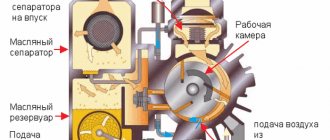
The operating principle is as follows:
- The device begins to work when the motor is turned on, which can happen either in automatic mode or from a manual control unit.
- Torque is generated directly by the motor. It is transmitted directly to the wheel with blades.
- During rotation, the blades pick up liquid, which begins to be affected by centrifugal force.
- The speed of movement of the blades is much greater than the speed of movement of the liquid, due to which a vortex is formed in the system. This process causes the transfer of converted energy from the installed electric motor to the liquid.
Repeated passage of liquid through a wheel with an impeller determines a significant increase in pressure. Compared to other versions, the pump in question is capable of creating high pressure at minimal cost.
Vortex pump - device and principle of operation
The high-pressure vortex pump has a fairly simple design.
The main part of its device is an impeller equipped with blades. It is located in a durable housing and is fixed on the shaft. There is a gap between the body and the wheel, no more than 0.2 mm wide. The main difference between these pumps and axial units is the method of supplying fluid inside the casing. In vortex devices, liquid is supplied along the line of contact with the impeller. This design of the vortex pump makes it easier to operate and repair.
The operating principle of the device is to rotate the wheel along with the liquid. The sucked water is affected by the centrifugal force of rotation and the suction force that is generated in the grooves. Thanks to centrifugal force, the liquid is directed towards the periphery of the blades. As a result, a vacuum is formed in the grooves, due to which suction force appears. When it suppresses the centrifugal force, the water begins to move towards the wheel.
This procedure is repeated until the impact forces become equal. As a result, a vortex appears on each of the blades, which increases the pressure. Despite the rather complex principle of operation, the design of a vortex pump is extremely simple.
Operating principle
The operating principle of vortex pumps is quite simple. When the pumped liquid medium and the impeller rotate together, centrifugal forces are created, under the influence of which the liquid is pushed into the outlet pipe under a certain pressure. If we compare centrifugal and vortex pumps according to their operating principle, a number of differences can be identified.
Schemes of operation of centrifugal and vortex pumps
So, the features of the functioning of a vortex pump are as follows.
- When the impeller rotates, a small volume of pumped liquid enters the receiving pipe, which begins to move along special grooves of the rotating element of the device.
- The liquid that gets into the grooves of the impeller moves along them from the peripheral part of the blades to the central part (a centrifugal self-priming pump works differently).
- The liquid inside the pump, under the influence of centrifugal force, moves along the grooves in the blades in the opposite direction (towards their periphery) and, under a certain pressure, is pushed into the outlet pipe.
- In the area of the receiving pipe, the blades, rotating, create a vacuum of air, which ensures the suction of liquid into the inside of the pump.
The design of the vortex pump is designed in such a way that during one revolution of the impeller, the cycle of suction of the pumped liquid and its expulsion into the pressure pipe is repeated many times, which leads to an increase in the energy of the flow of the liquid medium and, accordingly, an increase in the value of the generated pressure.
Advantages and disadvantages of vortex equipment
Vortex water pumps have several advantages. These include:
- Lower cost compared to other types of equipment;
- Simple design;
- Ability to independently absorb water;
- Possibility of use in liquid-gas mixtures.
Units of this type also have a number of certain disadvantages. Firstly, they have low efficiency - on average it does not exceed 45%. This indicator does not allow vortex pumps to operate at consistently high power. Secondly, the pumps cannot cope with pumping high-viscosity liquids.
Varieties
Vortex type pumping equipment can be divided into two types:
- open-vortex units;
- closed vortex pumps.
Their operating principle is slightly different, since the first type of pumps have:
- extended impeller blades;
- reduced diameter of the impeller in comparison with the clearance of the working channel;
- the annular channel in the device is connected to the pressure hole.
Closed-vortex units have the following structure:
Design and principle of operation of a plunger pump
- shortened blades installed at different angles of inclination (tilt forward, bend back, or at a certain angle back or forward);
- the diameter of the impeller is equal to the clearance of the working channel;
- the annular channel has a direct connection with the inlet and outlet.
The principle of operation is different for each variety. During operation of the open-vortex unit, water from the inlet pipe enters the annular channel through the inlet and the working chamber with the impeller. Here, the working vortex process contributes to the formation of a pressure flow. This flow is directed through the outlet into the main pipeline.
In closed-vortex type units, the aqueous medium from the suction pipe penetrates through the inlet into the annular channel. Here a pressure flow is formed and directed through the outlet into the main pipeline.
Classification of units by method of action
Depending on the mode of action, vortex pumps can be of the following types:
- Reciprocating - in such units, fluid circulation is carried out by moving a piston located in the cylinder. On sale you can find reciprocating vortex pumps, both with a piston and with a membrane;
- Rotary - in these devices a piston displaces water. Based on the type of working body, such pumps are divided into roller, screw, vane and gear pumps;
- Dynamic - in these pumps, the movement of liquid is carried out as a result of the transfer of kinetic energy to it.
Each of the listed types of units has found application in specific areas. They differ from each other in design and dimensions.
Design
A vortex pump for water wells has several main components:
- asynchronous electric motor – located in the lower part and covered with a casing;
- impeller made of brass or bronze with radial blades located on the periphery;
- flanges – upper and lower;
- stainless steel shaft;
- plates - upper and lower;
- stainless steel water intake mesh;
- pressure pipe.
The upper flange, which is also a housing, is combined with a pressure pipe, thanks to which the pump is connected to the pipeline. Eyelets are also located here, designed for lowering equipment into wells and, accordingly, removing it. The flange is made of cast iron or brass.
The vortex pump is connected to the engine using a lower flange.
The wheel is mounted on the shaft using a mechanical mechanical seal. The fixed part of the connection is made of ceramics and rubber, and the moving part is made of graphite and stainless steel. There are locking plates on both sides of the wheel.
Vortex pumps installed in wells are available in two types:
- closed - the size of the shortened blades corresponds to the cross-section of the channel. Water enters the peripheral cells, after which it is pushed out into the main channel by centrifugal force. Then it comes back, but into other cavities. As a result, vortex movement of the liquid occurs;
- open - water passes between the shoulder blades. Then it enters the channel and at the final stage ends up in the pressure pipe.
Separation of pumps according to the type of arteries and wheels
Depending on the location of the waterway, the following types of vortex pumps can be found on sale:
- Units with open artery:
- Pumps with a closed water artery.
According to the types of impellers, pumps are divided into:
- Open wheel equipment;
- Devices with a closed wheel.
Closed-type pumps are equipped with short blades. Liquid suction is carried out through a special pipe. Such units have a low cavitation rate. Due to the joining of the longitudinal vortex and the liquid substance, the rate of movement of the water at the inlet slows down slightly. In order to increase the cavitation properties, a centrifugal stage is connected in front of the vortex wheel. Such equipment is called centrifugal-vortex. These units have a slightly higher efficiency than vortex pumps, about 48%. Devices of this kind are widely used for water supply systems and boiler power supply.
Units with an open wheel differ from devices of the previous type by the longer blades. Due to this, their cavitation rates are an order of magnitude higher, which allows them to be used for pumping wastewater in industry and utilities.
Nowadays, many manufacturers combine the properties and advantages of several types of equipment in pumps. Thanks to this, on the modern market you can find vacuum, air and thermal vortex pumps. The main difference between these devices lies in the technical characteristics and areas of application. Units of the first type are successfully used in the chemical industry for working with gaseous substances. Thermal devices have found application in providing liquid to various steam power plants. Air vortex pumps are used to maintain the operation of deep industrial water wells.
Classification
Vortex devices can differ in several parameters. Currently, the following types of vortex pumps exist:
- open and closed - vortex;
- submersible and surface;
- combined.
Each of them has a different purpose and structure
Open-vortex and closed-vortex
An open-vortex pump differs from a closed-vortex pump in that it has longer blades, the impeller is smaller in diameter than the outlet channel, and the annular channel itself is connected only to the pressure pipe. In closed models, the blades are shorter and located at different angles, the diameter of the wheel coincides with the diameter of the internal chamber, and a channel connects the inlet and outlet.
The difference in operation is as follows. Water enters through the inlet and enters the working chamber, where it is sent in the form of a vortex into the connecting channel and through it, under pressure, exits through the outlet pipe. In closed devices, due to the same diameter of the working chamber and the wheel, water immediately enters the connecting channel, where a vortex is formed and the pressure increases.
Submersible and surface models
The difference between these models is clear from the name: submersible ones are located directly in the pumped medium, surface ones are located next to it. The first option is most often used simply for pumping liquids or not too viscous substances, the second is used for circulating water, for example, in irrigation systems or for water supply at home.
Combined options
Free-vortex models allow you to work with heavily contaminated substances. They are used as sewage or drainage pumps, used in wastewater treatment plants and in the mining industry for pumping water from wells during drilling.
Centrifugal vortex pumps have a higher efficiency compared to classic vortex models; they are capable of working with liquids with a heating temperature of no more than 105 degrees. The difference is that both a centrifugal and a vortex wheel are installed here at the same time.
Vortex type vacuum pumps are a type of blower. With their help, you can ensure the distribution of hot or cold air, as well as achieve a slight vacuum. Often used for drying glass containers and aerating water bodies.
Areas of application of vortex pumps
It is quite difficult to imagine modern industry without pumping equipment. Vortex pumps were no exception. Today they are used in the following industries:
- To maintain the operation of boiler stations;
- For pumping liquids containing gaseous components;
- To supply water to rural water stations;
- For the operation of automobile service stations;
- As elements of compressor units;
- For the purpose of pumping alkalis and acids.
Smooth operation in all these industries requires pumps to withstand mechanical damage, aggressive chemicals and wear.
Vortex pump: description of design, principle of operation and scope of application
20 photos of cats taken at the right moment Cats are amazing creatures, and perhaps everyone knows this. They are also incredibly photogenic and always know how to be in the right place at the right time.
Why are some babies born with an "angel's kiss"? Angels, as we all know, are kind to people and their health. If your child has the so-called angel's kiss, then you are out of luck.
These 10 little things a man always notices in a woman Do you think your man doesn’t understand anything about female psychology? This is wrong. Not a single little thing can be hidden from the gaze of a partner who loves you. And here are 10 things.
10 charming celebrity children who look completely different today Time flies, and one day little celebrities become adults who are no longer recognizable. Pretty boys and girls turn into...
Top 10 Broke Stars It turns out that sometimes even the biggest fame ends in failure, as is the case with these celebrities.
Never do this in church! If you are not sure whether you are behaving correctly in church or not, then you are probably not acting as you should. Here's a list of terrible ones.
Vortex or centrifugal pump - which is better?
In order to understand which is better - a centrifugal or vortex pump, you should decide on several factors - areas of application and characteristics of the units. Centrifugal pumps can be used to pump clean water or water containing small impurities from ponds no more than 9 meters deep. During operation, such devices create a small pressure, consume a significant amount of electricity and have quite large dimensions.
The main difference between a vortex pump and a centrifugal pump is that units of the first type create greater pressure while having the same power. They are smaller in size and consume much less electricity. In addition, vortex pumps can pump liquids containing gases.
For comparison, it is also important to note the disadvantages of vortex pumps, which centrifugal devices do not have. The main one is the instability of vortex units to frequent mechanical damage. In contrast, centrifugal pumps are made of cast iron, which can withstand shock easily.
When comparing units of both types, it is quite difficult to determine the best one. We can only note that if the buyer does not need high pressure and wants to pump out dirty water, then you can purchase a durable centrifugal pump, which, moreover, will operate much quieter. If you need to achieve maximum pressure, then it is better to purchase a vortex unit - it produces more noise, but costs an order of magnitude cheaper.
We should also not forget that manufacturers constantly combine the properties of different types of pumps. Today it is very easy to purchase a centrifugal vortex pump that will have all the properties and advantages of the units we are comparing.
Principle of operation
The operating principle of vortex pumping equipment, as in centrifugal-type devices, is based on the use of centrifugal force that occurs when the impeller rotates. However, unlike centrifugal analogues, vortex pumps have their own operating features, which are as follows:
- As the impeller of pumping equipment rotates, a small volume of water from the suction line enters the grooves on the impeller.
- As a result, it moves from the periphery to the center of the unit, which is not similar to the operation of a centrifugal pump.
- After this, this volume of water, under the influence of centrifugal force, begins to move along the blades from the central part to the periphery.
- As a result, the water gets accelerated and is thrown out into the outlet.
- Here the speed energy of water turns into pressure energy.
- Under the influence of pressure and the suction action of the blades, a new volume of liquid again enters the blades and the cycle repeats.
Important: during one revolution of the impeller, the cycle of pressure generation and the suction action of the blades is repeated many times, which contributes to an increase in energy and an increase in pressure.