Metal cutting is the process of separating a material into parts. This method is used to cut metal sheets or sections of long products. The impact of the cutting tool on the metal creates blanks for further processing. Based on the developed drawings, the surface configuration is formed. To process metal by cutting you need equipment. These can be hand tools, mechanical machines, or devices that heat the material.
Oxygen gas cutting
Cutting methods
There are several ways to separate material. The technology depends on the equipment used in the work process. The following types of metal cutting are distinguished:
- manual;
- waterjet;
- thermal.
Manual metal cutting
Manual cutting of metal is not highly efficient and is not used on an industrial scale. The following tools are used for manual cutting:
- scissors;
- hacksaw;
- jigsaw;
- Bulgarian.
Waterjet cutting of metal
The waterjet cutting method is based on the impact of a jet of water mixed with abrasive particles on the workpiece. The pressure of the supplied liquid is 5000 atm. The advantage of this type of metal cutting is the ability to obtain a variety of lines. Alloys of a certain grade with a small sheet thickness are processed.
Thermal cutting of metal
Hot cutting of metals is based on the absence of contact between the tool and the workpiece. The hot jet melts and separates the material in the right place.
Types of thermal cutting include:
- oxygen gas;
- laser;
- plasma.
Oxygen gas cutting
Oxy-fuel cutting consists of 2 stages:
- A jet of flame is directed to the cutting site, which comes out of the cutter. Acetylene is used as a flammable material.
- After heating, oxygen is supplied, which cuts through the softened metal surface. At the same time, oxides are removed.
During operation, the distance from the bottom point of the cutter to the surface of the product must remain constant. The quality of the cut depends on this.
Laser cutters are used for this purpose. The process is based on delivering a laser beam to a point on the surface. Thermal energy is focused. The area is heated, the material melts and then evaporates. As the beam moves, it cuts the surface.
The disadvantages of this method include the ability to work with products of low thermal conductivity and small thickness.
Laser cutting of metal
Plasma
A plasmatron is used as equipment for plasma cutting. Oxygen comes out through the nozzle in it under high pressure. Its temperature is up to 20 thousand degrees. Beam width 3 mm. The surface area is heated, partially burns out, and the melt is blown out.
The advantages of the method include high cutting speed and the ability to work with workpieces up to 150 mm thick.
Mechanical metal cutting
Mechanical cutting of metal is carried out using special steel with a high degree of hardening. Due to its high hardness, the tool cuts the product.
The following types of equipment are used for cutting:
- band-saw;
- guillotine;
- disk machine.
Band saw cutting
A band saw is a blade that is fixed in special equipment. The material of the tool is the same as that of a hand-made product. There are teeth on one side. During operation of the machine engine, the pulleys rotate, due to which the belt moves continuously.
During operation there is a slight waste, because the width of the blade is 1.5 mm. It is possible to cut both sheet metal and round workpieces.
Impact cutting of metal on a guillotine
Guillotine metal cutting is used to prepare sheet steel blanks for stamping operations. The fabric to be cut is placed on a horizontal surface, fed all the way and cut with guillotine shears across the entire width in one blow.
It is important that the knives do not touch the sheet along the entire length of the surface. The upper tool is positioned at an angle. Contact with the metal occurs at 1 point, which moves along the entire length of the cut. The process resembles the work of ordinary scissors.
Cutting on a disc machine
A disk is used as a working tool. There are teeth along its outer surface. There is a protective casing on top. An electric motor is used as a drive, which rotates the disk. The result is a high quality cut.
Pipe cutters are used to cut pipes using the same principle. During the work process, the workpiece is constantly rotated 360 degrees. It is possible to make cuts at different angles.
Industrial types of sheet metal cutting
Metal processing can be carried out in different ways. The specifics of the work depend on the type of equipment used for cutting metal sheets.
At large industrial enterprises, waterjet or thermal cutting is most often used.
1. Heat treatment of sheet metal.
Thermal cutting involves separating metal sheets with a jet heated to extreme temperatures. This type of cutting is also called non-contact cutting, since the tool does not interact with the surface of the sheet material.
Types of thermal cutting: oxygen gas, laser, plasma.
- Oxygen gas cutting of sheet metal.
Oxygen gas processing of sheet metal includes two stages:
- A jet of flame coming out of the cutter is supplied to the starting point of the intended cutting line. Acetylene is used as the working gas.
- After heating the material, the device supplies an oxygen flow, which easily cuts the softened metal. At the same time, oxides are removed.
In order for the cutting quality to be high, the distance between the cutter nozzle and the metal must be the same throughout the entire working process.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
Oxygen cutting is the most economical cutting method and is excellent for cutting low alloy steels. If all the nuances of the technology are observed and the craftsman has sufficient experience, the edge of the sheet metal after oxy-fuel cutting does not require additional processing.
The disadvantage of using this type of cutting is that it can only process metals with low thermal conductivity.
- Plasma cutting of sheet metal.
Plasma cutting is considered a more universal method of processing sheet materials. The first equipment for this type of metal cutting appeared in the second half of the 20th century. The equipment was not only bulky, but also expensive, and therefore only large industrial enterprises could afford its acquisition and use. Over time, equipment has become more accessible, and the popularity of plasma cutting has grown exponentially.
In this case, metal processing is carried out using a high-speed plasma flow, the temperature of which can reach +30,000 °C. In this case, drops of molten metal formed as a result of melting are instantly blown away by a stream of compressed air. Compared to the previous type of cutting, plasma processing is highly productive, because the temperature of the oxygen gas flow is only +1,800 °C.
It is worth noting that the popularity of plasma cutting is explained not only by its high productivity, but also by a number of other important parameters. Thus, the work process does not require regular refilling of gas cylinders, additives for cutting valuable metals or increased attention to fire safety measures. To work with plasma equipment, you only need electricity and air, which allows you to draw objective conclusions about the simplicity, convenience and economy of the work process.
Plasma cutting of sheet metal can be used to process:
- aluminum and alloys based on it up to 120 mm thick;
- copper up to 80 mm thick;
- alloy and carbon steels up to 50 mm thick;
- cast iron up to 90 mm thick.
If the metal thickness exceeds 120 mm, it is more advisable to use oxy-fuel cutting.
When selecting the optimal equipment for metal processing, it is very important to take into account such properties as thickness and thermal conductivity. Here you need to remember one simple rule: the higher the thermal conductivity of the material being cut, the greater the heat removal and the smaller the possible thickness of the sheet being processed (for example, the thickness of a copper sheet should be less than a stainless steel sheet).
Cutting tools
When working at home, it is important to know how metal is cut. The most commonly used tools are hand scissors or a hacksaw. Industry requires machines with a saw or guillotine installed on them. This is due to large production volumes and the need to maintain dimensional accuracy.
Cutting metal with scissors
Hand scissors
Hand scissors can cut material up to 3 mm thick. They have several types of metal cutters:
- Cutters for straight cutting.
- For curvilinear.
- Finger. There are direct and mirrored types. With their help, complex shapes are cut out.
- With one movable blade, and the second fixed, fixed to the workbench.
Saws
Saws are often used to cut metal. They come in several types:
- Manual. They are inserted into a special C-shaped frame.
- Disk. An electric motor or a manual device is used as a drive.
- Tape. Used only for industrial purposes.
- End They have the ability to make cuts at different angles.
- Pendulum. A distinctive feature is the presence of carbide brazing on the end part.
- Circular. The end is made of abrasive or carbide tips.
angle grinder
An angle grinder is used as a cutting machine. Its other name is Bulgarian. It has the following advantages:
- Thanks to its light weight and small dimensions, the device is convenient to use.
- Possibility of cutting products of different thicknesses.
- Large selection of replacement disc options.
Thanks to the process of metal cutting, it is possible to obtain any type of product. To do this, there are a variety of tools that are used not only to cut in a straight direction, but also to cut out complex shapes.
Laser cutting of metal
This is one of the advanced methods that involves intense exposure of the metal to a laser beam.
We will not dwell on the technical aspects of obtaining a laser, we will only say that this method has many advantages: the smallest cutting width, which can reach only 0.1 mm, high productivity, excellent surface quality, the absence of dynamic or static stresses affecting the metal, thanks to a clearly directed laser light stream into the cutting zone. The resulting edges of the metal products are smooth, without burrs, but a mark from exposure to high temperatures may be visible on the cut. If a “critical” part is being manufactured, then additional machining cannot be done.
The largest company producing special road equipment is Vermeer Manufacturing Co. uses only two laser cutting installations in its production, which cut 20-25 tons of metal per day and supply 9 assembly lines of road equipment with blanks.
The laser beam allows cutting metals up to 15-20 mm thick, although the greatest effect is achieved with a thickness of 6 mm. A significant disadvantage of laser cutting is the low efficiency of the laser itself (only 15%), which does not allow processing sheets thicker than 12 mm. In addition, not all metals can be cut with a laser: aluminum, titanium and high-alloy steels have strong reflective properties, and the laser power simply may not be enough to cover the entire thickness of the metal.
Metal cutting
One of the methods of preparing a part for finishing is metal cutting. It relates to metalworking operations. Its use allows you to solve the following problems:
- remove the remaining layer or parts of metal from the surface of the workpiece;
- eliminate the formed edges on the edges of the part after forging and casting;
- divide rolled metal into smaller parts;
- cut holes in metal products;
- cut grooves for various purposes.
The reference literature describing plumbing provides in detail the tasks solved by this operation and the methods for carrying it out. The great purpose of the metalworking cabin determines its widespread use in metalworking and mechanical engineering. It allows you to quickly and efficiently separate workpieces into specified sizes.
Metal cutting methods
Metal cutting technology is divided into the following types:
- according to the nature of the tasks being solved (cutting out parts according to a given shape, separating a piece of metal of the required size, cutting out grooves);
- method of operation (manual or mechanized);
- fixation method;
- direction of felling action (vertical or horizontal).
All types of metal cutting can be carried out both manually and mechanically. This is determined by the required quality of the resulting product, quantity (productivity), technical capabilities (availability of manual or mechanical tools).
When manual cutting, the following methods are used: vertical or horizontal. The choice of method depends on the possibility of fixing the metal.
It can be clamped in a vice (if size and weight allow). If this is not possible, the workpiece is placed on an anvil or metal plate. It is advisable to perform a horizontal operation using a bench vice.
When manually chopping, there are three ways to strike with a hammer. These are hand, elbow and shoulder blows. The speed of the operation and the quality of the resulting edge of the part depend on the force of the impact. The force of the blow is influenced by the mass of the striking part of the hammer and the length of the handle.
In equipped workshops and metalworking enterprises, various types of mechanized methods for chopping and cutting metal workpieces are used. These methods include:
- cutting using a press or hammer;
- chopping and cutting using a guillotine;
- use of special machines.
Mechanized types are based on mechanical, hydraulic or electrical principles of operating a cutting tool.
Advantages of metal laser cutting:
The highest quality processing of steel, as well as brittle materials, is ensured by the use of a laser beam instead of a drill or cutter. This cutting technique avoids deformation of the steel, which is its main advantage.
- laser cutting works using the “flying optics” method, which eliminates the mobility of the metal sheet when cutting, since in this case only the cutting head moves;
- the line thickness when using laser cutting is minimal - no more than 0.5 mm;
- complete absence of damage when cutting gloss and mirror surfaces;
- laser cutting of products with complex geometry;
- complete elimination of the possibility of burr formation due to the use of high-quality cutting;
- The use of CNC makes it possible to process parts with micron precision.
- the qualifications of the operator working with the machine have virtually no effect on the quality of the workpiece, since all control is completely entrusted to the computer, which operates cutting in automatic mode.
- the presence of a minimum amount of waste and the complete absence of chips, which makes the process economical.
Oxygen cutting
Oxygen cutting involves burning the metal being cut in an oxygen jet and removing the resulting oxides with this jet.
Rice. 1. The process of oxygen cutting of metal.
Oxygen cutting technology
The metal being cut is preheated by the preheating flame of the cutter, which is formed as a result of the combustion of flammable gas (Acetylene, propane) mixed with oxygen. When the ignition temperature of the metal in oxygen is reached, the pure oxygen valve (99–99.8%) opens on the cutter at a pressure of up to 12 bar and the cutting process begins. Pure oxygen from the central channel of the mouthpiece, intended to oxidize the metal being cut and remove oxides, is called cutting, in contrast to the oxygen of the heating flame, which comes mixed with flammable gas from the side channels of the mouthpiece.
A jet of cutting oxygen displaces molten oxides into the cut, which in turn heat the next layer of metal, which contributes to its intense oxidation. As a result, the sheet being cut is subjected to oxidation throughout its entire thickness, and molten oxides are removed from the cutting zone under the influence of a jet of cutting oxygen.
Oxygen cutting technique
The process of oxygen cutting begins with the fact that the surface of the sheet being cut should be cleaned of scale, paint, oil, rust and dirt. Particular attention is paid to cleaning the surface of the sheet from scale, since it prevents the metal from coming into contact with the flame and jet of cutting oxygen. To do this, it is necessary to heat the surface of the steel with the heating flame of the cutter, as a result of which the scale will bounce off the surface. Heating should be carried out in a narrow strip along the intended cutting line, moving the flame at a speed approximately corresponding to the cutting speed.
Before oxygen cutting, the metal is heated from the surface at the initial point of the cut to its ignition temperature in oxygen. After the cutting oxygen jet is launched and the process of metal oxidation begins along the thickness of the sheet, the cutter is moved along the cutting line.
Rice. 2. Oxygen cutting of metal.
As a rule, straight-line oxygen cutting of steel sheets up to 50 mm thick is performed first by installing the cutting nozzle of the nozzle in a vertical position, and then tilted to the side opposite to the cutting direction (usually 20–30º). Tilt of the cutting nozzle of the mouthpiece to the side accelerates the process of metal oxidation and increases the speed of oxygen cutting, and, consequently, its productivity. With a thicker steel sheet, at the beginning of cutting, the cutter is tilted 5º in the direction opposite to the cutting movement.
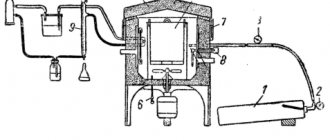
Equipment:
Oxygen cutting uses equipment such as cutters, hoses, a cylinder regulator, gas cylinders in combination with a gas train, or a gasifier.