Metal-cutting machines produced by domestic manufacturers are divided into several categories, which are characterized by the corresponding classification. You can determine which category this or that equipment belongs to by its labeling, which says a lot to those who understand it. However, no matter what category the metal-cutting device belongs to, the essence of processing on it comes down to the fact that the cutting tool and the part perform form-building movements, and it is they that determine the configuration and dimensions of the finished product.
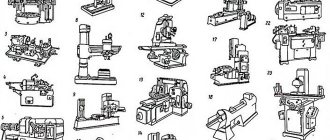
The most common types of metal-cutting machines: 1-6 - lathes, 7-10 - drilling, 11-14 - milling, 15-17 - planing, 18-19 - broaching, 20-24 - grinding.
Varieties
The variety of products is easily explained by the wide variety of operations that can be done with metal. In addition, there are many reasons on which differences can be made - depending on the drive, dimensions, type of steel. Let's look at how they can be classified.
By number of tasks:
- Universal. They are very suitable for small productions, when each order is individual. Typically, such a device requires preliminary adjustment, and also rarely has high accuracy. But it saves a lot of money, since you can install one device instead of two or three.
- Specialized. They are serial. Essentially they perform the same movements, but change sizes. Therefore, using one program you can make a whole series of identical parts with different dimensions.
- Special. These are even more narrow profile models for sheet metal processing and are often CNC based. Their task is to carry out one specified program as accurately as possible for multi-batch production of the same element.
In terms of accuracy, all equipment is divided on a five-point scale from the lowest (standard) to the highest level - master. This largely depends on the quality of the material from which the blade is made, as well as on its sharpening. The second important parameter is management. Manually, any machinations will not be very accurate, because the human factor matters. The most complete compliance with the specified dimensions of the part (in microns) will be achieved on CNC machines from . Milling and turning machines are suitable for the production of miniature elements. And the surface often does not require grinding or other finishing metalworking.
By automation level:
- Semi-automatic. The operator monitors and participates in each cycle, for example, placing the workpiece, adjusting the blades, pressing the start button, etc.
- Automatic. The employee's role is completely minimized. Work becomes easier, conditions in the workshop are much better.
There is also a separate type - this is equipment for metal processing with program control (PC). They are divided into two categories:
- Cyclic (C) – parameters are entered into the program for one completed cycle.
- Numeric (N), the most common. There is complete remote control over all processes: programming, searching for errors, changing indicators.
Also, all equipment is divided by weight. The greater the weight of the machine, the larger the workpieces can be cut.
By type of drive there are:
- Manual.
- Electrical.
The first, for example, metal shears, come into action after the application of human physical effort, while the second are powered by a motor.
But the most important classification, which is used most often, is based on the task of metalworking. Let's look at the images and talk below in more detail about each:
This is interesting: Safety check valve for a compressor: types, design, DIY production
Technology and processing features
Metalworking on CNC machines requires the correct setting of algorithms. The equipment can move along guides in different directions and perform various technological operations:
- Countersinking, drilling and reaming work.
- Milling of parts of different shapes.
- Turning of cylindrical workpieces.
These tasks are performed on machine tools that have three coordinate axes. If the installation has 5 coordinate axes, it becomes possible to perform more precise processing of metal workpieces.
After carrying out the work, the operator needs to turn off the equipment and clear the work areas of accumulated debris. It is necessary to lubricate moving mechanisms with machine oil in a timely manner and update the operating system. Check the integrity of the equipment before starting work. When uncharacteristic sounds or processing errors appear, you need to check all installation elements and double-check the correctness of the program settings.
CNC machines are gradually replacing manually controlled models. This is due to the fact that process automation increases productivity, accuracy of work, and speed. The operator needs to perform a minimum of actions. However, the high cost does not allow anyone to buy such models. Additionally, you need to understand how to configure the operating system.
Support the channel, just read our articles, and we will post useful information about metals for you! Also visit our website, where you will find a lot of information about metals, alloys and their processing.
General classification
Metal processing equipment is divided into 11 groups:
- Metal lathes. External and internal surfaces of rotation are processed. They have one thing in common: rotation of the part around its axis.
- Drilling machines. This group also includes boring machines. Used for passing through and blind holes. They are united by the rotation of the working tool and its simultaneous feeding. In horizontal boring mechanisms, feeding occurs due to the movement of the work table with the fixed part.
- Grinding machines. All such machines use an abrasive grinding wheel as a working tool.
- Polishing and finishing machines. A common feature is the use of abrasive wheels and polishing pastes.
- Gear processing machines. Designed for cutting gear and wheel teeth. This also includes grinding machines.
- Milling machines. In this group, the working tool is a multi-edge milling cutter.
- Planing machines. For these machines, the working stroke is a reciprocating movement of the cutter or workpiece.
- Slitting machines. They are used for dividing into parts by cutting a metal profile (angle, channel, rod, etc.).
- Broaching machines. The working tools are special multi-blade broaches.
- Thread processing machines. This includes equipment specifically designed for thread cutting. This group does not include lathes.
- Auxiliary and miscellaneous machines. They belong to a separate group and perform various auxiliary operations.
Classification by type
Equipment of the same type may have different layouts. A milling machine can be called horizontal or vertical - based on the location of the spindle axis. Kinematic schemes for transmitting movements, control systems, and cutting accuracy parameters differ.
Machines of the same type with a similar layout and kinematics, but having different sizes, will be combined into a size range. For example, gear hobbing machines are divided into 12 standard sizes depending on the parts being manufactured (from 80 mm to 12,000 mm). Each standard size of a machine designed for a specific processing of parts is called a model. Each model has its own designations: a combination of numbers and letters indicating the machine group, the maximum dimensions of the workpiece, the difference from the base model.
Classification by versatility
Processing mechanisms of the same group can perform different tasks:
- Universal ones process a wide range of products. The dimensions of the blanks may vary. Capable of performing any technological operations provided for this group.
- Specialized ones produce parts of the same type (body parts, shafts, similar in shape, but different in size).
- Special ones perform operations on one part of various sizes.
Classification by degree of accuracy
The degree of processing accuracy on a given machine is indicated by the letter included in its designation:
- N - normal accuracy;
- P - increased accuracy;
- B - high accuracy;
- A - particularly high accuracy;
- C - especially precise master machines.
Example: 16K20P - a lathe with increased accuracy.
Classification by degree of automation
Processing equipment is divided into automatic and semi-automatic. The working cycle of the machines is completely autonomous. In semi-automatic machines, loading of workpieces and removal of processed products is carried out by the operator. It also launches the next processing cycle.
Integrated automation of large-scale production of metal products involves the installation of automatic production lines from separate automatic machines. Products are produced in small batches using flexible production modules.
Machines that produce products under CNC control are designated by the letter C (cycle) or F. The numbers indicate a feature of the control system:
- F1 - digital display and preliminary selection of coordinates;
- F2 - positional control system;
- F3 - loop control system;
- F4 is a universal control system.
For example, the range of CNC metal lathes from the StankoMashKompleks company can be viewed at the link provided.
Classification by weight
Depending on the mass of manufactured parts, machines are divided into:
- lightweight, weighing up to 1000 kg;
- medium, weighing up to 10,000 kg;
- heavy, weighing from 10,000 kg, which, in turn, are divided into large (16,000-30,000 kg) and actually heavy (up to 100,000 kg);
- especially heavy - over 100,000 kg.
Machine numbering
Identification of any metalworking machine is based on assigning an alphanumeric code to it.
The numbers indicate which group the machine belongs to (lathe, milling, etc.), indicate the type and nominal size of the equipment. By deciphering the numbering, you can find out the height of the centers, the maximum dimensions of the workpieces or the drilling diameters of the workpieces.
Machining machines of the same size but with different characteristics are identified by the letter entered between the first and second digit. For example, lathes models 162 and 1K62 differ in maximum rotation speed. The first one has 600 rpm, the second one has 2000 rpm.
The difference between modifications of machines of the same model can be determined by the letter at the end of the number. If the numbering of the basic model of a horizontal milling machine is 6N82, then the simplified modification of this machine is 6N82G.
Numbering occurs when the fourth digit identifies an improved version of a machine of the same standard size. Thus, the horizontal boring machine model 262 has a modern modification, designated 2620.
Assigning alphanumeric indices to metalworking machines makes it easy to find the corresponding equipment in special catalogs. Indexing also makes it possible to quickly find the necessary spare parts.
Types of metalworking machines
To know what type of device is needed for operation, you should carefully study the general classification. Metalworking machines of the same type often differ in kinematics, parameters, design features, control method, and so on.
Depending on versatility:
- universal – used to create products of different sizes, names and shapes (custom orders);
- specialized - suitable for the manufacture of products of similar markings, but of different dimensions (series);
- special – designed for the production of parts with the same name and parameters (mass production).
Depending on accuracy indicators:
- normal (N);
- increased (P);
- high (B);
- especially high (A);
- master machines (C).
Depending on the level of automation:
- semi-automatic machines - the work cycle is automated, but the employee loads/unloads the parts independently;
- automatic machines - all processing processes are performed automatically.
To produce small-scale parts in automatic mode, devices have been developed that have special software control :
- cyclic (C) – the processing cycle is configured, the room parameters are set in a simplified manner;
- numerical (N) – constant control over the processing process using a unique control program (all data is recorded in digital format).
The control system for CNC equipment can be: digital display/coordinates (f1), positional (f2), contour (f3) and universal (f4).
Depending on weight:
- up to 1 ton – light;
- up to 10 tons – medium;
- from 16 to 30 tons – large;
- from 30 to 100 tons – heavy;
- from 100 tons and above – especially heavy.
According to the type of work performed and types of cutting mechanisms, metalworking machines are divided into groups:
| Name | Characteristics (“O” – processing, “RI” – cutting tool) |
| Turning | Required for "O" certain torsion surfaces. Cutting (turning) occurs due to the rotation of the workpiece |
| Drilling | This group includes boring devices. The main task is the production of “O” holes that have a round shape. Tool rotation/feed input |
| Grinding | “RI” – grinding wheel (abrasive) |
| Polishing and finishing | “RI” – sanding belts and bars |
| Gear processing | The main task is “O” of the wheel teeth |
| Milling | “RI” – device with rotating cutters (mill) |
| Planing | Cutting occurs due to the forward/backward movement of the cutter or workpiece |
| Split | The main task is sawing/cutting rolled profiles. “RI” – circular saw or hacksaw blade |
| Drawing | “RI” – special broach (device for cutting metal with blades) |
| Thread processing | This group does not include turning devices. Used for making carvings |
| Miscellaneous/auxiliary | Other devices not included in previous categories |
The manufacture of metalworking equipment is carried out in accordance with the developed requirements and standards. Each stage is carefully controlled; any errors made during the production process will make further operation of the equipment impossible. The correctness and accuracy of the device’s operation determine the quality characteristics of the workpiece.
Categories of metal cutting machines
Turning
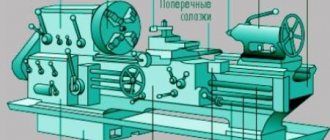
In the marking they are indicated by the number 1 . This equipment is most often used for processing cylindrical, conical, shaped surfaces. It is divided according to the degree of accuracy that it can provide into: special (C), high (B), especially high (A), normal (N), increased (P). Machines of this group, as a rule, have the main components: a bed, an apron, a spindle head, a support, a gearbox, and electrical equipment. According to the range of operations performed, machines are distinguished:
- Revolving . They are used for the production of single workpieces placed on the machine on several surfaces at once. Setting up such installations is a complex undertaking. It is simplified by the presence of a turret head, on which there are several slots that serve to accommodate cutting elements.
- Carousel . They are in demand for working with workpieces of short length but significant diameter - flywheels, gears. Used for turning, boring, and end processing. They can be equipped with additional devices that significantly expand the functionality of the units.
- Screw-cutting . The most common group of machines. Models 16K20, 16K50, 16B16A are found in almost every machine-building enterprise. Such units perform almost a complete list of basic turning operations.
- Multi-spindle automatic lathes . Complex, multifunctional, high-performance equipment that provides high precision when working with semi-finished products from pipe, square, hexagonal cold-rolled steel. It is used for cutting and rolling threads, boring, roughing and shaped turning.
- Automatic lathes for longitudinal turning . They are in demand in large-scale production for working with rods of various cross sections.
Drilling and boring
In the marking they are indicated by the number 2 . This is a wide group, including equipment for the production of through and blind holes, their finishing (countersinking, reaming), and cutting internal threads. Drilling machines:
- Vertical drilling is the most common model. They are divided into tabletop and column-mounted.
- Radial drilling . Heavy engineering enterprises use units transported on rails along workpieces or installed directly on large-sized products or structures.
- Multi-spindle . They are a complex of several single-spindle machines located on one table and bed. Such equipment ensures high productivity of the process, which includes several operations repeated in a certain sequence. For example, drilling, countersinking, reaming.
Other types of drilling machines:
- Drilling and milling . They are in demand for inclined face and horizontal milling, grinding with drills, reamers, and taps.
- Boring - horizontal boring (the most common), jig boring, diamond boring.
- Special units for the production of large-scale and mass batches. They are based on universal drilling machines equipped with multi-spindle heads and automation equipment.
Grinding, polishing, finishing
In the marking they are indicated by the number 3 . These are units capable of performing highly specialized functions or a set of operations to obtain a given degree of cleanliness of cylindrical, conical, profile, flat surfaces, including internal (cylindrical and conical). Manufacturers offer both compact devices used in home or small repair shops, and for large enterprises in the mass production of parts, products, and structures. To prepare samples for metallographic studies, benchtop grinding and polishing systems are designed to produce a very high quality surface.
Combined (special purpose)
In the marking they are indicated by the number 4 . This group includes electroerosive, electrochemical, electrospark, electromechanical, ultrasonic and others machines.
For the production of threads and gear elements
In the marking they are indicated by the number 5 . There are many methods and types of equipment for cutting threads. This operation can be carried out on a screw-cutting lathe using a cutter, on a drilling unit using a tap, or on a milling machine. However, for high-performance processes, specialized devices are used that can be used to produce threads of all standards - metric and inch on pipes, cylindrical, conical, trapezoidal.
- Thread rolling . The design resembles vertical drilling units. Thread rolling (internal and external) is carried out on conical and cylindrical workpieces and pipes. When rolling, threads are obtained not by removing chips, but by plastic deformation. This technology is used in large-scale and mass production.
- Thread milling machines . These are the most highly productive machines. A disk cutter produces threads of considerable length and pitch, while a comb cutter produces short, small threads.
- Thread grinding machines . Single- or multi-thread wheels with abrasive are installed on them.
Machines for making gear profiles:
- Gear cutters - for cylindrical and bevel wheels.
- Gear hobbing horizontal, vertical and others - allow you to produce a gear involute profile. Complex surfaces are produced using rolling technology. CNC units provide high precision operations and productivity.
- Gear grinding . They are used to obtain precise geometric dimensions and high levels of surface cleanliness of gears, shafts, and racks. Depending on the task and model, the equipment is equipped with grinding wheels of various types: worm, profile, flat, conical, disc.
Milling
In the marking they are designated by the number 6 . Units of this type process workpieces mounted on a table. In this case, the cutting tool is characterized by rotational motion, and the workpiece is characterized by reciprocating motion. The group of cantilever milling machines includes models:
- Horizontal milling machines with a fixed table . These units were most popular in factories built and equipped during the Soviet Union. They have a simple design that allows you to mill one surface without changing the cutter or reinstalling the part.
- Horizontal milling machines with rotary table . This unit can process several surfaces at the same time.
- Vertical milling . Structurally similar to vertical drilling. Can be used for drilling, boring, countersinking.
- Widely versatile . They differ from vertical milling machines by an additional spindle head. Perform operations: milling, drilling, boring.
The group of non-cantilever units includes models in which there is no console, and the base is a workshop floor or a reinforced concrete slab. This design makes it possible to process bulky parts, products, and structures.
Slotting, broaching, planing
In the marking they are indicated by a number 7.
- Slotting . Used to make keyways, splines, grooves on cylindrical and conical workpieces. Typically used for the production of single and small-scale batches at factories producing windows, furniture, and shipbuilding.
- Lengthy - standard and special . In demand for shaped, multifaceted, cylindrical calibration of holes, finishing of external profiles of complex configurations, cutting splines and keyways.
- Planing . These units are usually used to carry out operations following the jointers. There are longitudinal and transverse planing models.
For cutting operations
In the marking they are indicated by the number 8 .
Cutting machines are machines that allow you to separate parts of any size and cross-section from any metal into pieces of the required length. In standard versions, cutting is done at angles of 90° or 45°. Group 9 includes machines for a wide variety of purposes, for example, saw-cutters, centerless-grinders.
Division by accuracy classes
The entire variety of metalworking machines is divided by accuracy class:
- normal – H;
- increased – P;
- high – B;
- especially high – A;
- especially precise (master machines) – C.
The main part of the machine equipment provides processing according to 6–9 accuracy grades. Machines belonging to classes A, B and C have increased requirements for operating conditions, this is due to their very high accuracy. Their installation requires separate rooms with constant temperature and humidity.
Metal-cutting machines cannot exist without markings. The letter designating the accuracy class, except for machines with normal accuracy H, is added to the marking. For example, 16K20P.
What is an industrial machine?
An industrial machine is a unit for processing metals, stone, wood, glass and other production materials. The main elements of the frame are the grinding wheel, drill, and cutting devices. The equipment is used in enterprises and workshops as a separate unit or as part of an automated line. The most popular in industry are metalworking machines; with their help, mass production or single production of blanks is established.
Types of metal-cutting equipment
Depending on their purpose, metal-cutting machines are divided into nine main groups. These include the following devices:
- lathes - all types of lathe machines (in the marking they are indicated by the number “1”);
- drilling and boring - machines for performing drilling operations and boring (group “2”);
- grinding, polishing, finishing - metal-cutting machines for performing finishing, grinding, sharpening and polishing technological operations (group “3”);
- combined - metal-cutting devices for special purposes (group “4”);
- thread and gear processing - machines for processing elements of threaded and gear connections (group “5”);
- milling - machines for performing milling work (group “6”);
- slotting, planing and broaching - metal-cutting machines of various modifications, respectively, for planing, slotting and broaching (group “7”);
- cutting - equipment for performing cutting work, including saws (group “8”);
- different - examples of such metal-cutting units are centerless-grinding, saw-cutting and others (group “9”).
Groups and types of metal-cutting machines (click to enlarge)
In addition, metal cutting machines can be one of the following types:
- multi- and single-spindle, specialized (semi-automatic and automatic), multi-cutting copying, turret, drilling and cutting, rotary, frontal and special types of lathes;
- equipment for performing technological operations of boring and drilling: multi- and single-spindle, semi-automatic, drilling machines of vertical, horizontal and radial type, boring devices of coordinate, diamond and horizontal type, various drilling models;
- various types of grinding machines (flat, internal and cylindrical grinding), roughing and polishing equipment, sharpening and specialized units;
- types of metalworking machines designed for processing elements of gear and threaded connections: gear cutting machines (including those intended for processing conical wheels), gear cutting machines - for cylindrical gears, gear milling, thread cutting, thread and gear grinding, gear finishing, checking, thread milling, devices for processing the ends of teeth and elements of worm pairs;
- metal-cutting machines belonging to the milling group: cantilever (vertical, horizontal and universal models) and non-cantilever (vertical devices, longitudinal, copying and engraving models);
- planing equipment and models for similar purposes: longitudinal machines on which one or two stands are installed; horizontal and vertical broaching devices;
- cutting equipment: equipped with an abrasive wheel or a smooth metal disk, cutter or saws of various designs (band, disk, hacksaw); straightening-cutting types of metalworking machines;
- other types of machines for processing metal workpieces: dividing machines, used for monitoring drills and grinding wheels, filing, balancing, leveling and centerless roughing, sawing.
Vertical milling machine is one of the representatives of an extensive milling group
Classification of metal-cutting machines is also carried out according to the following parameters:
- by weight and overall dimensions of the equipment: large, heavy and unique;
- by level of specialization: machines designed for processing workpieces of the same size - special; for parts with different but similar sizes - specialized ones; universal devices that can be used to process parts of any size and shape;
- according to the degree of processing accuracy: increased - P, normal - N, high - B, especially high accuracy - A; There are also machines that can perform particularly precise processing - C, they are also called precision.
This is interesting: Inverter welding machines: which one is better and how to choose
Milling cutters
In the classification of milling machines, a special place is given to cantilever-horizontal and universal units. These modifications make it possible to process horizontal and vertical surfaces at any angle, and on “universal machines” with a rotary table it is possible to mill screw and gear parts with maximum accuracy. The technological operations of these machines are expanded by all kinds of attachments such as unified heads and other devices.
Console modifications differ from vertical-horizontal versions in that they are equipped with table rotation relative to its own axis. Multifunctional devices are equipped with a special trunk on the frame, which aggregates with the spindle head and other structural elements. Such equipment is used to perform operations on processing cast iron, steel, and non-ferrous metals. The console is located on vertical guide elements that hold a slide with a longitudinal plate and corresponding parts used for horizontal processing of material.
Exhibition of metalworking equipment
The metalworking exhibition is a serious, highly specialized event that brings together professionals in this field. Progressive equipment, new surface treatment techniques, modern software, components - all this is presented at the organized exhibition. Here you will find: information about the latest scientific achievements, meaningful communication with experts and a thoughtful business program.
Participants and visitors
The participants of the event are world-famous companies and little-known manufacturers/suppliers who strive to increase demand and effective product promotion. The main task is to demonstrate high-performance machine tools, tools, materials and the latest developments in this industry.
Among visitors :
- general directors and deputies;
- leading technologists;
- chief engineers.
Professionals in such industrial sectors as shipbuilding and mechanical engineering, metallurgy, energy, construction and so on gather here. Managers of manufacturing companies and factories choose high-performance machine tools to efficiently complete their tasks.
Advantages of exhibitions
Each side receives beneficial positive aspects, which we will discuss in more detail.
Event participants can, as soon as possible,:
- find potential buyers willing to purchase specialized equipment and tools for metalworking;
- increase the number of sales;
- expand the territorial boundaries of sales;
- arrange a demonstration of modern technological solutions and innovative developments of the company;
- learn an unbiased analysis of the technical characteristics and performance indicators of the exhibited equipment;
- establish communication with intermediary organizations and company managers using the proposed machine systems.
The benefits for visitors will be:
- a wide range of high-performance devices;
- direct analysis of technical indicators;
- studying the latest developments;
- testing of modern technologies in operating mode;
- execution of transactions on favorable terms;
- expert recommendations on the correct choice of metalworking products.
The conditions of highly specialized exhibitions allow participants and visitors to begin business relationships, which will subsequently lead to long-term mutually beneficial cooperation.
By degree of automation
Metal-cutting machines are often produced with an additional automation function. Depending on the degree of automation, machines are divided into the following types:
- manual control;
- semi-automatic, when the processing cycle is carried out automatically, and the operator changes the workpiece and turns on the machine;
- automatic machines, where many work cycles continuously occur automatically, without an operator, including tool replacement, loading and unloading of parts;
- CNC machines, they are produced with the function of quickly changing operating modes by adjusting the program.
CNC lathes
Modern metal-cutting machines are produced with additional equipment, this speeds up the process of processing the material. Craftsmen can increase the degree of automation in small-scale production by making greater use of machines with numerical (cyclic) program control (CNC). Their markings contain the letter F (C).
The number behind the letter indicates the type of control system:
- digital indication F1 – the system allows you to make a preliminary set of coordinates, the digital indication displays in numerical terms the current position and movement of the moving unit of the machine;
- rectangular or positional system F2;
- contour F3;
- universal F4 – combines contour and positional processing of a part.
Indexes and numbering in the classification of lathes
In the Soviet Union, a unified system of symbols was practiced. According to the standards of the experimental research institute, each group of machines was divided into a similar number of subgroups.
The table below shows the main parameters.
| Name | Turning | Drilling and sharpening | Grinding and finishing | Gear and thread processing | Milling cutters | Slitting and planing |
| 1 | Single-spindle, carousel and multi-function options | Semi-automatic | Multi-spindle | Cut-off with drilling capability | Working with the provided modes | Standard Operations |
| 2 | Circular grinders | Light-beam | Slot machines | Boring by coordinates | _ | _ |
| 3 | Light-beam | Focused on finishing conical products | Internal grinding | Specialized grinding | Standard program | Standard |
| 4 | Automatic | Continuous milling machines | Supplemented with light rays | Electrochemistry | _ | Standard |
| 5 | For cutting worm, round and other wheels | For processing conical workpieces | _ | For machining worm gears | Processing of all parts specified in the operating instructions | _ |
| 6 | Vertical console and milling models | Vertical milling versions | _ | Single flow longitudinal versions | _ | _ |
| 7 | Longitudinal versions with one working line | Continuous machines | Cross-planing units | Longitudinal version of leveler | _ | _ |
| 8 | Longitudinal cutting | Double and single post | Grinding wheel | Circular finish | Drilling vertical and horizontal holes | __ |
| 9 | Coupling modifications | Includes pipe processing devices in their segment | Centerless organization | All available options | _ | _ |
| 10 | Other options | Saws and notches | _ | _ | All typical services | _ |
Automation levels
Manual installations are giving way to CNC equipment. This automation system consists of several interconnected elements:
- Remote Control.
- Monitor for task of algorithms, control of work process.
- Sensors that determine the position of the workpiece on the work table and the movement of the equipment.
- Stepper motors that are controlled by a computer.
The operator must have practical experience in setting up and repairing such systems.
Selection principles
When choosing a metal cutting machine, you need to consider some factors:
- Control system.
- Dimensions, installation weight.
- Ability to perform one or more technological operations.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metal-cutting equipment has a number of strengths and weaknesses. Advantages:
- Automation of the work process with CNC.
- High precision metal processing.
- High performance.
- Reliability, durability.
Flaws:
- The need to install a cooling system.
- Difficulties in repair.
- Experience in CNC setup.
It is important to carefully monitor the work process to reduce the risk of injury or part rejection.
Manufacturers and cost
Among the manufacturers of metal-cutting machines there are:
- Caliber - Russia.
- Energomash - Russia.
- Jet - Russia.
The price depends on the type, size, performance, availability of additional functions, control system. The cost of standard industrial metal-cutting equipment starts from 500,000 rubles.
Design
Basically all devices consist of:
- strong frame;
- work area;
- clamps or other devices for holding the workpiece;
- engine and belts transmitting rotation;
- tool for cutting (grinding).
An interesting question is what paint coatings are applied to metalworking equipment. The peculiarity of paintwork is that it can withstand increased friction, as well as high temperatures.
In the article we talked about machines for metal processing, and to complete the topic, watch a video:
Advanced Metalworking Techniques
In industrial conditions, both the latest and long-known methods are used for metal processing. Modern types of metalworking equipment meet the following requirements:
- productivity – industrial volumes require high speed of operations;
- accuracy - you need to maintain dimensions when manufacturing even the smallest parts;
- reliability and wear resistance.
Industrial equipment for metalworking is divided according to the type of impact on the material. Cutting can rightfully be considered the most common operation at metalworking enterprises.
Gas metal cutting
This method has been known for a long time, but the machines currently produced are fully automated. This eliminates inaccuracies when cutting sheets, which can be caused by the human factor. The disadvantages of the method are low accuracy and heat shrinkage of the metal. Pros: low cost of equipment and high speed of execution.
Plasma cutting machines
Cutting occurs using a narrow plasma jet, which allows for high precision and arbitrary shapes of the workpiece. The high quality of the surface at the cut site, productivity and the ability to cut almost any part are offset by one drawback - plasma machines are not cheap.
Laser processing
Laser cutting machines are precise and prevent loss of material at the cut site due to its small width. This type of equipment is used for processing soft non-ferrous metals: aluminum, brass, bronze (including valuable ones). Laser cutting machines are often used to produce blanks for electronic circuit boards and parts for modern household appliances.
Waterjet and electroerosive machines
These types of equipment are used for precise cutting of any metal of any thickness. The relatively low processing speed is compensated by quality. Both methods guarantee high accuracy and very low cutting allowance consumption. Waterjet and electroerosive machines are used in space, electronics and other types of industries.
Gantry metal gas cutting machines
When processing industrial volumes of metal, modern enterprises use portal gas cutting machines. The design of the machine allows you to place sheets ranging in size from 1.5x3 m to 3x12 m in the working area.
This cutting method is economical, but there is also a small drawback. When processing sheet metal of small thickness, heat shrinkage and a decrease in cutting accuracy are possible. The operator will need maximum care and experience when working with a gantry gas cutting machine.
Equipment for working with metals from Warcom
The Italian company Warcom offers a wide selection of equipment for metal processing. Our product range includes press brakes, plasma and laser cutting machines, guillotines and other equipment used in the metalworking industry. You can choose budget models or machines for large enterprises with many functions. It is also possible to purchase used devices that have undergone pre-sale testing, guaranteeing their quality and performance.