A check valve allows fluid to flow through a pipeline in one direction and prevents it from flowing in the opposite direction. It is an important component of any water supply, heating, sewerage and industrial process installations. It is also used in anti-leakage systems in washing machines and dishwashers. Locking devices have a variety of designs, each of which has its own advantages and scope. Their common feature is that the valve opens when a certain pressure is reached and closes when the pressure drops below the set value.
What does a water check valve for a pump consist of and how does it work?
The water check valve consists of the following parts:
- housings;
- spool - a movable executive body, which in turn is assembled from a pusher, spool plates and an elastic gasket sandwiched between them;
- sealing gasket;
- springs (except for gravity-type lifting devices).
The design of a water check valve varies depending on its type.
The body is most often made of brass - this material is not susceptible to corrosion and the effects of chemically active substances contained in water in the form of a solution, it is strong and durable.
Sometimes a chrome or nickel coating is applied to the outside by electroplating. The spool parts are also made of brass or durable plastic. The water check valve gasket is most often rubber or silicone. And finally, the spring is made of stainless steel with a high elasticity coefficient.
This is interesting: Drill chuck: how to remove, replace, disassemble - video, photo
Valve components
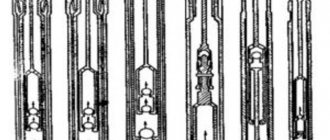
The ball check valve is characterized by a fairly simple design, which determines a long service life. The main structural elements can be called:
- Frame. Recently, monolithic type housings have been produced, which have high strength and reliability. The use of the casting method determines the absence of seams, characterized by low resistance to impact loads.
- Metal ball. The locking element of the valve in question is a ball, which is made of corrosion-resistant steel. The ball has a diameter that is slightly larger than the diameter of the passage hole. In addition, a special seat was created for it, which ensures a stationary locking element.
- The ball is in the closed position due to the spring. It is also made of corrosion-resistant steel, as it can withstand the environment.
- Sealing elements made of rubber provide a high degree of sealing.
Some valves can be serviced if necessary. The maintenance process involves replacing sealing elements that wear out under the influence of the environment. Access is provided by the location of the cover at the top of the housing, which is secured with bolts. Sealing is ensured by special seals. There are also non-removable designs on sale that are not equipped with a lid. If such a design malfunctions, it must be completely replaced.
The above information determines that the valve design is quite simple and reliable. Various materials can be used in the manufacture of basic elements.
Peculiarities
- ABRA sewer check valves have minimal hydraulic resistance, which significantly improves their performance characteristics.
- They are self-cleaning. Anything that accumulates on the locking element in the closed position is immediately removed when opened. Ideal solution for sewer networks.
- They have the most common construction length.
- Anti-corrosion coating (internal and external) reliably protects the unit from chemical damage. Its thickness is 250 microns. The mounting bolts are also protected.
- If operating standards are observed, its parameters remain unchanged throughout its entire service life.
- Operating costs are negligible.
Operating principle
The name of the valve is due to the fact that a steel ball is used as the main shut-off element. The design features include the following points:
- The main element is the body. In its manufacture, steel or cast iron, as well as some other non-ferrous alloys, can be used. Steel is characterized by high strength, and due to the inclusion of various alloying elements in the chemical composition, corrosion resistance increases. Cast iron has been used for a long period, but such a material does not withstand strong mechanical stress. Non-ferrous alloys are lightweight, corrosion and chemical resistant, and are most often used to create valves for household systems.
- The locking element is made in the form of a ball, which in its original position closes the passage hole. In order for the ball to be in the closed position, a spring is installed at a certain angle.
- When the medium is supplied in the correct direction, the pressure created is sufficient to overcome the resistance created by the spring. Due to this, the passage opening opens.
- When the pressure drops for a variety of reasons (leakage, pumping equipment stops), the spring expands and the ball takes its original position. Due to this, the possibility of reverse flow of liquid through the system is eliminated.
The specific location of the spring determines that during reverse current the spring is not pressed out. In addition, to overcome the force created by the spring, quite a lot of pressure is required, which is not created by the reverse free current.
Device
A typical ball valve is a cylinder containing a spring and a locking device. In our case it is a ball. Other types of mechanisms may use a plate. In the basic assembly, the valve is kept closed due to a spring located inside. However, under the influence of flow, this part can reduce the pressure force, and the valve will open. The flow will go through it.
If the pressure decreases (and this can happen due to leaks, stopping the pumping system or for other reasons), then under the action of the spring force the locking mechanism will close. If the pressure moves towards the valve, then, thanks to the shut-off element, the liquid will not be able to pass through.
Types of check valves
Depending on the type of locking element, the following types of check valves are distinguished:
- Lifting type. The disc check valve plate moves up and down. After applying pressure in the working direction, the valve opens, and when the pressure drops or the direction of fluid movement changes, it closes under the action of a spring or its own weight.
- Turning. A non-return valve is a flap that rotates and opens under fluid pressure, and closes with spring force when the pressure drops.
- Ball. The flow is blocked by a ball pressed against the valve seat by a return spring. The pressure of the liquid pushes the ball away from the seat, opening a passage for water.
- Wafer. It can be a disk - the design is similar to a lifting one, but the plate moves along the flow axis, and a double-leaf - the damper consists of two flaps that fold towards each other. The double-leaf design has minimal resistance to flow when open.
Based on the material used, check valves can be divided into the following types:
- Brass - reliable and wear-resistant, most often used in everyday life.
- Cast iron - inexpensive, but susceptible to rust, used only on main pipes.
- Stainless steel is the highest quality and most reliable, but also the most expensive. Used in the most critical systems.
Depending on the method of fastening the water return valve, there are:
- Coupled - the water valve is connected to the pipe break using two threaded couplings. Most common in household systems.
- Flanged - the gate valve is connected using flanged connections. Mainly used for cast iron devices on large pipes.
- Wafer type - the shut-off valve is located between two flanges, which are tightened together with through pins. Also used on main pipelines.
Sleeve check valve
Application area
The main design features of the device largely determine its scope of application. A ball check valve is installed in the following cases:
- To eliminate the possibility of reverse flow of wastewater in the sewer system. In such cases, the liquid may contain large impurities.
- On sale you can find versions designed for household and industrial systems.
- The mechanism performs well when the medium is supplied without impurities. The use of high-quality sealing elements allows us to achieve a high degree of sealing.
The scope of application largely depends on the type of materials used in manufacturing. An example is that in industrial sewer systems a cast iron version is installed. The use of this material has significantly reduced the cost of the product. In everyday life, mechanisms made from brass and other non-ferrous metals are most often used.
This is interesting: Technical characteristics of the IZH-250 screw-cutting lathe
Installation features
You can carry out installation work yourself, taking into account the basic rules. They look like this:
- When creating critical systems, valve installation should only be carried out by specialists who have undergone appropriate training and received documented evidence of this.
- Before starting work, the working environment is switched off. In this case, you can limit the work of only the serviced area.
- Immediately before carrying out work, you need to make sure that the return valve is suitable for the specific system. As previously noted, the most important parameters are the minimum and maximum operating pressure, as well as the diameter of the bore
- At the time of installation of the device, climatic operating conditions are taken into account. It is worth considering that low ambient temperatures can lead to freezing of the ball and jamming of the device.
- Before installing the check valve, flanges are installed. They are designed to fix the mechanism in place.
- After installing the valve, the system is tested. At the time of the test run, it is determined how efficiently the valve operates.
Today you can find on sale a huge range of different designs of ball check valves. That is why there are no problems with selecting such a device. Some design options are unprofitable to install due to high cost. An example is ball check valves with a large bore diameter made of brass.
Characteristics of ball valves
One of the main characteristics is the diameter of the bore or nominal diameter. This parameter is designated as DN. Reviews say that this parameter is conditional and does not always correspond to the actual internal diameter of the pipeline. It is also necessary to take into account the thickness of the pipe walls. There are other factors to consider when selecting a valve. For example, such a parameter as nominal pressure is important.
This is the maximum value at which a flanged ball valve can be safely operated. All acceptable numbers are indicated in GOSTs - you can use the index 26349-84 as a guide. Also, when choosing, you should apply European and American standards.
Valve installation locations
In domestic water supply and heating systems there are many places where it is necessary to install a check valve:
- At the entrance to the apartment there is a centralized hot water supply.
- After the meter to protect it from water hammer.
- In front of the pumping station of the individual water supply system - to stop water leakage from the pipes after a power outage.
- At the end of a water intake hose lowered into a well or borehole, or after a submersible pump - to prevent water from draining when the pump stops.
- At the inlet of an electric or gas water heater - to prevent heated and expanded water from escaping into the cold main.
- In the leakage protection system of washing machines and dishwashers.
These are the most common installation locations. If necessary, such a water valve is installed in all places where it is necessary to ensure water flow strictly in one direction.
How to make the right choice
To select a check valve that will work long and reliably in harmony with other elements of your water supply or heating system, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Purpose. The type of device selected must match it. For example, lift-type valves with gravity action can be installed strictly in the position provided for by the design, so that the stroke of the rod is perpendicular to the surface of the earth.
- Connection method. It is selected simultaneously with the design of the connectors to which the valve will be connected, in order to avoid a clutter of unnecessary adapters. For domestic systems, coupling connections are usually used.
- Size. Must exactly match the diameter of the pipeline. The use of a smaller diameter valve connected through adapters will reduce the reliability of the design and create increased flow resistance.
- Material. For hot liquids, it is better to use brass or stainless steel, since polypropylene has a noticeably reduced service life at high temperatures.
It is difficult for a novice home craftsman to take into account all the nuances, so if in doubt, do not hesitate to consult with an experienced engineer.
Materials
Ball valves are usually made of several metals, and the seat is made of soft materials such as Teflon, neoprene, and combinations of these materials. The use of soft materials provides excellent sealing ability. The disadvantage of soft seat materials (elastomer materials) is that they cannot be used at high process temperatures.
For example, fluoropolymer seats can be used for operating temperatures from -200°C (and above) to 230°C and above, while graphite seats can be used for temperatures from? ° up to 500 ° C and above.
Rod design
The stem in a ball valve is not attached to the ball. It usually has a rectangular portion on the ball that fits into a slot cut into the ball. The magnification allows the ball to rotate when the valve is open or closed.
Lid
The ball valve cover is attached to the body, which holds the stem assembly and ball in place. Adjusting the cap allows the seal that supplies the stem seal to be compressed. The packaging material for ball valve stems is usually Teflon or Teflon or O-rings instead of stuffing box seals.
Below are some typical applications of ball valves:
- Air, gaseous and liquid applications;
- Drains and vents in liquid, gaseous and other liquid media;
- Working under steam.
Check valve installation rules
It is not enough to select the optimal device model; you also need to install it correctly.
Incorrect installation of the valve may result in the need for repair or replacement, which can be quite time-consuming, especially if it is installed in a well.
- If an arrow is drawn or stamped on the body, then it must be installed strictly with the arrow pointing upward, even despite the presence of a return spring.
- If the depth of the well or well (more precisely, the distance to the water surface) is small, then a check valve is placed directly at the entrance to the pressure apparatus.
- In cases where the well depth is more than 8 m, it is better to install the device at the water intake, supplementing it with a mechanical coarse filter.
- When using a submersible pump, a valve must be installed at its outlet.
- If the distance to the well is large, it is better to install two valves - at the outlet of the pressure device and at the entrance to the house.
Installation diagram of a pumping station with a check valve
It is impossible to provide for all options, so before starting installation you should show the diagram of your water supply or heating system to a qualified and experienced plumbing engineer.
Design and advantages of ball type valves
The closing element of ball-type check valves, as mentioned above, is a ball, which can be made of cast iron, steel or aluminum. Quite often, to ensure greater reliability of such a shutter when closed, the ball is additionally covered with a layer of rubber. Ball check valves, which can be installed on both horizontal and vertical sections of pipelines, despite the simplicity of their design, are reliable in operation.
The ball check valve is highly versatile and is available for pipelines of various diameters, which makes it possible to use it to equip both domestic and industrial pipeline systems. Pipeline systems used for heating private houses and for heating large industrial facilities, pumping stations, as well as pipelines through which working media are transported for the needs of various industries are equipped with ball valves.
Ball type check valve device
Some models of ball valves are equipped with a removable cover, which allows minor repairs and maintenance of such shut-off devices without dismantling them. The cover is attached to the valve body using bolts, and a special sealing gasket is used to ensure the tightness of its connection. On large-diameter pipelines, elements of heating and pumping equipment, flanged ball check valves are most often used.
Types of locking elements
Any check valve (the outdated name is non-return) performs a simple task - it does not allow the coolant flow to change direction, passing liquid only in one direction. In water heating schemes, this function is not always needed and is implemented as needed.
The following types of check valves are used in heating systems of private houses and apartments:
- petal;
- disc-shaped;
- ball
For reference. In industrial production and the water supply sector, there are other types of products - double-leaf, lifting and disk, used as network elements on large pipelines. In private housing construction, such fittings are not used.
Industrial models are installed in large boiler houses and production facilities.
Let us analyze the design and operating principle of each type of valve separately. In the future, this will help you understand which product is best to select and install in a specific heating system.
Reed valves
The element, made of brass or stainless steel, consists of the following parts:
- body in the form of a tee with a unscrewing top plug (for maintenance);
- a butterfly valve mounted on an axis by means of a rotary lever;
- a seat with a seal into which the disc fits when closed.
Note. There are 2 versions of the products - with a free or spring-loaded petal. In the second case, the sash is forced to close with a spring so that the lock operates in a vertical position.
The general design of a reed check valve is shown in the detailed drawing. The principle of operation of the element is as follows: the coolant moving in the indicated direction deflects the locking disc and freely passes further along the pipe. When the direction of water flow is reversed, the valve, under the influence of gravity (or a spring), automatically slams shut and blocks the passage.
Typical gravity seal design
For reference. Due to the principle of operation, the products received several names - gravitational, rotary, “crackers”.
We list the important characteristics of petal check valves installed in heating systems of private houses:
- internal passage diameter – from 15 to 50 mm (½—2 inches);
- maximum working pressure – 16 Bar;
- low hydraulic resistance;
- There is a screw on the side of the body for disassembling and adjusting the shutter axis;
- The gravity version without spring can only work normally in a horizontal position.
The design and operating principle of the rotary valve is shown in detail in the video:
Poppet valves
The principle of operation of a poppet check valve is clear from its design, shown in the drawing:
- Inside the cylindrical brass body there is a platform with a round hole - a saddle.
- On the other side of the part there is a partition with a hole in the center.
- A rod with a disc-type valve at the end equipped with a seal is inserted into the hole in the partition.
- A spring is installed between the partition and the “plate”, pressing the disk to the seat.
Water flowing in the right direction overcomes the elastic force of the spring, opens the valve and moves on. Flow in the opposite direction is impossible - the duct instantly closes. What properties of a check valve are important for heating systems:
- ability to function in any orientation of the body in space;
- working pressure – not less than 10 Bar, diameters DN15 – DN100 (internal);
- type of connection – coupling (internal pipe thread);
- spring lock creates increased hydraulic resistance to fluid flow;
- The seal loses its tightness if solid particles, such as sand, enter.
In the utility networks of private houses and apartments, valves with coupling connections are used
Reference. There are more compact versions of spring check valves that are installed between flanges. Reducing the dimensions can be useful when installing boiler piping in conditions of limited combustion space.
Disc locks are also used in water supply networks, for example, in conjunction with submersible pumps. The valve prevents water from the pipelines from flowing back into the well or borehole.
Ball valves
This is a check valve of the simplest design, operating on the following principle:
- Inside the cylindrical brass body there is a ball made of rubber, less often aluminum.
- The ball is prevented from jumping out by 2 partitions with holes made along the edges.
- The coolant flow presses the rubber ball against the partition with ribs. These protrusions form a gap where water flows freely.
- If the coolant moves in the opposite direction, the ball will press against the second jumper - the seat. Since there are no ribs, the body of the ball will completely cover the passage hole.
The advantages of a ball check valve are low price, low hydraulic resistance and operation without any springs in any position, although vertical is preferable. The disadvantage is the loss of tightness when the pressure increases to 6-7 bar, which does not happen in individual heating networks.
Reference. Ball fecal valves, operating on a similar principle, are widely used in sewage systems. The purpose is to prevent waste from moving back to the plumbing fixtures.
To take a closer look at the ball valve, watch the following video: