One of the main technologies for processing plastics and manufacturing various parts and profile products from them is extrusion. It consists of preparing a polymer melt and then pressing it through molding nozzles - special attachments that give the material a given shape. The main element of a production line using a similar technique is a plastic extruder.
Extruder operating principle
An extruder is an electromechanical device directly intended for the process of molding plastic profile parts of their semi-finished products. General structure of an extruder for plastic:
- Housing with a heating system to the required melting temperature of polymers. can as a source of thermal energy , creating high temperatures due to high-frequency Foucault induction currents induced on their body.
- Loading unit through which raw materials enter the housing cavity in various ways.
- A working body that creates the necessary pressure to move raw materials from the loading unit to the forming nozzles. Various physical principles are used, so the mechanism can be piston, disk or screw. Screw extruders are the most widely used.
- An extrusion head (otherwise known as a die), which sets the shape of the resulting products.
- A mechanical drive (motor and gear system) that creates and transmits the necessary force to the working element.
- Monitoring and control systems that support the required technological regime.
Loaded in the form of granules, powder or scrap, the raw material is moved under the action of the working element into the working area of the housing, where, under the influence of pressure, friction and externally supplied temperature, it is heated and melted to the state required by the conditions of the technological process.
During movement in the cavity of the housing, the raw materials are thoroughly mixed to a homogeneous homogenized mass.
Under the influence of high pressure, the melt is forced through mesh filters and forming heads, where it is finally homogenized and given a given profile.
Then, cooling by natural or forced means, it polymerizes, and as a result, products of the required configuration with specified physical and mechanical properties are obtained.
Video: “How does an extruder work?”
Extruder: what is it, what is it intended for
There are a great many models of extruders, that is, machines designed for processing polymers into melt. They differ in characteristics and type of processed raw materials. Among the many options for their use, the most popular is the production of polyethylene or polypropylene films from which flexible packaging is produced. The resulting materials can be printed and bags can be welded. They also found their application in the food industry for the production of pasta.
Types of extruders
Modern extrusion plants differ both in the design of the working body and in their intended purpose.
Single and twin screw extruders
Screw (worm) extruders are the most common , as they almost fully meet all the requirements of the technological process. The working body is the extruder screw (Archimedes screw, known to everyone at least from home meat grinders).
The extruder screw blade grabs the raw material in the loading area and moves it sequentially along the entire length of the housing cylinder, through the heating, homogenizing and molding zone. Depending on the technological map and the type of source material, screws can be normal or high-speed, cylindrical or conical in shape, tapering towards the exit. One of the main parameters is the ratio of the working diameter of the screw to its length. Augers also differ in the pitch of the turns and their depth.
However, single screw extruders are not always applicable. For example, if a semi-finished powder product is used as a raw material, one screw will not be able to thoroughly mix it during melting and homogenization.
In such cases, twin-screw extruders are used, the screws of which can be in mutual engagement, perform parallel or counter rotational movement, and have a straight or conical shape.
As a result, the processes of heating, mixing and homogenization are carried out more thoroughly, and a completely homogeneous and degassed mass arrives at the head.
It should be noted that in some technological processes extruders are used with a large number of screws - up to four, and in addition, there are planetary machines, when up to 12 satellites rotate around a central screw.
This may be necessary when working with certain types of plastics, which, when exposed to high temperatures, tend to undergo destruction—loss of physical properties. Thus, their heating in such extruders is carried out due to the friction force and the high pressure created.
Extruder for PVC profile
The production of plastic or composite profiles in most cases is carried out using the extrusion method. For this, depending on the material and complexity of the product shape, single- or twin-screw machines with corresponding forming heads are used.
The range is very extensive - from thin threads or strips to sheets, large panels and profiles with complex geometries. The now familiar plastic window and door systems are assembled from PVC profiles made in exactly this way.
The addition of special components to the polymer makes it possible to produce complex composites, for example, wood-plastic structures, which are also often used in the manufacture of various building structures.
Extruder for pipe production
When producing pipe products, a very important condition is the absence of gas bubbles in the homogenized mixture , therefore pipe extruders are necessarily equipped with a degassing system. Typically these are twin-screw installations in which, among other things, so-called barrier screws are used, which reliably separate the still solid semi-finished product from the completely molten one. This ensures complete homogeneity of the composition, which is very important for the performance of the produced pipe.
Extruders for polyethylene
All polymer films are produced exclusively by extrusion. A blow extruder is used to produce films. The forming unit of the extruder for stretch film can be made in the form of a narrow slot - the output is a single-layer film of the required thickness and width.
Some models use round slotted dies of large diameter - the film is produced in the form of a sleeve.
Mini film extruders produce polyethylene with a sleeve width of up to 300 mm and a thickness of up to 600 microns. The small size of the device allows it to be installed even in an ordinary room.
general information
An extruder is a machine that turns raw materials in the form of small particles into a melt of a certain shape.
Such particles can be granules, powder, various pastes or scrap. The process consists of passing raw materials through a special forming tool (extrusion head, die plate). The shape of the finished product is determined by a calibrating device with a certain cross-section. It will depend on the type of hole in the forming device. If it is a slot, the output will be a sheet material; if it is a ring, then the product will have the shape of a pipe.
The process that occurs using this equipment is called extrusion. Depending on the design of the machine, it is divided into several types:
- cold blue molding, in which only mechanical action is applied to the material;
- warm extrusion, which consists of mechanical transformations that are accompanied by heat treatment;
- Hot molding is a high-speed process that involves the use of high temperatures and pressure.
Extrusion lines
In industrial conditions, an extruder is one of the main components of an entire extrusion line, which includes, in addition to it, a number of other installations and mechanisms:
- System for preparing and loading raw materials - sometimes the semi-finished product needs to be pre-dried and calibrated before being fed into the loading hopper.
- Cooling system – installed at the exit of the extruder to speed up the polymerization process of products. They can be of various types - air or in the form of cooling baths.
- Mechanisms for drawing finished profiles.
- Marking and laminating systems of various operating principles.
- Winding and cutting mechanisms for bringing products into the form required for storage and transportation.
Other mechanisms and technological devices can be used to automate the continuous production process.
Extrusion Line Manufacturers
Extrusion lines are in great demand, and their production is established in many countries in Europe and Asia. Austrian manufacturers are considered the traditional leaders in the production of such equipment, having been producing similar lines since the middle of the last century. European systems have always been distinguished by the highest quality, the use of the most modern innovative developments in the field of plastic processing technology.
Recently, products from Chinese manufacturers have been actively supplied to the extrusion line market. Contrary to popular belief, this does not mean its low quality - both the reliability and characteristics of the equipment produced generally meet modern requirements. In addition, prices for extruders from China can be significantly lower than in Europe.
Domestic industrialists are also trying to keep up with life. Thus, the extrusion lines of Polyprom Kuznetsk, produced in the Penza region, or the STR Group of Companies from Podolsk and Voskresensk near Moscow are in demand.
The price of plastic extruders varies depending on the country of origin and the individual characteristics of the device.
Principle of operation
A special loader places the raw materials into the machine’s hopper. This work can also be done manually. In this case, the granules are poured into the loading funnel. From the hopper they are pushed into the screw area, and from there into the plasticization cylinder .
Along the way, the raw material is mixed to ensure the homogeneity of the future melt, and is also exposed to high temperatures and pressure from the extruder elements. The output by melting is a viscous transparent mass, increased in volume due to stretching. If the extruder is disk, then two disks are used as a transport device, one of which is stationary, and the other is continuously rotating. The raw material entering the hole of the static disk is mixed and homogenized. Equipment equipped with such a device is perfect for producing homogeneous mixtures.
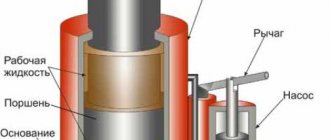
The piston extruder is characterized by low productivity, so its use is mainly limited to the production of pipes. The principle of operation is to extrude the material with a piston, which gives the finished product the required shape.
For all these purposes, one extruder is not enough. To establish mass production and obtain a high-quality product, you have to use additional machines or devices. All together they will form an extrusion line.
Thus, you can not only obtain a melt, but also immediately transform it into a finished product, for example, packaging film, plastic pipes or a PVC profile.
Co-extrusion and co-extrusion.
Coextrusion is a technology used to produce multilayer films.
The following raw materials can be used: low and high density polyethylene, polypropylene, polyamide film and other polymers. The granules of these plastic masses are melted in different extruders, after which they are combined and passed through one molding die (head). For strong bonding, the molecular network of polymers must be similar in structure. But if you need to bind a barrier layer, for example, EVOH and linear polyethylene, then special binder copolymers are required.
Co-extruded multilayer films are used for vacuum sealing of products, such as transport packaging, agricultural film (for mulching, film with antifog effect), pharmaceutical packaging.
Using a similar technology, called co-extrusion, siding panels and PVC profiles are produced. Polyvinyl chloride is the basis of the profile, occupies about 80% of the panel thickness, the remaining 20% is acrylic. As in the case of coextrusion, the operation of two coextruders is used, where PVC and acrylic are melted separately. These melts are combined in a slot filler, from where they emerge as a ready-made soldered product.
Extruder, on the shelves.
An extruder is a machine for the production of polyethylene film (HDPE, PSD, LDPE low, medium, high pressure polyethylene). How and where it begins, I will tell you below, friends.
A bunker, raw materials are poured into it and all sorts of additives are added, for example chalk, chalk is needed to save raw materials and to increase the mass of polyethylene.
This is the brain, the control panel and buttons with the inclusion of individual parts of the extruder, on top there is a display of heating zones - heating elements, temperatures are set, the temperatures for each material are individual, the temperatures for HDPE are shown in the photo, on HDPE they go lower from 155 to 165, on PSD you can put the following the same as for HDPE, but they recommend something between HDPE and LDPE.
1.) Embossing, it is done in rolls and forms a rough surface of the bag. One is rubber, the other is metal, they have a motor that rotates them, thereby pulling the package onto the winder.
2.) A winder, the rollers are actually wound on it, there are shafts and a pair of adjustment buttons for loosening or tensioning the polyethylene web, and a roll meter sensor. It also has a motor that rotates the shafts.
3.) Airflow. It cools the material, with its help a crystallization zone is formed, roughly speaking, with its help polyethylene passes from a molten to a solid state, forming a “glass” of a sleeve; below I will give an example in the photo.
In the first photo there is a blowing ring, corrugated hoses are connected to it, air flows through them and exits through the hole shown in the first photo. On the second, a black marker shows the ringing of crystallization where a “glass” is formed, a red marker shows how air enters, the material goes molten to the crystallization zone. Let's call what goes above the glass a sleeve, so that it would be easier to explain further.
This is a clamping ring and an eye for inflation. The sleeve of the glass is clamped with a ring so that it does not move to the left or right, but goes straight. The eye inflates the glass if it becomes smaller in diameter, the eye works simply, it is a laser pointer that catches the size of the glass, if it decreases, then air is supplied inside the glass, thereby inflating it to the desired size.
We call this lattice “ribs”; it also clamps the sleeve, they stabilize it and thus prevent the sleeve from moving.
4.) These are exhaust shafts. The rubber one rotates counterclockwise, the metal one rotates clockwise, they are pressed against each other, thereby pulling the sleeve further into the embossing and onto the winder.
5.) The extruder screw is a spiral shaft, which is heated using a heating element, about two meters long on this model. Snails on the sides to cool areas if they start to overheat. Each heating element is 1 zone.
This is a mandrel and a die, the mandrel is the penultimate photo, the die is the last, I’ll just add that periodically you need to disassemble and clean these parts, since the material burns to the walls and comes out unevenly, which leads to different thicknesses of the canvas, for example, one edge is thinner, the other is thicker, and this is already considered a marriage. In the first photo below, there is a plug with four bolts on which the filter is clamped, I will show you about the filter and its replacement in the video, you will clearly see how it is clogged with dirt, dirt in the raw materials leads to breaks and poor quality of the bag.
What is polymer extrusion?
The extrusion process occurs when polymers are heated to a maximum of 250 0 C. Production occurs at speeds of up to 120 meters/minute. About 30% of the total volume of polymers is processed using extrusion technology using extruders. Let's try to understand the intricacies of this process.
Polymer extrusion is a technology for producing molded products from thermoplastics and their compositions on screw presses. It is carried out by pressing (under pressure) a homogeneous melt through the slot of the extruder molding head.
The gap has a certain shape, which determines the geometry of the product - siding, film, PVC window profile. Granules of LDPE and HDPE polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, polystyrene and other polymers are used as raw materials.
Extrusion includes the following steps:
- obtaining a homogeneous melt in the extruder;
- molding;
- product cooling;
- tension and winding (films), cutting (profile, pipe).