What are gas cutters and what types do they come in?
Gas cutters are designed for cutting rolled metal and dismantling metal structures. The principle of operation of a cutter for cutting metal is quite simple - gas burns at the end of the torch, creating a high temperature zone exceeding the melting point of the metal. Gas is supplied to the burner through a hose from a portable cylinder built into the handle or from an external cylinder through a hose. Air oxygen can be used to oxidize flammable gas; in other designs of oxygen cutters, gas is supplied from a separate cylinder through a separate hose.
There are many types of gas cutters and torches. Existing types of cutters are classified according to the following criteria:
- by type of cutting; superficial;
- dividing;
- manual;
- propane;
- injection;
- low;
- multi-nozzle;
- small - up to 100 mm;
Mini gas cutter
In addition, there are ultra-portable pocket-type mini gas cutters, the power of which allows, however, to cut several millimeters of steel or copper sheet. This gas cutter is ignited by a match or by a built-in piezoelectric element.
An injection cutter for manual oxygen cutting not only does not fit in a pocket, but also requires an impressive cart to transport its cylinders. Stationary cutters for cutting sheet metal are complex automated industrial installations with an area of tens of square meters; gas is supplied to them through a stationary gas pipeline from large gas tanks.
Classification of devices
Gas cutters have many types and are classified according to the following criteria:
- type of cutting: surface and separation;
- purpose: manual and mechanized;
- type of fuel: acetylene, propane, methane, kerosene;
- design: presence or absence of an injector;
- oxygen supply: low and high pressure;
- mouthpiece type: multi-nozzle and slotted;
- power: low (20 cm).
Read also: How can you dissolve rosin?
Today, different manufacturers produce more than a dozen modifications of such equipment, but structurally they differ little from each other. Such devices are characterized by the presence of a handle with valves for changing the supply of flame-forming gases, and a tip with a head in which the flame is formed.
The figure shows an example of a gas cutter from KRASS
Externally, the cutter and welding torch have much in common. As noted above, the main difference is that the latter oxygen supply does not have a cutting jet and a different head device. You can read more about burners in the article: gas-air burner for gas-flame processing of materials.
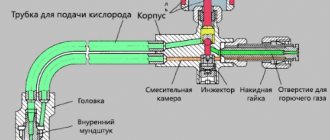
Cutting torch design
The construction of a gas cutter is quite simple. The main nodes are:
- nozzle for forming a torch;
- gas supply barrel;
- frame;
- lever.
The barrel, in turn, consists of an ejector, inlet pipes for connecting hoses, nipples, shut-off and control valves and connecting fittings.
All units, despite different performance and other characteristics, have a similar operating principle. Combustible gas and oxygen are supplied to the mixing chamber, after which they flow out under pressure through the working nozzle. The gas flow rate and the proportion of their mixing are controlled by two independent valves at the inlet to the device. This determines the intensity of the flame and its temperature.
Cutter device
The torch, hitting the metal of the workpiece, quickly heats it up to the melting point. Some of the metal evaporates and is carried away along with combustion products into the atmosphere, some oxidizes and turns into slag, and some flows down in the form of drops. A cut is formed in the metal. If you smoothly move the torch along the intended line, the heating zone will move and the cut will increase until the desired part of the workpiece is cut off.
In-nozzle mixing
In devices with intra-nozzle mixing, the mixture is formed in slotted channels between the outer sleeve and the inner mouthpiece. The supply of cutting oxygen is carried out by a lever valve, and the heating and combustible gas is supplied by regulators installed on the handle.
This equipment is available in 3 versions: for working with acetylene, propane and natural gas. Since the gas is mixed not at the handle, as in injection devices, but at the head, such devices have an increased level of safety. At the same time, this principle of operation requires a more complex design, which leads to an increase in the cost of the device. Also, for stable operation, an increased pressure of combustible gas is required - from 20 kPa.
Devices with intra-nozzle mixing
Portable portable cutters with oxygen and propane cylinders
An oxygen gas cutter for metal with 40-liter cylinders on a heavy trolley significantly limits the mobility of the gas cutter. There are enough heavy hoses to reach every point in a small workshop, and when working in open areas, the gas welder spends more time rolling the cart than working. A portable, portable propane torch can help you get out of the situation. It is equipped with small, lightweight hoses, a five-liter oxygen tank, and allows you to connect two-, three-, or five-liter propane tanks. For carrying, use a plastic container-suitcase or a rubberized bag, reinforced with metal corners and stripes.
portable cutter
The device easily fits in the back seat of a car and is widely used for home repairs of air conditioners, refrigerators, heating and water supply systems. This gas cutter is also very convenient for a home workshop.
Device with collet connection advantages and disadvantages
If you are not involved in artistic metal work, then the need for gas welding or cutting arises infrequently. In this case, there is no point in investing in expensive professional equipment. As a solution, many people choose portable collet-type gas cutters for metal.
The burner itself is an attachment to a portable gas cylinder with a capacity of 0.22 to 0.5 liters, used in conjunction with camping gas stoves. By adjusting the shape of the torch of such a burner, it is possible to obtain both a wide torch tens of centimeters in size and a narrow concentrated cone. The wide torch is suitable for cooking in weather conditions, warming frozen metal pipes and locks, etc. A narrow cone can melt solder when soldering and even cut thin sheets of metal. The temperature at the top of the torch reaches 1300 °C. The disadvantages of the device are:
- High consumption of flammable gas (up to 0.22 l/hour). For long-term work you will have to stock up on cylinders.
- Using only atmospheric oxygen does not allow developing high pressure in the jet. The torch may go out in strong winds.
Gas cutter with collet connection
You shouldn’t expect to use such a device to cut reinforcement for the foundation, but dismantling the old porch frame is quite possible.
Gas cutter for metal: varieties
Gas cutters for metal are divided according to different criteria. For example, there is a classification based on the gas used, dimensions, type of cutting, design, and method of mixing consumables.
Acetylenic
It is a metal cutter that is used for cutting thick metal parts. Acetylene equipment is equipped with additional valves that allow you to set a high gas supply rate. There are industrial and portable models of cutters. Acetylene provides maximum flame temperature. This results in a greater depth of metal cutting.
Acetylene metal cutter
Propane
Propane-powered equipment is used for cutting alloys, non-ferrous and ferrous metals. The maximum cutting thickness is 300 mm. Propane cutters are more reliable, which ensures their durability during active use. Masters pay attention to the safety of such devices. They are often used when carrying out independent work in private workshops.
Portable cutting torch
You can buy a device for autonomous operation. Mini cutters fit in the palm of your hand. They are a metal canister of gas onto which a nozzle with a flammable substance supply system is screwed. You can compare a hand-held device with a turbo lighter. Using matches, a lighter or an installed ignition system, the gas is ignited and passes through special nozzles and nozzles, which form a thin stream of high-temperature flame. It does not go out in strong winds, which makes it easy to use a handheld cutter outdoors. To fill a small can, you can use a special refill nipple or buy a new full container.
Small cutting torch or torch in your pocket
An ultra-portable cutter that fits in the palm of your hand, it's not a spy movie prop, but a real gas cutting device. It resembles the turbocharged lighters that have become popular and do not go out even in strong winds. This effect is achieved by accelerating the gas flow in the nozzle of a small turbine and forming a torch in a special nozzle. When burning for a long time, the upper part of the lighter begins to heat up and even melt. The mini-cutter uses special materials and design solutions to avoid this. The gas stream is also accelerated and formed by a specially shaped nozzle, forming a narrow high-temperature torch. The gas reserve is enough for several minutes of work; it can be replenished from a standard collet cylinder through the nipple.
This device cannot cut a five-millimeter steel corner, but it is quite capable:
- lighting a fireplace or barbecue;
- soldering of jewelry;
- soldering of thin-walled copper tubes.
It is inexpensive, and a thrifty owner can simply have it in the house just in case.
A cutter instead of a soldering iron melts tin and copper
A standard oxygen torch has not only a maximum, but also a minimum burner power. It can cut steel sheet, angle or I-beam or weld them together, but is not suitable for delicate work or spot welding.
In addition to the already mentioned ultra-portable cutter with a reservoir located in the handle, which is enough for several minutes of work, there are miniature cutters that are connected to a standard collet cylinder with a flexible hose.
Unlike the ultra-portable version, they have slightly less mobility, but significantly longer continuous operation time.
Most mini-cutter models have two operating modes:
- Wide cone with a diameter and length of up to 5 cm. Used for melting solder, soldering tin and copper products.
- Short and narrow high-temperature torch. It is used for spot soldering of small parts and for soldering electrical and radio components.
Micro burner
It is also not suitable for cutting steel sheets and profiles, despite the high temperature of the torch - up to 1300 °C. Low pressure and low flame intensity have an effect. The device is very economical - gas consumption is 12 g/hour.
Preparing for work
Fine tuning is carried out at the manufacturing plant as the final phase of the technological process and quality control. Independent “improvements” and “finishing”, descriptions of which can be found in the blogs of folk craftsmen, should in no case be attempted to be repeated. Interfering with the design and settings of gas equipment is expressly prohibited by the rules of its operation and can lead to fire, explosion, serious injury or even death.
Before you begin, you should assemble and check the gas equipment in strict accordance with its operating instructions.
Let us recall the general rules for preparing for gas cutting:
- Carefully inspect all equipment, including cylinders, hoses, reducers and valves, for mechanical damage.
- Listen and sniff to see if there is a gas leak. This operation should be repeated after connecting the hoses and the torch.
- Check the condition of all gaskets. They cannot be repaired; if there is the slightest suspicion of a defect, they should be replaced.
- Inspect the oxygen valve for oil and grease stains. Even the slightest traces can cause an explosion. Wipe the valve with solvent or degreaser and wipe dry with a clean rag.
- Inspect the fittings for any burrs or irregularities that could damage the seal. If found, carefully correct the defect with a velvet file.
- Connect the reducers to the cylinders: blue – oxygen;
- red – propane.
If the cutter is injection, then the operation of the injector must be checked BEFORE connecting the propane hose to the cutter:
- Connect the oxygen hose to the connector.
- Open the valve on the gearbox.
- Open both valves on the burner.
- Place the tip of your finger near the hole in the propane fitting.
- If the injector is working correctly, the pad will be sucked into the hole.
Next, you can connect a propane hose and set the pressure in a ratio of 1:10. So, if the oxygen pressure is set to 4 atmospheres, then the propane pressure should be set to 0.4 atmospheres.
First, you should open the oxygen supply half a turn, then the propane supply by the same amount and set the mixture on fire. Bring the burner into the work area and increase the oxygen supply until a torch forms in the form of a “crown”
After cutting is completed, first stop supplying propane and then oxygen.
It is strictly prohibited:
- change the sequence of gas supply when igniting and turning off the burner;
- swap hoses.
Violation of these rules may result in fire and explosion.
Operating principle and types of cutters
Regardless of the size of the autogen and the types of heating gas mixture, cutting can occur using the process of metal combustion in a stream of oxygen of a pure mixture, pumped through a special nozzle in the head of the working zone.
The main and fundamental feature of gas cutting is the combustion temperature, which must be no less than the melting temperature. Otherwise, the metal, without having time to flare up, will melt and flow all the time. Low-carbon fats must meet these conditions, but non-ferrous metals and cast iron do not.
A large number of alloy steels will also not be amenable to the gas cutting process - there are significant restrictions on the maximum indicator and permissible dosages of alloying components, carbon, impurities, the process of exceeding the combustion of which inside oxygen will become the most unstable or will cease to occur at all.
The cutting itself should be divided into two stages:
- Heating one part of a part to a temperature at which the metal begins to burn. In order to obtain a heating flame, part of the technical oxygen in a certain ratio is mixed with gas .
- The process of combustion (oxidation) of heated metal in a stream of oxygen and the general removal of the combustion product from the cutting zone.
If we start to consider the classification of only hand-held cutters, then this value will have the following features:
Type of fuel, power and method of producing a mixture of gases for a heating-type flame.
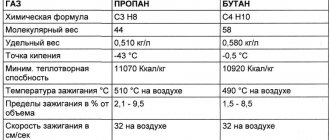
- Classification by type of flammable gas: propane-butane, methane, universal MAF, and acetylene.
- Power feature: small (cutting metal with a thickness of 3 to 100 mm) - marking P1, medium (up to 2-0 millimeters) - marking P2, higher (about 300 millimeters), marking - P3. There are special samples with a cutting thickness of about 500 millimeters.
- And if the first feature will only affect the overall temperature of the heating flame, as well as the power - the maximum thickness of the metal, then another feature will determine the design feature of the cutter.
How to use an oxypropane torch
Safe and productive work with an oxygen cutting torch must comply with the following rules:
- be sure to use personal protective equipment: welder’s mask or welder’s goggles;
- split leather gloves;
- dense workwear that does not leave exposed skin and has fire-resistant impregnation;
- respirator;
Work post
When starting for the first time or in case of a long break in operation, be sure to check the operation of the injector
Strictly follow the sequence of actions to prepare for work, set up operating modes and complete work.
Kerosene-oxygen cutters
Equipment for cutting metal that runs on kerosene has design differences from gas machines, since in order to produce a flame it is necessary to transform the liquid into a gaseous state. This process is carried out in an evaporator, in which the kerosene is heated using a special heating nozzle.
Fuel is supplied from the tank through an oil- and petrol-resistant hose under a pressure of 30 kPa. The container is equipped with a safety valve and a hand pump, and taking into account the design, it allows you to fill up to 8 liters of fuel. A device of this type is in demand when working in the field.
What you need to know when working with cutters
First you need to know the operating principle and classification of these devices. To do this, you can watch the video below:
- Each valve handwheel is marked with the gas whose flow it regulates.
- The arrows on the valve indicate the direction of opening and closing (“O” - opening, “Z” - closing).
- The gas index is indicated on the replaceable mouthpiece (“A” - acetylene, “P” - propane, “M” - methane).
- The oxygen fitting nut has a right-hand thread, and the fuel gas fitting has a left-hand thread.
- Parts in contact with acetylene before the mixing chamber are not made of copper and copper-containing alloys (>65%).
We also recommend watching a video on how to choose this device:
You can purchase high-quality cutters that perform gas cutting of metal (up to 30 cm), and also fill a propane cylinder at the best price.
What to look for when choosing a gas cutter
When choosing a device, you need to check the following few points:
- It is better to choose brass nipples, they will last longer than aluminum ones;
- the aluminum handle is more durable than the plastic one;
- the valves should rotate without jamming, but with a constant slight force;
- choose a model with an oxygen valve washer from 4 cm in diameter - adjusting the flow will be more accurate and convenient;
- body and tube material; for propane cutters - copper alloy or stainless steel;
- for acetylene torches for copper in the alloy should be no more than 60%.
It is also worth making sure that spare parts and consumables are available.
Do-it-yourself cutting torch
This version of a small-sized and simple gas cutter for DIY assembly does not require expensive parts, but at the same time demonstrates stability and sufficient operating efficiency. They can cut copper wire and sheets.
In order to make the device, you will need:
- two infusion systems (droppers);
- soccer ball needle;
- aquarium air pump;
- propane cartridge for refilling lighters;
- some copper wire;
- electric soldering iron, solder, flux;
- gun for working with thermal glue;
- nipple from a car wheel;
- velvet file.
Homemade gas cutter
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- bend the needle from the dropper at an angle of 60° approximately a quarter of its length from the plastic adapter;
- drill a small hole in the needle for inflating balls and insert a curved needle from a syringe into it so that its tip protrudes 2-3 mm;
- wrap the hole with copper wire and seal it hermetically;
- attach plastic tubes from the dropper to the shanks of both needles;
- attach a thin needle to the compressor, and a thick one to a propane bottle;
- Use plastic clamps to regulate gas supply.
Be careful and careful when making the cutter and when working with gas.
Types of gas cutters and how to use a propane + oxygen cutter
To dismantle metal structures and cut any type of rolled metal, metal cutting is necessary before machining or welding.
And if the sheet or profile is of small thickness, it can be cut with a mechanical tool (manual, electric or hydraulic). To work with metal workpieces of large thickness, you need a gas cutter, or in professional slang - an autogen. The designs of different models of such a device may only differ in size or some details, but the principle of operation is the same for all.
Application area
The scope of application of gas cutters is very wide. They are used wherever metal needs to be cut, soldered or welded:
- in procurement areas of machine-building and metalworking plants;
- on construction sites - from country houses to hydroelectric power stations;
- in a car service;
- at shipyards;
- in the defense and aerospace industries;
- when dismantling old metal structures;
- in the production of electronics and radio engineering;
- in jewelry;
- in artistic crafts.
In addition, a gas cutter can become your reliable and productive assistant in your home workshop.