Today, gas cutting is the most popular method, due to the absence of strict requirements for the work location and the ease of operation. In this article you will learn about the features of the technology, the advantages and disadvantages of this method, the operating principle of the equipment and its types.
Gas cutting of metal is a technology that is widely used today, since it involves the simplicity of the operation and does not require additional energy sources or complex equipment.
It is these methods that are used by specialists in repair, construction and agricultural work. Almost all devices designed for cutting metal with gas are mobile, easy to transport and use in another place.
Pros and cons
Gas cutting and welding of metals has many advantages, but we are only interested in cutting that has the following advantages:
- It is in demand when thick metal is being cut or cutting according to a stencil is needed, and the grinder cannot cope with curved sections.
- The gas analogue is much more convenient to work with, is lightweight, and operates twice as fast as equipment with a gasoline engine.
- Propane is less expensive than acetylene and gasoline, so its use is more profitable.
- The cut edge is much narrower, and the structure is cleaner than from an angle grinder or gasoline equipment.
Disadvantages - a narrow range of metals subject to similar processing.
Equipment
Oxygen cutter diagram
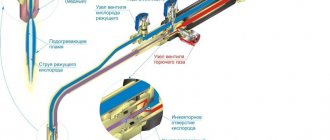
The main equipment for gas cutting is a cutter. The kit includes: a nozzle for welding and melting.
Thanks to the cutter, you can control the dosage of the gas mixture and oxygen. Also, with the help of this equipment, the flammable mixture is ignited and a flame is supplied to the processing site.
The cutter consists of two blocks: cutting and heating. The first is represented by an oxygen stream outlet tube, a valve and an internal type mouthpiece.
The heating block includes valves that are designed to regulate the pressure of the gas mixture and oxygen. There is also a supply tube, an external mouthpiece, a mixing chamber and an injection cell.
Cutters are either manual or machine. The latter are stationary, so for repair work it is preferable to use manual ones.
Gas cutter assembly diagram
Additionally, the following gas cutting equipment is used:
- reducer – designed to reduce pressure;
- device for changing pressure;
- steel cylinder with gas and oxygen;
- connecting hoses.
Diagram of acetylene and propane cylinder valve
Before using the equipment, it is important to check its serviceability in order to avoid explosion of the cylinder or reducer. The cutter is pre-purged with oxygen.
Oxygen reducer diagram
Features of application
To understand how to properly cut metal with a cutter, you need to study the design and know that such equipment is not used for cutting steels with a high carbon content, since it is not possible to create a temperature capable of ensuring stable melting. When cutting cast iron workpieces or structures, a concentration of graphite occurs between the grains of the metal, which makes work difficult.
The cutter cannot be used to cut products consisting of aluminum, copper and copper-based alloys.
Kickback when cutting with gas
When using a cutting torch, there is a possibility of kickback.
In this case, the gas flow begins to burn in the opposite direction, and the process speed is higher than the gas flow rate. This effect can damage equipment by causing an explosion of cylinders or gearboxes. There are also risks of causing significant harm to the health of the welder and other people nearby. An effective solution to these hazards is to install a valve.
You can watch some more features of cutting metal with gas in the video:
If you have information on this topic, interesting facts or tips on using this technology, we invite you to share them in the comments section.
Surface cutting
Users, of course, are interested in the following question: how to use the cutter during shape cutting. This technique is performed using a tool nozzle, while the molten slag heats the metal, but without exceeding the melting point . The cutter is positioned at an angle of up to 80 degrees, and after oxygen is supplied, the angle changes within 18-450.
Grooves are formed when adjusting the cutting speed; if a larger size is needed, then change the angle of the mouthpiece and slow down the cutting speed slightly, adjusting the oxygen supply. The width of the grooves is changed by adjusting the supply of a jet of burning gas through the nozzle; this parameter is equal to 1 to 6, while care must be taken to ensure that there are no backflows.
To keep the edges of the recess clean, you need to increase the oxygen supply.
Gas metal cutting technology
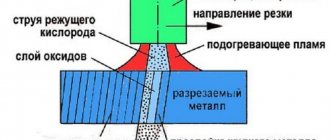
The essence of the oxygen cutting process is as follows. The heater heats the metal to an average temperature of 1100 degrees C. Then a stream of oxygen is supplied to the working area. The flow, in contact with the heated metal, ignites.
The burning jet easily cuts a metal sheet, provided there is a constant and stable gas supply.
The metal's combustion temperature must be lower than its melting temperature. Otherwise, melted but unburnt masses are difficult to remove from the work area.
Thus, the cutting operation is performed by burning the material in a gas stream. The main module of a gas cutting tool is the cutter. It provides precise dosage of mixing gases or liquid fuel vapors with oxygen masses into a gas-air mixture.
The cutter also provides ignition of the resulting mixture and a separate supply of oxygen to the workplace.
Gas cutting refers to thermal methods of metal processing. Its advantages are that you can work with material of any thickness, and with high productivity. The daily output of a welder can be measured in tons.
Experts note the advantages of this technology in that gas plasma cutting is completely autonomous and does not depend on the presence/absence of power sources. Since the welder often must work in the field or does not have the opportunity to connect to a power source at a specific site.
Manual oxy-fuel metal cutting is available to work with a wide range of materials, with the exception of brass, stainless steel, copper and aluminum.
Preparatory work
How to set up a cutter for cutting metal - first of all, you need to make sure that the product is in good condition and ready for work, then perform the following procedure:
- The hoses from the cylinders are connected to the cutter, having previously purged the product to remove foreign inclusions from the inside.
- Oxygen is connected to a right-hand thread fitting, and propane is connected to a left-hand thread fitting.
- Set the propane supply level to 0.5, and oxygen to 5.0 atmospheres.
- We check connections for leaks, as well as the operation of gearboxes and pressure gauges.
If gas leaks are detected, tighten the nuts or change the gaskets.
The diagram shows the correct connection of the cylinders to the cutter.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
Metal cutting with oxygen has the following advantages:
- the ability to cut sheets and products of considerable thickness;
- the cut can be performed to any degree of complexity;
- possibility of surface treatment of the material;
- optimal ratio of cost of work and its quality;
- A fairly fast and universal method.
Among the disadvantages it should be noted:
if a specialist has little work experience, he should not take on precision operations, since skills and knowledge are required to perform them;
- the method is not safe, since an explosion of the gas-air mixture is possible;
- a significant area is exposed to thermal effects;
- low cutting accuracy.
Beginning of work
How to cut metal with a gas cutter - having completed the preparation, the performer slightly opens the propane valve, ignites a gas stream, and the nozzle of the product rests on the surface of the metal. Now you need to adjust the flame strength by alternately adding propane and oxygen. After setting the optimal force of the jet of the burning mixture, the product is located at a right angle to the surface of the part, the nozzle is located no closer than 5 mm.
If the cut begins in the middle of the sheet, then the starting point is set at the beginning of the cut. The surface is heated to a temperature of at least 1000 0C, in appearance it becomes wet, then the oxygen supply is increased to form a powerful, narrowly directed jet.
Material deformation when cutting with gas
Since cutting metal with gas involves a thermal effect on the material, deformation is a natural consequence of the operation. Uneven heating and cooling can measure the shape of the workpiece. But there are several ways to eliminate this defect:
- use of tempering or firing;
- straightening of sheet steel on rollers, after which the material becomes more stable;
- to avoid warping, you can fix the product before surgery;
- perform the operation at the maximum permissible speed, and others.
VIEW Gas cutter on AliExpress →
Cutting Features
The cutter must be moved smoothly along the cutting line and monitor the angle of inclination, which deviates 5-6 degrees against the movement of the tool. When the metal thickness is more than 0.95 m, the deflection is increased by cutting through the metal to a depth of about 20 mm, and the deflection angle decreases again. We have already explained in detail how to cut with a cutter so that the cut is even in the previous section.
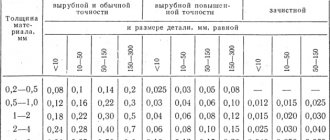
How much gas is consumed?
Gas consumption when cutting metal with a propane-oxygen cutter depends on the thickness of the structure and the configuration of the cut. For clarity, we present the table below:
| Workpiece size (thickness), mm | Hole time, sec | Cut size (width), mm | Consumption, per m3 cut | |
| propane | oxygen | |||
| 4,0 | 5—8 | 2,5 | 0,035 | 0,289 |
| 10,0 | 8—13 | 3,0 | 0,041 | 0,415 |
| 20,0 | 13—18 | 4,0 | 0,051 | 0,623 |
| 40,0 | 22—28 | 4,5 | 0,071 | 1,037 |
| 60,0 | 25—30 | 5,0 | 0,087 | 1,461 |
Gas consumption is significantly reduced when surfacing or soldering is performed.
Nuances
The main task of the performer is to maintain the speed correctly:
- normal mode - sparks fly at right angles relative to the surface of the workpiece;
- low speed - flying away from the performer and an angle of less than 85 degrees.
After the process is completed, the oxygen supply is turned off first, and the propane is turned off last.
T. N. Ishkulov, education: vocational school, specialty: fifth-class welder, work experience: since 2005: “Performers who perform cutting for the first time using oxygen equipment must remember that they must start a new cut after a sudden stop from a different point, and not where the process was over."
Negative deformation
Beginning welders are concerned with the question of how to properly use a propane-oxygen cutter so that warping of the surface of the part does not occur. First you need to figure out what factors contribute to the occurrence of these defects:
- with uneven heating of the surface;
- a high cutting speed was selected;
- there was a sharp cooling of the heating area.
To eliminate the occurrence of the listed factors on the workpieces, they are first securely fixed and heated, and the speed is increased gradually. If warping does occur, then the original shape can be returned by firing or tempering, and the sheets can be straightened on rollers.
Kickback hazard
If the jet burns in an incorrect mode, a bang occurs and the flame is drawn inside the product, which leads to an explosion, as the fire spreads through the hoses and reaches containers with gases. To prevent a dangerous situation, the cutter is equipped with a non-return valve, which cuts off the flame and prevents it from spreading.
Terms of use
They are similar to safety precautions when welding, but have specific additions:
- It is not recommended to neglect protective equipment, as this leads to injury in the form of skin burns or damage to the cornea of the eyes from flying sparks, so goggles and gloves with long bells up to the elbow are required.
- The performer's clothing and shoes are made of non-flammable material.
- Gas cylinders are located no closer than five meters from the cutting site.
- The flame of the cutter is directed only in the direction opposite to the hoses.
- Cutting is carried out in rooms equipped with strong ventilation or in open areas.
If the equipment is idle for a long time, it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance before using the cutter for its intended purpose.
Propane cutter, device, operating principle, types
A propane cutter is a simple piece of equipment for manually cutting metal using propane as a flammable fuel. The cutting process consists of the combustion of metal with supplied oxygen, but before this, with a well-heated metal surface to the required ignition temperature of oxygen on the metal surface. This is followed by the removal of oxides from the cutting zone using a jet of flame.
Nowadays, a universal-purpose propane cutter is more often used. They can cut steel with a thickness of 3 to 300 mm, in any direction, have good resistance to kickbacks, and are mobile in handling. The oxygen-propane cutter consists of a main barrel and a tip. The barrel is attached to a handle that has two nipples, one for oxygen and the other for flammable gas. A little higher, the barrel has control valves for oxygen and gas, mixing chambers for oxygen and gas, tubes, a cutter head with an internal and external mouthpiece, and a cutting oxygen supply tube.
An oxygen-propane cutter will perform a high-quality cut if you select the appropriate nozzle size correctly, as well as select the appropriate ratio of gas supply pressure to metal thickness. A lack of oxygen supply results in incomplete oxidation of the metal and poor removal of oxides, while an excess of oxygen leads to unnecessary cooling and heat removal from the cutting zone. The purer the oxygen, the cleaner the quality of the cut edges and the less slag that is difficult to separate later. The cutting speed must be optimal, otherwise the edges will melt or incomplete cutting at low speeds.
The propane cutter RZP can also operate on acetylene or propane-butane. It cuts metal up to 300 mm thick quite efficiently, has a low weight of 0.8 kg, a cutter length of 520 mm, has 100% resistance to backfire, high-quality durable components, thanks to a special lubricant that is not dangerous to oxygen. Propane cutter RZP (2.3), Izhevsk, is designed for manual cutting of carbon steel, as well as low-alloy steels. Produces high-quality cutting of metals with a thickness of 3-300 mm. and cutting up to 450 mm. It has a mass of 0.91 kg, models of these cutters operate on propane-butane, acetylene and can also use natural gas. Conditional diameter of hoses, mm-dy9, if by special order dy6. Such cutters have a different set of mouthpieces, which allows high-quality cutting of different thicknesses of steel.
The propane cutter RZP type “MAYAK” is also capable of cutting thick steel up to 300 mm. The weight of the cutter is 0.75 kg, there are four internal nozzle numbers and one external one. Universal nipple d6/9. This type of cutter is designed for cutting long and low-carbon steel sheet metal. Slotted nozzle, valve gas supply, high resistance to blowback.
The propane cutter RZP-03M type KRASS operates on propane-butane and successfully cuts sheet and long metal made of low-carbon steel. Cutter weight 0.75 kg, length 475 mm. Capable of cutting steel from 8 to 300 mm thick. Propane cutter of the listed types of cutters do not have significant differences in the quality of cutting and the ability to cut metals, but they have different lengths, weights, the number of attached mouthpieces, and sometimes the thickness of the metal being cut
Leave your comment Cancel reply
Cutting metal, especially on an industrial scale, is labor-intensive and...
Safety precautions
The equipment is classified as explosive, so the work site must be equipped with the following accessories:
- fire extinguisher;
- sand box;
- fire stand with appropriate tools.
Each performer must have a set of protective clothing.
Protected clothing is not allowed to be made of easily flammable material, such as synthetics, and the edges of the sleeves must fit tightly to the body to prevent sparks from getting inside.
What to look for when choosing a gas cutter
The selection of a quality tool directly depends on the result. If certain parameters are neglected, certain properties of the cutter are lost and safety parameters are reduced. Propane and oxygen are explosive substances that require compliance with certain operating requirements:
- The handle is made of aluminum alloys; plastic is used with cheaper tools; over time it melts and loses its shape.
- A brass nipple will last longer than an aluminum structure, as it has a greater resistance to deformation.
- The rotation of the valves should be done with little force to stop the process in case of an unusual situation. The recommended valve size is at least 4 cm.
- The most reliable spindles are made of stainless steel and can withstand up to 1500 cycles without replacement; brass spindles cannot withstand such a service life. The most suitable option is combination spindles, which have a favorable price-quality ratio.
- The design of the cutter must be dismountable; maintenance is carried out to extend its service life. Mouthpiece material is copper.
Valve-type oxygen-propane cutter
It is necessary to pay attention to the availability of repair kits and spare parts for the cutter. If they are not available for free sale, problems may arise during repairs.
What materials is the nozzle made from, what problems does it solve?
The nozzle is an element of the laser optical head for welding and cutting.
The vast majority of nozzle models are made of copper, since this material dissipates heat well and retains its capacitive characteristics at significant temperatures.
Some versions are chrome plated. The purpose of the latter is to eliminate the possibility of sticking of melt droplets blown from the cutting zone.
The nozzle part is installed in the laser head immediately behind the optical system. Thanks to its presence, the following tasks are solved:
- supply of working gases to the cutting zone (with flow adjustment).
They blow out molten metal. This improves the quality of the edges and eliminates the occurrence of sag.
- ensuring the alignment of the gas jet and the laser beam;
- small protection for laser optics.
The contact of the tracking sensor is closed directly to the nozzle (most often through a ceramic insulator). The latter generates signals that allow maintaining a specified distance between the nozzle and the surface of the workpiece during operation.
Any nozzle, regardless of model and brand (IPG Photonics, WSX, Raytools, others) has sealing, clamping, ceramic rings, spacers, and body parts.
The more actively the head is used, the more often the nozzles should be changed.
Special moments in cutting
Metal cutting technology says that there is no need to rush to open the valve of a propane cutter, because in this case, you expose yourself to the danger that may arise due to the interaction of oxygen with heated metal. To prevent the flame from flashing back, it is necessary to release the oxygen stream, strictly following the angle of the burner.
At first it is equal to 90 degrees, after which a small deviation is made, about 6 degrees, in the opposite direction to the movement. If thick metal is being cut, the deviation can increase up to 70 degrees.
It is important to remember that the process of cutting metal must occur at the same speed, which is selected by a visual method, for example, you can estimate the speed of the scattering of sparks.
At optimal speed, a stream of sparks flies out at an angle of 90 degrees. If sparks fly in a direction other than the direction of movement of the cutter, then the cutting speed is very low. A spark angle of less than 80 degrees indicates high speed.
The thickness of the metal plays an important role, because if the thickness of the metal is quite large, then you cannot move the cutter monotonously until the sheet is cut across its entire thickness. Towards the end of the cut, you need to increase the bevel angle by about 15 degrees.
There should be no long pauses during the procedure. If the work was stopped at some point, then cutting must be started from the very beginning and a new starting point must be selected.
The end of cutting should be accompanied by the following actions, in this order:
- cut-off oxygen supply;
- cessation of supply of regulating oxygen;
- Propane shutdown.