Features of register heat exchangers
To supply heat in residential and public buildings, heating registers made of smooth pipes are installed. These are devices that are designed to increase the efficiency of heat exchange between the external environment and the coolant.
Structure of a sectional heater
The registers consist of several smooth-walled steel pipes connected by special pipes of smaller diameter. In their shape they resemble a zigzag or a “fence”. In this regard, there are sectional, coil, registers made of smooth pipes with columns, and registers with heating elements.
What materials are registers made from?
Depending on what material the register is made of, the efficiency of its heat transfer, appearance, size, weight and cost will depend. Each material has its pros and cons that need to be taken into account when choosing:
- steel registers. You can choose from carbon, galvanized or stainless steel. The first has high resistance to high temperatures and endurance. The carbon material is susceptible to corrosion, so it must either be painted or coated with special products. Steel pipes are connected by welding. Heating registers made from such pipes, made independently, will be inexpensive and of high quality, and installation will not cause difficulties. Galvanized steel is protected from corrosion, is cheap, but has an unattractive appearance and requires the use of electric welding. Stainless steel does not need to be painted, it does not rust, is easy to install, but is more expensive. The disadvantages of any type of steel are that it has low heat transfer (45.4 W/m x0 C);
- aluminum registers. Compared to steel, they have a higher heat transfer rate (209.3 W/m x0 C). In addition, the material is lightweight, which makes it easier to install. The disadvantage of aluminum is its high cost. Such registers cannot be made at home, because this requires special equipment;
- copper registers. The heat transfer rate of copper is 389.6 W/m x0 C. This is the highest level of thermal conductivity compared to all materials. The advantages of copper include its low weight, plasticity, which allows the manufacture of devices of various shapes, resistance to corrosion and beautiful appearance. The disadvantages of the material are its high price, inability to use with alloys incompatible with copper, and instability to mechanical damage. Only clean coolant with a chemically neutral environment can flow through copper registers;
- cast iron registers. The thermal conductivity of cast iron is 62.8 W/m x0 C. They are purchased only in finished form. Due to their large weight and size, cast iron appliances are difficult to install yourself, but it is possible. The material takes a long time to heat up and also takes a long time to cool down. However, the disadvantages are compensated by low cost, resistance to damage and durability.
Steel heating registers
In addition to monometallic ones, there are also bimetallic registers. They are manufactured only in factories. They consist of a stainless core and a copper or aluminum casing with fins. The inner surface of bimetal pipes is protected from corrosion, and the outer surface with plates serves to increase heat transfer. Such devices are expensive, but effective and will last a long time.
Features of heat exchangers
Section registers
Such devices consist of one or several pipes, which are closed with plugs. Through the pipe, hot water enters the upper pipe, after which it flows into the next one, located one level below. According to this principle, water is distributed to all parts of the device.
The transition from one section to another is made as close to the edge as possible to ensure sufficient supply of the working medium and high heat transfer.
Such a heat exchanger is made from steel pipes with a diameter of 25 to 400 mm. Registers made of smooth pipes with diameters of 76 mm, 89 mm, 108 mm, 159 mm are widely used. The inlet and outlet pipes are made threaded, flanged or welded. Plugs – flat or elliptical. The kit for such a device includes a threaded fitting to which an air vent is connected. The heat exchanger can withstand a working pressure of 10 kgf/cm 2 or 1 MPa.
Coil heat exchangers
This type of heat exchanger is made from one solid pipe. Smooth tube s-shaped registers are efficient in their heat transfer, since the entire surface of the pipe gives off heat.
Coil heater shape
Another advantage is that this configuration does not provide for the presence of pipe narrowing sections. This feature prevents an increase in hydraulic resistance.
Traditionally, heating registers are made of smooth-walled steel, often carbon, although there are also homemade cast iron models, stainless steel or low-alloy steel pipes.
Pipes for register heat exchangers
The compactness and high efficiency of registers allows them to be widely used in the construction of residential, office premises and those facilities that are characterized by increased sanitary and fire standards.
Registers with heater
Devices with heating elements are installed in those rooms where there are problems with laying communication lines.
The power of the heating element ranges from 1.6 to 6 kW at a voltage of 220 V. In operating condition, the heating element maintains the register surface temperature within 80˚C.
To increase the efficiency of heat exchange processes, the device is equipped with a circulation pump.
Working as an element of a central heating system, the heater reacts to decreases and increases in temperature. In accordance with this, it either compensates for heat loss or, on the contrary, turns off.
Such heat exchangers have many advantages:
- fire safety;
- easy accessibility during cleaning;
- large heat transfer area;
- economy;
- multifunctionality.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of registers made of smooth pipes:
- The simple design allows you to make heating devices yourself from available materials (from round or profile pipes) and save a considerable amount of the family budget.
- The simple shape of steel products contributes to less salt deposition on the walls and less silting compared to radiators; this reduces the frequency of flushing the heating device.
- The large cross-section and simple shape provide low hydraulic resistance and the ability to reduce operating pressure in the system (as well as the possibility of use in an open heating system with natural circulation, including with coal boilers).
- Tubular heating devices have a large extent; most of the heat is transferred into the room by radiation - this creates a comfortable thermal zone with uniform heating below throughout the entire area of the room. With radiators and convectors, most of the heat is transferred by convection and rises to the ceiling - and people are in the lower part of the room.
- Long service life: steel structures - at least 25 years, cast iron and aluminum - forty years, copper can potentially last up to 100 years.
- The smooth surface is easy to clean and paint, making the devices easier to operate. The smooth, washable surface of the devices allows them to be used in rooms with special sanitary requirements or in dusty production workshops.
Disadvantages of registers made of smooth pipes:
- A large amount of water makes the system inert, complicates temperature regulation, and requires the use of powerful pumps.
- A small heat-transfer surface per unit length of the device requires the use of large-sized devices - this leads to an increase in the amount of metal and water in the system, an increase in the weight of structures and the inertia of the system.
- Traditional budget models are ugly, they require decorative screens, and they significantly reduce the efficiency of the entire system.
- Exclusive, beautiful designer register models have high prices; finding a company that will make them is also not easy.
Manufacturing of heating registers
Preliminary calculations
To make a heat exchanger with your own hands, you need to calculate a register made of smooth pipes.
The calculations are based on the following formula:
Q = Pi x dn x l x k x (tg - to)x(1 - ηiz),
dн – outer diameter of the pipeline (in meters);
I – section length (in meters);
k – coefficient (equal to 11.63 W/m²*°С);
to – temperature in the room intended for installation of the device;
tr is the temperature of the working medium in the pipeline;
ηiz – coefficient of heat conservation by insulation (if the device is not insulated, this coefficient is equal to zero, if insulation exists, ηis = 0.6÷0.8).
The resulting result will show the thermal power for smooth pipe registers, which is applied to one horizontal pipe. If the device has several rows, a reduction factor of 0.9 is used for each additional row.
If you are having difficulty figuring out how to calculate a smooth pipe register, look for online calculators. As practice has shown, this method of solving the problem is not always accurate, so it is recommended to double-check the result obtained with a formula and only then begin manufacturing the device.
Installation of registers is carried out according to GOST standards. To fix it, you will need a welding machine, since the fastening must withstand the weight of the working medium and the weight of the heat exchanger itself.
Characteristics
Operating principle of registers made of smooth pipes
Registers made of smooth pipes have the following technical characteristics:
- do not require the use of highly professional equipment (use an angle grinder, electric welding);
- they heat large rooms with only a register of 2 or 4 smooth pipes;
- made from available materials (stainless steel, steel, cast iron);
- available for various working environments (work not only on water, but also on steam, oil and other liquids);
- multivariate in their shape, use of fittings, coating materials, plugs;
- in production it is possible to use drawings for reuse;
- available according to their own pricing policy.
Types of registers
The problem of replacing heating system radiators arises for many owners of apartments and private houses. I want to respect the design of the room, save money, and provide warmth and comfort. To achieve these goals, you should choose reliable, safe and durable radiators. The issue of cost also cannot be cast aside.
Heating systems, including radiators and registers, can be domestic or imported, stationary or portable. They can be made from different materials. Registers are made of aluminum, cast iron, and bimetallic. They all have their advantages, but each also has its disadvantages.
Bimetallic radiators are made of 2 different metals. Inside there are copper or steel pipes. From the outside they are covered with an aluminum casing, which is why they look like aluminum. It's easy to confuse them. From the outside it all looks like a single monolithic structure. Plus - high heat transfer. Aluminum coatings can have a variety of patterns. The downside is the high price.
- Aluminum radiators are very similar in appearance to bimetallic ones. They are cheaper, but are not intended for installation in a central heating system. Their purpose is to heat a private home. Reason: aluminum has direct, harmful contact with chemical inclusions in the central heating water. Aluminum radiators can be decorated with elegant cast patterns on the outside. Pros: the price is slightly lower than bimetallic and cast iron radiators. Disadvantages: predisposition to corrosion, some restrictions in use.
- Panel radiators are relatively new heating devices. Very popular in the USA and in a number of European countries. They are distinguished by a large heat transfer area and a high degree of reliability.
Video: heating from smooth steel pipes
Did you like the article? Share it:
- Izhora Pipe Plant (ITZ)
- Royal Pipe Works (KTP)
- Chelyabinsk Pipe Insulation Plant (ChZIT)
- Kstovo Pipe Plant
- Engels Pipe Plant (ETZ)
- We carry out pipe deflection calculations ourselves
- Features of tapping into gas pipes
- Fighting condensation from exhaust pipes
- Methods for eliminating pressure pipe leaks
- How to make a fungus on a chimney pipe with your own hands
TrubSovet .ru We know everything about pipes
© 2015–2017 TrubSovet.ru. All rights reserved
When copying materials from the site, be sure to place a back link to trubsovet.ru
Heating registers: production, application, characteristics
A heating register is an integral part of the heating system, a device consisting of several parallel horizontal smooth pipes. This type of heating device has not gained much popularity among private homeowners, and there are objective reasons for this. A register-based heating system has a large volume of coolant, which requires much more energy to heat than with conventional radiators.
A mobile heating register with a built-in heating element allows you to move the device to another location in a short time in case of an emergency.
Features of installation
There is nothing particularly difficult about installing a heating register. Difficulties are possible only when welding it from individual pipes. If you don’t have much experience in welding work, it’s better to practice first. When purchasing a ready-made, factory-made device, installation problems should not arise at all.
The pipe register is hung on the walls using powerful brackets (hooks). If it is placed on the floor, then iron legs will suffice. It is important to remember that the steel heater in question weighs quite a lot. Plus, the weight of the water inside is added, so the mounts and stands must be extremely reliable.
The ends of the pipe section are closed with special spherical plugs or welded using small steel rounds cut from sheet iron. Male threaded fittings for installing an air vent valve and connecting to the heating system are cut directly into the pipe walls or into the end plate.
The surface of a battery made of steel should be coated with heat-resistant paint. Thanks to it, the device will not only become more aesthetically pleasing in appearance, but will also acquire additional anti-corrosion protection.
Detailed instructions for creating heating registers with your own hands can be found in this material.
Application area
Currently, water heating registers are mostly used in industries (workshops, workshops, warehouses, hangars and other buildings with large areas). The large volume of coolant and large dimensions allow the registers to efficiently heat such rooms.
The use of heating registers in industrial buildings ensures the most optimal efficiency of the heating system. Compared to cast iron or steel batteries. registers are characterized by better hydraulics and heat transfer. The relatively low cost of their manufacture reduces the cost of installing the entire factory heating system. In addition, they are not expensive to operate.
Registers are also recommended for use in premises with high sanitary safety requirements (medical institutions, kindergartens, etc.). The devices are easily washed from dirt and dust.
Despite this, the concept of efficiency does not apply to this type of heating device. As noted above, heating a large volume of coolant requires a lot of energy.
Registers are most suitable for heating industrial premises.
Heating registers made of steel electric-welded pipes can be used in both single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems with forced or gravity circulation of the coolant (based on water or steam).
Note! Due to the large volume of coolant, which requires a lot of fuel to heat, only enterprises can afford to use heating registers, but not the owners of private houses, for whom the efficiency of the heating system is important.
Types of registers for heating systems
Devices are divided into two categories. The technical characteristics of the system as a whole depend on the first. From the second - coolant circulation through the pipeline.
By material: steel, iron, aluminum and cast iron pipes
There are four types, although many other substances and their alloys can be used in production.
Steel
It is used more often than other metals.
This is due to several factors:
- cheapness;
- ease of processing;
- widespread;
- a wide variety of shapes.
Welding technology is used to create it.
Important! Sometimes registers are made of galvanized or stainless steel. It should be borne in mind that both options are expensive, and the first one is also difficult to process.
Smooth
Iron pipes with a high carbon content have this characteristic. To put it simply, the base is steel. To obtain a smooth surface, electric welding is used. They hold much more pressure than regular ones, while being nicer and a little more expensive. Similar registers are described in GOST 10704-91.
Aluminum
It is quite rare because welding requires special equipment that is not easy to find. This is their only disadvantage: the material is cheap, conducts heat well, almost without losing the latter.
Some registers are made from an alloy of steel and aluminum. Bimetallic devices are difficult to obtain, but they have better characteristics than their analogues.
Cast iron
They are almost never used because the registers are bulky and heavy. It is not advisable to create racks specifically for them. In addition, the metal is fragile and is capable of splintering or cracking from impact. Accordingly, you need to purchase protective covers that will reduce thermal conductivity. They are difficult to install, although they are reliable, and operation does not depend on the chemical composition of the pipes.
An almost identical description can be given to copper. It should be noted that it is much more expensive, but it transmits the temperature to the room 3-5 times better. Accordingly, a small harness is required. Among the disadvantages:
- fragility;
- poor compatibility with other metals;
- high requirements for coolant;
- mandatory grounding.
The material should be chosen according to personal preference, but it is also important to carry out calculations. They will help you calculate in advance the required installation dimensions for each type of metal.
By design: sectional, coil
Sectional registers are made from sections of large diameter pipes. They are connected by pipes to admit water. The latter are made of the same metal, and their size must correspond to the supply harness.
It is recommended to install the devices together with a circulation pump, since they create excess hydraulic resistance.
Creating sectional devices is not difficult. A grinder is used to cut out several registers and the connections between them. The system is assembled in one of two ways. In a continuous transition, transitions are made from each edge, and in a stepped transition, alternating. In the latter case, racks in the form of metal plates are placed at parallel sides.
Coil pipes are made from a single section of pipe. It is bent, which makes the creation process difficult. This applies to independent work: such devices are not uncommon in production. To speed up the work, the extreme sides, near the turns, are connected to each other.
For safety, small plates are installed between the bends to support the upper parts.
Sectional ones are slightly better for circulation, and are much easier to manufacture. Coil ones look a little more aesthetically pleasing and go well with a tubular electric heater.
Advantages
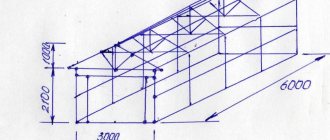
- The large length of the devices (up to 6 m) allows you to heat the entire area of the room evenly and in the shortest possible time.
- High hydraulic characteristics.
- Relatively low price. The cost of a mobile 3-pipe device (designed for heating a room with an area of up to 200 m²) with steel pipes with a diameter of 108 mm, a wall thickness of 3.8 mm and a length of 3 m, with a built-in heating element with a power of 2.5 kW is about 13,000 rubles.
- Easy to use. The devices can be easily and quickly cleaned from accumulated dust and other contaminants.
Flaws
- The large volume of coolant does not allow efficient use of registers in private homes. Home boilers simply will not be able to heat such an amount of water, or the heating will be insufficient.
Advice! To increase the power of the entire heating system of a private house, in addition to the boiler, a tubular electric heater can be installed. The heating element is mounted in the lower pipe of the register and is an additional source of heat. In the coldest weather, when the boiler cannot cope with heating the house, you can turn on the heating element.
Technical characteristics of heating registers
- Working pressure: 10 atmospheres
- Working medium (coolant): water, steam.
- Connection type: threaded or welded.
- Heat dissipation: 500-600 W/meter
There are 3 main types of registers:
- sectional U-shaped;
- S-shaped coils;
- “mixed” (U-shaped coil).
Manufacturing of heating registers
For the production of heating registers, steel pipes of various diameters (25-200 mm) are used, which are welded together at a distance of 50 mm from each other (reducing the distance between the pipes can lead to a decrease in heat transfer). This distance allows you to achieve maximum heat transfer and minimize mutual radiation.
The register includes supply and return, as well as an air vent with a ball valve installed in the upper part of the device. The supply and return pipes can be made in two versions:
- Threaded connection;
- Welded connection.
When ordering registers individually at the manufacturer, registers can be supplied either ready-made, assembled, or disassembled, which allows you to save money on logistics.
Advantages of steel heating registers and their disadvantages
Steel heating has a number of advantages:
- When working, you can realize any individual drawing.
- Not only water, but also heated steam can serve as a heat carrier.
- Easy to connect to the system.
- Its high heat output makes it an excellent option for installation in a large building.
- Low cost.
Video
There are also disadvantages. These include:
- Low heat transfer rates.
- Fear of corrosion.
- Unpresentable appearance.
- Such products require regular painting.
How to make a heating register with your own hands?
Unlike other heating devices, the production of which requires complex, expensive equipment, water heating registers can be made with your own hands. The main thing you will need for manufacturing is smooth steel pipes and the ability to use a welding machine. If you weld it yourself, you will get the cheapest option, but if you have to invite a third-party welder to carry out welding work, such a register may be more expensive than the factory one. In this case, you should think about whether it’s worth doing this yourself or whether it’s easier to buy a factory device.
Connection diagram for heating registers.
So, if registers are made for use in a private home, you will need the following tools and materials:
- Steel pipes with a diameter of 25 to 100 mm, or profile pipes of a similar size;
- Jumpers made of steel pipe with a diameter of 25-32 mm;
- Pipe plugs;
- Inlet and outlet pipes for welding or threaded connection;
- Branch pipe for air vent with ball valve;
- Fastening elements (brackets for fastening to the wall, or floor stands);
- Welding machine;
- Electrodes;
- Welder personal protective equipment (mask, gloves).
- Gas key;
- Angle grinder;
- Centimeter;
- Building level;
Important! If a heating register made of steel pipes acts as an autonomous heating system for a separate room, when the heat source is a heating element built into the device, then in this case it is necessary to install an expansion tank.
Portable heating register with expansion tank and heating element.
After completing the welding work and connecting the components (air vent valve Mayevsky, etc.), the register is pressurized under pressure. If no leak is detected, the device is painted. If a leak is detected, the coolant is drained and the problem area is welded again.
Heater design calculation
First you need to calculate the required heating power for a specific room.
According to the rules, such a thermal calculation should be done taking into account:
- area and orientation of external walls (in the southern sunny direction or not);
- cubic capacity of the heated room;
- the level of maximum possible negative temperatures in the region;
- degree of thermal insulation of walls facing the street;
- the presence of another heated room below and/or above;
- quantities, sizes and types of windows installed;
- presence/absence of doors opening directly to the street.
Building codes even recommend taking into account the prevailing wind rose in winter. On the windward side near the wall, heat loss during the winter period will obviously be higher.
Simplified, for a room with a ceiling height of around 2.7 meters, the required thermal power is calculated by multiplying the area of the room by 100 W
If the ceilings in the room are located at a level of 3 meters or higher, then for a simplified calculation the cubic capacity of the heated space should be multiplied by 34 or 41 W. The first coefficient is taken for brick buildings, and the second for reinforced concrete buildings.
Multiplying a couple of numbers is not difficult. But we must be clearly aware that such conditional calculations can be very far from real figures, since there are many nuances here.
The best way out is to order the required calculation from a specialist who will take into account all the parameters of the room. Heat loss occurs through walls, windows, floors, ceilings and even ventilation. To obtain accurate numbers, everything must be taken into account without exception.
Next, you need to calculate the dimensions of the pipes for the heating register. To do this, use the formula:
Q= K* St*dt
letter designations:
- Q – thermal power of the register;
- K – heat transfer coefficient, depends on the pipe material;
- St – heat transfer area (equal to the number PI multiplied by the diameter and length of the pipe);
- dt – thermal pressure.
Accordingly, knowing Q and dt, all that remains is to select the diameter of the pipe and its total length. Then, depending on the design of the register, this pipeline can be divided into several sections, which will subsequently be connected by crossbars. In order not to complicate the calculations, it is better not to take into account the heat transfer from the latter.
The dt figure, in turn, is calculated based on the required room temperature (Tv) and its indicators in the supply (Tp) and return (To) - total dt = (Tp+To)/2-Tv
When connecting pipes with a snake, each subsequent horizontal segment receives approximately 10% less thermal energy than the one located above. Each such section of the register pipeline should be considered as a separate battery. And as the coolant moves through them, it gradually and inevitably cools down, and the heat goes into the room.
Another parameter is the distance between the horizontal sections (main pipes), which reflects the height of the individual pipe. If this gap is made too small, then the heat flows from above and below will begin to overlap, negatively affecting each other.
This figure must be selected so that it is slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe. Then the efficiency of the register will be maximum possible.
More detailed calculations of the power of heating batteries and their quantity can be read here.
How to improve register efficiency?
Registers have a relatively small heat-transfer surface and to increase it, metal plates can be used, which are welded vertically to the pipes. The result is a kind of finned tube.
4-pipe register with profile convector pipes.
In addition, the registers can be improved in such a way that they will “produce” convector heating. To do this, instead of metal plates, round or profile pipes are welded vertically onto the front of the device, which will create a convection effect. Convection is based on the fact that hot air always rises. Cool air located in the floor area is drawn in through the bottom of the pipe and, when heated, rises. As the air passes through the pipe, it heats up and exits, already heated, through the top of the pipe.
Adviсe
Before you start making registers, you should take care of purchasing the appropriate materials.
You will need pipes of one diameter or another and some length. Exact numbers are not given here, since the device of the type in question can be assembled from any pipes without focusing on their diameter and thickness. More important is to ensure optimal heat transfer, which implies calculations regarding the required surface area of the register
To do this, you will need to determine the outer area of the entire system. The resulting value is then multiplied by 330 W. The use of this method is based on the statement that 1 m2 gives off 330 W of heat if the temperature of the medium is 60 °C and the air inside the heated room is 18 °C.
For people skilled in welding, assembling the structure will not be difficult. It will be necessary to prepare pipes and cut them into sections, and also take care of the plugs, for the manufacture of which a steel sheet will be required. Register assembly does not imply the presence of a strictly defined order of actions. Upon completion of welding work, it is necessary to ensure the tightness of the created structure. Otherwise, the following advice can be given:
- you should select pipes with an optimal wall thickness, since too thin ones cool quickly enough, and thick ones take a long time to warm up;
- the upper section must be supplemented with a Mayevsky valve, with the help of which air is released;
- assembly of the register in the form of a coil involves the use of a pipe bender; if this is not possible, the rotary sections can be assembled from ready-made elbows;
- the coolant inlet must be equipped with a tap, and the outlet with a valve;
- The installation of the register should be carried out with a slight slope in the direction where the supply pipe is located, which ensures that the Mayevsky crane occupies the highest position.
Heating registers made of smooth pipes
The most popular type of heating device in homes is a variety of radiators. And as a rule, they do an excellent job of their duties, evenly warming the living spaces. However, in special purpose rooms - bathroom, storage room, a standard type of battery is not the optimal solution.
Selecting a register for heating
Smooth pipe registers: characteristics
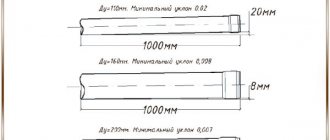
The heating device consists of several steel pipes connected to each other by jumpers and placed along the wall. The heated coolant - water, antifreeze - enters the pipe on one side and is discharged on the other. Between the elements, according to GOST, a distance must be maintained equal to the sum of the diameter plus 50 mm: this way mutual irradiation is eliminated and heat transfer to the room increases.
- The diameter ranges from 25 to 400 mm, but the latter is rarely used as it requires high coolant consumption.
- The maximum pressure allowed in the registers is 1 MPa.
- The manufacturing material most often is an electric-welded smooth pipe made of carbon steel (GOST 10704-91), as well as stainless and low-alloy. There are also registers made of cast iron elements, usually a home-made product. Aluminum products provide more efficient heat transfer, but are not durable: the quality of the coolant significantly affects the service life.
- The pipes are made in three versions: threaded, flanged and welded.
Heaters are most widely used for heating large premises - industrial workshops, warehouses, public institutions, hangars. This is due to the high efficiency of the device and its large length. The latter ensures the formation of not a local heat source, but a volumetric one.
In homes, registers are traditionally used in bathrooms and toilet rooms, where installing radiators with their complex surface is unprofitable.
Classification of smooth pipe registers
The device is available in several configurations to suit different needs.
- Sectional - consists of several elements closed with plugs - flat or elliptical. Water or oil is supplied through a pipe to one end of the pipe and removed from the other, thus ensuring maximum complete heat transfer. The device is equipped with a fitting through which an air vent is connected.
- S-shaped (serpentine) - elements are connected to each other by means of arcs, with a diameter equal to the sectional one. This shape provides greater efficiency to the heater, as it increases the heat exchange area. At the same time, the serpentine configuration does not contain sections with a smaller diameter - narrowings, and, therefore, does not contribute to an increase in hydraulic pressure.
Both types of devices do not have such a developed surface as batteries, and therefore accumulate dust and condensation to a lesser extent.
In addition to the number of heating elements in the register, its design is important. There are five main types shown in the drawing:
- U-shaped, double-row;
- S-shaped, three-row;
- sectional with jumpers of 2 or more rows;
- U-shaped, double-row with a jumper;
- sectional, double-row, with lintel.
There are also more original solutions, but the latter are design projects. The photo shows an example of such a heater.
- Somewhat less frequently, and usually in residential premises, a register made of smooth pipes with a heating element is installed. Its power is low, so this option is used for small premises.
Advantages and disadvantages
Smooth pipe registers are very effective heating devices due to a number of useful qualities.
- High heat transfer - allows you to effectively heat large areas with the small size of the device itself.
- Installation is carried out in accordance with GOST requirements, and is quite simple. No preliminary drawing is required. To make your own register, a welding machine and a grinder with a cutting disc are sufficient.
- The device can withstand high pressure - up to 1 MPa, and is insensitive to pressure changes.
- Water, antifreeze and steam can be used as a coolant.
- Thanks to its length, it promotes uniform heating of the room.
- Easy to clean as it does not accumulate dust and dirt.
- It is characterized by a very affordable cost and does not require additional connecting elements for installation.
The disadvantages of the heater are associated with its own advantages.
Source
Work order
- The jumpers are fixed in place and secured by welding at 2-3 points.
- Having positioned the structure vertically, the jumpers are finally welded. It is recommended to first make a thin seam at low current, which will allow the gaps to be filled well. Next, a thick main seam is performed at increased current.
- The internal space of the register is cleared of metal debris and slag.
- The plugs are applied, tacked and welded to the ends of the profile pipes.
- Welding seams are processed. The protruding parts are knocked down with a hammer, then each seam is cleaned with a grinder.
- Holes in the register are drilled depending on the selected connection diagram. In this case, it is better to place them not in the center of the ends, but slightly higher or lower.
- Connecting pipes are welded to the holes.
- The seams are cleaned and all holes except one are plugged. The register is filled with water under pressure and the welding quality is checked. The seams must withstand pressure up to 13 atm.
- The outer surface is cleaned, degreased and painted with heat-resistant paint.
- A fitting is welded to the top row and a Mayevsky valve is installed.