Metal cable is the main element of cable rigging. Despite the fact that the design of the cable resembles a regular rope, the product itself is considered a complex engineering object. All steel cables are classified according to two GOST standards - 3066-80 and 3067-80. In them you can find information about the mechanical features of the cable, its properties, composition and other important points.
The properties of a rope depend on its size, construction, quality, core type and finishing. Ropes are also divided by diameter size. In this review, we will look at the main classification groups of steel ropes, determine the advantages and disadvantages of cables, and come to a conclusion when it is best to use steel ropes.
Steel cable structures
The cable structure includes the following components: core, strand, wire, central wire. Most often, each individual wire is arranged around a central wire, forming a strand of wire.
Strands are formed around a central core to form a cable. Depending on the number of strands, the thickness of the cables is determined. There are quite a lot of them, but there is a limit on the number of threads - 25. The size and number of wires in each strand, as well as the size and number of strands in the rope, greatly influence the characteristics of the rope.
Mostly a large number of wires and small strands form flexible cables that have good bending resistance. Such options are suitable for organizing trigger mechanisms.
Fewer, thicker wires and strands result in a less flexible rope with good corrosion resistance and durability. This option is suitable for use in static conditions. Rope design is also important for assessing ropes for corrosion resistance and wear levels.
Application depending on type
The strength, physical and mechanical characteristics of a steel cable and the area of use largely depend on its design and type.
Metal-polymer cables are used for tying cargo, laying overhead communication lines and installation work. Traveling ropes GOST 16853-88 have found application in the gas and oil industry during drilling. LK-O have excellent wear resistance, which is why they are used in most lifting mechanisms. LK-R are resistant to temperature changes, high humidity, and precipitation, which makes them possible to use in almost any environmental conditions. With the help of special towing ropes, it is possible to pull passenger cars, road trains and huge trucks weighing more than 40 tons.
Types of cores in steel cables
Cables come with three types of cores:
- A wire core that has the same construction as the outer cores.
- Fiber core is more often used for rigging. Such cables have high tensile strength, and due to the increased wire diameter, they are more resistant to abrasion. For the manufacture of such cables, sisal (coarse fiber) or polypropylene is most often used. This makes it possible to provide a flexible base for the strands in the rope structure. Fiber cores are used to make ropes where elasticity is required. Fiber cores are not suitable for outdoor use.
- Independent steel cable core. This type is suitable for the manufacture of cables that are used in tension, subject to severe compressive loads, and high operating temperatures. This type of rope is heavier and stronger than fiber-core rope.
Breaking load depending on the characteristics of the cables
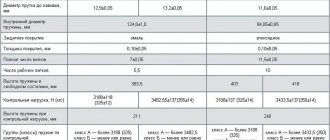
The working load is about 25% of the force after which the product is destroyed (partial or complete) and its further use is not ensured by strength. Using the table below, you can select the cable according to its cross-sectional diameter and maximum load.
| Cable diameter, mm | rope elasticity ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ | ||||
| DIN 3052 | DIN 3053 | DIN 3055 | DIN 3060 | DIN 3066 | |
| 1×7 | 1×19 | 6×7+FC | 6×19+FC | 6×37+FC | |
| 1 | 0.75 kN | 0.83 kN | |||
| 1,5 | 2.25 kN | ||||
| 2 | 3.01 kN | 3.33 kN | 1.95 kN | ||
| 2,5 | 3.2 kN | ||||
| 3 | 7.71 kN | 7.49 kN | 4.39 kN | ||
| 4 | 13.3 kN | 7.8 kN | |||
| 5 | 12.2 kN | ||||
| 6 | 17.5 kN | 16.2 kN | |||
| 8 | 31.2 kN | 28.9 kN | |||
| 10 | 48.8 kN | 45.1 kN | 43.4 kN | ||
| 12 | 65 kN | 62.4 kN | |||
| 14 | 88.5 kN | 85 kN | |||
| 16 | 116 kN | 117 kN | |||
| 18 | 146 kN | 141 kN | |||
| 20 | 181 kN | 173 kN | |||
| 22 | 210 kN | ||||
| 24 | 250 kN | ||||
| 26 | 293 kN | ||||
| 28 | 340 kN | ||||
| 30 | 390 kN | ||||
This is interesting: Anchor bolt with nut: parameters, installation, GOST
Lay in steel cables
The lay in metal cables determines how the wires in the strands form the structure of the rope. In simple words, the wire strands have a twisting algorithm that provides a tightly formed structure. The term “lay” is used to describe the direction of the twisted wire in relation to the strands in the finished cable. With correct laying, the strands are wound around the rope core clockwise, with left-handed or right-handed - counterclockwise.
Conventional lay means that the wire in the strand is laid in the opposite direction to the direction in which the strands are laid in the final rope. The direction of lay of a cable rope does not affect the breaking force of the cable. However, the combination of strand lay and rope lay greatly influences the performance of the cable. For example, if we are talking about a rope structure where rotation is prevented when right-handed and left-handed strands are involved.
Types of touch in the plexus of cables
- Linear. In this type of rope weaving, the ropes are wound in circulation. In this case, the reliability and type of cable depend on the diameter of the wire from which it is twisted. Such cables have different ability to withstand loads. It is recommended to choose models with maximum load.
- Spot. In these cable models, the weaving is not repeated. Such slings are universal, and it is advisable to use them in various fields of activity with different loads. Otherwise, the rope will quickly become unusable and stretch. The correct choice of cable is the key to its long service and reliability. Various product models and their modifications can be used for any activity associated with heavy loads and movement of goods or materials.
Our company offers wholesale supplies of cables and ropes of various configurations and models. Our website presents a catalog of various models designed for different activities and loads. PVC coated steel cables are popular. The additional sheath protects the rope, which allows it to be used in different conditions and for different activities. Metal-polymer cable, which is also presented in our catalog, is the basis for fences. To protect against weather conditions, the cables are coated with zinc, which increases their wear resistance and service life.
Classification of cable products
Steel cable is widely used and there is a large selection of products on the market. There are several classifications of metal cables:
- by appointment;
- according to the shape of the sections;
- the number of strands in the rope, which determines its scope of application;
- material of the main element - the core;
- wire properties;
- direction of strands in the structure – left-sided, right-sided;
- type of wire processing;
- type and genus of Vitya.
To determine the nominal diameter of the cable, you need to take measurements in two sections. There should be a distance of 1 m between them. In sections, the diameter is measured twice along the line of the maximum distance between the limit points.
Purpose of the product
Most often, the product is used for towing, rigging and lifting operations. Durable and flexible, the cable is certainly part of the equipment of excavators, cranes, and drilling rigs. It is also used in the mechanisms for raising and lowering freight and passenger elevators and for concrete reinforcement. Cables are most widely used in lifting operations: the flexibility and high strength of the products allows them to be made into lifting devices that can withstand severe mechanical loads.
Taking into account the complexity of work involving the use of steel cables, the choice of products should be approached with all responsibility. The modern market presents many types of steel ropes and cables, so an ignorant person may get confused because of all this variety. Therefore, in case of difficulties, it is better to seek advice from a professional who will help you choose a product for specific tasks.
Strict performance requirements are imposed on both metal cables and the additional elements with which they are used. Before operation, such products are subjected to various tests and inspections and, if successfully passed, receive certificates and permits allowing use for their intended purpose.
Main settings
The main parameters by which cables are selected are as follows:
- Strength;
- Flexibility;
- Load capacity;
- Tension limits.
To increase resistance to aggressive environments where the cables will be used, in some cases they are subjected to additional processing. Regarding individual areas of use of the product, one of the most significant parameters may be its weight.
Quality and types of cable materials
The quality of steel used determines the tensile strength of the cable. Modern production technologies offer consumers durable products with anti-corrosion resistance and resistance to external factors. Steel ropes are typically available on the market in tensile ranges from 1570 to 2160 N/mm square.
Galvanized ropes are made from galvanized material to resist corrosion. For the use of heavy equipment (for example, winches, mining machines), there is a demand for the manufacture of ropes with an increased tension range of the rope wire. On the other hand, since strength is not the only criterion when choosing a rope, it is important to evaluate the specific conditions of use of the ropes.
Stainless steel is the most popular material for cable production. Since products made from it can be used in harsh climatic conditions, this indicates high protection against corrosion. Stainless steel has high tensile strength and is considered suitable for almost any environment. Modern steel processing techniques mean that stainless steel can be cut, welded, shaped and manufactured quite easily. The flexibility of cables made from this type of material means that steel can be used to produce products of any size and shape.
There are many different grades of stainless steel, depending on their alloying element content, as well as their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. They are marked in accordance with GOST and other international standards.
It is important to consider environmental factors when selecting the grade of stainless steel in a cable composition. There are methods for classifying environmental factors that allow you to select a brand for a more precise application.
Varieties
There are different types of cables. First of all, they are qualified by design:
- With a single lay. These are one-, two- and three-layer wire products. They twist into concentric spirals. If the cable is used for future weaving, then it is called a strand.
- With double lay. With this design, at least six strands are twisted into one layer. If further laying of the rope is performed, strands are obtained.
- With a triple lay. They consist of strands that are twisted into one layer using special equipment.
Types of steel cables, differing in touch:
- With touching at points. Marked as TK. The arrangement of elements in such ropes leads to quite serious problems: during shifts during operation, such a rope quickly wears out, fatigue cracks and other defects appear in it.
- With linear touch. Marked as LC. The wear resistance and service life of such cables is higher than that of TK rope products.
- With point-linear touch. This rope design involves obtaining a product with increased non-torque characteristics.
In addition, steel ropes are available in unwinding and non-unwinding types. In the first type, the wires after laying are not free from internal stresses, and after removing the dressings they unwind. In the second case, stresses are removed by straightening, and preliminary deformation is also used. After this, they not only maintain their position when the dressings are removed, but also have other advantages - they become more flexible, and stronger resistance to fatigue stress appears.
Straightened cables, being in a free state, do not twist into a circle at the end, while unstraightened ones, due to tension, tend to form a circle.
Depending on the conditions under which the rope will be used, its coating is selected. Sometimes it is not treated with anti-corrosion compounds, but this reduces the service life of the product, even if it is used in a dry environment. More often, the cable is treated with zinc, and to varying degrees. There are ropes for work in:
- Medium aggressive environment, marked as “C”.
- Harsh aggressive environment, marked as “F”.
- Ultra-harsh aggressive environment, labeled as “coolant”.
Quite often, cables are treated with polymers, then the product is designated by the letter “P”.
Purpose of steel cables
Cable products are designed for lifting and moving heavy structures. The hoisting steel cable is also capable of performing the following tasks:
- moving cargo on tower or container cranes;
- holding crane structures;
- installation and dismantling of cranes and others.
If you need to manipulate an uncontrollable load or lift it to great heights, you will need ropes that are resistant to rotation. Only they ensure the stability of the load, so the load is able to rotate. Rotation-resistant ropes attached to the crane structure do not transmit torque to the attachment point. Due to this, it is possible to ensure operational safety. These types of ropes have production requirements in accordance with GOST standards. They differ in the level of rotational resistance depending on the type of structure.
There are several conditions where the use of rotation-resistant ropes is inappropriate and unjustified. For example, if ropes of the same design are used as a pair consisting of right-handed and left-handed ropes. In this case, rotational stability is ensured, so the load does not rotate. This is explained by the balance of torque.
Rotation-resistant ropes are less prone to bending. Therefore, if elastic compounds are needed in a specific situation, then you should not stop at this type of cable. Assess the conditions for using ropes and the risks of using different types of products.
Types and classification of ropes
Steel ropes are wire products made by coiling. The cable is part of the rigging that carries the mass of the load. Such products are used in shipbuilding, water/road transport, energy, coal, ore, oil, etc. Depending on the tasks performed, many types of ropes are produced.
According to the cable structure
- Single - consist of individual wires woven in the form of spiral-concentric layers (one or more). A rope made of round threads in one layer is called a spiral or strand. Made from profiled (Z-/omega-shaped, wedge-shaped) wire – closed type.
- Double - made up of strands twisted in layers. These cables are used independently or serve as a part for stronger ropes - strands.
- Triple - made up of several strands, spirally twisted into one layer.
Strands, depending on the cross-sectional configuration, can be round or shaped (flat or triangular). The latest varieties are distinguished by a larger contact area with the pulley surface.
Depending on the type of weaving
- TC – point contact of wires between layers.
- LC – linear contact of wire in adjacent layers.
- LK-O - linear contact of wires between layers, if the threads in the strands are of the same cross-section.
- LK-R - linear wire contact between layers with different diameters of threads in the outer row of the strand.
- LK-Z – linear contact of the threads between the layers of the strand and the filling wire.
- LK-RO - contact along a wire line between layers, inside of which there are rows of threads of the same and different diameters.
- TLC is a combination of point and linear contact of wires within one strand.
The types of most common spiral ropes or strands are:
- a, b – LK-O;
- c – LK-R;
- d – LK-Z;
- d – LK-RO;
- f, g – TK;
- z – TLK-O
| Cable categories | Cable according to DIN | Cable according to GOST | |
|
|
| |
| Let's select the necessary cable! Contact us! Phone, email | |||
Depending on the material, for the core:
- OS – organic , when synthetic/natural fiber is placed in the center of the cable or its strands. Cotton yarn, hemp, sisal, polypropylene, polyethylene, nylon, viscose, lavsan, asbestos are used here.
- MS – metallic . A double weave cable is used, consisting of 7 strands or a strand of the same structure as the twist. The core increases the structural strength of the ropes and reduces their elongation when stretched or when the air temperature rises.
Ropes with organic cores:
a, b – from natural materials; c – polymer
Ropes with metal cores:
a – homogeneous; b and c – multi-strand
By winding
There are non-unwinding (H) and unwinding . In the first case, after removing the tie from the end of the cable, its threads and strands will retain their location or can be easily woven by hand. This is helped by deforming the wires and strands before winding them. With an unwinding rope, its components do not deform before weaving. Therefore, the strands and steel threads unwind due to the removal of the ligament.
a – ordinary unwinding;
b – non-unwinding
By balance:
There are straightened ropes (designation P), which maintain straightness with a given tolerance. The reason is that the tension in the threads and strands after winding is removed by straightening. If this operation is not done, the end of the unstraightened cable is twisted into a ring.
The direction in which the cable is wound can be right or left (L). This is determined by how the outer row of threads of the spiral rope is wound; strands for double-wound products or strands for triple-weave rope.
Depending on the direction of winding of the rope and the position of its components, cables are distinguished
- With cross weaving , when the strands and strands are wound in the direction opposite to that of a rope.
- Unilateral (O) . In this case, the winding direction of the cable, its strands and strands coincide.
- Combined (K) . This is typical when strands with left and right winding are simultaneously used to make a rope.
a - left, b - right;
1 - one-sided, 2 - cross-shaped;
| Cable categories | Cable according to DIN | Cable according to GOST | |
|
|
| |
| Let's select the necessary cable! Contact us! Phone, email | |||
Depending on the degree of twist, ropes are:
- Spinning . When the winding direction of the strands of concentric layers of the cable coincides. This is typical for 6- and 8-strand products with a core.
- Low rotating (MK) . The strands in the layers are woven in opposite directions (single-wound, multi-layer and multi-strand cables). Due to the correct choice of winding directions of threads and strands, axial rotation of the rope with a freely suspended load is excluded.
Cables come in different qualities, depending on the mechanical properties of the wire used:
- high (VK)
- elevated (B)
- normal (1)
Ropes may differ in the coating of the wire surface, when there is no protective layer or the threads are coated with zinc. In the latter case, three groups of galvanization are known (according to operating conditions):
- C (medium aggressive)
- F (hard)
- Coolant (extra hard)
The cables are intended for:
- movement of cargo/people (cargo-human GL)
- or exclusively lifting operations (D)
Depending on the quality of manufacture, ropes are divided into products of normal and increased (T) accuracy.
The cables are marked by strength and are distinguished by their temporary tensile strength ranging from 1370 (140) to 2160 (220) N/mm2 (kg/mm2).
Why is cable lubrication needed?
To increase the service life of steel cables, you need to properly care for them. Smoothing of ropes is a mandatory measure, the main task of which is to protect against corrosion and mechanical damage. Experts advise applying lubricants in a thin layer of about 0.2 m. Lubricants are used in the manufacture of cables and their operation.
Regular lubrication of ropes ensures longevity and performs other tasks:
- Prevents deformation by ensuring maximum penetration of individual strands.
- Protects against corrosion, preventing premature failure of the metal product.
- Provides resistance to washout, guaranteeing protection in wet conditions and other external factors.
- Reduces friction, reducing abrasion and wear.
The lubricant guarantees resistance to water, ideal for high pressure spraying - low viscosity product. It exhibits high temperature stability, providing protection at high temperatures. The composition can be used at low temperatures.
Application area
One of the most notable types of steel cables produced by modern industry is a product made of galvanized wire. For additional protection against corrosion, this steel cable is encased in a PVC sheath. Thanks to these features of its design, the cable can be successfully operated even in the most unfavorable conditions. Thus, products of a similar design are used for tying loads lowered into liquid media; they are used to install antennas and masts, power transmission and communication lines.
Modern manufacturers have also mastered the production of metal-polymer cables, the wire of which can be additionally galvanized, which gives the product even greater corrosion resistance. There is a simpler way to protect the cable from the occurrence and development of corrosion processes, which is also used by modern manufacturers. To do this, a flexible steel cable is coated with a layer of special lubricants or an additional layer formed from galvanized wire is introduced into its structure.
On the modern market you can also purchase cables whose surface is protected by a material that can successfully withstand combustion, high temperatures and temperature changes.
Deformation and wear of ropes
Most often, wire connections fail due to tension, corrosion or mechanical stress. When ruptures are detected under loads, it is important to check the level of safety, especially if the rope is used for heavy loads.
Corrosion damage occurs as a result of operation in wet, salty, acidic conditions or exposure to other chemical elements. In this case, you need to make every effort to fix the problem. Alternatively, you can use a special lubricant.
Mechanical damage consists of cuts or punctures. This occurs due to careless handling, impact. Mechanical rupture also occurs due to sudden release of heavy weight.
Deterioration of the strength of cable strands often occurs as a result of bending wear. The reasons for abrasion of strands may be:
- bending and twisting of ropes due to load;
- contact stresses between individual strands;
- wind fluctuations and other dynamic effects. The source of the oscillation is called a "reclaimer".
When choosing a cable for specific purposes, it is important to pay attention to the quality of the material and its properties. If you intend to use the rope in harsh environmental conditions, be sure to lubricate the product. Steel cables are a complex engineering object, the selection of which must be approached wisely.
Steel cable - product types and markings
Each type of steel cable design has its own specific features that must be taken into account when choosing a product for a particular purpose. Don’t forget about the general parameters that you should know when going to the supplier - length, diameter, maximum load that the product will have to withstand. Now a few words about the design features. There are single lay cables, where a round wire is wound in a spiral around the core. As a rule, this is a strand for making more complex structures - ropes. Double lay cable is no longer produced from individual wires, but from the strands mentioned above, which are applied to the core according to certain rules. Here you can make single-layer and multi-layer cables. They are able to withstand considerable weight and, with a certain method of wrapping, cannot twist during operation; this property sometimes greatly simplifies operation. There is also a triple lay, such a cable is twisted from strands, this is the name of double lay products, specially designed for subsequent use in the manufacture of more complex and stronger cables.