Metal-cutting machines produced by domestic manufacturers are divided into several categories, which are characterized by the corresponding classification. You can determine which category this or that equipment belongs to by its labeling, which says a lot to those who understand it. However, no matter what category the metal-cutting device belongs to, the essence of processing on it comes down to the fact that the cutting tool and the part perform form-building movements, and it is they that determine the configuration and dimensions of the finished product.
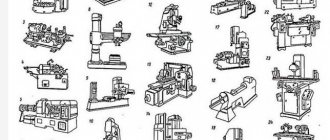
The most common types of metal-cutting machines: 1-6 - lathes, 7-10 - drilling, 11-14 - milling, 15-17 - planing, 18-19 - broaching, 20-24 - grinding.
Types of metal-cutting equipment
Depending on their purpose, metal-cutting machines are divided into nine main groups. These include the following devices:
- lathes - all types of lathe machines (in the marking they are indicated by the number “1”);
- drilling and boring - machines for performing drilling operations and boring (group “2”);
- grinding, polishing, finishing - metal-cutting machines for performing finishing, grinding, sharpening and polishing technological operations (group “3”);
- combined - metal-cutting devices for special purposes (group “4”);
- thread and gear processing - machines for processing elements of threaded and gear connections (group “5”);
- milling - machines for performing milling work (group “6”);
- slotting, planing and broaching - metal-cutting machines of various modifications, respectively, for planing, slotting and broaching (group “7”);
- cutting - equipment for performing cutting work, including saws (group “8”);
- different - examples of such metal-cutting units are centerless-grinding, saw-cutting and others (group “9”).
Groups and types of metal-cutting machines (click to enlarge)
In addition, metal cutting machines can be one of the following types:
- multi- and single-spindle, specialized (semi-automatic and automatic), multi-cutting copying, turret, drilling and cutting, rotary, frontal and special types of lathes;
- equipment for performing technological operations of boring and drilling: multi- and single-spindle, semi-automatic, drilling machines of vertical, horizontal and radial type, boring devices of coordinate, diamond and horizontal type, various drilling models;
- various types of grinding machines (flat, internal and cylindrical grinding), roughing and polishing equipment, sharpening and specialized units;
- types of metalworking machines designed for processing elements of gear and threaded connections: gear cutting machines (including those intended for processing conical wheels), gear cutting machines - for cylindrical gears, gear milling, thread cutting, thread and gear grinding, gear finishing, checking, thread milling, devices for processing the ends of teeth and elements of worm pairs;
- metal-cutting machines belonging to the milling group: cantilever (vertical, horizontal and universal models) and non-cantilever (vertical devices, longitudinal, copying and engraving models);
- planing equipment and models for similar purposes: longitudinal machines on which one or two stands are installed; horizontal and vertical broaching devices;
- cutting equipment: equipped with an abrasive wheel or a smooth metal disk, cutter or saws of various designs (band, disk, hacksaw); straightening-cutting types of metalworking machines;
- other types of machines for processing metal workpieces: dividing machines, used for monitoring drills and grinding wheels, filing, balancing, leveling and centerless roughing, sawing.
Vertical milling machine is one of the representatives of an extensive milling group
Classification of metal-cutting machines is also carried out according to the following parameters:
- by weight and overall dimensions of the equipment: large, heavy and unique;
- by level of specialization: machines designed for processing workpieces of the same size - special; for parts with different but similar sizes - specialized ones; universal devices that can be used to process parts of any size and shape;
- according to the degree of processing accuracy: increased - P, normal - N, high - B, especially high accuracy - A; There are also machines that can perform particularly precise processing - C, they are also called precision.
General classification
Metal processing equipment is divided into 11 groups:
- Metal lathes. External and internal surfaces of rotation are processed. They have one thing in common: rotation of the part around its axis.
- Drilling machines. This group also includes boring machines. Used for passing through and blind holes. They are united by the rotation of the working tool and its simultaneous feeding. In horizontal boring mechanisms, feeding occurs due to the movement of the work table with the fixed part.
- Grinding machines. All such machines use an abrasive grinding wheel as a working tool.
- Polishing and finishing machines. A common feature is the use of abrasive wheels and polishing pastes.
- Gear processing machines. Designed for cutting gear and wheel teeth. This also includes grinding machines.
- Milling machines. In this group, the working tool is a multi-edge milling cutter.
- Planing machines. For these machines, the working stroke is a reciprocating movement of the cutter or workpiece.
- Slitting machines. They are used for dividing into parts by cutting a metal profile (angle, channel, rod, etc.).
- Broaching machines. The working tools are special multi-blade broaches.
- Thread processing machines. This includes equipment specifically designed for thread cutting. This group does not include lathes.
- Auxiliary and miscellaneous machines. They belong to a separate group and perform various auxiliary operations.
Classification by type
Equipment of the same type may have different layouts. A milling machine can be called horizontal or vertical - based on the location of the spindle axis. Kinematic schemes for transmitting movements, control systems, and cutting accuracy parameters differ.
Machines of the same type with a similar layout and kinematics, but having different sizes, will be combined into a size range. For example, gear hobbing machines are divided into 12 standard sizes depending on the parts being manufactured (from 80 mm to 12,000 mm). Each standard size of a machine designed for a specific processing of parts is called a model. Each model has its own designations: a combination of numbers and letters indicating the machine group, the maximum dimensions of the workpiece, the difference from the base model.
Classification by versatility
Processing mechanisms of the same group can perform different tasks:
- Universal ones process a wide range of products. The dimensions of the blanks may vary. Capable of performing any technological operations provided for this group.
- Specialized ones produce parts of the same type (body parts, shafts, similar in shape, but different in size).
- Special ones perform operations on one part of various sizes.
Classification by degree of accuracy
The degree of processing accuracy on a given machine is indicated by the letter included in its designation:
- N - normal accuracy;
- P - increased accuracy;
- B - high accuracy;
- A - particularly high accuracy;
- C - especially precise master machines.
Example: 16K20P - a lathe with increased accuracy.
Classification by degree of automation
Processing equipment is divided into automatic and semi-automatic. The working cycle of the machines is completely autonomous. In semi-automatic machines, loading of workpieces and removal of processed products is carried out by the operator. It also launches the next processing cycle.
Integrated automation of large-scale production of metal products involves the installation of automatic production lines from separate automatic machines. Products are produced in small batches using flexible production modules.
Machines that produce products under CNC control are designated by the letter C (cycle) or F. The numbers indicate a feature of the control system:
- F1 - digital display and preliminary selection of coordinates;
- F2 - positional control system;
- F3 - loop control system;
- F4 is a universal control system.
For example, the range of CNC metal lathes from the StankoMashKompleks company can be viewed at the link provided.
Classification by weight
Depending on the mass of manufactured parts, machines are divided into:
- lightweight, weighing up to 1000 kg;
- medium, weighing up to 10,000 kg;
- heavy, weighing from 10,000 kg, which, in turn, are divided into large (16,000-30,000 kg) and actually heavy (up to 100,000 kg);
- especially heavy - over 100,000 kg.
Machine numbering
Identification of any metalworking machine is based on assigning an alphanumeric code to it.
The numbers indicate which group the machine belongs to (lathe, milling, etc.), indicate the type and nominal size of the equipment. By deciphering the numbering, you can find out the height of the centers, the maximum dimensions of the workpieces or the drilling diameters of the workpieces.
Machining machines of the same size but with different characteristics are identified by the letter entered between the first and second digit. For example, lathes models 162 and 1K62 differ in maximum rotation speed. The first one has 600 rpm, the second one has 2000 rpm.
The difference between modifications of machines of the same model can be determined by the letter at the end of the number. If the numbering of the basic model of a horizontal milling machine is 6N82, then the simplified modification of this machine is 6N82G.
Numbering occurs when the fourth digit identifies an improved version of a machine of the same standard size. Thus, the horizontal boring machine model 262 has a modern modification, designated 2620.
Assigning alphanumeric indices to metalworking machines makes it easy to find the corresponding equipment in special catalogs. Indexing also makes it possible to quickly find the necessary spare parts.
Machine markings
The classification of equipment intended for processing metal workpieces assumes that, having seen its markings, any specialist will immediately be able to tell which metal-cutting machine is in front of him. This marking contains alphabetic and numerical symbols that indicate individual characteristics of the device.
The first number is the group to which the metal-cutting machine belongs, the second is the type of device, its type, the third (and in some cases the fourth) is the main standard size of the unit.
Decoding the markings of metal-cutting machines
After the numbers listed in the model marking, there may be letters that determine whether the model of the metal-cutting machine has special characteristics. These characteristics of the device may include its level of accuracy or indication of modification. Often in the designation of a machine, the letter can be found after the first digit: this indicates that this is a modernized model, in the standard design of which some changes have been made.
As an example, you can decipher the markings of the 6M13P machine. The numbers in this designation indicate that we have a milling machine (“6”) of the first type (“1”), which belongs to the 3rd standard size (“3”) and allows processing with increased accuracy (letter “P” ). The letter “M” present in the marking of this device indicates that it has been modernized.
General classification
The classification of metal-cutting machines is carried out according to various factors. These are divisions by weight, dimensions, type, accuracy class, degree of automation, and versatility. We need to talk about each of their groups in more detail.
Classification by type
There are 9 types of installations based on the type of equipment:
- Lathes. They occupy approximately 30% of the total mass of metal-cutting devices. The workpiece is clamped in a special clamp. The cutting process begins after installing the cutters, which remove a layer of metal under the influence of rotation.
- Boring, drilling units. They occupy 20% of the total mass of machines. The parts are fixed on the work table. Cutting occurs due to the rotation of the spindle with a drill clamped in the chuck.
- Grinding, grinding, polishing machines. They occupy 20% of the total mass of metal cutting installations. Metal cutting occurs due to the rotation of the abrasive material, which comes into contact with the working surface. The processing speed depends on the size of the abrasive.
- Devices for physical and chemical cutting of workpieces. Least common equipment.
- Devices for processing threads and teeth. Occupies 6% of the mass. Used for threading, manufacturing, and sharpening gears.
- Slotting, broaching, planing machines. They occupy 4% of the mass of metal-cutting equipment.
- Milling machines. They occupy 15% of the total mass. Processing of metal workpieces occurs due to the rotation of cutters of different shapes.
- Split installations. Used to separate reinforcement, profiles, corners.
- Machines for performing various operations related to cutting.
Classification by versatility
A separate division of metal-cutting machines is based on their versatility. There are two groups:
- Narrow profile installations. Used to perform one specific technological operation.
- Universal units. They are large-sized structures that are designed to perform various technological operations.
For better performance of technological operations, it is better to buy several machines with a narrow profile.
Classification by degree of accuracy
In terms of accuracy, metal-cutting machines come in several types, each of which has its own marking:
- Increased - denoted by the letter P.
- Normal - designation N.
- High - indicated by the letter B.
- Particularly high - designation A.
- The highest accuracy is indicated by the letter C.
To use units marked B, A, C, you need to prepare the room in advance. It must maintain a constant temperature and humidity level.
Classification by degree of automation
Based on the degree of automation, the following types of metal-cutting machines are distinguished:
- Manual models. The worker needs to clean, prepare workpieces, set up all moving elements independently, and coordinate the work process.
- Semi-automatic machines. The worker needs to change parts independently, turn on and off moving mechanisms.
- Automatic machines are units that process workpieces independently. Used in mass production.
- CNC equipment. The operator sets the required algorithm through the program. The moving mechanisms work independently, select optimal modes, load and unload parts.
CNC machines are gradually replacing other machines due to high processing accuracy and increased productivity.
Metal cutting automatic machine
Classification by weight
Industrial metal-cutting machines are divided by weight. Highlight:
- Lightweight - structures weigh up to 1000 kg.
- Medium - weight starts from 1 ton and ends at 10 tons.
- Large - weight from 16 to 30 tons.
- Heavy - weight from 30 to 100 tons.
- Super heavy - structures weigh more than 100 tons.
Designations are indicated in the technical data sheet.
Automation levels
Types of lathes, as well as devices for any other purpose that are used in mass and large-scale production, are called aggregate. They received this name due to the fact that they are assembled from the same type of units (units): beds, working heads, tables, spindle units and other mechanisms. Completely different principles are used when creating machines that are necessary for small-scale and single-piece production. The design of such devices, which are highly versatile, can be completely unique.
CNC lathe
Classification of lathes (as well as equipment of any other categories) according to the level of automation implies their division into the following types:
- manual models, all operations on which are carried out manually;
- semi-automatic, in which part of the technological operations (installation of the workpiece, starting the device, removing the finished part) is performed manually (all other auxiliary operations are carried out in automatic mode);
- automatic, for which you only need to set processing parameters; they perform all other operations independently, in accordance with a given program;
- metal-cutting units with CNC (all processes on such machines are controlled by a special program that contains a coded system of numerical values);
- metal-cutting equipment belonging to the category of flexible automated modules.
The most prominent representatives of metal-cutting machines are CNC devices, the operation of which is controlled by a special computer program. Such a program, which is entered into the machine’s memory by its operator, determines almost all parameters of the unit’s operation: spindle speed, processing speed, etc.
Even the most compact desktop machines can be equipped with a CNC system
All types of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system contain the following standard elements in their design.
- The operator's console (or console), through which a computer program that controls its operation is stored in the machine's memory. In addition, using such a remote control, you can manually control all parameters of the unit’s operation.
- The controller is an important element of the CNC system, with the help of which not only control commands are generated, transmitted to the working elements of the equipment, and the correctness of their execution is monitored, but also all the necessary calculations are made. Depending on the degree of complexity of the unit model, either a powerful compressor or a conventional microprocessor can be used as a controller to equip it.
- A screen or display that acts as a control and control panel for the operator. This element allows you to monitor the operation of a metal-cutting machine in real time, control the processing process, and, if necessary, quickly change parameters and settings.
The operating principle of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system is simple. A program is first written that takes into account all the requirements for processing a specific workpiece, then the operator enters it into the machine controller using a special programmer. The commands embedded in such a program are sent to the working elements of the equipment, and after they are executed, the machine automatically turns off.
The use of metal-cutting machines equipped with numerical control allows processing with high accuracy and productivity, which is the reason for their active use to equip industrial enterprises that produce products in large series. Due to their high level of automation, such units are perfectly integrated into large automated lines.
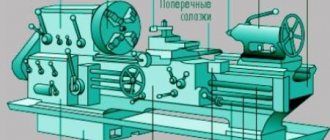
The device of a screw-cutting lathe
What accuracy classes exist and how do they differ?
The accuracy class is a generalized characteristic of measuring instruments, which is determined by the limit of errors (main and additional), as well as a number of properties that influence the accuracy of measurements made with their help.
The error limit is the greatest error of the measuring device at which it is suitable for measurement. The limit of permissible basic error is expressed in the form:
- absolute;
- relative;
- given
Errors. The class characterizes the property of accuracy of measurements using this device. And the accuracy of measuring instruments is the quality of a measuring device, which indicates that the error of the measurements is close to zero.
If we are talking about the class of accuracy that is provided, for example, by a lathe, then here we mean the class of surface finish of the part that this equipment is capable of providing during the processing of the workpiece.
Measuring instruments, as well as processing equipment, have the following accuracy classes: 0.01; 0.015; 0.02; 0.025; 0.04; 0.05; 0.1; 0.15; 0.2; 0.25; 0.4; 0.5; 0.6; 1.0; 1.5; 2.0; 2.5; 4.0; 5.0; 6.0. In addition, there are several categories of accuracy classes:
Special
This “Class C” is the highest class of equipment accuracy (both measuring and processing). This class includes machines (in our case, lathes) that must process workpieces to obtain the highest class of surface finish (0.01-0.015).
High
For example, jewelry, medical and laboratory scales have a high level of accuracy. Another name for such equipment is precision. It is marked “class B”. If we are talking about turning equipment, then a high class of cleanliness (0.02-0.025) is provided by polishing lathes.
Normal
The normal accuracy class (the marking is “class H”, but as a rule it is not placed) means such a characteristic of equipment or a part that ensures identical results in no less than 98% of obviously identical objects. The absolute indicator of the normal cleanliness class is in the range (2.0-0.6).
Particularly high
Equipment of a particularly high accuracy class is marked “Class A” for this indicator. When designing high-precision equipment, increased attention is paid to the quality of spindle bearings.
Here, rolling bearings are mainly used, also of high accuracy classes, and sliding bearings are made in the form of adjustable tapered bushings. (All standards here are established by GOST 1969-43).
Increased
This accuracy class is marked “class P”. The use of elements of a higher accuracy class (primarily bearings) increases the cost of the finished product processed on such turning equipment.
However, if it is necessary to obtain a higher class of workpiece processing, then elements of a higher accuracy class are used for positioning machine shafts, where higher accuracy and rotation speed are required.
Machine design
All machines belonging to the metalworking category have many common features in their design. In fact, the design and technical characteristics of such units must ensure the correct execution of two types of technological movements:
- the feed movement performed by the cutting fixture or the workpiece itself;
- the movement by which cutting is accomplished.
To perform these movements, as well as to ensure the stable functioning of all other elements of metalworking equipment, its design includes the following working parts:
- a control system responsible for starting and stopping the machine, monitoring all parameters of its operation;
- a unit with the help of which the movement from the electric motor is converted and transmitted to the actuator;
- directly the drive itself, which can be electrical, mechanical, pneumatic or hydraulic.
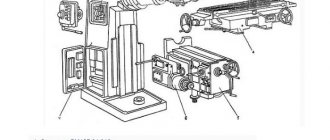
An important design element is also the units of metal-cutting equipment on which the cutting tool is installed and secured. It is with the help of such units that the main function of the device is realized - processing parts made of metal.
Selection principles
When choosing a metal cutting machine, you need to consider some factors:
- Control system.
- Dimensions, installation weight.
- Ability to perform one or more technological operations.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metal-cutting equipment has a number of strengths and weaknesses. Advantages:
- Automation of the work process with CNC.
- High precision metal processing.
- High performance.
- Reliability, durability.
- The need to install a cooling system.
- Difficulties in repair.
- Experience in CNC setup.
It is important to carefully monitor the work process to reduce the risk of injury or part rejection.
Metal cutting precision
Manufacturers and cost
Among the manufacturers of metal-cutting machines there are:
- Caliber - Russia.
- Energomash - Russia.
- Jet - Russia.
The price depends on the type, size, performance, availability of additional functions, control system. The cost of standard industrial metal-cutting equipment starts from 500,000 rubles.