Requirements for check valves
Lifting check valve for central heating
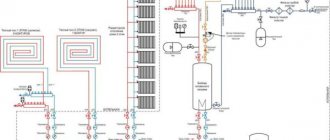
During operation of a heating system, hydrodynamic pressure differences inevitably occur in certain areas. One of the consequences of this phenomenon will be a change in the direction of the flow of hot water. By installing a heating bypass check valve, you can avoid an emergency situation and achieve stable operation of the entire system.
What is this device? Its main task is to prevent the reverse movement of the coolant. It is important to choose the right check valve for the heating system: petal, spring disc or ball. But first, let’s look at the reasons for the emergency:
- Uneven cooling of the coolant in a gravity heating system. If the expansion rate of water in the return pipe is greater than in the main pipe, there is a high probability of a change in flow;
- Several heating circuits. In this case, it is problematic to ensure uniform pressure inside each of them. Therefore, the fluid will move along the path of least resistance, which is not always the right direction. Example, connecting a water heated floor with a mixing unit. If you do not install a check ball valve for heating, then the flow of hot coolant may not flow into the distribution manifold, but into the return pipe branch pipe;
- Complete set of bypass - an intermediate line between the forward and return pipelines for uniform distribution of thermal energy among the radiators in the system.
Based on these requirements, the heating battery check valve must ensure the unhindered passage of hot water, prevent its reverse movement and not affect the technical and operational characteristics of the system. The latter is considered an impossible task, since as hot water flows, the valve will create additional hydraulic resistance. That is why the choice of a particular model must be approached more than scrupulously.
The installation of a check valve on the heating bypass can be done in any spatial orientation. Regardless of the angle of inclination of the structure, it will perform its functions. But this only applies to spring models.
Types of devices and areas of their application
The selection of the device is dictated by the conditions in which it will be used; it depends on the type of heating networks and their internal pressure. An incorrectly selected mechanism can itself cause emergency situations. For example, the liner part that is proposed to be placed inside the cold water meter can completely block its current if the pressure is insufficient, or significantly limit it. On the other hand, installed at the water supply inlet, it will prevent coolant leakage, maintaining pressure, pressure and amount of water in the system.
Gravity check valve for heating
It is also called a firecracker valve and is used only in gravity systems, usually installed at the inlet to the boiler. It consists of a metal “petal”, which is pressed tightly against the edge using a spring.
The spring in the gravity check valve is quite weak and does not interfere with the natural circulation of the coolant.
The spring in such a device is quite weak and does not interfere with the natural circulation of the coolant, like the next presented option.
Ball valve for heating
It is used less often, since there is a danger that the ball, which moves inside the mechanism, opening and closing the flow of water, may jam in one position and then the device will not perform its job properly.
This feature has led to the fact that today the ball check valve is practically not used in heating networks of private houses.
Disc-shaped
This product is used in networks that operate with a pump, as well as those with several active heating circuits. This is due to the fact that the spring located inside the device has greater rigidity, and therefore resistance.
Inside there is a metal or plastic disk (metal is always used for heating), combined with a sleeve on which a spring is attached. Thus, when the proper pressure occurs in the pipe, the plate rises and does not interfere with the flow of coolant. However, as soon as the pressure drops, the opening closes, preventing the outflow of water in the opposite direction.
Coupled
All the products discussed above were completely autonomous and were not subject to external influences, working only in one direction. But in cases where it is necessary, for example, to drain coolant from pipes, a device is needed that makes it possible to open the coolant flow in the opposite direction - such a device is a coupling or valve valve.
When it is necessary to drain coolant from pipes, you need a device that makes it possible to open the coolant flow in the opposite direction; for this, a coupling or valve valve is used.
The choice between a coupling and a valve is most often determined by the internal operating pressure of the network; if it is high, a valve is used; if it is average, a coupling will suffice.
Check valve selection options
Spring-loaded check valve
Regardless of whether you have chosen a reed check valve for heating or a ball check valve, you must first determine its connection parameters to the pipeline. The basic rule is that the bore diameter of the fittings matches the entire line. Those. if the section of the cut is 32 mm, then this parameter for the valve should be the same.
Then you need to select the type of connection to the system. Currently, the following models of check valves are available on the market:
- Couplings . With threaded connection unit. A similar scheme is used for a spring disc check valve installed in the autonomous heating system of a private house or apartment. The maximum size usually does not exceed DU-50;
- Flanged . Designed for installation on large diameter pipelines - from 50 and above. The most commonly used heating valve is a ball valve;
- Wafer . They are mounted between pipe flanges and are characterized by small dimensions. The optimal choice is a reed check valve for central heating.
For systems with pipes of small diameters, spring-type coupling threaded models are most often installed. They are characterized by simplicity of design and reliability. But at the same time you need to pay attention to the material of manufacture. It is best to install check valves for heating systems made of stainless steel. They are able to withstand pressure up to 10 atm., the surface is practically not subject to rust. However, their cost is the highest, which is determined by the manufacturing features.
Brass valves are less reliable, but are quite suitable for a home autonomous heating system. This material rusts very slowly, but compared to stainless steel it is characterized by lower mechanical strength. Often, a check ball valve for heating with a diameter of up to 32 mm is designed for a maximum pressure value of 5 atm.
For central heating, the best option is to install cast iron products. Despite their massiveness and heavy weight, they can withstand critical pressure values, which is one of the mandatory parameters of shut-off valves of this class. Alas, the specifics of manufacturing do not allow the production of cast iron check valves for heating systems with a diameter of less than 40 mm.
Once you have decided whether a check valve is needed in the heating system, you can begin to make a choice. Let's consider the main design features and installation conditions for each of them.
For a one-pipe heating system with one circuit, a check valve is often not needed. The only exceptions are bypasses for radiators, where its installation is required.
Making your own check valve for water
A homemade check valve for installation on a pipeline through which water is transported does not require expensive consumables and complex equipment in its manufacture, which makes it possible to save a lot of money. So, to make a check valve yourself, you need to prepare:
- a coupling with an external thread cut into its body;
- female tee;
- a spring, the diameter of which allows it to freely enter the tee;
- a steel ball, the diameter of which is slightly smaller than the cross-section of the internal cavity in the tee;
- screw plug;
- sealing tape FUM.
If you don’t find a spring with a suitable diameter, you can make it yourself, using a rod of the appropriate diameter and rigid steel wire. It is necessary to drill a hole in the rod on which the homemade spring will be wound; the end of the wire will be inserted into it. To make winding the spring more convenient, the rod can be clamped in a vice, and the wire winding itself can be done using pliers.
Diagram of a homemade check valve for water
After all the materials for making a homemade check valve have been prepared, you can begin assembly, which is performed in the following sequence.
- A coupling is screwed into the internal threaded hole of the tee. This is done in such a way that it overlaps the side hole by approximately 2 mm. It is necessary to fulfill this requirement when tightening the coupling so that the ball, which will be located in the inner part of the tee, does not jump out into its side hole.
- A ball is first inserted into the hole located on the opposite side of the tee, and then a spring.
- The hole in the tee into which the ball and spring were inserted is plugged with a screw plug, tightened using FUM tape.
A check valve made according to the proposed scheme will work as follows: the flow of water entering such a device from the coupling side will push away the ball, pressed by the spring, and exit through the perpendicularly located hole of the tee.
The most important thing when making a check valve of the proposed design with your own hands is to correctly adjust the spring so that it does not deviate at the moment when the water pressure in the pipeline decreases, and at the same time is not too tight so as not to impede the flow of water passing through the device. In addition, all threaded connections must be made very well to ensure absolute tightness of the check valve.
The check valve can also be made from a polypropylene tube and fitting. The manufacturing process is very simple and is shown in the photo below.
Ball check valve for heating
Operating diagram of a ball check valve
A ball check valve for heating is considered truly universal. To create a locking mechanism, it uses a sphere, which, under the influence of the coolant flow, rises into a special end pipe. If the pressure level decreases or the movement stops altogether, the ball falls down, blocking the entire passage. In this case, its diameter must be equal to the cross-section of the pipe. The advantage of using such a mechanism is its reliability. The design does not include moving parts or other mechanisms. The probability of failure of a check valve for heating with a ball is very low.
However, you need to take into account its operational features:
- High cost due to the complexity of manufacturing;
- The working diameter can vary from DN15 to DN. This makes it almost impossible to install them in an autonomous heating system of a private house for a pipeline of small cross-section up to 40 mm;
- The minimum pressure to lift the ball is usually 25 bar.
Taking this specificity into account, in the vast majority of cases they install a check ball valve for central heating when laying large pipelines. Exceptions are autonomous systems with a high pressure indicator - industrial and commercial applications.
Models with a rubberized ball have proven themselves best. Limescale does not form on it, and the protective shell protects the metal from corrosion.
How does a check valve work?
The device connection diagram described above allows it to block the occurrence of reverse coolant flow through the pipes, which can be caused by a number of factors:
- Pump malfunction;
- Uneven heating of the coolant;
- Air lock;
- Overheating of the system;
- Pipeline accident.
Whatever the true cause of this situation - at the slightest movement of liquid in the direction opposite to the side specified by the engineering design - the device instantly blocks the movement through the pipe, preventing the accident from spreading to the entire network.
Reed check valve for heating
Leaf check valve for heating
Due to the shortcomings of the model described above, another type of shut-off and control valves was developed - a single or double leaf check valve for heating. Steel plastic is used as the main mechanism for regulating the direction of fluid flow. The hinge system ensures free movement of the valves under the influence of coolant pressure.
Depending on the design, there are two types of petal check valves for heating - double-leaf and rotary. In the first case, the rotary axis is located in the middle of the highway, and steel plates are installed on its sides, performing the functions of valves. For models, the valve is mounted on a special internal platform. In this case, hydrodynamic losses will be minimal.
Double check valve
Leaf double check valves are often manufactured with wafer mounting, since their design allows installation with the minimum permissible gaps between pipes.
Swivel swing models are most often made from cast iron alloy for large diameter pipelines - from 50 mm.
Installing a petal model will ensure maximum pipeline capacity in this section. This especially applies to the rotating design.
Spring Disc Valve
Design of a spring check valve
For an autonomous system of a country house or apartment, another check valve for heating is required. The pipe diagram for them rarely provides for the installation of large cross-section pipelines. Therefore, all of the above models cannot be installed due to dimensions and restrictions on the mounting diameter. As an alternative, a spring check valve, which is also installed on radiators, has proven itself well.
For its operation, a central rod with a spring is provided, which rests against the disk stop. Under the influence of hot water pressure, the disk shifts and the coolant flows further along the line; if the direction of flow changes, the saddle prevents the liquid from flowing in the opposite direction.
The advantages of installing this type of check valve are as follows:
- Large selection of mounting diameters - from 16 to 40 mm;
- Low cost;
- The coupling method of connecting to the system, which is the most suitable for private autonomous heating.
The disadvantage of a spring valve is the likelihood of scale forming on the disk and jamming after a long period of inactivity. This will lead to the formation of an artificial plug in this section of the pipeline, which will prevent water from circulating further along the heating circuit.
Before purchasing, you need to pay attention to the material of the stem. For heating, you should buy models with a brass or steel core.