Data from archaeological excavations, as well as historical chronicles, confirm that bronze casting can be classified as an ancient method of metal processing. The technology, which required virtuoso skill while strictly following the rules, was kept secret by the artisans of the past. Modern bronze casting is a durable alloy of ancient foundry secrets with advanced technologies, which allows you to admire the beauty of designer products.
Where to begin?
To organize a small business of your own, you will need to purchase equipment for bronze casting. To set up a small workshop you will need to buy devices and tools such as:
- Melting furnace.
- Crucible.
- Forceps.
- Horn.
You will also need to purchase charcoal and metal for smelting. All materials and tools can be purchased in specialized stores or online. You can make a smelting furnace yourself, but only if you use materials that are resistant to high temperatures for this purpose.
Once the necessary equipment has been purchased, you can begin making artistic bronze castings with your own hands immediately, but to obtain high-quality products you need to correctly follow all the norms of the technological process.
This is interesting: Properties of bronze: color, density, grades, markings, application
Features of working with bronze at home
When casting bronze at home, the room is prepared in advance in compliance with fire safety precautions. Ventilation is required.
Induction or arc furnaces are used for this. You can also use a gas burner or blowtorch as a heating source. If a clay oven is installed, then a forge, coal and tongs are prepared.
Stages of artistic bronze casting
Cast bronze figurine
Before starting the process of casting bronze products, a casting mold is made. It consists of the following stages:
- Drawings are developed based on the generated model.
- According to the drawings, a casting mold is made. For this, quartz sand or clay is used. It consists of 2 halves. A cavity is formed inside into which molten alloys will be poured. Forms are disposable and reusable.
- To eliminate the risk of destruction of the casting structure, a flask is formed from the outside. The mold is placed there after the alloy is poured.
An important step is placing the mold in the flask. If this is not done, the material may fail under the influence of internal forces. The best option is to make the flask from metal. However, wooden products also perform their function well when forming small bronze castings.
After removal from the mold, the finished casting must be modified. Remove sprues and flashings. Further processing of the sculpture is carried out in order to make it decorative. The workpiece removed from the mold has many external defects, which can be eliminated with the help of a grinding machine. The last operation is minting. The molten metal does not always fill all corners of the mold cavity, so the figurine often has an unfinished appearance. With the help of embossing, all these defects are eliminated.
Subtleties of technology
Before the metal is poured into the mold, it is heated to a molten state.
An important step is the complete filling of the casting mold with the alloy. Otherwise, defects will form:
- shells;
- burns;
- underfilled;
- solders.
The molten metal does not always fill the pockets of the mold, so the resulting design of the product before it is finished has unclear outlines.
Main stages
To obtain high-quality cast products, strict adherence to the technological sequence is required. The casting process is as follows:
- Making a model or copy according to a sketch or drawing. Materials for the model are easily melting at low temperatures: stearin, paraffin, wax and others. The ability to completely fill the volume of internal space in a mold has made these materials widely used.
- The gating system is attached to the model by gluing, soldering or mechanical fastening. Thus, feeders, channels, vents and other elements are formed.
- The production of injection molds is made from a refractory mixture. The main composition of the mixtures is fireclay or alumina clay and quartz sand.
- The mold is released from the model composition by heating with steam or immersion in heated water.
- Typically, bronze casting is carried out by free pouring using centrifugal machines, excess or insufficient pressure (vacuum).
- Cooling is done in air or using a thermostat.
- After cooling, the model form collapses. The gating system is cut off. The workpiece is sent for cleaning using washing or chemical compounds.
Opening a large enterprise
- Purchase of a reverberatory furnace - the equipment is used for melting metal. The following fuels can be used: gas, electricity, diesel fuel. Approximate energy consumption is 30 kW/h. Furnace loading is up to 1 ton. The productivity of a reverberatory furnace is up to 600 kg/h.
- Chill machine - used for casting bronze products. For the production of artistic products on an industrial scale, 2 types of machines can be used:
- Single-position - used for the manufacture of bronze objects that do not have reverse angles. The mold in this type of machine opens only in one direction.
- Multi-position - the mold in such devices can open in different directions, so such equipment is more suitable for casting complex bronze products. The power consumption of both types of machines is about 2.5 kW.
- Renting premises is a significant expense item. Taking into account the specifics of using the equipment, it is recommended to independently build a room where the casting equipment will be installed.
- Salaries to employees - In a large enterprise for the production of bronze art products, it is impossible to do without attracting competent specialists, so the volume of monthly contributions to the wage fund will also be significant.
- Registration of an LLC or individual entrepreneur - before starting a business activity, you will need to complete the necessary documents. You can register an enterprise for a small amount of money if you deal with this issue yourself, but with a legal way of doing business you will also need to pay income tax and various social contributions to the pension fund and compulsory medical insurance.
- Utility costs - a large amount of energy is spent in the process of artistic casting, so payment of utility costs for a factory for the production of bronze products will amount to tens of thousands of rubles per month.
- Purchase of metal - The purchase of metal for smelting will be the main expense item during the entire operation of the enterprise for the production of artistic products, but it should be understood that the price of consumables will be included in the final cost of the product and with a properly established sales process, income from the sale of such products will also be significant. You can buy bronze for casting from suppliers involved in the sale of raw materials. It is possible to purchase both wholesale quantities and small amounts of metal for home production.
The cost of a set of equipment consisting of a reverberatory furnace and a chill mold is about 6 million rubles; in addition to the cost of purchasing equipment, you will also need to build or rent premises. Based on rough calculations, opening a large enterprise will require a one-time expenditure of at least 7 million rubles. Monthly costs for maintaining the production process will also be high and amount to at least 500,000 rubles. Despite the high costs, full payback of the enterprise is possible within 2 - 3 years, but only if there is a well-developed strategy for selling finished products.
Selecting equipment for bending reinforcement.
Which CNC laser engraver to buy?
Do-it-yourself powder painting technology at home.
Necessary equipment
Here is a list of the main equipment for making figures from these materials.
- Casting shape. Made from various materials.
- Tongs for removing the finished part from the mold.
- A crucible for melting the charge in it. The material used to create it is graphite and clay.
- Heating equipment, furnaces . You can use a gas torch and a heat-resistant container to melt brass.
- Various auxiliary materials: coal, forge.
It is necessary to use a strict sequence of technology. First, place the crucible on the furnace, then put pieces of metal into it. When completely melted, the mixture changes color. Then, using special equipment - a hook, the crucible is taken out of the furnace and the melt is carefully poured into the injection mold. After complete cooling, the part is removed using tongs and subjected to final processing.
History and essence of technology
Lost wax casting: technology, advantages and disadvantages
Humanity became acquainted with metal a very long time ago, but the earliest attempts to produce castings from it most likely date back to the fourth millennium BC. e. Such assumptions allow us to make archaeological finds in the Middle East. According to research, the first molds filled with liquid metal were simple depressions in open ground.
The ancient masters did not immediately achieve significant progress in the accuracy and quality of castings. The first surviving artifacts that can be attributed to the sculptural genre date back to approximately the second or third millennium BC. During this period, casting became not only a craft item, but also a way to create high-level works of art.
The essence of the technology lies in the property of molten metal (like any other liquid) to fill the vessel into which it is poured. After cooling, the finished casting becomes an exact geometric copy of the voids in the container. The main steps look simplified like this:
- Production by a sculptor of an original model from plastic non-metallic materials.
- Preparation of materials for molding, creation of a casting mold based on the original.
- Melting metal, pouring it into a mold, cooling.
- Release of the finished product from the mold, cleaning and mechanical processing.
Overview of casting models
Before you start casting the finished product, you must first create a sketch of the future shape. The drawing is carried out by special master artists. Then a casting mold will be created from it, into which the main melt is poured. Creating a casting mold is a rather labor-intensive and responsible task. For this purpose, special compositions for molding, tools and devices are used. The finished model plays a major role in the entire technological process. Its internal cavity must be an exact copy of the finished product using lost wax molds. A molten solution is poured into it, which subsequently, while inside, cools and takes on its final form.
To impart stability, so that during the pouring of the melt into the mold it does not collapse, flasks are used. This is a special device made of two rectangular connecting parts, similar to a box. Usually made of wood or plywood. In metal flasks, not only the creation of a casting mold occurs, but also the casting itself. Models for making brass and bronze are reusable and disposable. It depends on what they are made of.
Materials
Ivory, wood, gypsum and polymers. Steel is also used to make reusable molds. The least common material used is plastic to create a casting model. At home, the melt is most often cast into a permanent plaster mold. After the alloy has cooled and hardened into a finished shape, the mold is carefully broken with a special hammer.
Constructions
Structurally, casting molds can be of three types.
- Detachable. This is a structure consisting of two or more parts, connected along a straight or complex surface. Disconnects to remove the finished product. Most often used in production for reusable use.
- One-piece . To remove the finished part, it is broken with a hammer. Suitable for one-time use only. Made for a specific product according to sketches. Often used in home production. Gypsum is most suitable for creating such forms.
- Special . This is a complex molding or skeletal pattern. It features a multi-part component. Created for melting figures of complex design.
This is interesting: How and with what to clean bronze products at home
Subtleties of technology
In order to perform artistic bronze casting or make a practical product from this alloy, it is necessary first of all to obtain molten metal. Various types of furnaces are used for melting metal: induction, arc, flame, etc. In the simplest version (when casting at home), you can use a regular gas burner to melt bronze, placing it under a special container for the melt.
The capabilities of small furnaces, which you can make yourself, are quite enough to melt non-ferrous metals and their alloys, which also include brass and bronze.
To melt a small amount of bronze you need a fire brick and a gas burner
The most important step in bronze casting is filling the mold with molten metal. Despite the fact that such pouring lasts only 1–2 minutes, the correctness of its execution directly affects the quality characteristics of the finished product. The result of incorrect filling can be such defects as:
- adhesions;
- burns;
- slag shells;
- underfilled.
These bronze castings developed cavities due to poor cleaning of the crucibles before pouring.
When casting small-sized brass and bronze products, the molten metal is poured not from the crucible itself in which it was heated, but using a special device used as a hand ladle or spoon.
The metal, which has already been poured into the mold, must be allowed to cool to the required temperature, which, depending on the brand of alloy used, may vary. The procedure for removing the finished product from the mold depends on what type it is - disposable or reusable. In the first case, it is simply broken with a hammer, and the casting is removed using pliers. Reusable molds, accordingly, do not need to be broken: they are simply opened along the surface to be joined and the casting is carefully removed from them.
The newly removed casting needs to be reworked. This modification consists in the fact that the sprues, spurs, profits and bays formed during the casting process are removed from the surface of the product. This operation, which can be performed using various mechanical tools, is called trimming.
Basic subtleties of casting
Centrifugal casting
Using this casting method, parts and equipment are manufactured for mechanical engineering and other industrial sectors. The basis of the technology is centrifugal force. It appears due to the rotation of the casting model. This type of casting is used mainly for the manufacture of bodies of revolution. Molding can be carried out by machines with vertical and horizontal pouring. On machines with a horizontal axis of rotation the following are produced:
- inserts;
- bushings;
- rings.
On machines with a vertical axis of rotation they produce:
- propellers;
- worm wheels;
- gears.
During the casting process, the molding mixture is compacted and foreign elements are forced out.
Artistic casting
This method of making bronze is used at home. But this copper alloy has a high fluidity, so it does not completely fill the mold, unlike a brass alloy. Because of this, the intended pattern on the surface of the part is blurry. To give clarity, embossing is used. This is a rather labor-intensive and time-consuming process. But at the same time, the most creative moment of artistic casting. The quality of the final product depends on the level of embossing performed.
Stages of artistic casting:
- creating a sketch and working drawing;
- manufacturing a structure for creating a casting mold;
- production of a casting model;
- model preparation;
- melting of the charge;
- pouring the molding mixture into the casting model;
- cooling;
- extraction from model;
- processing the finished product with a grinding machine, sometimes using a metal brush.
Finished individual components are combined into one product if, according to the final design, it should be single, but consisting of several parts. Then the resulting finished figure is processed to remove minor imperfections and covered with a top protective layer.
Injection molding
This casting method is based on the influence of excess vacuum pressure. The principle of the press is used; the melt is fed into the injection mold with excess pressure. A pneumatic or hydraulic system acts on the piston. Due to the high speed at which the high-viscosity melt is supplied, excess pressure is created and the mold is completely filled.
Then, using vacuum suction, the mold mass flows into the cavity of the crystallizer. It has thin walls surrounded by cold water. Cooling moves from the edges to the center. The melt is drawn in over a certain period of time. Then the pressure normalizes, and excess molding mass flows down the walls.
Due to shrinkage after cooling, the product is easy to remove from the mold. Due to automation, the mold is filled with melt in a fraction of a second, which significantly reduces the production time of parts and is an undoubted advantage of this casting method. Regardless of the casting method used, safety precautions must be observed when making products from bronze and brass.
- When working, you need to use safety glasses to protect your eyes from drops of molten material and fumes.
- Before starting work, you should wear gloves made of special heat-resistant material.
- The room must be well ventilated and ventilated , since when these alloys melt, gases harmful to humans are released.
- Do not allow flammable materials and liquids to come into contact with heating devices.
- It is necessary to strictly follow the process technology. Since this production is quite traumatic.
To learn how bronze sculptures are made, see the following video.
Artistic metal processing. Securing stones in products and artistic casting
There are several ways to secure stones and products: prong setting, grisant setting, smooth setting, corner setting, stroke setting and some others.
The place in which the stone is attached is called caste (frame).
The cast should hold the stone firmly and for a long time, emphasize its beauty, and serve as a connecting link between the metal part of the product and the stone.
Of the main types of fastenings, the most common is fastening with prongs.
The prongs resemble paws, the ends of which are bent and cover the stone on all sides.
With grisant setting, the upper part of the caste is pressed tightly and the metal rim around the stone is finished with a fine notch called grisant.
With smooth setting, the stone is fixed in a caste or without a caste in a drilled socket. The edges of the caste or socket are polished with a smoothing iron, and the stone is firmly held in the product.
When using a coner setting, fixing a stone in the shank (rim) of the ring, the metal is removed or a socket is drilled, along the edge of which, using a special cutter, metal shavings are pushed towards the stone being fixed and then corners are rolled from these shavings, which secure the stone in the caste.
Line setting is used in rings and other jewelry. This type of setting is carried out by lifting thin shavings from the body of the frame using a cutter, which holds the stone in the caste.
Inserts made from inexpensive stones from cut glass are also secured with glue. After fixing the stones in the frame, the reliability of their fastening is checked, and then the products are polished again on a wool wheel.
Features of the production of artistic metal products
There are many different manual and mechanical methods of artistic metal processing. They have different properties and qualities. Some methods are very ancient, but have not lost their value even today, for example, engraving, casting, casting, filigree, etc.
They, as before, are based on manual artistic processing techniques. These techniques are labor-intensive, low-productivity, require a certain amount of skill and are applicable for unique works, such as embossing, notching, etc.
Other methods have emerged relatively recently on the basis of new scientific discoveries and technological developments - electroplating, the latest types of casting, electrochemical processing methods, etc.
When choosing one or another technology to realize his artistic concept, the master must, in addition to economic efficiency, take into account the features of various processing methods, which influence both the process of forming products and its aesthetic side.
It should be taken into account that an artistic product made by one or another technology acquires certain features and characteristic features inherent in it.
Thus, parts turned on a lathe are distinguished by accuracy and clarity of shape, while forged or forged parts are distinguished by softness and ductility.
Cutting allows you to obtain sharp corners and clear edges, and sheet stamping is constantly associated with the need to apply bending only along radii, albeit minimal ones.
Therefore, already when designing artistic products, the master must take into account the specific characteristics of the material and methods of its processing, since there is a certain interdependence between the material and its processing.
Some metals and alloys can be processed well in many ways. For example, gold and silver can be both cast and forged; they are well cut and processed by pressure.
However, there are metals whose technological properties are quite limited.
For example, cast iron is well cast and cut, but due to its fragility it is not processed by pressure (forging, stamping, etc.).
On the contrary, red copper is poorly cast and cut, but is well processed by forging, stamping, and embossing.
Artistic casting
Casting is one of the most ancient methods of metal processing by pouring molten metal into special molds. Archaeological excavations confirm that already 5000 thousand years BC people knew how to cast metal. Monuments of ancient Greek and Roman culture are very perfect examples of foundry.
In ancient Rus', casting has been known since the period of Scythian culture. The excavations revealed not only beautiful openwork castings of gold and silver, but also a large number of copper and bronze castings representing jewelry and religious items, as well as foundry tools - furnaces and forges in which metal was melted, as well as stone molds for casting .
A variety of metals and their alloys can be used to perform artistic works using the casting technique. For expensive, unique products, gold, silver, and bronze have been used before and now.
The artistic quality of the work performed by casting depends primarily on the quality of the model from which the casting mold is made.
The casting process itself is largely technical work, but it requires highly qualified craftsmen performing it.
Moreover, the craftsman had to modify the casting: clean the seams where the mold joins, remove the remains of the sprues (the place from which the molten metal flowed into the mold), and stamp the shape of individual parts.
In this regard, the casting itself is performed differently.
Andrei Chokhov was a remarkable craftsman, who cast bells and cannons. He worked as a foundry worker for more than half a century and trained a large number of students.
His main work is the “Tsar Cannon,” weighing 40 tons, which is an example of artistic bronze casting from the 16th century.
An equally high example of artistic casting is the huge “Tsar Bell”, also cast from bell bronze in 1735 by I.F. Motorin and his son Mikhail. The weight of the bell reaches 200 tons.
From the end of the 17th century, artistic statue casting began to develop. One of the first major bronze casters and sculptors was Carlo Rastrelli, invited by Peter I to work in Russia.
His most significant works are the bronze bust of Peter I and the statue of Empress Anna, which were cast by Russian craftsmen, as well as the Equestrian statue of Peter I, cast after the death of Rastrelli by the foundry Martelli and installed in St. Petersburg.
E.M. had a huge influence on the development of statuette casting using a wax model. Falcone, who created “The Bronze Horseman,” on which he worked for 12 years.
A talented bronze caster was the sculptor P.K. Klodt, who perfected the most complex technology of casting large figures from wax figures. The statue of Nicholas I cast by him is a masterpiece of foundry art.
Art castings from Ural factories have received worldwide recognition. They are famous for their chamber cast iron sculpture, including the finest openwork, almost jewelry casting, creating miniature chains, each link of which barely exceeds 3 mm in length and weighs only 0.5 grams.
In the future, artistic casting is characterized by the mechanization of foundry production, the development of new technology, the introduction of the latest casting technologies, such as chill casting, shell casting, centrifugal casting and others. Old casting methods began to develop on a new basis.
Currently, there are various casting methods that allow the casting of products of various sizes and weights - from a few grams of precious metal in jewelry to large statues and monuments made of cast iron and bronze.
In the field of production of artistic products, casting methods are used such as centrifugal casting, injection molding, permanent metal molds, shell molds, earth molds, and lost-wax molds.
Earth casting
One of the oldest methods of casting, which has not lost its significance even today, is casting in earth molds.
The process of producing a casting using this method consists in making a casting mold using a model or template from the molding earth, which is filled with molten metal.
When the finished casting is removed, the mold is destroyed and for the next casting the process of making the mold is repeated again, i.e. Each mold only serves once.
Models for preparing casting molds are copies of the author's original. They are made of plaster, wood, plastic or metal, depending on the edition.
Plaster models are used for unique castings or small series, since they are quickly destroyed during molding. To increase strength, they are varnished.
Wooden models are more durable, but damp soil causes them to deform, warp and swell. As they dry out, they shrink in size and crack.
To strengthen wooden models, they are painted and coated with waterproof varnish.
Plastic models have smooth and clean surfaces, light weight, and water resistance. But they are not strong enough and cannot withstand large print runs.
The most durable and durable metal models are made of bronze, cast iron, and aluminum. Aluminum ones are the most economical.
They are lighter in weight, do not rust, and are quite durable.
The size of the model is usually made slightly larger than the original by the amount of linear shrinkage, so that the product cast on it after shrinkage corresponds to the dimensions of the original or drawing.
When making a model, subsequent machining of the casting is also taken into account, so it must have an allowance for processing. Simple, solid models, for example, a model of low bas-relief, i.e. a product on the surface of which there are no undercuts or protrusions that would interfere with the removal of the mold.
When casting products with more complex configurations, split models are used, as well as models with detachable parts. Such models are made cut into two more or less equal parts in accordance with the parting line of the flask.
Both halves are connected to each other by spikes that fit tightly into the corresponding sockets on the other half of the model.
When molding, each part of the model is removed from the mold separately, which greatly simplifies the molding process.
When casting products with protruding parts, all parts that interfere with the removal of the model from the mold are made removable. At the beginning of molding, the model is assembled, with all removable parts secured to it using special tenons, pins, screws, etc., and after the model is molded, the fasteners are removed and the model is easily removed from the mold.
In this case, the detachable parts remain in the mold, then they are removed, each separately.
Models for hollow castings…
end of introductory fragment
Source: https://iknigi.net/avtor-ilya-melnikov/60643-hudozhestvennaya-obrabotka-metalla-zakreplenie-kamney-v-izdeliyah-i-hudozhestvennoe-lite-ilya-melnikov/read/page-1.html
Peculiarities
Artistic casting of brass is almost no different in technology from casting bronze. Let us present the subtleties of the process.
- The melting temperature of brass is quite low, in the range of 880-965 C. This allows the use of different types of furnaces. Even a gas burner, just choose heat-resistant cookware. But sometimes the temperature is increased to 1070 C due to additives (for multi-component brass). The melting point of bronze is higher. The alloy of copper with tin is 900-950 C, and bronze without tin is 950-1100 C. Bronze alloys have high viscosity, so to improve their quality they are heated 100 degrees higher. To save energy, it is better to use induction or crucible furnaces.
- The main stage of casting is pouring the melt into the mold. The duration of the process should not exceed 2 minutes. Otherwise, the product will be defective. Splits, burns and adhesions will appear. The item will be completely damaged and unusable. Or additional processing will be required.
- For brass there should be uniform gradual cooling, without the use of special solutions. When cooling bronze, coolants are used.
- The final stage is processing of the finished part . Removal of bays, sprues, and vents is required. To keep the composition unchanged, fluxes are added to the alloy. Thanks to them, it is possible to protect the surface of the melt and degas its composition. This reduces defects in the finished product.
Accepting orders for artistic casting
1).
You send by email a sketch, drawing or photograph of the future product with dimensions and the desired number of pieces in the batch. Or call us by phone and we will advise you in detail. 2). We will evaluate the work as soon as possible and respond in any convenient form.
3). We conclude a stage-by-stage agreement for artistic casting, which includes 3D modeling or 3D scanning, creation of a master model and casting, as well as an obligation on our part to complete the order with high quality and on time at a pre-agreed price.
4). You make payment in any way convenient for you.
Stages of work
Process costs
To reduce the unprofitability of the process, conventional casting methods for disposable models have been modernized to create high-strength polymer compositions. To do this, they began to cast into shell containers made of thermosetting powdered polymer. When exposed to temperature, it turns into a solid shell, forming a liquid alloy.
This method is used to cast water and steam heating radiators, assemblies of automobiles, machine tools, aircraft, and other types of high-tech mechanisms. This technology makes it possible to produce large-sized parts and any complex modifications.
Chill casting is considered traditional when a durable mold is used.
The part is pulled out of it after the metal has hardened. In this way, simple steel products of small size are produced. Most often, copper and aluminum alloys with low casting temperatures are cast into the chill mold.
The model for them is made of heat-resistant steel or cast iron, which have a higher melting point than copper or aluminum.
The advantages of this technology include:
- low cost of the production process and the possibility of its inexpensive automation;
- ease of execution;
- safety of casting molds that are used repeatedly;
- accuracy of parameters of manufactured products;
- high-quality metal structure, in which there will be no non-metallic particles;
- smooth surface of the product, which is obtained using this casting method.
Traditional lost wax casting technology has now been improved by the advent of new materials.
If previously the model for pouring the alloy was made of wood or other organic matter, which could be destroyed by high temperatures during burning, today low-melting materials such as paraffin and stearin are used.
Lost wax casting is used when casting artistic products with complex configurations. This is a costly casting technology that is used to create monuments or other artistic products.
The steel container for such pouring is made on the basis of models made of fusible materials, it has precise dimensions, and its surface is carefully polished.
Analysis of the process step by step
The procedure for making bronze objects is a very important undertaking that requires a sequence of actions.
To begin with, the artist creates a sketch of the future souvenir. After this, based on the sketch, a drawing is drawn up with clearly indicated dimensions, which subsequently assists production. It is on the basis of the scheme that the subsequent preparation of the casting model takes place, into which the hot liquid substance will be poured. Usually it can be used many times, which makes it possible to produce a whole series according to one idea. The inner side of the casting is coated with a special hardening non-flammable solution and pouring begins. This is not a difficult, but important stage. In order for the created specimen to meet the declared characteristics, it is necessary to correctly calculate the number of initial components in order to develop high-quality products. If you violate the algorithm, you can get visible and invisible defects (underfilling, burnt marks, etc.).
After the contents have hardened, they must be carefully removed. Depending on the type of casting structure, the extraction option depends. If it is reusable, it is opened along the connecting plane; if it is disposable, it is broken, and the product is carefully removed with pliers.
General characteristics of metal
Bronze is not a homogeneous metal, but is a copper-based alloy reinforced with alloying additives of aluminum, beryllium, lead, silicon, and tin. Based on the number and type of additional components, in addition to brass, the bronze alloy acquires a certain color and a number of chemical and physical characteristics.
Bronze is classified as a particularly strong and resistant alloy; its melting point is 900–1100 degrees. Taking into account the basic characteristics of the material, it is used in production, as well as for the production of artistic castings due to the abundance of useful properties:
- high strength, wear resistance;
- exceptionally low level of corrosion;
- ease of processing, steam resistance;
- ability to conduct current and heat;
- resistance to external damage.
From the point of view of chemical composition, bronze can be of two options - tin-free and tin alloys. The combination of tin and copper gives the final material strength, but lowers the melting point and thermal conductivity. An example of a bronze-tin alloy is bell bronze, but products made from it become more fragile.
Bronze without tin
Tin-free materials include the following types:
- especially resistant lead with a wide range of anti-friction properties, refractory;
- beryllium - the most durable and ductile after hardening;
- silicon-zinc with a high melting fluidity index;
- aluminum – resistant to the aggression of chemical elements and the environment.
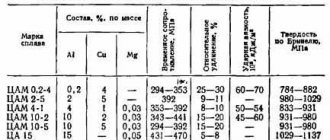
The multicomponent alloy without the presence of tin contains 2.5% alloying elements, which significantly improve the set of useful qualities of the bronze metal. The presence of iron impurities helps to improve the structure and strength characteristics of the alloy. To mark bronze, a combination of the letters “Br” is used, followed by the first letters of the name of the additive (aluminum, beryllium, lead, etc.) and the percentage of its content in the alloy.
Melting temperature
Information on the melting and casting temperatures of individual types of bronze is given in the table below:
According to the technological characteristics of bronze there are two types:
- deformable type that withstands mechanical processing well, used for stamping, wire production, sheet production;
- the foundry variety is resistant to high temperatures and is used for casting large-sized products with particularly complex configurations.
The name “bronze” was given to the metal by analogy with the oldest seaport in Italy – Brindisi. In the fourth millennium BC. e. local metallurgists achieved perfection in the mass production of an alloy of copper and tin, and the era began to be called the Bronze Age.
Main characteristics of bronze alloys
The color of the bronze alloy depends on the quantitative composition of alloying elements. They influence the physical properties: ductility, wear resistance, melting point of bronze. The alloying components are metals (tin, aluminum, beryllium, lead, manganese) and non-metals (phosphorus, silicon). You can melt any bronze alloy at home. Knowing the markings of the scrap, it is easy to determine the exact melting point of bronze. But usually the composition of bronze pieces prepared for melting varies. Then the appearance of the metal is assessed.
Bronze alloys are classified into two categories:
- tin ones are more ductile;
- tinless ones are less easy to process:
- beryllium are characterized by high strength, maximum tensile strength and torsion;
- aluminum has a low melting point, is resistant to corrosion, and has good anti-friction properties;
- lead plastic, easy to machine;
- with additives of zinc and silicon, they are characterized by fluidity; when melted, they evenly fill the casting mold;
- the alloy with iron can be welded well, but its contact with aggressive environments is undesirable;
- manganese improves strength characteristics while maintaining the ductility characteristic of copper;
- Tin-lead bronzes are malleable, they are subjected to hot deformation, and the alloy is made into hot-rolled products.
For industrial casting, tin bronze with a low melting point, up to +1000°C is used.
Unlike brass, bronze is more viscous at its melting point. When filling forms of complex configurations in production shops, centrifuges are used. The alloy, heated above the melting point by 5°, is given additional acceleration so that it spreads evenly. When making handicraft castings, it is advisable to take into account the viscosity of the bronze alloy at the melting point so that there is no defect on the surface. Foundry workers consider low shrinkage during cooling to be an advantage of non-ferrous metal. It is possible to obtain castings that do not require lengthy finishing to the specified geometric dimensions. High-quality shaped castings are made from bronze alloys.
Preparing for work
The metal is popular not only in various branches of modern industry (shipbuilding, aviation, rocketry, etc.), but also for casting sculptural compositions due to its durability and resistance to mechanical damage. Highly artistic forms of bronze products decorate theaters and palaces, halls of special events.
Despite the complexity of the technology, artistic bronze casting remains a popular procedure, which will actually become a profitable business due to low market saturation. First, the future master will need a starting capital of at least 200 thousand rubles in order to purchase equipment and comprehend the secrets of working with the material.
Necessary equipment
To set up a small smelting workshop you need to purchase:
- a simple melting furnace;
- cast iron or steel crucible;
- a special type of tongs for removing the crucible;
- casting molds, auxiliary hook;
- a forge will be required if the furnace is not a muffle;
- supply of charcoal if using a forge for smelting.
When selecting a room for foundry work, it is important to provide it with effective ventilation and prepare a set of reliable means that provide fire protection. For casting small items, you can use a small room. Casting large-sized structures is best done in a workshop or garage.
The general outline of the process is as follows:
- creating a sketch and then a model for the cast;
- loading scrap metal into a crucible, melting inside the furnace;
- filling the casting mold with liquid alloy;
- removal of the finished product, elimination of defects.
Before the process of casting bronze yourself, you need to stock up on raw materials. A small supply of bronze scrap is suitable for this - industrially produced metal ingots or parts of plumbing fixtures.
Final processing
After removal from the mold, the product usually has an unpresentable appearance. It has various surface defects. To give a bronze product a normal condition, it must be cleaned with a grinding machine or a wire brush.
Multifunctional grinder
In addition to cleaning, chasing will also be required, although bronze has good fluidity and, when filling the mold, easily fits into all the recesses. However, in order to achieve a clear design on a product, one cannot do without embossing. This stage of work often takes a long time, especially if the product has openwork elements.
Embossing is the most creative stage of the foundry procedure, and its quality will determine the final appearance of the product. Finished products are often plated with silver or gold, chrome or nickel. Often figurines are covered with an additional layer.
Products with complex designs can be cast in separate parts rather than as a whole. Afterwards, the elements of the product are connected with special locks. It is recommended to label each part to avoid confusing the locks during assembly.
Video: Casting bronze into a steel mold
Where to sell bronze products
Bronze products made at home are valued higher than factory products. Small scales make it possible to obtain high-quality castings. These are small figurines or sculptures of famous people.
In order to make a profit, you can do custom work. The sale of finished products is organized through specialized stores. An implementation option is advertising on the Internet. When expanding production, intermediaries are involved in distribution. Sales in wholesale quantities begin.
Organizing bronze casting at home requires large investments. However, such products are in demand. Properly planned production quickly pays off.
Titanium production
To produce high-strength alloys from titanium and steel, vacuum casting is used to reduce the gas content in the metal. In this way, a denser structure of a metal alloy is created by melting in a vacuum. The hot metal is then poured into multiple containers in which it cools.
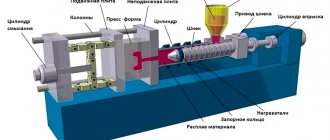
When introducing injection molding technology, special equipment is used to fill molds with liquid metal. It is supplied under high pressure in the range of 7–700 MPa.
This production method is carried out by hot or cold pressing machines.
This technology is used for pouring aluminum, copper, zinc and tin-lead alloys. All these metals have a low melting point, which increases the technological characteristics of products made from them.
Cold and hot injection molding methods make it possible to obtain a product with perfectly accurate dimensions and a smooth surface, which does not require additional processing after completion of the process.
This technology allows you to increase labor productivity. It also reduces the time of the entire technological cycle and simplifies the production of metal products. It also has disadvantages, which include the inability to produce products of complex configurations, since they can become deformed when removed from the mold. This method produces only metal products with a small diameter.
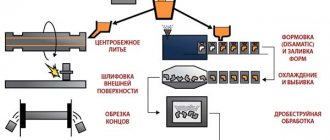
Centrifugal casting uses special molds rotating in a horizontal or vertical plane.
The action of centrifugal forces ensures uniform filling of all cavities in the casting mold. This casting technology is being introduced in the production of pipes, bushings or metal disks. It is also used in the casting of openwork jewelry.
Bronze casting technologies
Melting, like cutting, is a widespread operation for producing parts. For melting, it is recommended to use induction melting or crucible heating furnaces. The choice is determined by economical electricity consumption.
To preserve the chemical composition of alloys, fluxes are used. With their help you can:
- Protect the outer layer of the melt surface: from oxidation;
- increase the volume of suitable melt;
- exclude non-metallic components;
- Degas the composition, which reduces the formation of: gas pores;
- shells
To obtain smooth surfaces on the casting and ease its removal after cooling, non-stick paints are used. Their use ensures:
- mold lubrication;
- protection from destruction upon contact with the melt;
- no burns.
Injection molding
Injection molding occurs when exposed to excess or insufficient (vacuum) pressure. The press principle is used to supply the melt under excess pressure. The piston is subject to force from a hydraulic or pneumatic system. The high feed rate coupled with high viscosity creates high pressure to completely fill the mold. The resulting castings have high precision and a fine-grained structure.
Due to vacuum suction, the melt is drawn into the mold of the crystallizer. Cooling occurs towards the center of the mold. The required amount of melt is drawn in over a certain period of time.
A crystallizer is a container with thin walls that are cooled with water.
After normal (atmospheric) pressure is restored, the excess melt drains off. After cooling due to shrinkage, the part is independently removed from the mold. Automation of the vacuum suction process allows you to fill the mold in a minimum amount of time, down to 0.1 seconds.
Finished bronze product
Centrifugal casting
It is advisable to use centrifugal casting, pouring bronze and brass in the manufacture of parts such as rotating bodies. The formation of parts occurs on machines with horizontal and vertical axes of rotation. On machines with horizontal pouring the following is cast:
- bushings;
- inserts;
- rings.
On machines with vertical pouring the following is cast:
- gears;
- worm wheels;
- propellers.
Centrifugal casting
The technology is based on centrifugal force, which is generated when the mold rotates. The melt is compacted under the influence of forces, displacing third-party components.
Artistic casting
Modern trends dictate the use of casting not only in the production of parts for mechanisms and assemblies, but also in the production of interior elements. Thus, using artistic casting technology it is possible to produce:
- bas-reliefs, sculptures;
- elements of fences, gratings, gate fences;
- souvenirs;
- lamps, sconces;
- interior elements.
The stages of technology for producing castings are as follows:
- making a model;
- mold making;
- preparing the form;
- melting of the charge;
- preparing the melt for pouring;
- cooling;
- demolding;
- stump;
- cleaning and presentation.
Finished castings, according to the master’s plan, are combined into a single product if it is multi-component. After which they can be chrome-plated, nickel-plated, covered with patina and other metals.
Bronze casting: artistic bronze casting technology
Bronze casting allows us to produce products that have exceptional decorative appeal. The technology of casting from this alloy, which is based on copper, has been known for many centuries, but even in our time it continues to be improved.
The appearance of bronze products speaks of the painstaking work of the master, turning faceless metal into a work of art
History of technology
According to historians, the bronze casting is 12 thousand years old. Initially, using this technology, jewelry and simple tools were made from bronze. Over time, this technology has been improved, and today it is a method by which many unique products are created from this alloy.
The current level of development of bronze casting makes it possible to produce various objects from this copper alloy not only in production, but also at home.
Thanks to the invention of bronze, as well as the development of its processing technologies, the main of which is casting, we can still enjoy the sight of works of art that were created by masters back in the Middle Ages and ancient times.
Antique bronze set of writing instruments
Bronze casting, as well as brass casting, another alloy based on copper, gained the greatest popularity in the era of classicism and European Baroque. It was in those days that people learned to use these materials to create unique interior elements and decor.
Such alloys created on the basis of copper are still actively used in the manufacture of:
- items used for interior decoration;
- gates and fences that perform not only a decorative, but also a protective function;
- sculptural compositions and souvenirs;
- bas-reliefs and design elements of lighting fixtures - chandeliers and sconces;
- elements of staircase structures and entrance groups.
Bronze casting for making knife handles
Many of these products, which are not large in size or complex in shape, can be made from bronze and brass not only in production, but also at home.
Stages of artistic bronze casting
In order to perform high-quality casting from a metal such as bronze, it is necessary to adhere to a certain sequence of actions. First of all, you should reflect in the sketch the shape of the product that you plan to cast from bronze.
Based on the sketch, which is created by professional artists and designers at modern enterprises, specialists create a drawing that accurately reflects all the dimensions of the future casting.
It is the drawing that is the basis for making an accurate model, which is used to produce a casting mold.
To create a model of a product that will subsequently be made from bronze by casting, various materials can be used, in particular:
- Ivory;
- wood (in this case, preference is given to such varieties of this material as pine, alder, beech, linden);
- gypsum;
- various types of polymer materials.
The cavities of the wax model of the future figurine are filled with clay, which will be removed after casting
To make the surface of the model as smooth as possible, it is primed, puttied and covered with several layers of varnish. When making a casting model, not only different materials can be used, but also different design approaches. So, models can be:
- detachable (these are complex structures consisting of several component elements that can be connected to each other along flat or complex surfaces);
- one-piece (monolithic models, the simplest type, most often used for casting at home);
- special (this includes skeletal or molding templates used in cases where it is necessary to make a casting mold for the manufacture of objects with a complex configuration).
The next step after creating an accurate model of the future bronze product is the production of a casting mold. For this purpose, special devices and equipment are used, and the main materials used in this case are molding mixtures created on the basis of clay and carefully cleaned quartz sand.
The longest stage of bronze casting is molding - making a casting mold
In such a technological process as casting, made from bronze and any other metal, the casting mold plays a decisive role.
It is into such a mold, the internal cavity of which must exactly repeat the product being cast, that the molten metal is poured, and in it it cools, forming the finished casting.
Foundry molds, used both in production and at home, can be single-use or reusable, which is determined not only by the material from which they are made, but also by the features of their design.
To ensure that the compressed and solidified mixture from which the casting mold is made does not collapse at the moment when the molten metal begins to act on it, it is placed in special devices called flasks.
The mold is often made from plywood or wood
The size of such flasks, which can also be disposable or reusable, entirely depends on the geometric parameters of the future product. In flasks, which are usually made of metal, both the creation of the casting mold and the casting itself take place.
An educational video about the advantages and features of artistic bronze casting.
Subtleties of technology
In order to perform artistic bronze casting or make a practical product from this alloy, it is necessary first of all to obtain molten metal.
Various types of furnaces are used for metal melting: induction, arc, flame, etc.
In the simplest version (when casting at home), you can use a regular gas burner to melt bronze, placing it under a special container for the melt.
The capabilities of small furnaces, which you can make yourself, are quite enough to melt non-ferrous metals and their alloys, which also include brass and bronze.
To melt a small amount of bronze you need a fire brick and a gas burner
The most important step in bronze casting is filling the mold with molten metal. Despite the fact that such pouring lasts only 1–2 minutes, the correctness of its execution directly affects the quality characteristics of the finished product. The result of incorrect filling can be such defects as:
- adhesions;
- burns;
- slag shells;
- underfilled.
These bronze castings developed cavities due to poor cleaning of the crucibles before pouring.
When casting small-sized brass and bronze products, the molten metal is poured not from the crucible itself in which it was heated, but using a special device used as a hand ladle or spoon.
The metal, which has already been poured into the mold, must be allowed to cool to the required temperature, which, depending on the brand of alloy used, may vary.
The procedure for removing the finished product from the mold depends on what type it is - disposable or reusable. In the first case, it is simply broken with a hammer, and the casting is removed using pliers.
Reusable molds, accordingly, do not need to be broken: they are simply opened along the surface to be joined and the casting is carefully removed from them.
The newly removed casting needs to be reworked. This modification consists in the fact that the sprues, spurs, profits and bays formed during the casting process are removed from the surface of the product. This operation, which can be performed using various mechanical tools, is called trimming.
Giving the cast product an attractive appearance
The product, which has just been removed from the mold, looks quite unpresentable. Burnt molding sand may remain on its surface and other surface defects may be detected.
The first step in bringing a bronze cast object back to normal condition is cleaning it.
To perform this procedure, metal brushes or grinding machines are used (a wire wheel is installed on them as a working tool).
Despite the fact that brass and bronze have good fluidity and, when casting, fill all the recesses in the mold well, it is almost impossible to obtain a fine pattern on the finished product.
To form such a pattern, a finishing operation such as embossing is used. It is performed using a special tool.
Depending on the complexity and subtlety of the pattern that needs to be formed on the surface of a cast bronze product, the embossing operation can take a different amount of time.
Hand-chased bronze figurine
It should be borne in mind that embossing is the most creative stage of the casting procedure; the quality and thoroughness of its execution directly determines how the product will ultimately look. That is why such an operation should be approached very responsibly and with maximum care.
Depending on the idea of the craftsman who casts bronze or brass, as well as on the requirements for decorativeness, the surface of the casting can be covered with artificial patina, gilding, silver, or a layer of nickel or chromium.
Objects that have a complex structure are often cast not as a whole, but in separate parts, which then must be correctly connected. This connection is made using special locks originally provided for in the design.
In order not to confuse such locks and to correctly compare their elements with each other, they are often marked.
Areas of use
The technological process of metal casting is in demand, since its use makes it possible to produce a variety of high-quality products without resorting to bulky equipment and a huge number of workers.
This production method is used to create and produce various metal products, which, in turn, are widely used in the following industries:
- automotive;
- aviation;
- mechanical engineering;
- electrical engineering;
- medical (in particular, dental and orthopedic);
- jewelry, etc.
In the modern metal industry market, this production technology is in high demand. Moreover, metal casting is one of the top ten best technologies in the world, the most effective and most used.
Prices for manufactured products
In order to determine whether it is profitable to purchase a ready-made mini, you need to compare your own costs with the cost of the final product. It is quite difficult to unify prices in the industry, since they are formed taking into account the manufacture of molds or molds, as well as production volume, type of metal, and complexity of the product. Therefore, the cost of work will be calculated individually for each customer. You can give an example of prices for castings from various metals:
- gray cast iron – from 69 rubles per kg;
- alloy cast iron – from 170;
- high-strength cast iron – from 118;
- carbon steel – from 87;
- low alloy steel – from 126;
- alloy steel – from 210;
- heat-resistant steel – from 350;
- castings from aluminum alloys – from 320;
copper castings – from 580.
Partner advertising
The first stages of artistic casting technology
First, a sketch of the bronze structure is created with the help of trained artists and designers. Based on it, a working drawing is developed, according to which a casting model is made, which is required to form the imprint (contours) of the future product in the foundry mold.
Models for artistic casting are made of ivory or wood (pine, alder, beech, linden), less often of plastic or plaster. Putty, primer and several layers of special varnish must be applied to their surface so that it is even and as smooth as possible.
Structurally, the models are of the following types:
- Detachable - prefabricated structures from individual elements that can be separated after removal from the mold along a plane or along a complex surface.
- One-piece - monolithic products, most often used at home (for manual casting).
- Special – skeletal or molding templates. They are used when complex structures are made from bronze.
After receiving the desired model, production of the casting mold begins. This is a long and labor-intensive process, carried out using special molding compositions (clay plus quartz sand), devices and special equipment.
Casting molds are divided into multi- and disposable. They are filled with molten bronze (watch the video), which, when cooled, forms a casting identical to the shape of the created model.
During compaction, the molding composition is held by two flasks - half-molds that make up one casting mold. Selected combinations of various inorganic and organic substances are usually poured into these flasks. At home, it is recommended to use small flasks (based on geometric parameters and weight). But in large enterprises engaged in artistic casting, as a rule, they use larger-scale hemispheres.
Casting process
Bronze casting begins with preparing the workplace. Install a stand under the flask and a crucible. It is made of fire-resistant material. You can pour a layer of sand into a tray or use a metal plate.
Before loading the crushed scrap into the furnace, it is necessary to prepare the flask. It is heated well and kept for at least 2 hours at +600°C. The refractory crucible at this temperature begins to emit a yellowish glow. While the heated mold is cooling, begin melting the crushed scrap.
The melting pot is filled to 1/3 of its volume. Place the pieces of scrap in a hot oven and leave until completely melted. The crucible or other melting vessel is set to heat when the temperature in the furnace is close to or has reached the melting point of bronze. Tin bronzes become liquid up to 1000°C; tin-free bronzes have to be heated longer and have a higher melting point.
When all the bronze has melted, it is left in the oven for 3-5 minutes so that the melt warms up well and becomes less viscous. Then the melting pot is removed with tongs or a special hook. The melt is ready. It's time to start making the casting.
Pouring bronze into a mold
The molten metal is poured into the hole of the mold in a thin stream; the bronze should evenly fill all the voids. It compacts under its own weight. To ensure that the hot form is filled well, it is placed on a rotating stand with a manual or electric drive. This trick is necessary to obtain high-quality casting. If you pour bronze calmly, the corners of the casting will be rounded. Spin the mold with the hot melt during filling. Once the bronze sets, the casting shape cannot be changed. In factory conditions, technological centrifuges are used. At home, craftsmen make similar industrial installations based on used washing machines.
It is necessary to impart movement to the alloy when making small complex castings. The bronze melt will not have enough of its own weight to fill all the voids. It will harden unevenly, and cavities and folds will appear on the surface of the casting.
How to make a casting mold
Independent production of a casting mold begins with the selection of a body into which the future casting will fit freely and half of the space will remain free. This can be a tin can or a specially made container. Traditionally, the size of the flask is 1.3–1.5 times greater than the dimensions of the casting. This ratio is necessary so that the sand-clay mixture forms an even layer on all sides of the part. The filling for the flask is made from materials that can retain heat. The cast workpiece will only be of high quality if it cools gradually.
Foundry models
Artistic casting of bronze and brass involves obtaining the smoothest possible surface, so fairly hard materials are used to recreate the model:
- wood;
- gypsum;
- Ivory.
To obtain the smoothest possible surface, it is subjected to elimination of porosity by puttying, priming and varnishing. Casting models are made split; one-piece - suitable for casting products of simple shapes; special for parts with a rather complex configuration.
History of technology
Brass casting, like bronze, appeared 12 thousand years ago. At first, tools and jewelry were made from these materials, and later dishes and household items. Products made of bronze and things made of brass were widely used in all spheres of life. The first methods of making bronze and brass originated in the ancient era in the age of classicism. We can still contemplate many masterpieces of art from that era to this day. At the moment, these low-melting alloys are used mainly for making decorative items for decoration and works of art.
Copper alloys with the addition of metals are widely used in production:
- sculptures and souvenirs;
- gratings and other fencing elements;
- fences and gates;
- interior details;
- in the decoration of chandeliers and sconces.
Over time, the casting method was improved. And in the modern world, it has become possible to smelt bronze and brass parts not only industrially, but also in domestic conditions.
Casting from aluminum, bronze, brass, as well as gold and silver
Not many manufacturers that provide artistic casting services in silicone molds can boast of an excellent price/quality ratio. We, in turn, optimize the process as much as possible, creating works of art from aluminum, bronze, brass, as well as gold and silver.
Using artistic casting, we produce various unique gifts, jewelry, decorative elements, awards of various kinds, souvenirs, statues, bas-reliefs and much more.
We have taken the ancient process of decorative casting to a new level, using the experience of craftsmen and introducing new equipment, thereby increasing the speed of our work without losing quality. And you have information on each stage in the casting cycle.
Accepting an order