are many types of electrodes, specific electrodes are used for different types of welding. There is an indication that before starting welding, the electrodes must be dried and other nuances of this process.
Manual arc welding is potentially dangerous for the welder, so much attention is paid to safety requirements.
The technological map indicates methods for preparing the edges of parts and the assembly method.
Tacks are most often specified as the assembly method.
When welding using the butt method, the shape of the bevels of the parts plays an important role in obtaining a good seam. The technological map indicates how it is recommended to make the bevel. The V-shape is used for thin sheets, and the X-shape is used for welding thicker parts.
According to the technology, the electrode along with the weld pool should be smoothly moved along the connection line at a speed that depends on the material of the parts. The recommended speed is indicated in the technological map. The basic principle is that thin parts require greater speed. For thick and massive people, a slower one would be preferable.
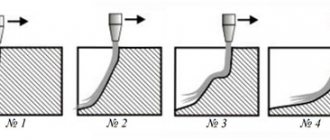
Based on the width of the seam and the depth of penetration, it is necessary to choose the method of moving the electrode - straight, zigzag, loop. When performing manual arc welding, the direction of movement of the electrode plays a significant role. You must choose one of three options: along the axis of the electrode, along the axis of the roller, across the seam.
Gas welding is also carried out by the fusion method. This uses a mixture of oxygen and flammable gas. The advantages of gas welding include the ability to weld non-ferrous metals, including very thin ones. The disadvantage is the strong heating of the part.
The type of welding in which the connection occurs due to the fact that a wire is fed into the welding zone, acting as an electrode, is semi-automatic welding. Shielding gas is supplied to the same area as the electrode, the function of which is to protect the welding site from negative environmental influences. Ferrous and non-ferrous metals can be welded in this way. Another advantage is that you can weld thin and thick parts.
This type of welding is very common. A welder of lower qualifications can also cope with the work using this method, which makes a technological map for welding metal structures especially in demand. Automatic welding differs in the equipment used.
The machines used are complex equipment, therefore, in the technological map, it is important to describe its settings, which should ensure operability. There are many types of machines, so those recommended for welding a particular joint must be indicated.
TIG welding is mainly used for welding parts made of aluminum and alloys that contain it. It can also be used to connect stainless steel parts. In this type of welding, as a rule, a tungsten electrode is used, which should be reflected in the technological map.
Mechanical welding class
The main feature of welding methods belonging to this class is the mechanical effect on the metal for the purpose of heating. The heat generated melts the metal and joins it. The methods by which welding is performed are friction, explosion, pressure, ultrasound.
5.1 Friction
The essence of the process: rotation and pressure are applied to the metal elements being welded. Friction welding technology is considered a promising development. In the process, either both workpieces or one of them can rotate, while the other is fixedly fixed.
Depending on the characteristics of the technology, the following welding is distinguished:
- Friction with stirring.
- Inertial.
- Oscillatory.
- With continuous drive.
- Radial.
- Orbital.
In all cases, the friction force heats the metal to its melting temperature, which makes welding of parts possible.
The main advantages of this method are its high quality and strength of the resulting structure, low energy consumption compared to other methods. Welding in this way can be used to join metals with different melting points. The process lends itself well to automation and is widely used for industrial purposes. Most often, such welding is used when working with rod structures and small-diameter pipes.
5.2 Cold
The use of this welding method involves connecting parts by pressure. A permanent fastening is formed when the elements are deformed and pressed into each other. The joining of parts becomes possible thanks to interatomic bonds.
Cold welding is divided into three categories:
- suture;
- butt;
- spot.
The technology is used to connect busbars, pipes or wires. To obtain a high-quality and durable connection by cold welding, it is necessary to carefully prepare the joint. The result also depends on the degree of compression and the nature of the impact - vibration or static.
5.3 Explosion
A detailed methodology for this welding method has not yet been developed; it is considered one of the rarest.
The explosion welding process begins with placing the workpiece to be welded above the base metal. Then a detonator is installed on the welded part. The most commonly used explosives are granulotol, ammonite, and hexogen.
After the explosion, the shock wave directs the moving part at high speed - it hits the bottom plate. The pressure at the point of contact significantly exceeds the strength of metals, at which they turn into a liquid state. In a fraction of a second, a molecular connection of two metal parts with a common crystal lattice occurs. That is, strong welding is ensured by synchronous plastic deformation of the two elements. In this case, diffusion occurs only in the upper layers of the metal due to the short duration of the process.
Explosion welding is used for industrial purposes to join dissimilar metals. With its help, large-sized workpieces and parts are manufactured, including bimetallic ones, and a wear-resistant layer up to 45 mm thick is applied to metal workpieces.
5.4 Ultrasonic
Ultrasonic welding is the joining of parts using ultrasonic waves. They create vibrations that bring the atoms of the workpieces being welded together to a distance that allows them to combine into a common structure. The high quality of connections makes ultrasonic welding quite popular, despite the high cost of equipment, in the production of small-sized electrical circuits and joining metals with non-metals. Welding can be used spot, contour or seam.
Before ultrasonic joining of parts, there is no need to pre-clean the surfaces, which saves time. When welding plastic elements, it is important to be able to control the temperature range to avoid overheating. Ultrasound heats the surface in a fraction of a second without emitting harmful vapors and gases.
Cherepovets Metal Structures Plant has many years of experience in the manufacture of bridge structures, canopies, decks, hydraulic structures and other metal structures. Welding and assembly takes place in compliance with technology and quality standards. Our clients receive products on time and at competitive prices.
Standard cards
To facilitate the work of process engineers, standard technological maps for welding work are drawn up - TTK. This is a document that will be developed for each type of work and technological process. It gives a general idea, and the standard welding flow sheet is not tied to a specific job.
It makes sense to develop technical specifications for welding work in mass or multi-batch production. Carrying out welding work according to a standard flow chart simplifies the entire technological process. The number of points on the map depends on the complexity of the work being performed. The standard chart describes all the main stages of the welding process.
Spot resistance welding
During this type of welding, the surfaces to be joined are located between two electrodes. Under the action of the press, the electrodes compress the parts, after which voltage is applied. Heating of the welding site occurs due to the passage of current. The diameter of the welding site completely depends on the size of the electrode contact pad.
Depending on how the electrodes are positioned in relation to the parts being joined, contact welding can be one-sided or two-sided.
There are many types of resistance welding that work on a similar principle. These include: butt welding, seam welding, capacitor welding.
Filling out the technological map
It is convenient to fill out all the columns of the document using a sample welding flow chart. The technological map must contain information about the metal of the parts being connected, their dimensions, preparatory work, and the necessary measures for cleaning surfaces.
If preheating of parts is required, this must be reported. The sequence of actions for forming a seam should be indicated, and what equipment can be used for this specific type of work. An important role is played by information about what value the current should have, as well as the voltage value, polarity, and the speed at which the welding process should take place.
The development of a welding process sheet according to the sample will facilitate and speed up this process. The welding mode will be selected not on the basis of the welder’s experience, but according to the recommendations available in the relevant regulatory documents. At the bottom of the technological map there should be the name of the developer and his signature.
Welding process map - sample filling:
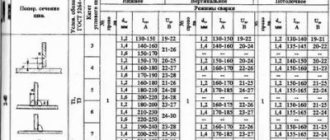
First, the object on which the welding process will be carried out is indicated. In the first column “Welding method” it is written: manual arc, gas, semi-automatic, automatic or other method. In the example given, RD(111) means “manual arc”, and in brackets is the digital code for this type of welding.
Then follows a column that should contain information about the grade of the base material from which the parts being welded are composed. This information can be found in the product design. In the column “Name (code) of NTD” enter a list of regulatory documents that must be followed during the welding process.
Then information is provided on the type of seam, its diameter and thickness, as well as the type of connection in accordance with existing regulatory documentation and the GOST applicable to it. Then there is information about the position of the seam, the type of connection, and the method of assembly. If tacks are used to securely fix the products being welded, then their number, length and height are indicated. For welding materials, the brand and standard or specifications according to which they were manufactured must be indicated.
An important column is the one where there are recommendations for choosing the equipment used, for example, a welding inverter.
An integral part of the technological map are sketches. The design, structural elements of the seam and the welding order are shown separately. The required dimensions with tolerances are indicated on the drawings.
As technological type parameters for each roller, the method by which welding should be carried out, the diameter of the electrode, the type of current and its polarity, the current strength, voltage, the speed at which the electrode should move, gas consumption and other necessary information are indicated.
Below are additional welding technology parameters:
- type of electrode, for example, tungsten;
- flux;
- shielding gas;
- method of protecting the reverse side of the seam;
- mode in which preliminary and accompanying heating is carried out;
- welding temperature;
- heat treatment mode.
Additional welding mode parameters include:
- width and thickness of the roller of one pass in millimeters;
- electrode extension in millimeters;
- the distance at which the torch nozzle should be from the workpiece being welded, in millimeters;
- vibration amplitude in millimeters;
- oscillation frequency in min-1;
- pulse mode parameter values: pulse current in amperes, pulse duration in seconds, pause current in amperes, pause duration in seconds.
Additional technological requirements for welding may include:
- Preliminary drying of the ends of parts if there is moisture on them.
- Requirements for tacks. Uniform placement of tacks for fixing products. Preliminary cleaning of tacks with a grinding wheel.
- What electrodes should be used for root weld welding and their coating.
- Grinding the root layer with an abrasive wheel.
- What electrodes should be used to weld the facing layer.
- Layer-by-layer cleaning of each layer from slag and splashes.
- Leveling rough areas of the facing layer using a grinder or file.
An important component is the methods for monitoring the resulting connection and the equipment used for this. In multi-batch production, it is necessary to indicate what percentage of products are subject to control. At the bottom of the technological map there should be signatures of the employee who developed the technological map, the one who checked the correctness of its completion, with whom the approval was carried out, with an explanation of the names and an indication of the position.
Slag welding
This type of connection is considered a fundamentally new way of producing a weld. The surfaces of the parts to be welded are covered with slag, which is heated to a temperature exceeding the melting of the wire and base metal.
At the initial stage, welding is similar to submerged arc joining. Then, after the formation of a weld pool from liquid slag, the arc stops burning. Further melting of the edges of the part is carried out due to the heat that is released when current flows. A feature of this type of metal welding is the high productivity of the process and the quality of the weld.
Welding of pipelines and steel pipes
Pipelines are structures of increased complexity, therefore, increased requirements are placed on their welding. This is reflected in the technological map for welding pipelines, as well as in the technological map for welding steel pipes.
Technological map of pipeline welding - sample:
The operational and technological map of pipeline welding contains:
- Card code.
- Construction object.
- Names and designations of regulatory documents.
- Pipeline type.
- Joining elements, for example, pipe with pipe, pipe with flange.
- Pipe characteristics: material grade, diameter, wall thickness, strength class.
- Welding modes of root and facing layers: current value, polarity.
- Welding materials.
- Preheating required.
The figure of the technological map for welding pipelines shows a sketch with the required dimensions.
At the bottom of the technological map for pipeline welding there is a section with additional requirements and recommendations.
general information
What is welding? What are the basics of welding? Many beginning craftsmen ask these questions. At its core, welding is the process of joining different metals. A connection (also called a seam) is formed at the interatomic level using heat or mechanical deformation.
The theory of metal welding is very extensive and it is impossible to describe all the nuances within one article. Just as it is impossible to describe all the methods of welding metals, since at the moment there are about a hundred methods. But we will try to briefly classify welding methods so that beginners do not get confused.
So, at the moment, thermal, thermomechanical and completely mechanical welding of parts made of metal or other materials (for example, plastic or glass) is possible. When choosing a welding method, every nuance is taken into account: the thickness of the parts, their composition, working conditions, etc. The metal welding technology depends on this.
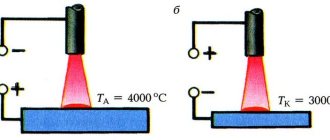
Thermal welding is the process of joining parts using only high temperatures. The metal melts and a reliable welded joint is formed. Thermal methods include, for example, arc and gas welding (we will talk about them later).
Thermo-mechanical welding is the process of joining parts using high temperatures and mechanical influence, such as pressure. Resistance welding belongs to this type. The part does not heat up as much as in the case of conventional thermal welding, and mechanical load is used to form the seam, rather than melting the metal itself.
Mechanical welding is the process of joining parts without the use of high temperatures and generally thermal energy. The key element here is mechanical action. This type includes cold welding, ultrasonic welding or friction joining of parts.
There is also a classification of welding methods according to technical characteristics. Using this classification, we can quite briefly describe all available types of welding. They are divided into:
- Welding in a protective environment (for protection, flux, inert gas, active gas, vacuum can be used, protection can be combined and consist of several materials at once).
- Intermittent and continuous welding.
- Welding: manual, mechanized, semi-automatic, automatic, robotic.
If you have never encountered welding before and everything listed above seems confusing and incomprehensible, then don’t worry. Next, we will tell you what the most popular welding methods are used in home and industrial settings.
You will be given a description of the main types of welding and some features that need to be taken into account. By the way, we have devoted separate articles to many types of welding, which you can read by opening the “Types and Methods of Welding” section on our website.
Test welded joint
In mass or multi-batch production, a connection called a control connection is made. It can be cut from existing connections or made separately from materials identical to the main one. It is easier to control such compounds and draw appropriate conclusions based on this.
The welding process map for the control welded joint is as follows:
It must indicate the base material, welding method, position of the seam, type of connection, and welding equipment used. The technological parameters of welding are indicated: diameter of the electrode or wire, current strength, voltage, time required for the process, consumption of electrodes. It is reported what method should be used to control welded products, for example, visual or radiographic.
The control connection may be subjected to destructive testing methods, which is unacceptable when testing the main connections.
Arc connection methods
Electric arc welding is carried out in three ways:
- Manual method. In this case, all connection stages are performed manually, using simple electric arc welding.
- Semi-automatic metal welding is more productive. With this method, the weld is made manually, and the filler wire is fed automatically.
- Automatic welding is carried out under the supervision of an operator, and all work is done by a welding machine.
Control
Inspection of edges and finished joints is carried out by the technical control service. For control, various methods can be used that identify the presence of defects - acceptable or subject to correction. If correction is not possible, the resulting connection is rejected.
There are many types of control methods. One of the most common is ultrasonic. Technological map of ultrasonic testing of welded joints:
The technological chart for ultrasonic testing of welds indicates such information as control parameters, the flaw detector used and preparation for testing.
Welding methods and technologies
In addition to the above traditional methods, there are other methods that allow you to join unique metals. They have pronounced properties, due to which conventional methods are not suitable for connecting them.
One such method is laser welding, which is performed using semi-automatic or automatic equipment. This method involves applying heat strictly to one point to connect very small parts.
ATTENTION: To weld several parts at once, it is recommended to use a prism, with which you can split the laser and direct it in different directions.
Manual arc welding using non-consumable electrodes
The method of manual arc welding of different metals using non-consumable electrodes is one of the most popular methods among both home craftsmen and professionals. Manual arc welding is generally one of the oldest welding methods. Thanks to a large selection of welding machines for arc welding, this method has become available to a wide range of welders.
An electrode is a rod that acts as a current conductor. It can be made of various materials and have a special coating.
The technology of arc welding with a non-consumable electrode is extremely simple: the parts are adjusted to each other, then the electrode is tapped or struck on the surface of the metal, igniting the welding arc. Welding inverters are used as the main equipment.
For welding with an inverter, non-consumable electrodes made of coal, tungsten or graphite are chosen. During welding, the electrode heats up to a high temperature, melting the metal and forming a weld pool in which the seam is formed. This method is used for welding non-ferrous metals.