The essence of the method
The Vickers hardness determination method is based on studying the dependence of the depth of penetration of a diamond cone (indenter) into the material under study on the magnitude of the force. After removing the force, an imprint remains on the surface of the sample corresponding to the immersion depth of the indenter. Due to the fact that the geometric dimensions of the indenter are known and strictly regulated, instead of the immersion depth, the area of the indentation in the surface layer of the test material is determined.
Determination of Vickers hardness is possible for substances with the highest values, since the test cone is a pyramid of diamond, which has the maximum known hardness.
The indenter is made in the form of a quadrangular pyramid with angles between the faces of 136°. This angle was chosen in order to bring the values of the Vickers method closer to the Brinnell method. Thus, hardness values within the range of 400-450 units are practically the same, especially in the area of lower values.
Vickers method
Vickers hardness is determined by pressing a pyramid into the test sample under the influence of a force of a certain magnitude. Knowing the applied force and the area of the indentation, it is possible to determine the surface hardness of the test material.
Instead of calculating the area of the print, the values of the measured diagonals of the rhombus are used, between which there is a direct relationship.
The final result of hardness is determined by the formula:
HV = 1.854∙F/d2
In this formula, F is the force value, and d is the diagonal of the diamond.
As a rule, when making Vickers measurements, no calculations according to the given formula are used, but tabulated values are used based on the applied force, exposure time and the resulting trace area.
Download GOST 2999-75
The value of the applied force is regulated and is 30 kg. The exposure time on the surface is usually 10-15 s. These are the most common values, but in many situations it is necessary to act on the sample material using other force values.
Most measuring instruments are adjusted to some discrete and strictly standardized force values.
The magnitude of the load depends on the material being measured (its expected hardness). The harder the surface of the test material, the greater the load. This is caused by the desire to reduce the error in determining the area and reduce the influence of the viscosity of the material.
To reduce the error, restrictions are also imposed on the size of the test sample. The minimum thickness of the sample should be 1.2-1.5 times the expected diagonal of the print, depending on the type of metal (the smaller value corresponds to steel, the larger value is intended for non-ferrous metals). The distance between the edge of the sample or the edge of the previous print and the center of the print must be at least 2.5 times the diagonal.
Special requirements are also placed on surface cleanliness. Its roughness should not exceed 0.16 microns, which means that the surface needs to be polished.
Table for determining Vickers hardness
The small linear dimensions of the sample require the use of a microscope to measure the size of the print, and the harder the sample, the clearer the image the microscope must convey to maintain measurement accuracy.
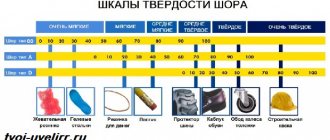
Vickers hardness. Vickers scale and method
Taming of the Shrew. This can be figuratively called Vickers hardness measurement . The method is used to work with particularly hard metals and their alloys.
These require a special approach. Diamonds are also present in laboratories. In what capacity?
Vickers hardness measurement
Indenter tips are made from diamonds. The latter are pressed into the metal in order to determine the degree of its resistance.
Only now, only diamond can be immersed in some alloys - the hardest mineral on Earth, with an index of 10 on the Mohs scale.
In most hardness testers, for example, Rockwell devices, a hardened steel cone is installed on the indenter.
It will work for certain metals. Even the hardest uranium on the Mohs scale can boast only 6 points, and hardened steel – 7.5-8.
However, if we take uranium alloys, they can be equivalent to 9-grade corundum.
The specialization of the method does not mean that Vickers hardness is prohibited from being applied to soft materials. A machine that can handle the toughest ones will also measure the malleable ones.
Simply, enterprises working exclusively with soft alloys do not need to buy an expensive hardness tester with a diamond tip.
Hardness measurement using the Vickers method is distinguished not only by the use of diamond indenters, but also by the ability to determine the degree of resistance of objects of different sizes.
Do you have a wristwatch? The springs in them are tested using Vickers apparatus.
How they are adapted to work simultaneously with both massive and miniature objects will be discussed in the next chapter.
Vickers measuring principle
To determine Vickers hardness, you need a tetrahedral diamond pyramid. The correct shape of the indenter is required.
Yes, yes, the stone is precisely pressed into the surface of the material being tested. If the angle between the opposite faces of the pyramid is exactly 136 degrees, the measurements should be correct.
Experiments are carried out using a special device. It has a support table on which the test sample and the same indenter with a diamond pyramid are placed.
There is a press, pressing the tip, and load regulators. The results are written in numbers, to which the letters HV .
Vickers hardness corresponds to the diagonal of the imprint from the diamond pyramid. This print is examined under a microscope, the accuracy of which is 1 micrometer.
There are no such “devices” on other hardness testers. Therefore, the accuracy of Vickers measurements is increased.
The description of the method can be reduced to the formula: HV=P/F(ean/ii 2). P refers to load. F denotes the area of the print.
Interestingly, the result is almost independent of the applied load. It seems that you can press harder or lighter.
However, the pyramidal shape of the indenter helps. The print profile is triangular, that is, it has similarity properties.
To ensure that the measurements are correct, you can repeat the experiment using a Brinell hardness tester. This is an engineer from Sweden.
Its metal hardness scale coincides with Vickers marks ranging from 100 to 450 units. Within these limits lies, for example, the Vickers hardness of steel .
The dwell time on both hardness testers is 10-15 seconds. This is the time of pressing the indenter tips into the test surface.
It shouldn't be rough. Otherwise, the results may not be accurate on both devices. This is considered a disadvantage of the methods.
Application of Vickers measurements
The Vickers hardness scale allows you to test not only watch springs, but also sheet materials up to galvanic coating.
Electroplating is a metal coating designed to protect an object from corrosion, improve properties and aesthetics.
The film thickness can be only a fraction of a millimeter. No hardness tester other than a Vickers apparatus will “undertake” this.
The Vickers hardness tester can be adjusted to loads from 1 to 500 grams. With the same success, the device produces pressure of half a ton.
The use of different weights and well-functioning electronics make the Vickers hardness tester universal for any enterprise, especially for a wide profile.
Vickers hardness - GOST , which is part of the national standard of the Russian Federation. Not only the requirements for this or that product are specified, but also requests in relation to hardness testers.
It turns out that the Vickers marking is an indicator of the quality of goods. Particularly often, hardness needs to be determined in the automotive industry.
Designers of spaceships, satellites, and aircraft are also guided by Vickers. All of them need housings and other parts of increased strength.
But it is not enough to develop an alloy that must be exceptionally hard. It is also necessary to prove that it is exactly as stated in the documents. Vickers hardness comes to the rescue
The principle of determining the resistance of metals is also important in the jewelry industry. When purchasing jewelry, people want it to be wearable.
This largely depends on the hardness of the alloys. A gold item can be expensive, but it will lose its luster after just a few months of use.
Application area
Hardness measurement using the Vickers method is a universal method, but it gives the most accurate values when studying substances with high hardness. Low forces and, accordingly, small linear dimensions of the print make it possible to practically not disturb the surface of the material being measured.
The Vickers method was further developed in microhardness measurements. The pressure ranges from 2 to 500 g, and the immersion depth of the indenter does not exceed 0.2 μm. Such small values require the use of microscopes with high magnification power.
Vickers hardness tester
The reason for using this technique is to measure the strength of coatings of almost any thickness and hardness. Thus, there are no fundamental restrictions on the characterization of anodized, cemented and nitrided parts and tools. This is important when determining the quality of galvanic and chemical coatings.
Measurements of very thin surface layers are possible. For example, if we use the Vickers method for determining microhardness with an immersion depth of 0.2 µm, then the permissible material thickness is 0.3 µm. The depth of the hardened steel layer using various techniques is tenths of a millimeter, the thickness of the rhodium layer is tens of micrometers.
In domestic laboratories, the most common type of hardness tester is TP-7R-1. It has five fixed test load values with HV measurement limits from 8 to 2000.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
The main disadvantage of the Vickers method lies in the measurement principle itself - the dependence of the obtained value of the measured quantity on the applied load. To avoid errors, the magnitude of the applied forces and the time of exposure to the sample are strictly regulated.
Another drawback that is common to most measurement methods is the need for careful preparation of the surface under study.
Among the advantages of the method is the specific form of the measuring tool - the indenter. The small interaction area makes it possible to measure the hardness of individual inclusions or grains in the body of the sample.
The essence of the Vickers measurement method
Who first proposed the method?
For the first time, the method of measuring hardness was proposed by the British military-industrial concern Vickers-Armstrong
and has become a widely used and standardized method for measuring hardness.
What is the essence of the Vickers method?
The essence of the Vickers method
is the smooth introduction of a tetrahedral diamond pyramid (with an angle of 136 degrees between opposite faces) into the test sample with a certain load
P
, and the subsequent determination of the indentation diagonal
d
and calculation of hardness using tables.
What kind of indenter is used to determine hardness?
To determine Vickers hardness, a tetrahedral diamond pyramid is used.
What hardness tester is used to determine hardness?
To determine the Vickers hardness of samples (HV), stationary hardness testers are used (for example: hardness testers of modifications ITV-1, ITV-5, ITV-10, ITV-30, ITV-50)
.
Advantage of the Vickers method
The advantage of the Vickers method is the ability to measure the hardness of samples and small products made of hard alloys, ferrous and non-ferrous metals, thin sheet steels, hardened and non-hardened steels, castings, semi-precious and precious stones, galvanized, chrome-plated and tin-plated surface coatings of various thicknesses. Measuring hardness does not take much time (requires careful preparation of the surface being tested).
How is the Vickers hardness of test samples calculated?
After the test is completed, the lengths of the indentation diagonals are measured and, based on the average length, the hardness of the sample is calculated according to the tables (for more details, see GOST 2999-75).
Source
Hardness designation
Like any physical quantity, hardness has its own designation. Due to the presence of many measurement techniques, each of them requires its own designation to avoid confusion. It should be noted that some methods give the desired value as dimensionless, but according to the Vickers method, hardness is measured as kgf/mm2. The dimension is not written in the notation, implying its presence.
Vickers hardness is indicated by the symbols HV, where the symbols may be followed by the value of force and holding time:
- HV 500 – standard load 30 kgf (294.2 N) with a holding time of 10-15 s;
- HV 150 10/40 – load 10 kgf (98.07 N) with a holding time of 40 s.
Translation of values measured by other methods is carried out using standard tables, which are included in documentation sets for measuring instruments, and are also present in reference literature.