Plastic products are now ubiquitous. And engineering communications are no exception. Plastic is cheap and durable, but you should choose polypropylene water pipes for your home wisely. Any break in the internal water supply pipeline means an incredible amount of problems for home owners. It’s good if there is no major flood, you can endure a couple of days of repairs with bottled water. Otherwise, you will have to repair not only the plumbing system, but also the interior decoration.
Characteristics of polypropylene pipes
It is difficult to come up with a better option than a polypropylene pipe for organizing water supply in the house. In almost all technical characteristics, polypropylene (thermoplastic polymer of propylene, PP, PP) is superior to polyvinyl chloride and polyethylene. This plastic has the lowest density (0.91 g/cm3) among analogues used for the production of pipe products and fittings for them.
A wide range of products are made from polypropylene
At the same time, polypropylene pipes are characterized by increased resistance to alkalis and acids, as well as high operating temperatures and good resistance to deformation upon impact. PP begins to melt at 160–170 degrees C, and soften at approximately 140 degrees C. It all depends on the additives and plasticizers used in production.
Table of service classes of plastic pipes according to GOST R 52134-2003
| Class | Description | Temperature |
| 1 | Hot water supply | 60° |
| 2 | Hot water supply | 70° |
| 3 | Low temperature underfloor heating | 60° |
| 4 | High temperature floor and low temperature radiator heating | 70° |
| 5 | High temperature radiator heating | 90° |
| HV | Cold water supply | — |
Polypropylene pipes are suitable for both water supply (hot water supply and hot water supply) and heating. However, here you need to look carefully at the markings. Now different versions of this plastic are produced, differing in manufacturing technology and characteristics.
Polypropylene or metal
Polypropylene pipes without reinforcement can be unconditionally used for cold water supply systems. The working pressure of the pipe must be at least one and a half times higher than the maximum pressure in the water supply.
Let's say, for an autonomous water supply to a private house with water supplied from a well or well, the capabilities of a PN10 pipe are quite sufficient, but for a high-rise building with powerful pumping it is better to prefer a PN20 pipe.
Is polypropylene suitable for external water supply (for example, for country water supply)? I guess, yes.
But it is not the best material for this purpose:
- Polypropylene pipes are supplied only in straight sections, which complicates the installation of long-distance water pipes;
- The polymer has low elasticity (especially at low temperatures), so water frozen in the water supply is guaranteed to tear it.
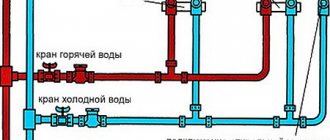
That is why external water pipes are usually laid with a pressure polyethylene pipe on compression fittings (see Fittings for water supply to a private house). The pipe is supplied in coils up to 500 meters long, remains flexible in cold weather, and can be easily dismantled if necessary.
The external water supply is laid with a polyethylene pipe on compression fittings
Is polypropylene suitable for hot water supply? According to the manufacturers, yes. It is not for nothing that they indicate a temperature range of up to 90-95 degrees for pipes. In practice, the answer depends on the type of water supply system.
Autonomous hot water supply
The following are responsible for heating water in such a system:
- Electric storage or instantaneous water heater;
This apartment is provided with hot water by an electric boiler.
- Indirect heating boiler;
- Instantaneous water heater of a double-circuit boiler or gas water heater.
Two parameters of autonomous hot water supply are important for us:
- The water temperature is completely controlled by the owner, never exceeding 70-90 degrees. When overheating, the water heater protection is triggered;
- Stable pressure (exactly equal to the pressure in the cold water system) and guaranteed absence of water hammer (see Water hammer in the water supply system: why it occurs and how to avoid it).
Help: water hammer (an instantaneous surge in pressure in a filled closed circuit) occurs when the movement of water in it suddenly stops. Examples of such a situation are a ball valve on one of them that is suddenly closed during the circulation of hot water through paired risers, or the rapid filling of the riser with the mixer tap open. In the latter case, water hammer occurs at the moment when all the air is displaced from the riser.
The mechanism of water hammer occurrence
The peak parameters of an autonomous hot water system are within the declared characteristics of polypropylene pipes with a margin. Accordingly, you can safely use polypropylene for hot water supply.
Centralized hot water supply
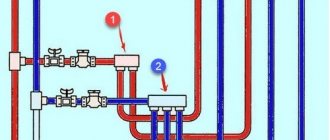
In houses with a centralized supply of hot water from a heating main (typical for cold regions of the country), the picture is different. DHW taps are located in the elevator unit between the inlet valves and the water jet elevator. The hot water supply system communicates directly with the heating main.
Elevator unit with hot water supply connections
In theory, the parameters of hot water supply in this case also fall within the stated for polypropylene 25 kgf/cm2 at +20°C or 8-9 kgf/cm2 at +90°C. Alas, in our country theory and practice are often far from each other.
- The temperature in the supply line of the heating main, according to the temperature chart, during maximum winter cold can reach +150°C. Water does not boil only due to excess pressure.
If the supply exceeds +90, the hot water supply must switch to the return pipeline with its lower temperature; however, the human factor has not been canceled.
If your plumber forgets to switch the water to return, your line will end up with water heated above the boiling point. Even if the pipes withstand overheating, their service life will be catastrophically reduced;
The supply temperature of the heating main during the peak of cold weather reaches 150 degrees
- In the spring, heating mains undergo temperature tests: the supply is again heated to a maximum of +150°C. The hot water supply, powered at this time of year from the supply, should be turned off for the duration of the tests, however, if the shut-off valves are faulty and for some reason not repaired on time... It seems that there is no need to explain further;
- Finally, the hot water supply system in houses with a centralized water supply is not protected from water hammer at all. It is worth quickly opening the valves or stopping the circulation of hot water in the risers by sharply turning the ball valve - and at the front of the water flow the pressure will instantly increase to 25-35 kgf/cm2. Yes, water hammer lasts a fraction of a second, but it is often enough to destroy a water supply system.
Reinforced pipe destroyed by water hammer
Conclusion: if your house is connected to a heating main, do not install polypropylene for the hot water supply: it is better to install the water supply with metal pipes. The author, in particular, strongly recommends a corrugated stainless pipe - extremely easy to install, flexible and withstand pressure up to 210 atmospheres at temperatures up to 150°C.
The distribution of centralized water supply is made with Kofulso corrugated stainless pipe
Types
Polypropylene pipes are presented in three main types on the market:
- PPH (PP-1) is a homopolymer.
- PPB (PP-2) is a block copolymer.
- PPR (PP-3, PPRC, PP-random) – random copolymer.
Ordinary PP is practically not used for making pipes. Its characteristics are too low for such products. The most common options in plumbing stores are PPH and PPR. They are the cheapest and ideal for installing plumbing. Plus, PP pipes can also be found with the brands PP-S, PP-PURE, etc. But these types are more intended for use in industry and work with aggressive environments.
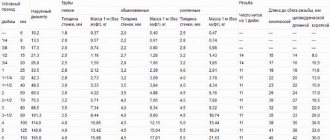
Pipe diameters for water supply
Material
PPH pipe is highly durable, but does not withstand temperatures below zero and ultraviolet radiation quite well. According to GOST and SNiPs, it is recommended to use it only for cold water. PPB is slightly stronger than homopolymer and has a wider operating temperature range - from -20 to +800C. However, this option costs more than the first. Polypropylene block copolymer products are usually used in the installation of “warm water floors”.
Changing the length of pipes when heated from 0 to +60 C
Among this trio, PPR stands out for its greatest heat resistance (able to withstand temperatures of +900C for a long time) and UV resistance. A pipe made from it can be used both for plumbing with cold and hot water, and for heating systems. Only such pipelines should be located in a heated room; it is not recommended to use PPR outdoors.
Sectional view of polypropylene pipes
Reinforced
All of the above three types of polypropylene pipes are single-layer products. In addition, there are multilayer reinforced analogues in which polypropylene is also the base. However, between its two layers an additional layer of more rigid material is inserted.
Reinforcement in such PP pipes is carried out:
These types of polypropylene pipes have increased technical characteristics in terms of strength, rigidity, heat resistance and thermal conductivity. But because of the high cost, it is better not to use them for plumbing. They are more intended for heating systems. It’s the same as with replacing electrical wiring in an apartment - in this situation, wires with wires that are too thick cannot be used. They cost more, but are of no use. Moreover, their use poses problems.
Types of polypropylene pipes
Classification by cross-country ability
Additionally, pipes are classified according to permeability. The internal size of polypropylene pipes indicates how much water they can pass in a certain period of time. The external dimensions of the PP pipe in this case do not matter. This suggests that the wall thickness can be any - only how strong the pipes will be depends on this parameter.
How to correctly calculate pipe patency
To calculate the internal diameter of PP pipes, you need to use the following formula:
D = √(4 - Qtotal - 1000/π∙V), where:
Qtotal – maximum total water consumption;
V – speed of water movement.
If the pipes are thick, then the speed is assigned a value of 1.5-2 m/s, but for thin pipes this value is usually equal to 1.2 m/s. That is, the smaller the pipe cross-section, the higher its surface/lumen ratio. In other words, in a thin pipe, almost the entire volume of water will slow down against the walls.
PP pipes with sections of 10-25 mm are selected if the water movement speeds are low. But if the V values are large, then the pipe cross-sections must be at least 32 mm.
In any case, it is advisable to proceed from the highest speeds, since polypropylene has very smooth walls. If a water supply system is installed, then in this case the friction of water on the inner surface of the pipes will be minimal.
The exact values of the permeability and cross-section of pipes are of great importance only in the case of designing a water supply system in multi-storey buildings. If you do not use the table of polypropylene pipe sizes and choose a pipe with a cross-section smaller than the required one, then during periods of peak water consumption, residents will simply be left without water.
However, you may want to take a pipe with a spare cross-section
In this case, it is worth paying attention to the feasibility of such a decision from an economic point of view. Larger diameter pipes will require more expensive fittings
As a result, costs may increase significantly. If you wish, this can be prevented, the main thing is to use a rational approach.
It is not advisable to use PP pipes of large cross-sections in places where thin pipes would be sufficient, again for the purpose of economy. The fact is that when you drain cold water from a tap for a long time, with a larger cross-section of pipe and water, more will be spent before the water becomes hot. If there is no water intake, then a significant part of the heat from hot water will simply dissipate idle.
It is recommended to organize a circulating water supply system, so you will not need to drain the water every time it gets hot. If this is a private house, then you only need to install a simple circulation pump, as well as purchase and equip the system with an additional pipe through which the water will return to the boiler.
There is a huge range of polypropylene pipes on the market for heating and more. If you are making a water supply riser, then polypropylene pipes with a cross-section of 25 mm are suitable if it is a five-story house, and 32 mm for houses from nine to sixteen floors. In this case, when deciding on the diameter, it is worth taking into account the exact number of plumbing fixtures that will be used in this system.
Large cross-section polypropylene pipes are most often used to supply cold water to one or more houses. Polypropylene is not used for laying pipes in heating mains, as it does not like hot water. In addition, this is a place where the pipes will be subject to a large load, which can simply damage the soft polypropylene.
With cold water, everything is much simpler - due to its low temperature and low pressure in the system, cast iron is increasingly being abandoned in favor of polypropylene when installing water pipelines. Quite often you can find systems with a nominal diameter of polypropylene pipes of 500 mm or more, which supply entire small areas.
Marking of polypropylene pipes
When choosing polypropylene pipes, in addition to the PP type and the presence of reinforcement in the marking, you must also look at the maximum operating pressure. According to GOST, this parameter is designated PN and a number from 10 to 25.
Marking of polypropylene pipes
Depending on this designation, PPR pipes are distinguished as follows:
- PN10 – thin-walled for cold water and “warm floors” with water up to +450C.
- PN16 – universal for cold water and hot water supply up to +600C.
- PN20 – thick-walled for water with temperatures up to +950C.
- PN25 – with reinforcement for hot water supply and heating (also up to +950C).
For a short period of time, one or another PPR pipe for water supply can withstand exceeding the specified temperatures. But with prolonged excessive heating, it will gradually begin to collapse. And as a result, its service life of half a century declared by manufacturers will be significantly reduced.
Welding and heating time of polypropylene pipes
Main pipe diameters according to GOST
The diameter in the marking of PPR water pipes is indicated as the outer diameter. Moreover, the larger it is and the higher the PN, the thicker the pipe wall. Products of 16–20 mm are used for installing water pipes throughout the apartment and cottage. 25–32 mm is for the riser. Larger diameter options are intended for pipelines in multi-storey buildings, main networks and sewerage.
How to correctly calculate the diameter of a pipe based on its purpose
Voting for the best pipes for heating or for laying a water supply system
What pipes would you choose for heating or for laying a water supply system or would you recommend?
Pipe Valflex PR-R SDR 11
16.67 % ( 1 )
Pipe TEBO SDR 11
16.67 % ( 1 )
Pipe Pro Aqua SDR N11
0.00 % ( 0 )
Reinforced pipe Vikma PN 25
0.00 % ( 0 )
Pipe SPK 1020PM
0.00 % ( 0 )
Reinforced pipe Banninger WATERTEC Stabi
16.67 % ( 1 )
Glass fiber reinforced pipe Lammin 20 mm PP-R PN 20
16.67 % ( 1 )
Pipe VALTEC PP-FIBER PN 20
33.33 % ( 2 )
Popular manufacturers
On the domestic PPR market, water pipes are represented by products of Russian and foreign manufacturers. There is no particular difference between them; the plastic production technology is used in all cases. However, it is extremely important to look at the numbers written on the product label. Manufacturers often add various plasticizers to their plastic to enhance certain characteristics.
Popular manufacturers of polypropylene pipes
Among the popular manufacturers of the pipes in question are:
- Banninger and Rehau (Germany);
- Valtec (Italy);
- Ecoplastic FIBER (Netherlands);
- TEBO and Vesbo (Türkiye);
- BLUE OCEAN (China);
- ProAqua and Politek (Russia)
The quality of these manufacturers is almost the same. But for German pipes you will have to pay a little more due to the brand, and for Chinese ones, on the contrary, a little less. At the same time, Russian analogues also maintain their brand, having a very affordable cost per linear meter.