Argon welding is a unique and only method of joining parts made of non-ferrous metals, characterized by impeccable quality and speed. For this type of welding, a special argon torch (AG) is used, made with a ceramic nozzle and a tungsten electrode holder. The device is of high quality and reliable enough to work in high temperature environments. The torch head must rotate 180 degrees so that it can be aimed at the seam, while protecting the handle from overheating temperatures.
Design and principle of operation
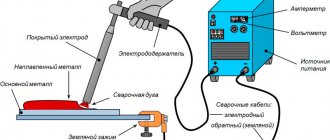
Argon welding is similar to ordinary arc welding, only the weld pool is filled with argon, which is 38.0% heavier than atmospheric air; it descends into the weld pool, displacing air and isolating it from atmospheric O2. Due to this treatment, the weld comes out without an oxide film, and the welding quality improves. Argon is not an expensive gas; it is present in the air and is a by-product gas during the production of O2 and N2.
The main element of the device is the burner. A working current is supplied to the electrode, and the welding site is protected by argon from contact with O2 from the atmosphere, thereby preventing oxidation of the surface. The device kit includes a cable, a gas supply hose and a power cable. Sometimes the kit does not include a cable, so you will need to pay attention to this when making a purchase. AG welding can be performed manually, semi-automatically and 100% automatically. The design of the unit will depend on this; the greater the percentage of automation, the more complex the design and the higher the cost.
The AG design has a tank for water circulation with 2 fittings for inlet and outlet. In the center of the vessel, on dielectric stops, there is an electrode with a wire and a point for connecting the cable. Gas from the cylinder is supplied to the nozzle into the free space next to the electrode.
What does an argon burner look like?
The procedure for connecting an argon burner:
- The welder starts the circulating cooling system and the welding machine.
- Open the argon supply to the AG.
- After creating the protective layer, the arc is ignited.
- Heating begins, at melting temperature a metal bath is formed at the joint boundary, into which filler material in the form of a wire is fed.
- Once a good joint has been formed, the welder moves the torch further along the seam.
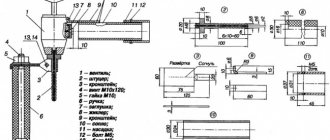
Adapters
Article: 072.700.002 Adapter M12x1–M16x1.5 DAB1216
The adapter M12x1–M16x1.5 is designed for transition from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG argon arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 072.700.001 Adapter M12x1–3/8 DAB1238
The M12x1–3/8 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG argon arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 690 RUR
Article: 070.100.052 Adapter M14x1–M12x1 DAB1412
The adapter M14x1–M12x1 is designed for transition from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.114 Adapter M14x1–1/4 DAB1414-1
The M14x1–1/4 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.043 Adapter M12x1–M10x1 DAB1210-1
The adapter M12x1–M10x1 is designed for transition from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 673 RUR
Article: 070.100.042 Adapter M12x1–M10x1 (internal) DAB1210
The adapter M12x1–M10x1 (internal) is designed for transition from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 636 RUR
Article: 070.100.041 Adapter M12x1-1/4 DAB1214
The M12x1–1/4 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.032 Adapter 3/8–M12x1 DAB3812
The adapter 3/8–M12x1 is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.031 Adapter 3/8G–OKS (water) DAB3800
Adapter 3/8G–OKS (water) is intended for transition from one thread to another. Used to connect water-cooled TIG arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 676 RUR
Article: 070.100.022 Adapter 3/8–1/8 DAB3818
The 3/8–1/8 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.021 Adapter 3/8–1/4 DAB3814
The 3/8–1/4 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 668 RUR
Article: 070.100.012 Adapter 1/8–M12x1 DAB1812
The 1/8–M12x1 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.011 Adapter 1/8–3/8 DAB1838
The 1/8–3/8 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.002 Adapter 1/4–M14x1 DAB1414
The 1/4–M14x1 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
Article: 070.100.001 Adapter 1/4–3/8 DAB1438
The 1/4–3/8 adapter is designed to change from one thread to another. Used to connect TIG hot-arc torches to welding machines. The adapter is made of brass.
Price: 697 RUR
To connect valve torches to manual arc welding (MMA) machines, you can use OKS cable lugs with quick release.
Types of argon burners
Argon burners are divided according to the type of cooling: air or water. Many TIG models are air based, since the water method will require complex equipment. According to the method of supplying the inert medium, there are ATs with a valve or a button. Many modern devices are equipped with both. AT is not classified according to the type of connector with a welding machine due to the variety of options. Usually the manufacturer completes them for specific types of inverters, the only condition is that the connector must match the socket of the device. Problems arise with this, especially when purchasing online, since many manufacturers forget to indicate the type of connector. The kit should also indicate the cable length of 4 or 8 meters.
The characteristics of the torch can be determined by the name marking, for example TIG 26, which means large water-cooled torch. AGs are divided into two groups: small and large. The first include markings 9 (air cooling) and 20 (water cooling). Consumables and spare parts for them are interchangeable.
By type of design
AGs are divided into valve and push-button. The first design is the simplest; to start the process, simply open the valve on the cylinder. Often such burners are connected only to the inverter. The process of igniting the arc involves tapping the wire on the surface to be welded. This AG design is not used for connecting aluminum parts.
The push-button model is a more advanced type. The button is comfortable, functional and has several mode positions: gas supply, welding current setting, ignition, arc formation and others. Such burners are easy to use and provide decent quality seams.
Combined torches with a valve and a button are rare; they are not recommended for use by beginners in argon welding, since they are difficult to set up, but experienced specialists choose this version of the torch, as they have more functionality for creating different welding modes.
By cooling type
Cooling options in AG include air, which operates on the natural principle of circulation, and water, with forced supply of coolant. The first method is structurally simple; the parts are cooled with air under the influence of O2. This system is used when welding small seams and with a current of up to 200 A, otherwise the argon torch device will overheat.
Water cooling - the process is carried out using special structural elements to supply cold water to the housing.
Types of argon torches for manual welding
Welding can be done manually, semi-automatically or automatically. Accordingly, the design will be different. The more automated the process, the more complex the device.
Let's look at devices exclusively for manual welding (TIG): what they are, what to look for when choosing a particular model.
The main functions of the torch are to hold the welding electrode, which creates the arc, and to supply gas to the welding zone. Even the simplest burners can handle this. For a high-quality result, in addition to the experience of the welder, it is required that it be convenient to work and one cannot expect a catch in the form of, for example, a falling electrode or other unpleasant “trifles.”
Argon burners can be classified according to the type of cooling: air or liquid. Most TIG torch models are air cooled. A water heat sink requires additional equipment.
According to the method of gas supply, burners are distinguished, equipped with a valve or a button. Some models come with both.
It is difficult to classify torches based on the type of connector connected to the welding machine due to their diversity.
Typically, the manufacturer installs connectors for certain types of inverters. The connector must match the socket of the welding machine. This is where problems may arise when purchasing a burner online, since only a few manufacturers indicate the type of connector in the name. For example, in the FUBAG FB TIG 26 5P torch there is a 5pin control connector, in the TORCH 24 WATER 4m M12x1 there is an M12x1 connector. As a last resort, the connector is soldered.
But the length of the train must be indicated. Its most common size is 4 meters, less often - 8 meters, and even less often - intermediate values.
What can the labeling tell you?
On most burners or in the product name on websites, sellers still indicate a “defining” numerical value. For example, TIG 26 after the manufacturer's name.
When choosing a torch, a novice welder should have an idea of the differences between torches hidden under the numbers.
By and large, argon burners can be divided into two groups by size: small and large. The small ones include 9 (air-cooled) and 20 (water-cooled). Consumables and components for them are interchangeable. For large (suitable for household welding) torches with numbers 18 (water cooling), 17 and 26 (air) the same applies to replacement.
In the designation of inexpensive domestic burners, a designation like WP 17 is often found (the manufacturer’s name is indicated somewhere, but you will have to look for it). In principle, the minimum information was obtained: a large air-cooled argon burner under pure tungsten electrodes.
Electrodes for argon welding
When argon welding, electrodes made of refractory tungsten are used, sometimes pure, sometimes with additives. The presence of additives makes it easier to work with a number of metals and alloys.
In addition to letter markings, different types of tungsten electrodes are marked by the color of the shank.
For convenience, the information is presented in the table.
| Letter designation. | Color | Current (DC or AC) | Metals to be welded | Note |
| W.P. | green | A.C. | Magnesium, aluminum, alloys | |
| WZ | white | A.C. | Bronze, aluminum, nickel, alloys | |
| W.T. | red | DC | Stainless steel, tantalum, molybdenum | Special safety measures: mandatory ventilation in the room. |
| W.Y. | blue | DC | Carbon, low alloy, stainless steels, titanium | |
| W.L. | golden | DC,AC | Any steels and alloys | |
| W.C. | grey | DC,AC | Any steels and alloys |
The diameter of the electrode is selected depending on the operating current: up to 50 A - diameter 1 mm, up to 100 A - 1.6 mm, up to 200 A - from 2 mm to 2.4 mm, over 200 A - 3.2 mm, over 300 A – 4 mm.
In addition to the current strength, the thickness of the metal being welded is taken into account. It would be more correct to say that the choice of electrode and current depends on the thickness and composition of the metal. Non-consumable tungsten electrodes require sharpening before use. The general principle for choosing the sharpness of an angle is that the wider the planned seam, the thinner the point.
The tip itself is cleaned.
What else does a welder need before work?
Concern for safety precautions when performing welding work falls on the shoulders of the welder himself. A mask (with a shield is less convenient), overalls or a jacket with pants, mittens made of specially treated fabric are mandatory equipment. Exposed skin areas are not allowed.
It is necessary to check the workplace for the correct connection of the torch to the welding machine and cylinder, the integrity of the cable and hose, the presence of a fire extinguisher, and the absence of flammable and combustible objects nearby.
Criterias of choice
TIG welding is most applicable where the type of weld being made matters or where the parts being welded are thin and arc parameters will need to be controlled. TIG machines are used to weld thin stainless steel and non-ferrous parts that require precise arc mode, since the components will be deformed if overheated.
When selecting AG, the following criteria are used:
- Current mode from 5.0 to 230.0 A, welds 0.5 mm stainless steel and 6.3 mm aluminum components.
- The stability of the welding mode is an important parameter of a quality process, especially at the end of the process.
- Current mode - alternating or constant. If you plan to weld not only stainless steel, but also non-ferrous metals, then the unit must be dual-mode.
- When connecting with alternating current, its direction changes. When aluminum parts are welded, in the “+” direction the surface is freed from oxides, and in the opposite direction, the melting process is carried out. The balance between directions is also important, so it is permissible to change the duration of welding with electric current of a certain direction.
- Ease of use. This type of argon welding can be performed by a highly qualified craftsman. Therefore, novice users will need a simple device with clear control functions.
- Availability of a fan for air cooling. It can turn on automatically based on a temperature sensor or operate in constant mode.
- Profitability and performance are important factors when choosing an AG; they are influenced by the design and consumables. When purchasing the latter, you need to pay attention not only to the price, but also to the period of use.
When choosing an argon torch, it is necessary to take into account the stability of the welding mode
Advantages and disadvantages
Argon welding, in general, is complex equipment for beginners; you need to prepare for the fact that in this case the work speed will be low. However, there is often no alternative to these devices. The main advantages of argon arc welding:
- Creation of a protective seam from the harmful effects of the atmosphere.
- No metal overheating with certain work experience.
- There is no damage to the crystal lattice at the joints.
- Wide range of applications for all types of alloys.
- Rare electrode changes.
- Availability of components for argon burner on the market.
Disadvantages of AG:
- Protection from ambient air can easily be compromised if the welder works in a draft, since the shielding gas will simply be “blown away”;
- in high current mode, periodic cooling of the welding will be required;
- powerful ultraviolet radiation when using helium;
- The equipment is quite complex; in order to connect and use it, it is necessary to configure it;
- The welder must have qualifications and experience.
Connection nuances
An argon apparatus differs from a conventional arc apparatus, so the welder must follow certain rules:
- The seam should be applied exclusively in the direction of the edge being processed; any oscillatory movements will thicken the seam and reduce its strength characteristics.
- When performing work, you will need to monitor the operating speed of the arc and the depth of metal penetration.
- It is better to perform manual welding using inverter equipment equipped with a mechanical supply of filler material.
- In order to create a protective argon cloud, gas is supplied 20 seconds before welding begins and ends after 5 seconds. The gas protects the resulting seam from microcracks, thereby ensuring its strength.
- Finish the seam using a rheostat, slowly reducing the arc voltage.
- The arc is ignited using an oscillator with a power source. Then you can create high-frequency pulses to ionize the arc gap, for example, with a network frequency of 55 Hz and a voltage of 220 V, the oscillator can supply a voltage of 5000 V at a frequency of up to 450 Hz, which will easily ignite the electrode.
- In contrast to conventional arc, AG cannot be started by touching the parts being welded with the electrode.
- First, gas is applied to them for 20 seconds, then the argon torch nozzle is smoothly brought to the metal 2 mm, the arc is drawn slowly and evenly along the seam, avoiding oscillatory movements, while the filler wire is placed in front of the nozzle and fed also smoothly.
Selection of TIG welding torches
A argon arc welding torch is an important piece of welding equipment that uses an electric discharge as an energy source. With its help, the flame necessary for the welding process is formed. Structurally, it consists of such parts as an argon supply hose, a power core and a handle with a head. Manufacturers offer a variety of TIG torch models to choose from, which differ in power, cable length, method of connection to welding equipment, type of cooling and control.
1 / 1
What is argon arc TIG welding
TIG welding is suitable for both joining the joints of thick products and creating neat thin seams. It is widely used in car services and various enterprises. Welding is performed using a non-consumable electrode in a protective environment of inert gas. One of the main advantages of TIG is that this method is suitable for welding a wide variety of materials: aluminum, magnesium, stainless steel, copper, nickel and other metals. It is also successfully used for welding dissimilar metals.
The main element of TIG welding is a tungsten electrode with a melting point of just under 4000°C. For accurate and precise work of the seam, it requires periodic sharpening, because... Both the cleanliness of the seam and its thickness largely depend on this. Before use, the tungsten electrode is placed in a collet and fixed in the TIG torch. At the end of the latter there is a ceramic nozzle with an electrode located in the center. During operation, an inert gas is supplied around the circumference - usually argon. The filler wire most often uses the same type of metal from which the products being welded are made. Argon arc welding is ideal for joining aluminum products, because... Without an inert gas, this metal begins to oxidize under the influence of oxygen during the melting process.
Main selection criteria
To make the optimal selection of a TIG welding torch, first decide on the type of cooling. It can be air or water. In the first case, the cable through which the welding current passes is cooled by air - there is no need to connect additional devices. In the second case, the cable is cooled by water circulating in the burner. For this purpose, the equipment is supplemented with a special unit. Which cooling to choose:
- If you plan to work at high currents, then you will need water cooling, if at low currents - air cooling.
- Welding thin metals requires air cooling, thick metals require water cooling.
Pay attention to the torch connector for TIG. Usually it has 2pin and 7pin connection. To avoid making a mistake with your choice, find out which socket your device has.
What do the Latin letters in the device name mean? A few words about this:
- F (from Flexible - “flexible”). A device with this letter can bend in different directions. This is very convenient when performing work in hard-to-reach places.
- V (from Valve - “valve”, “valve”). The model with this letter is suitable for manual arc welding equipment, but with a TIG welding function.
- TS. This is how the world refers to torches designed for TIG welding.
You can find a gas burner suitable for your device in our catalog. Additionally, you can order from us reliable and high-tech welding machines belonging to the semi-professional and professional segments. The ability to fine-tune the main and auxiliary process parameters will make your work easier and help you achieve the desired result. If you have any difficulties choosing a suitable device, our managers are ready to help you. They will tell you about the features of our equipment, payment methods and delivery conditions.
Brief overview of popular manufacturers
The most popular AG models according to the 2021 rating:
- AURORA TIG 9V 110A - a domestic torch that works with welding units of the SVAROG brand, has good availability in the retail network for both consumables and spare parts
- The cost depends on the modification and ranges from 2.5 to 4.5 thousand rubles.
- SvarogTS 26V (M12-1) - an air-cooled welding unit with a maximum operating current of 180 A for direct and 130 A for alternating, acceptable electrodes - from 0.5 to 4 mm, price in Moscow - from 4 to 6 thousand rubles.
- Bars TIG-17V - for mode with direct current 140 A and air cooling, cable, 4 m long, large set of components, price 3.5 thousand rubles.
- TORCH burners for alternating and direct current, price up to 3.0 thousand rubles. BlueWeld No. 9 from 9.0 thousand rubles. thousand, and No. 26 - from 15.0 thousand rubles.
Argon torch AURORA TIG 9V 110A
Thus, we can summarize that the argon arc torch is the main element for the welding machine (WIG/TIG), allows you to work with materials of different thicknesses, including dissimilar metals, which makes it indispensable for such types of work . In the hands of an experienced craftsman, she makes a neat seam, with virtually no metal spattering.
Water-cooled burners
Article: 072.258.120 TIG torch TP 25 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) 8m TBW2501-08
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 25 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made via a nut with M12×1 thread. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUR 7,542
Article: 072.254.120 TIG torch TP 25 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) 4m TBW2501-04
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 25 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made via a nut with M12×1 thread. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUR 6,493
Article: 072.208.100 TIG torch TP 20 (OKS 35-50, w/r, 2PIN) 8m TBW2002-08
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 20 (OKS 35-50, non-ferrous, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made through OKS 35-50. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUR 8,522
Article: 072.204.100 TIG torch TP 20 (OKS 35-50, w/r, 2PIN) 4m TBW2002-04
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 20 (OKS 35-50, non-ferrous, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made through OKS 35-50. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUB 5,689
Article: 072.208.120 TIG torch TP 20 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) 8m TBW2001-08
Argon arc torch TIG TP 20 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made via M12x1. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUR 7,418
Article: 072.204.120 TIG torch TP 20 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) 4m TBW2001-04
Argon arc torch TIG TP 20 (M12x1, 1/4G, 3/8G, 2PIN) with water cooling. The connection is made via M12x1. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling.
Price: RUR 4,841
Article: 072.188.100 TIG torch TP 18 (250,315AC/DC) 8m water cooling TBW1808-02
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 18 (250,315AC/DC) with water cooling. The connection is made through the OKS 35-50 with the gas supply hose removed. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling. The first meter of cable is made of leather.
Price: RUR 9,522
Article: 072.184.100 TIG torch TP 18 (250,315AC/DC) 4m water cooling TBW1804-01
Argon-arc torch TIG TP 18 (250,315AC/DC) with water cooling. The connection is made through the OKS 35-50 with the gas supply hose removed. Connection via 2 PIN. Two hoses for water cooling. The first meter of cable is made of leather.
Price: RUR 5,978