Designations
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | St2ps |
| Designation GOST Latin | Ct2pc |
| Translit | St2ps |
| By chemical elements | 2 |
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | VSt2ps |
| Designation GOST Latin | BCt2pc |
| Translit | VSt2ps |
| By chemical elements | 2 |
Interpretation of steel grade St2sp
Decoding of steel: The letter at the beginning indicates a group of steel which defines the criteria for the ultimate strength for the chemical composition; if there is no letter, then such steel belongs to group A, and is supplied to consumers based on mechanical properties (such steel may have a high sulfur or phosphorus content). Letters St. indicate that the steel is of ordinary quality, although most steels are high quality. The numbers from 0 to 6 are the conventional brand number depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. Typically, the higher the number, the more carbon and the greater the strength. In our case, 2 indicates the carbon content in the alloy is 0.09–0.15%. The letters after the brand number indicate the degree of deoxidation: cn - calm. In terms of price, calm steels have become more expensive than semi-calm and boiling steels. Mild steel is steel obtained as a result of deoxidation. It is obtained by deoxidation with aluminum, manganese and silicon. The level of oxygen in it is so reduced that during metal processing no reaction occurs between carbon and oxygen, and the presence of non-metallic slags and their inclusion is reduced to a minimum. Calm steel has a dense structure and good mechanical properties. It is less prone to negative reactions to welding heat and to aging. The features of a homogeneous microstructure give the alloy maximum corrosion resistance and ductility.
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Ribbons | B34 | GOST 19851-74 |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | B62 | GOST 3262-75, GOST 8639-82, GOST 8642-68, GOST 8644-68, GOST 8645-68, GOST 8646-68, GOST 8696-74, GOST 10704-91, GOST 10705-80, GOST 10706-76, GOST 10707-80, GOST 12132-66, GOST 13663-86, GOST 20295-85, GOST 24950-81, GOST 13664-68, TU 14-3-1160-83, TU 14-3-1428-86, TU 14 -3Р-56-2001, TU 1373-022-05757850-08, TU 1373-013-02949352-2003 |
| Low carbon steel wire | B71 | GOST 3282-74 |
| Ribbons | B24 | GOST 3560-73, GOST 6009-74, STP M309-74 |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | IN 20 | GOST 380-2005 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B22 | GOST 5422-73, GOST 5781-82, GOST 8239-89, GOST 8240-97, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8282-83, GOST 8283-93, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 9234-74, GOST 10551-75, GOST 11474-76, GOST 19240-73, GOST 19425-74, GOST 19771-93, GOST 19772-93, GOST 30565-98, GOST 535-2005, GOST 30136-95, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006, GOST 2879-2006, OST 5.9086-85, OST 5.9087-84, TU 14-2-341-78, TU 14-1-5283-94 |
| Sheets and strips | B23 | GOST 82-70, GOST 8568-77, GOST 14637-89, GOST 14918-80, GOST 16523-97, GOST 19903-74, GOST 16523-89, GOST 16523-70, GOST 103-2006, GOST 19903-90 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | B31 | OST 3-1686-90, TU 14-1-4944-90 |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | TU 14-1-3579-83, TU 14-1-4431-88 |
| Test methods. Package. Marking | B29 | TU 14-106-485-99 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | TU 14-2-849-89, TU 14-11-245-88, TU 14-136-367-2008 |
Mechanical properties 2ps at normal temperature
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Pipes, GOST 8696-74 | 334 | 225 | 24 |
| Pipes, GOST 10705-80 | 333 | 206 | 24 |
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 335-430 | 195-225 | 29-32 |
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 320-410 | 185-215 | 30-33 |
| Wire rod, GOST 30136-95 | 420-470 | 60 |
Mechanical characteristics
| Section, mm | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | d4 | y, % |
| Electric welded straight-seam pipes (Dy=10-530 mm) as delivered. The mechanical properties of the base metal are indicated |
| — | ≥206 | ≥333 | ≥24 | — | — |
| Electric-welded profile pipes in delivery condition according to GOST 13663-86 (samples) |
| — | — | ≥353 | ≥10 | — | — |
| — | ≥206 | ≥333 | ≥24 | — | — |
| Long products |
| — | ≥230 | ≥395 | ≥33 | — | ≥69 |
| — | ≥210 | ≥370 | — | — | — |
| — | ≥145 | — | — | — | — |
| — | ≥125 | ≥350 | — | — | ≥71 |
| — | ≥105 | ≥210 | — | — | ≥75 |
| — | ≥55 | ≥140 | ≥42 | — | ≥87 |
| Hot-rolled thin sheets in delivery condition. Strength group OK300V |
| ≤2 | ≥215 | 300-480 | — | ≥21 | — |
| 2-3.9 | ≥215 | 300-480 | — | ≥23 | — |
| Cold-rolled thin sheets in delivery condition. Strength group OK300V |
| ≤2 | ≥215 | 300-480 | — | ≥24 | — |
| 2-3.9 | ≥215 | 300-480 | — | ≥26 | — |
| Hot-rolled thick sheets, sections and shapes in delivery condition |
| ≤20 | ≥225 | 335-430 | ≥32 | — | — |
| 20-40 | ≥215 | 335-430 | ≥31 | — | — |
| 40-100 | ≥205 | 335-430 | ≥29 | — | — |
| 100 | ≥195 | 335-430 | ≥29 | — | — |
Characteristics of steel grade 2ps
St2ps - Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality, welds well, welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, KTS, ESW. For thicknesses greater than 35 millimeters, heating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended; it is not prone to flake sensitivity and there is no tendency to temper brittleness. Cutting machinability in the hot-rolled state at HB 137 Kυ hard alloy. = 2.0 and Kυ b.st. = 1.6, has found its application in the production of non-critical parts that require increased ductility or deep drawing, in lightly loaded elements of welded structures operating under constant loads and at positive temperatures; St2ps steel has relatively high toughness and ductility, slightly higher than St2kp steel. Forging at a temperature range from 1300 to 750 0C, cooling is carried out in air, cooling in air. St2ps steel is not prone to temper brittleness and is magnetic.
Technological properties
| Name | Meaning |
| Weldability | Weldable without restrictions; welding methods: RDS, ADS under submerged arc and gas shield, ESW, KTS. For thicknesses greater than 36 mm, preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | not inclined |
| Forging temperature | Start - 1300 °C, end - 750 °C. Air cooling. |
| Flock sensitivity | not sensitive |
| Machinability | In the hot-rolled state at HB 137 Kn tv.all.=2.0 Kn b.st.=1.6 |
Steel St2ps - carbon steel of ordinary quality
Decoding
Number 2 - indicates the serial number of the grade, and not the average carbon content in it ps - semi-quiet (the ps index indicates the degree of deoxidation) If a number is not indicated after the letter index, then the steel is category 1 . Standardized indicators: tensile strength and relative elongation.
Type of delivery
Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 8239-89, GOST 19772-93, GOST 19771-93, GOST 8278-83, GOST 8281-80, GOST 8283-93, GOST 380 -94, GOST 8509-93, GOST 8510-86, GOST 8240-89, GOST 535-88, GOST 2879-88. Thick sheet GOST 19903-74. Thin sheet GOST 19903-74, GOST 16523-89. Tape GOST 503-81. Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70. Wire GOST 3282-74, GOST 17305-91. Pipes: GOST 10705-80, GOST 10706-76, GOST 3262-75.
Purpose
Non-critical parts with increased ductility, lightly loaded elements of welded structures operating under constant loads and positive temperatures.
Temperature of critical points, °C
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-94)
| C, carbon | Mn, manganese | Si, silicon | P, phosphorus | S, sulfur | Cr, chromium | Ni, nickel | Cu, copper | As, arsenic |
| no more |
| 0,09-0,15 | 0,25-0,50 | 0,05-0,17 | 0,04 | 0,05 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,08 |
Mechanical properties
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5(δ4), % |
| no less |
| 380-94 | Hot rolled products | Up to 20 Above 20 up to 40 Above 40 up to 100 Above 100 | 225 215 205 195 | 330-430 | 32 31 29 29 |
| 16523-89 (Transverse samples) | Hot rolled sheets
Cold rolled sheets | Up to 2.0 incl. St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. Up to 2.0 incl. St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | — | 330-430 | (21) (23) (24) (26) |
Impact strength KCU
| Delivery status | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C |
| +20 | 0 | -20 | -40 |
| Hot rolled rod with a diameter of up to 150 mm | 24-64 | 13-16 | 8 | 8 |
Mechanical properties of rolled products at elevated temperatures
| tsp.,°C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % | KCU, J/cm2 |
| 20 | 230 | 395 | 33 | 69 | 104 |
| 100 | 210 | 370 | — | — | 126 |
| 300 | 145 | — | — | — | 120 |
| 400 | 125 | 350 | — | 71 | 89 |
| 500 | 105 | 210 | — | 75 | 86 |
| 600 | 55 | 140 | 42 | 87 | 80 |
NOTE : At σв = 323-412 MPa, endurance limit σ-1 = 176-196 MPa
Technological characteristics
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1300, end 750. Cooling in air. Weldability - weldable without restrictions; welding methods: RDS, ADS under submerged arc and gas shield, ESW and KTS. For thicknesses greater than 36 mm, preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. Cutting machinability - Kνb. st = 1.6 and Kνtv. spl = 2.0 in the hot-rolled state at HB 137. Flock sensitivity - not sensitive. Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone.
Find out more
Structural carbon steel of ordinary grade...
Carbon tool steel…
Steel grade 20: explanation, characteristics, chemical...
Low-alloy structural steel for welding…
Chemical composition
Alloy D2 belongs to cutting high-carbon alloy steels and has the following composition:
- carbon (C) – 1.55%;
- manganese (Mn) – 0.35%;
- chromium (Cr) – 11-13%;
- silicon (Si) – 0.45%;
- molybdenum (Mo) – 0.9%;
- vanadium (V) – 0.9%;
- phosphorus (P) – 0.03%;
- sulfur (S) – 0.03%.
With the help of manganese, the hardening process occurs. The element does not worsen the toughness of steel, but increases its strength and improves the structure of the product.
Alloy D2 has the highest degree of corrosion resistance among high carbon steels. When the composition contains up to 13% chromium, the alloy is called semi-stainless, but the formation of rust depends on the contact of the product with an aggressive environment, the processing method and other factors. Chromium increases the viscosity and hardness of the metal, and provides less susceptibility to wear.
Silicon gives the alloy strength and elasticity.
Molybdenum facilitates hardening. It enhances the ability of steel to be annealed, evenly distributing the internal stress that arises in the process. Adds strength, hardness, and increases corrosion resistance. Adds resistance to high temperatures to the product.
Vanadium improves hardenability, provides strength and lack of fragility.
Carbon is the main element, like most alloys. Gives the metal greater strength, sharpness, and increased toughness.
The content of sulfur and phosphorus, which are considered harmful impurities, is brought to a minimum, and in such quantities they do not have a negative effect on the alloy.
Foreign analogues of steel grade St2sp
| USA | A192, K02502 |
| Germany | 1.0034, RSt34-2, S185, St35, St37-2 |
| France | A34-2, A34-2NE |
| England | 1449-3420HR,, 3420HS, S360 |
| European Union | E195, S235JR |
| Italy | Fe330BFN |
| China | Q215, Q215A, Q215A-Z, Q215B, Q215B-Z |
| Bulgaria | ASt0, BSt2sp, WSt2ps, WSt2sp |
| Hungary | Fe310O |
| Poland | St0S |
| Romania | OL34.1 |
| Czech | 10000 |
- Structural steel
- Tool steel
Brand: steel, metal St2sp
Brand: St2sp
| Brand: | St2sp |
| Classification: | Structural carbon steel of ordinary quality |
| Application: | non-critical parts requiring increased plasticity or deep drawing; lightly loaded elements of welded structures operating under constant loads and at positive temperatures |
| Foreign analogues: |
| C | Si | Mn | Ni | S | P | Cr | N | Cu | As |
| 0.09 — 0.15 | 0.15 — 0.3 | 0.25 — 0.5 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.05 | up to 0.04 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.008 | up to 0.3 | up to 0.08 |
| Weldability: | no limits. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | not sensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | not inclined. |
| Assortment | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Thermal change |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Pipes, GOST 8696-74 | 334 | 225 | 24 |
| Pipes, GOST 10705-80 | 333 | 206 | 24 |
| Rolled goods, GOST 535-2005 | 335-430 | 195-225 | 29-32 |
| Thick sheet, GOST 14637-89 | 330-430 | 195-225 | 29-32 |
| Wire rod, GOST 30136-95 | 420-470 | 60 |
| Hardness St2sp, | HB 10 -1 = 116 MPa |
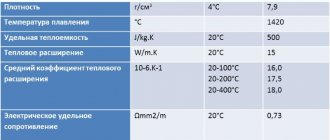
| T | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 7850 |
Foreign analogues of the material
Both exact and closest analogues are indicated!
| USA | Germany | France | England | European Union | Italy | China | Bulgaria | Hungary | Poland | Romania | Czech |
| — | DIN,WNr | AFNOR | B.S. | EN | UNI | G.B. | BDS | MSZ | PN | STAS | CSN |
|
| | | | Mechanical properties : | | sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] | | sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] | | d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] | | y | — Relative narrowing, [%] | | KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] | | HB | — Brinell hardness, [MPa] |
| Physical properties: | | T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [Deg] | | E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] | | a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] | | l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] | | r | — Material density, [kg/m3] | | C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] | | R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] |
| Weldability: | | no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment | | limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment | | difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
|
|
|
|