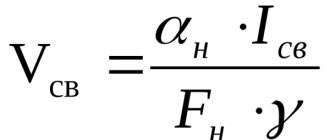- Home page
- •
- Articles on welding
- •
- How to weld with electrodes for beginners
We tell you how to properly weld metal with electrodes for beginners and what mistakes to avoid when doing so.
In the garage, at the dacha, in a private house, something has to be cooked. For such tasks it is not at all necessary to complete welding courses - it is enough to have a household welding machine, protective equipment, consumables and a little practice. We tell you how to properly weld metal with electrodes for beginners and what mistakes to avoid when doing so.
Welding machine and its capabilities
Connections of metal parts are considered the strongest and most reliable. Using welding, it is difficult to make seams unnoticed, so either additional finishing is required, or seams are made in places where aesthetics are not important. Metal products are connected under the influence of high temperatures. The electric arc used in modern devices melts. This electric welding method is most popular in the construction industry.
The optimal heating temperature is 7 thousand degrees. The electric arc works due to the current generated from the welding electrode to the electrode itself. When exposed to heat, the melt forms a weld pool. As a result, the electrode is connected to the metal. Due to the slag, a protective film is formed. As it cools, a seam will form.
Distance between electrode and workpiece
It is important at what distance to hold the electrode when welding. This affects the shape, width, and roughness of the seam. The length of the electric arc depends on this parameter. A welding arc 2-3 mm long is considered ideal.
A short distance should be chosen when thick parts are to be welded. Transverse movements become optional. A short arc is obtained when the distance from the end of the electrode to the metal surface is equal to half the diameter of the electrode. This distance increases the penetration depth. The seam width is reduced. A short arc is relevant for obtaining a vertical seam, but can also be used in other positions and all types of joints.
The average arc is equal to the diameter of the welding electrode. The seam expands significantly and the tension increases. At this welding distance, the current and penetration depth increase, and the weld width and voltage decrease. The advantage is the excellent protection of the bath. A medium arc occurs when the distance between the electrode and the metal surface is equal to or slightly greater than the diameter of the electrode.
A long arc is one and a half times the diameter of the electrode. This is not particularly desirable, since the seam becomes too wide, the penetration depth decreases, and splashes of hot metal begin to fly in all directions. Pores will form in the weld. The protection of the bath is significantly reduced.
Types of Welding Machines
There are a large number of models of welding machines of different types on the market.
Of all their diversity:
- transformers;
- rectifiers;
- inverters;
- semi-automatic;
- machine guns;
- plasma;
In a home workshop, transformers are most often used because of their low cost, and inverters because of their simplicity and ease of use. The rest require either special working conditions, achievable only in production, or special training and long-term acquisition of skills.
Transformer
The design of such devices is extremely simple - it is a powerful step-down transformer, in the secondary winding of which a working electrical circuit is connected.
Transformer welding machine
Transformer advantages:
- unpretentiousness;
- survivability;
- simplicity;
- cheapness.
Flaws
- very large weight and dimensions;
- low arc stability;
- AC operation;
- causes voltage surges in the supply network.
Such a device requires skill and extensive experience from the welder. It is not suitable for teaching a novice welder how to weld correctly.
Inverters
The inverter device has a much more complex design. The inverter unit repeatedly converts the input mains voltage, bringing its parameters to the required ones. Due to the transformation of high frequency current, the dimensions and weight of the transformer are many times smaller.
Inverter
Inverter advantages:
- low weight and dimensions;
- stabilized voltage and current in the circuit;
- additional anti-stick and hot start functions;
- possibility of precise adjustment of current and arc parameters;
- does not cause voltage surges in the supply network.
The inverter also has disadvantages:
- high price;
- low frost resistance.
It’s best to start learning how to cook properly with an inverter. The stability of the arc parameters and additional functions that make starting easier and preventing “sticking” will allow the beginner to concentrate on the seam and quickly master the technology.
Electric arc welding equipment
For electric arc welding, it is enough to have a traditional transformer machine. This is a long-known classic welding equipment. The principle of its operation is simple: the transformer lowers the voltage while increasing the current. The equipment is designed to operate with an alternating current source. But such installations have critical disadvantages: large size and weight. It is inconvenient to move both to the work site and during the welding process. To make things easier, specialists install equipment on mobile platforms. But this is of little help, since the dimensions are only increasing and the equipment is becoming less agile.
In cases where mobility and performance are required, a converter is the way out. The operation of the installation is to convert alternating household current into high frequency. After that, it transforms into a permanent one. The units are characterized by compact dimensions and low weight. The inverter is characterized by a stable electric arc, which has a positive effect on the quality of the seam. It provides the ability to work with current of direct or reverse polarity.
What types of electric welding exist?
- MMA. A simple and easy-to-use hand-held device that requires coated electrodes. Suitable for home use, inexpensive, but its use is impossible for a number of metal structures, only for stainless steel and ferrous metal.
- TIG is a technology that opens up the possibility of working with a large number of substances. The peculiarity is in the electrode that is used to create the arc, as well as in a special atmosphere of inert protective gas to obtain an even seam. The advantage is the purity of action and the power of the equipment. The downside is that special training is required, since it is difficult to learn how to properly weld with this type of electric welding.
- MIG-MAG. This is a semi-automatic device. Instead of an electrode, welding wire is automatically fed. Its use is suitable for atmospheres with inert and active gases, with various metals. Modern equipment that can be used at home. The welded joint is smooth and neat, productivity and speed of work increases. But in a garage or workshop, the installation itself along with the cylinder will take up a lot of space.
- SPOT, also known as spot welding, is used in cases where careful soldering is required and appearance is important, for example, when body repairing cars in a car service center.
Arc welding
The heat source is an electric arc that occurs between the end of the electrode and the product being welded when welding current flows as a result of the closure of the external circuit of the electric welding machine. The resistance of the electric arc is greater than the resistance of the welding electrode and wires, therefore most of the thermal energy of the electric current is released into the plasma of the electric arc. This constant flow of thermal energy keeps the plasma (electric arc) from decaying.
The released heat (including due to thermal radiation from the plasma) heats the end of the electrode and melts the welded surfaces, which leads to the formation of a weld pool - a volume of liquid metal. During the process of cooling and crystallization of the weld pool, a welded joint is formed. The main types of electric arc welding are:
- manual arc welding
- non-consumable electrode welding
- consumable electrode welding
- submerged arc welding
- electroslag welding
Manual arc welding
Manual arc welding with a consumable coated electrode is performed using a welding power source and welding electrodes. The electrode is supplied to the welding zone and moved along the joint by the welder himself. The power source can be either AC (transformer) or DC (rectifier). A welding electrode is a metal rod with a coating applied to it.
During the welding process, an electric arc burns between the workpiece and the electrode, melting them. The molten metal of the electrode and the product forms a weld pool, which, upon subsequent crystallization, forms the seam of the welded joint.
The substances that make up the coating either burn, forming a gas protection of the welding zone from the surrounding air, or melt and fall into the weld pool. Some molten coating substances interact with the metal of the weld pool, deoxidizing and/or alloying it, others form slag, which protects the weld pool from air, promotes the removal of non-metallic inclusions from the weld metal, the formation of a seam, etc.
Manual arc welding is designated by code 111 according to the GOST R ISO 4063-2010 standard; in Russian-language literature the designation RD is used, in English - SMAW (from the English shielded metal arc welding) or MMA (from the English manual metal arc welding).
Non-consumable electrode welding
Main article: Non-consumable electrode welding
Non-consumable electrode welding, in the English-language literature is known as gas tungsten arc welding (GTA welding, TGAW) or tungsten inert gas welding (TIG welding, TIGW), in the German-language literature - wolfram-inertgasschweißen (WIG).
The electrode is a rod made of graphite or tungsten, the melting point of which is higher than the temperature to which they are heated during welding. Welding is most often carried out in a shielding gas environment (argon, helium, nitrogen and their mixtures) to protect the seam and electrode from the influence of the atmosphere, as well as for stable arc burning. Welding can be carried out both without and with filler material. Metal rods, wire, and strips are used as filler material.
Gas shielded welding
Gas shielded arc welding is welding using an electric arc to melt metal and protecting the molten metal and electrode with special gases.
Applications of gas shielded welding
Widely used for the manufacture of products made of steel, non-ferrous metals and their alloys.
Advantages of gas shielded welding compared to other types of welding
- high performance,
- easily automated and mechanized,
- no need for electrode coatings or flux.
A metal wire of a certain brand is used as an electrode, to which current is supplied through a current-carrying mouthpiece. The electric arc melts the wire, and to ensure a constant arc length, the wire is fed automatically by the wire feeder.
To protect from the atmosphere, special gases are used, supplied from the welding torch along with the electrode wire. Special gases are divided into inert (argon, helium) and active (carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen). The use of a mixture of gases in some cases improves welding productivity and quality. If it is not possible to carry out semi-automatic welding in shielding gases, self-shielding wire (flux-cored) is also used. It should be noted that carbon dioxide is an active gas - at high temperatures it dissociates with the release of oxygen. The released oxygen oxidizes the metal. In this regard, it is necessary to introduce deoxidizing agents (such as manganese and silicon) into the welding wire. Another consequence of the influence of oxygen, also associated with oxidation, is a sharp decrease in surface tension, which leads, among other things, to more intense metal spattering than when welding in argon or helium.
International designation.
In English-language foreign literature it is referred to as gas metal arc welding (GMA welding, GMAW), in German-language literature - metallschutzgasschweißen (MSG). Welding in an atmosphere of inert gas (MIG) and in an atmosphere of active gas (metal active gas, MAG) are distinguished.
Submerged arc welding
In English-language foreign literature it is referred to as SAW. In this type of welding, the end of the electrode (in the form of a metal wire or rod) is fed under a layer of flux. Arc combustion occurs in a gas bubble located between the metal and the flux layer, which improves the protection of the metal from the harmful effects of the atmosphere and increases the depth of metal penetration.
Electroslag welding
The source of heat is the flux located between the products being welded, which is heated by an electric current passing through it. In this case, the heat generated by the flux melts the edges of the parts being welded and the filler wire. The method finds its application when welding vertical seams of thick-walled products.
Hyperbaric welding
Hyperbaric welding is a welding process at elevated pressures, usually carried out under water. Hyperbaric welding can take place in water or dry welding, that is, inside a specially built chamber in a dry environment. The applications of hyperbaric welding are varied - it is used to repair ships, offshore oil platforms and pipelines. Steel is the most common material for hyperbaric welding.
Orbital welding
Orbital welding is a type of friction welding or automatic arc welding (depending on whether the pipe is rotating or not). The name comes from the use of orbital welding - for welding joints of pipes, flanges, etc. It is used for welding steel pipes made of high-alloy steels or large-diameter aluminum alloys with a thick wall.
When the pipes being welded rotate coaxially, friction in the joints occurs when the axes of rotation are shifted parallel to each other. This type of welding uses friction to heat the joint. The combined action of forging pressure and heat leads to welding of the joints.
If the pipes do not rotate, then orbital welding uses welding heads that move along the joint and conduct arc welding with or without filler wire.
Gas flame welding
Acetylene-oxygen flame (temperature about 2621 °C at 2-3 mm from the core)
The source of heat is a gas flame formed by the combustion of a mixture of oxygen and combustible gas. Acetylene, MAF, propane, butane, blast gas, hydrogen, kerosene, gasoline, benzene and their mixtures can be used as flammable gas. The heat released during the combustion of a mixture of oxygen and combustible gas melts the surfaces being welded and the filler material to form a weld pool. The flame can be oxidizing, "neutral" or reducing (carburizing), this is controlled by the ratio of oxygen to combustible gas.
- A new type of fuel is used as a substitute for acetylene - liquefied gas MAF (methyl acetylene-allen fraction). MAF provides high welding speed and high quality of the weld, but requires the use of filler wire with a high content of manganese and silicon (SV08GS, SV08G2S). MAF is much safer than acetylene, 2-3 times cheaper and more convenient for transportation. Due to the high temperature of gas combustion in oxygen (2430 °C) and high heat release (20,800 kcal/m3), gas cutting using MAF is much more efficient than cutting using other gases, including acetylene.
- The use of cyanogen for gas welding is of great interest due to its very high combustion temperature (4500 °C). An obstacle to the expanded use of cyanogen for welding and cutting is its increased toxicity. On the other hand, the efficiency of cyanogen is very high and comparable to an electric arc, and therefore cyanogen represents significant prospects for further progress in the development of gas-flame processing. The flame of cyanogen with oxygen emanating from a welding torch has a sharp outline, is very inert to the metal being processed, is short and has a purplish-violet hue. The metal being processed (steel) literally “flows”, and when using cyanogen, very high speeds of welding and cutting metal are permissible.
- Significant progress in the development of gas-flame processing using liquid fuels can be achieved by the use of acetylenedinitrile and its mixtures with hydrocarbons due to the highest combustion temperature (5000 °C). Acetylenedinitrile is prone to explosive decomposition when heated strongly, but is much more stable in mixtures with hydrocarbons. Currently, the production of acetylenedinitrile is very limited and its cost is high, but with the development of production, acetylenedinitrile can very significantly develop the areas of application of gas flame processing in all its fields of application.
Thermite welding
In most cases, thermite welding is classified as a thermal class. However, there are technological processes that belong to the thermomechanical class - for example, thermite-press welding. Thermite welding is the welding of parts with molten metal formed during a chemical reaction accompanied by high temperature (a large amount of heat). The main component of this type of welding is the thermite mixture.
Plasma welding
The source of heat is a plasma jet, that is, a compressed arc produced using a plasma torch. The plasma torch can be of direct action (the arc burns between the electrode and the base metal) and indirect action (the arc burns between the electrode and the plasma torch nozzle). The plasma jet is compressed and accelerated under the influence of electromagnetic forces, exerting both thermal and gas-dynamic effects on the welded product. In addition to welding itself, this method is often used for technological operations of surfacing, spraying and cutting.
The plasma cutting process is based on the use of a direct current air-plasma arc of direct polarity (electrode - cathode, metal being cut - anode). The essence of the process is local melting and blowing of molten metal to form a cutting cavity when the cutter moves relative to the metal being cut.
Electron beam welding
The source of heat is an electron beam obtained due to thermionic emission from the cathode of an electron gun. Welding is carried out in high vacuum (10−3 - 10−4 Pa) in vacuum chambers. The technology of electron beam welding in an atmosphere of normal pressure is also known, when the electron beam leaves the vacuum region immediately in front of the parts being welded.
Electron beam welding has significant advantages:
- A high concentration of heat input into the product, which is released not only on the surface of the product, but also at some depth in the volume of the base metal. By focusing the electron beam, it is possible to obtain a heating spot with a diameter of 0.0002 ... 5 mm, which makes it possible to weld metals with a thickness from tenths of a millimeter to 200 mm in one pass. As a result, it is possible to obtain seams in which the ratio of penetration depth to width is up to 20:1 or more. It becomes possible to weld refractory metals (tungsten, tantalum, etc.), ceramics, etc. Reducing the length of the heat-affected zone reduces the likelihood of recrystallization of the base metal in this zone.
- Low amount of heat input. As a rule, to obtain an equal penetration depth in electron beam welding, it is necessary to introduce 4-5 times less heat than in arc welding. As a result, product deformation is sharply reduced.
- Lack of saturation of molten and heated metal with gases. On the contrary, in a number of cases, degassing of the weld metal and an increase in its plastic properties are observed. As a result, high quality welded joints are achieved on chemically active metals and alloys, such as niobium, zirconium, titanium, molybdenum, etc. Good quality of electron beam welding is also achieved on low-carbon, corrosion-resistant steels, copper and copper, nickel, aluminum alloys .
Disadvantages of electron beam welding:
- Possibility of formation of non-fusion and cavities at the root of the weld on metals with high thermal conductivity and welds with a large depth-to-width ratio;
- It takes a long time to create a vacuum in the working chamber after loading products.
Laser welding
The heat source is a laser beam. All types of laser systems are used. The high concentration of energy, the high speed of laser welding compared to arc methods, and the insignificant thermal effect on the heat-affected zone due to high rates of heating and cooling of the metal significantly increase the resistance of most structural materials to the formation of hot and cold cracks. This ensures high quality welded joints from materials that are difficult to weld by other welding methods.
Laser welding is performed in air or in shielding gases: argon, CO2. A vacuum, as with electron beam welding, is not needed, so large structures can be welded with a laser beam. The laser beam is easily controlled and adjusted, with the help of mirror optical systems it is easily transported and directed to places that are otherwise difficult to reach. Unlike the electron beam and electric arc, it is not affected by magnetic fields, which ensures stable formation of the seam. Due to the high concentration of energy (in a spot with a diameter of 0.1 mm or less) in the laser welding process, the volume of the weld pool is small, the width of the heat-affected zone is small, and high heating and cooling rates. This ensures high technological strength of welded joints and small deformations of welded structures.
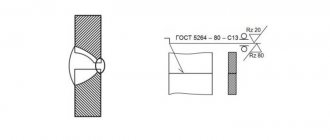
Manual arc welding
The parameters of manual electric arc welding are specified in the interstate standard GOST 5264-80 , which replaces GOST 5264-69 . It takes into account:
- connection type;
- shape of prepared edges;
- nature of the weld;
- cross-section of the seam and edges;
- thickness of welded parts.
GOST regulates maximum deviations in combinations of the above characteristics. The requirements of GOST 5264-80 do not apply to welded joints of steel pipelines; for them - GOST 16037-80.
Operating principle
The source of heating of the joint is the welding arc - concentrated radiant energy in the gap between the electrode and the workpiece. Power comes from a transformer for alternating current or a converter for direct current. From the source, power is supplied by wires to the electrode clamped in the holder and to the product. Upon contact, an arc occurs between them. The seam is formed by melting the electrode and the edge being joined.
Creating an Arc
The arc arises from heating the end of the electrode, which is the cathode in the electrical circuit. It comes into contact with the product, the circuit closes. When current passes through a contact with high resistance, a large amount of thermal energy is released. When the electrode is lifted to a distance of 1-2 millimeters, an arc is ignited and thermionic emission begins. Ignition and combustion are possible in the presence of three components:
- An electrical power source whose open circuit voltage is higher than the arc voltage.
- Ionization in the arc column.
- Reactance in the welding circuit - this increases combustion stability.
Welding arc diagram
Welding arc areas
The welding arc includes three main zones:
- Cathode – located between the arc column and the cathode surface.
- The arc column is between the cathode and anode zones.
- Anodic - consists of an anode spot and a near-electrode part. The current in it is formed by the flow of electrons from the column.
Under the influence of high voltage near the cathode, free electrons escape from its spot and fly to the anode. Due to the bombardment of electrons, the cathode is intensively heated.
Power supplies
A transformer is a power source for an electric arc . The voltage of the current supplied from the network is changed by adjusting the distance between the primary and secondary windings: proximity reduces the inductive reactance and increases the current. Removal reduces it. The winding connected to the network is primary, to the holder and the welded product is secondary.
Approximate cost of transformers. Yandex Market
Electrodes used
When welding with direct and alternating current, different electrodes are used; the first ones are marked with the letter abbreviation UONI, the second - MR. Both are coated with a special coating for welding steels:
- carbon and low-carbon structural;
- alloyed structural;
- alloyed heat-resistant;
- highly alloyed with special properties;
- for surfacing surface layers with special properties.
The thickness of the coating is directly dependent on the ratio of the diameter of the electrode to the diameter of the steel core:
- with a thin coating, ratio less than 1.20;
- with average, D/d between 1.20 and 1.45;
- with thick, D/d between 1.45 and 1.80;
- with particularly thick ones, D/d more than 1.80.
The composition of the coating is marked as follows:
- sour – A;
- cellulose – C;
- rutile - P;
- main – B;
- others - P.
Mixed coverage is marked by a combination of symbols corresponding to it.
Another marking is based on the position of the electrode in relation to the surface of the part:
- for all – 1;
- for all except vertical – 2;
- for lower, horizontal to vertical welding plane and vertical from bottom to top – 3;
- for the bottom and bottom in a boat (welded surfaces at right angles) - 4.
Approximate cost of electrodes. Yandex Market
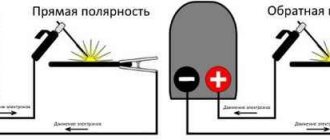
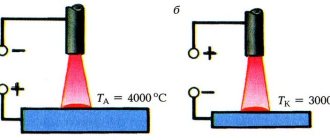
Forward and reverse polarity
Melting of the metal for welding occurs under the influence of an arc. It, as noted above, is formed between the surface of the product and the electrode, since they are connected to opposite terminals of the device.
There are two main options for welding, differing from each other in the order of connection and called direct and reverse polarity.
In the first case, the rod is connected to the minus, and the part to the plus. In this case, an increased flow of heat occurs into the metal. As a result, a deep and narrow melting zone is formed.
Direct and reverse polarity.
With reverse polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive, and the product to the negative. In this case, the melting zone is wide and shallow.
The choice of polarity is entirely determined by the product you are working with. Welding can be performed with two types of polarity. When choosing, you should take into account the fact that the element connected to the positive is subject to greater heating.
For example, it is difficult to weld thin metal products due to possible overheating and burning. In this case, the part is connected to the minus. Currents are also selected according to the diameter of the electrode and the thickness of the metal. This data is taken from a special table.
Welding arc areas
The arc completes the circuit between the electrode and ground. From the point of view of welding theory, there are several areas in the welding arc:
- cathode;
- anode;
- near-electrode.
The cathode is a “minus”, a source of current (recall that current is formed by moving electrons - negative particles). The anode is accordingly “plus”.
The anode region releases ions as a result of bombardment by a stream of electrons, therefore a so-called crater always forms on the anode - a concave spot, the area of which depends on the area of electron bombardment.
DC electric arc units have a fixed anode and cathode. In alternating current devices, the anode and cathode constantly change places. This causes instability of the welding arc, severe spattering of metal and other unpleasant factors, and in addition, it does not allow welding of certain metals that require special equipment.
What is the basis for the reliability of welding: the basics of welding work
Strength is due to plastic deformation, which occurs at the molecular level, because the molecules mutually penetrate into the bodies being welded. This is achieved by heating metals using a welding arc. The classic production method to date is electric arc, when an electron and current are used. But now technologies using laser and ultrasonic radiation are becoming more and more relevant. They actually leave no seam behind. The devices mainly operate on the basis of an inverter, that is, a device that creates alternating voltage.
Basic physical principle
Electric arc welding is based on not one, but two electrical principles: the phenomenon of short circuit, with which everyone who has a set of school knowledge in electricity is familiar, and the phenomenon of breakdown. This is where you should pay attention.
This refers to the breakdown of a dielectric, which occurs as a result of saturation of its interatomic space with particles carrying an electric charge. The positive charge is carried by ions, the negative charge by electrons.
Theoretically, breakdown is possible for any dielectric (under certain conditions), but in the case of electric arc welding, breakdown of the air space between the electrode and the mass (part) is specifically used.
The technological process involves creating a low-voltage, but high-power current charge on the electrode - about 80-200 A, and a huge density - up to several thousand A/cm2.
When the electrode touches a mass, that is, another material with high electrical conductivity, in the case of metal welding, a short circuit occurs, initiating a powerful electric field.
The breakdown occurs in this field. Due to saturation with charged particles, the air layer turns from a dielectric into a current conductor.
It is at this moment that the welding arc occurs, giving the name to electric arc welding. The temperature in the area of contact between the arc and the metal can reach 5000 °C.
Purchasing consumables
In addition to equipment, it is necessary to purchase consumables. The main thing is the welder’s mask, which protects his face from possible damage. An attractive option is the “Chameleon”.
The lighting is adjusted automatically, which makes it unnecessary to remove the mask during short breaks in work in order to evaluate the result of work or replace a burnt electrode. The light filter reacts by darkening to changes in the brightness of the electric arc.
In addition to the mask, you need to take care of protecting the body, hands and head by purchasing or selecting a suit, mittens and a hat. Sturdy shoes must be worn. Nothing should be left unprotected.
You will need a hammer to knock down the scale. An ordinary hammer is of little use for this, since it weighs a lot and is inconvenient for beating off slag in hard-to-reach places. A slag hammer is a very useful tool for doing DIY welding work. With its help, you can easily clean the boiled layer before applying the next one on top of it.
To securely fix the parts to be welded, you may need a vice or clamps. A metal brush will help get rid of rust before you begin the actual process.
It is necessary to ensure that there is a container of water near the welding site in case of fire.
Tools and protective equipment
Uniforms and personal protective equipment include:
- welder's mask with a built-in light filter to protect the eyes from bright light and ultraviolet radiation from the arc;
- split-leaf gloves—gaiters to protect hands from splashes of hot metal;
- thick clothing made of non-flammable fabric;
- cap under the mask;
- durable shoes.
- a respirator to protect the respiratory system from generated gases and dust, especially when working with non-ferrous metals.
Tools, materials and equipment you will need:
- Angle grinder (grinder) for cutting workpieces and cleaning seams;
- A set of hand tools - hammers, chisels, pliers, etc.;
- Metal brush for cleaning workpieces;
- Clamps and clamps for connecting workpieces;
- Electrodes.
And finally, the inverter with the included cables and holder.
Video: how to choose a welding inverter
How to learn
The easiest way to master electric arc welding is to start with a household inverter connected to a 220 V network. After you learn how to weld correctly at home, you can move on to learning more complex technologies, such as, for example, argon arc welding.
In addition to the inverter you will need:
- thick clothes with long sleeves;
- welding gloves or mittens;
- mask;
- hammer;
- chisel;
- metal brush;
- a pack of universal electrodes;
- a workpiece in the form of a piece of thick metal - best of all, ordinary steel.
It is necessary to connect the electrode to the cathode (minus) of the device using a special holder. Plus, accordingly, it is necessary to submit for procurement. All that remains is to turn on the electric arc welding machine.
The electric arc is ignited by tapping or striking the mass. After the flash, it is necessary to move the electrode away from the metal by about 5 mm. An arc will form and the metal will begin to melt.
There are two ways to guide the electrode - with an acute angle away from you and towards you. The first method is more difficult, but allows you to make a shallower seam (this is necessary when working with thin metal). The second is simpler, this is the standard method of work.
When using electric arc welding, the electrode must be moved not in a straight line, but in a zigzag motion, to create a seam similar to the lines of a sewing machine. The electrode stroke should cover both sides of the sheets being joined.
First you just need to train on a piece of steel, then move on to welding sheet metal.
Which electrodes to use
To learn how to weld with electric welding, you need to choose the right consumables. Let's pay attention to the electrical conductor. It can be in the form of wire for semi-automatic machines and is made like sticks with a metal core and winding. For beginners, we recommend taking the second one, they are easier to control. The optimal cross-section diameter is 3 mm. Less will be needed for welding thin-sheet products, more for industrial purposes and powerful equipment.
Precautionary measures
Safety precautions are of great importance in the work of a welder.
Whatever types of electric arc welding are used, the welder must work in a protective mask or have a shield.
Special clothing and shoes are used. To prevent electric shock, special dielectric mats are often used. The equipment must be grounded. The welding machine must be in good working order. Do not carry it by the hose during operation. Each welding unit has a special handle for these purposes. In the event of an emergency, the welder must know how to provide first aid to a victim. To protect the eyes of surrounding people, it is recommended to organize a fence. Collective protection measures also include the use of natural or artificial ventilation.
Step-by-step instructions for beginners
Start by preparing your work area. There should be no flammable or combustible substances nearby. The floor in the room can be concrete or earthen. It is best to weld structures outdoors or in a well-ventilated, large space. There should be fire extinguishing equipment and a first aid kit nearby. Now let's move on to the stages of learning how to learn how to weld with a welding machine.
External inspection of equipment
An external inspection of the welding inverter is carried out by the welder himself before the start of each work shift. During this procedure, the condition of the insulating sheaths of the welding and supply cables is first checked and, if necessary, they are replaced or repaired. Next, the electrode holder and the ground cable clamp are checked, as well as the condition of the plugs and sockets for connecting to the welding inverter. The next step is to inspect the welding control panel for the integrity of toggle switches, switches, buttons and indicators. In addition, the overall dust content of the device is determined and, if necessary, it is cleaned.
Machine modes and welding parameters
Experienced welders know how to weld thin metal by testing a variety of machine settings. As a result, optimal parameters were derived that are well suited for this type of work. Here are the main settings:
| Metal thickness, mm | Current strength, A | Electrode diameter, mm |
| 0.5 | 10 | 1 |
| 1 | 25-35 | 1.6 |
| 1.5 | 45-55 | 2 |
| 2 | 65 | 2 |
| 2.5 | 75 | 3 |
It is important to set the welding current lower than when working with thick plates. This will help avoid burns and leaks. Inverters that allow cooking with alternating voltage but at high frequencies, as well as direct current devices, have proven themselves to be excellent in this area.
If the unit settings allow you to set the starting voltage level, then you should take advantage of this and set a lower value (by about 20%) than the operating current. This will prevent the area from being scorched when starting to ignite the arc and will help to start welding immediately at the joint. If the starting current is not regulated, then you can ignite the electrode on a thick surface and then transfer it to the joint.
Welding thin metal involves working at low currents. To do this, the inverter settings must support the operating values of the ammeter at 10-30 A.
If the minimum adjustable value is higher than these parameters, then it is possible to reduce the current strength with additional resistance in the circuit. For this, a high-carbon steel spring is used, placed between the product and the ground cable.
Installing an additional ballast that reduces the current to the required level will also help.
If the device settings support the pulse mode, then you can use this. Especially thin steel is welded with an intermittent arc. The pulsed current will automatically break the arc, allowing the metal to cool.
How to connect the electrode
Insert it into the holder; it should not wobble. Then connect the two welding cables. They have different markings (plus and minus). A positive charge is applied to the part (using a clamp), and a negative charge to the electrical conductor. This polarity increases the heating of the metal.
In the article we told you how to learn how to weld from scratch yourself.
Use of protective equipment
When carrying out welding work, the greatest danger is the possibility of electric shock, burns from flying drops of molten metal and light exposure to the retina of the eye from the radiation of an electric arc. In addition, mechanical injuries and gases released during the welding process may enter the respiratory tract. Therefore, any novice welder who decides to master a welding inverter, in addition to the machine itself, is required to purchase a set of personal protective equipment, as well as carefully study the safety rules when performing welding work. The standard set of welder protective equipment includes a mask and spark-resistant gloves, as well as overalls and shoes made of non-flammable and non-melting materials. In addition, during welding with an inverter, a special respirator may be required, and the cleaning of workpieces and seams must be done using safety glasses.
Start of welding: light the arc
An electric arc is created independently when polarly charged elements come into contact in two ways:
- by striking - draw a strip along the joint;
- tapping - tap 2-3 times on a place where the mark is not important.
If a spark does not form immediately, you need to cut off the excess winding. We can continue to work.
Incline
Tilt the electrode in your direction at an angle in the range of 30-60 degrees. This ensures good heating of the slag bath. But in some cases this is not necessary, then they use the “backward angle” method, that is, away from themselves, then the seam stretches behind the tip of the protective coating.
How to learn to use welding and determine the speed of movement
You cannot tightly attach an electrical conductor to a metal structure; there should be 2-3 mm between them, this distance is necessary to form a slag bath. How quickly to perform manipulations depends on the voltage and degree of heating; usually this is an individual indicator; it can be determined by the degree of heating and heating upon contact.
Current setting
Correct selection of the current value of the welding inverter is the key to the quality of the weld. In order to select a value corresponding to the thickness of the metal and the diameter of the electrode, it is best for a novice welder to use the corresponding table from the inverter passport. After this, you need to turn on the device’s power switch, and then, by turning the regulator, set the required current value. For some devices, the scale of its values is marked on the front panel of the inverter along the arc of rotation of the regulator, for others it is displayed on a digital indicator (see photo below).
In any case, this will be an approximate value, so it is quite possible that the current strength for good penetration will have to be adjusted during the process of making test welds.
How to weld parts correctly
Before starting the process, you need to create temporary fastenings - ties, rivets. They will allow you not to pull the structure to one side so that it does not deform. Then the seam will be smooth, and the shape will be the way it was intended. Only after this can you begin to take active action.
Current selection
It always depends on the type of metal connections and the electrode. If the voltage in the home network is not enough for the required strength, you can go through two layers or work more slowly to achieve the optimal temperature. Table of correspondence:
| Electrode diameter, mm | Metal thickness, mm | Welding current, A |
| 1,6 | 1-2 | 25-50 |
| 2 | 2-3 | 40-80 |
| 2,5 | 2-3 | 60-100 |
| 3 | 3-4 | 80-160 |
| 4 | 4-6 | 120-200 |
| 5 | 6-8 | 180-250 |
| 5-6 | 10-24 | 220-320 |
| 6-8 | 30-60 | 300-400 |
Making various seams
Depending on their location, the seams can be vertical, horizontal, ceiling, or inclined.
Making a seam:
- prepare the plates;
- turn on the inverter, set the current;
- make a small gap between the plates, create weld pools;
- make a welding connection;
- beat off the slag.
Each seam is made using this algorithm, but in the photo you can see visual differences in the process.
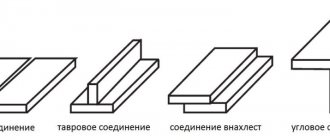
Depending on the design of the connection, the seams can be butt, tee or overlap. You can learn how to make seams experimentally, using detailed photo instructions as a guide. Welding will become beautiful over time. The main thing is to start and try to work with hardware.
Features of the work
A high-quality welded joint can only be obtained if all requirements of the technological process are met. Any deviation will lead to a deterioration in the quality of the seam or to an outright manufacturing defect.
Features of electric arc welding technology:
- First of all, preparation of the surfaces to be welded is required. The joints are cleared of debris and degreased. In some cases, additional edge cutting is required. Afterwards you can proceed directly to welding. To do this, the electrode is brought to the joint and an electric arc is produced by tapping on the surface.
- To make the process faster and the welds to be of the highest quality, there are auxiliary elements on the electrode. Calcium, sodium and potassium are best for this purpose. Thanks to them, the metal is more energetically divided into particles.
- For the welding process, both open and closed electric arcs can be used. When the arc is open, a lot of atmospheric nitrogen penetrates into the welding area. It negatively affects the quality of the connection and the structure of the weld. To reduce the negative impact on the surface of consumables, a metal layer is applied. On an industrial scale, the most commonly used method is welding workpieces using a closed electric arc. In this case, the working area is protected from exposure to atmospheric oxygen and other gases.
- Metal welding can be performed using different devices. Inverters have become widespread. They are designed for the use of electrodes of different diameters. To start work, the rod is installed in the holder, and the mass is connected to the working surface. After turning on the device, you need to run the end of the electrode over the metal parts a couple of times to ignite the arc. It is important that up to this point the operating parameters, especially the current, are set to optimal values.
- During welding of parts, the electrode moves smoothly along the joint line. It is gradually filled with a melt, which is also called a weld pool. It consists of metal blanks and consumables. As the melt solidifies, it forms a weld. Guided by the technological map, a specialist can accurately calculate operating parameters, including power, duration of arc exposure, etc.
- When forming vertical seams, the electrode is held in a straight position. However, a slight deviation (up to 10 degrees inclusive) will not affect the quality of the result in any way.
- To avoid welding in one place, different welding techniques are used: herringbone, triangle, several times and others.
The choice of welding method and technique depends on the work conditions and the materials being joined.
Common mistakes made by newbies
Arc welding diagram.
Beginner welders tend to make mistakes due to ignorance of the basics regarding the use of welding equipment. For example, beginners may not know how to choose the correct polarity for welding with an inverter, which will lead to poor-quality joint formation or even burning of the part.
The following main errors can be identified:
- neglect of safety precautions;
- incorrect choice of welding machine;
- use of low-quality or unprepared electrodes;
- work without trial seams.
For beginners, it is worth separately noting one feature if you cook Resanta by welding. This equipment is very popular, but it has short connection cables, which can create inconvenience in operation.
Manual arc welding technology
Before the main process, preparatory work is carried out, without which the weld will not be of high quality: straightening, cleaning, marking, cutting and assembly. Ignition of the arc between the electrode and the product is performed in two steps: touching the surface, short circuit, and separation at a distance equal to the diameter of the electrode. They light it in two ways: end-to-end and by striking. In the first case, the metal is heated at the point where the short circuit occurs, in the second - in several places.
After ignition, the electrode and base metals begin to melt, and a melt pool is formed at the weld site. The welder’s task is to maintain the arc length constant , the quality of the connection depends on this. The optimal arc length is from 0.5 to 1.1 times the diameter.
The angle of inclination to the surface provides a sufficient depth of melting of the welded parts. It also depends on the thickness and composition of the metal, the diameter of the electrode, the thickness and type of coating, and the location of the weld in space.
conclusions
The task of initial training is completed. We talked about the basic fundamentals and technologies of welding with an inverter for home craftsmen. Let us repeat, everyone has the opportunity to make beautiful, even and high-quality seams. They are obtained only with regular practice and several kilograms of electrodes burned.
Tips for novice welders:
- Before welding, do not forget to use protective equipment. Very important! Do not cook without a mask, leggings and special clothing - a welding suit, the material of which will not be burned by sparks and splashes of hot metal, otherwise you can damage your eyes or get burned in open areas of your body.
- Store electrodes in a dry place. Do not cook with damp electrodes or electrodes with chipped coating. You can dry the electrodes in an electric oven or in a household oven.
- The more you practice and use metal and electrodes, the better your welds will be. Starting with welding a fence made of corrugated sheets, over time, you will move on to more complex work. Welding of arches, greenhouses, sliding and swing gates, gates, canopies over the house, homemade tools and devices that are used in the home workshop.
- Welding is especially useful when building a house if you plan to work with metal structures and use a pipe profile, fittings, angle, channel, etc.
Sources
- https://uniform-met.ru/articles/kak-pravilno-varit-svarkoy-sovety-ekspertov-pravila/
- https://stankiexpert.ru/spravochnik/svarka/kak-pravilno-varit.html
- https://www.rocta.ru/info/kak-nauchitsya-pravilno-varit-svarkoj-ehlektrosvarkoj-v-domashnih-usloviyah/
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A1%D0%B2%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BA%D0%B0
- https://tutsvarka.ru/vidy/svarka-invertorom-dlya-nachinayushhih
- https://osvarka.com/obuchenie-svarke/kak-pravilno-varit-svarkoy
- https://WikiMetall.ru/metalloobrabotka/svarka-invertorom-dlya-nachinayushhih.html
- https://master-azov.ru/metally/kak-varit-metall-raznoj-tolshchiny.html
- https://stroy-podskazka.ru/svarka/kak-varit/
- https://www.forumhouse.ru/journal/themes/28-pravilnaya-svarka-likbez-dlya-chajnikov-i-sekrety-masterstva
Security measures
When performing manipulations for electric arc welding of metals, the following safety precautions should be observed:
- Be sure to wear welder clothing made of special fire-retardant material. The suit and other elements of equipment protect the body from the possibility of getting burned. Hot metal scatters in different directions during operation. You need to be especially careful when equipping yourself before ceiling welding.
- Cotton overalls are allowed in cases of short-term work. Under no circumstances should you wear clothing made from artificial materials. It ignites easily and maintains fire well.
- The eyes and face must be protected with a special welder's mask.
- Welding work should be performed in an open area or in a well-ventilated area.
- Before starting work, you need to stock up on fire extinguishing equipment: a fire extinguisher, water and sand.
Electric arc welding is well suited for a variety of metals being welded. When performing work, you must adhere to technology and all safety requirements. Only in this case will the specialist be protected from possible injury that can be caused by an electric discharge or hot metal.
Process description
During electric welding, metal parts are joined together using copper clamps. Electricity passes through the joints, heating and fusing them at the point where the two metal parts meet. The surface where the metals lock and touch first becomes hot and then radiates outward as a seam.
The heat distribution is controlled by ensuring a constant flow of current using a control lever. This ensures that both metals become soft and bond to each other at the same time.
Advantages of electric welding include the fact that this method does not waste unnecessary fuel and ensures precision in joining parts. The heat does not extend far beyond the welding point. This makes it ideal for insulated wires. The ends of each wire can be welded, leaving the insulation.
Although welders can theoretically use up to 50,000 amps of current, they are actually much safer and work with different current levels. This makes the welding machine incapable of electrical shock or shock to a person when using electric welding. Welding can take from a few seconds to tens of minutes. Much depends on the volume of metal structures being connected: the wider the contact area, the larger the scale of work.
Advantages and disadvantages
The electric arc welding method has both advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages of the technology include:
- Manufacturability.
- Partial or complete automation of work.
- Small heat affected zone.
- Ease of process adjustment.
- Cheapness of consumables.
- High speed of welding of parts.
The list of disadvantages includes:
- The need for preliminary preparation of samples before welding
- Energy dependence.
- The need to use power supplies (transformers or converters).
Features of welding thin metal
In everyday tasks, we are most often faced with the need to join thin metal. In this case, it is necessary to remember the basics of inverter welding for beginners, namely the importance of connecting the product to the correct pole. Thin parts are connected to the “minus” of the welding machine.
To learn how to weld correctly and get beautiful seams, you need to practice.
Here are some useful tips that can help improve your skills:
- start cooking using the minimum current;
- form the seam at an angle forward;
- use reverse polarity;
- secure the part to reduce distortion during welding.
Effect of electrode feed speed
The feed rate of the welding electrodes must provide the required amount of molten material supplied. Not having enough of it can lead to undercutting. This factor is very important in both direct and reverse polarity when welding.
During electric arc welding, due to the rapid movement of the rod along the joint, the arc power may not be enough to heat the metal. The result is a shallow seam that lies on top of the metal. The edges remain unmelted.
Slow advance of the electrode leads to overheating. In this case, it is possible to burn the surface and deform the thin metal.
Modern welding machines have a wide range of different functions and capabilities. Nevertheless, at the moment, most of the quality work done is still determined by human skill.