23.04.2018
The rules for installation and subsequent operation of external sewer systems are described in SNiP. The main purpose of sewer networks is to drain wastewater from objects such as residential buildings, industrial buildings, public institutions, etc. When designing such networks, it is necessary to take into account the architectural features of the facility, the rules and regulations for installation work, as well as the technical characteristics of the pipes themselves.
Types of sewer networks
First, we need to define what a sewer network is. In technical language, this is communication with numerous branches mounted in a single system of individual pipes. The pipes are designed to transport wastewater from consumers into containers for the accumulation and processing of aggressive liquids. There are two types of sewerage:
- external sewer networks. These include waste pipes and treatment plants located off-site on the street;
- internal sewerage is an extensive network of sewage pipes inside buildings.
In most cases, wastewater is transported by gravity, but in some types of sewer networks it is pressurized. Therefore, pipelines can be of pressure or non-pressure type. In a pressure sewer, wastewater pressure is pumped up by a special pump. These systems are also classified according to their purpose:
- production;
- household;
- storm or drainage.
The household network can be central and serve the entire populated area or autonomous exclusively for one object. As for the installation method, networks are also classified according to it:
- general alloys are intended for melt and household wastewater;
- semi-separate ones accumulate melt and waste water in one treatment plant, but they are discharged in different ways;
- separate systems drain wastewater and melt water along different paths into different containers.
Consider all the principles of installation and operation of external sewer networks in detail
Pipes used for external sewerage
There are a number of requirements for the pipes from which external sewerage is constructed. Since they are subject to external influences, the requirements for them must be:
- reliable;
- lungs;
- resistant to the external environment.
Cast iron pipe
Once upon a time, all pipes for sewer systems were made of cast iron. Now this material has lost ground under the onslaught of modern materials: polyethylene, polypropylene and PVC (polyvinyl chloride).
This happened due to increased compliance standards for the sewer system. It must be insensitive to temperature changes, corrosion and chemicals.
In addition, cast iron also loses in such indicators as:
- transportation;
- installation;
- service.
All this played a role and cast iron is gradually being replaced by other materials.
Plastic pipes
The most popular material for sewer pipes is plastic (PVC). It is the plastic pipe that has the greatest number of advantages.
They are not afraid of exposure to chemicals, are lightweight, reliable, durable and at the same time cheap. In addition, PVC is not afraid of frost, corrosion, is easy to transport and install, and does not require maintenance.
External networks
External sewerage can be laid using several methods:
- the routing method involves installation of the structure from the consumer to the treatment plant and is used not only in the private sector and individual facilities, but also in multi-apartment residential buildings;
- the street network is a system of pipelines and storage wells from which wastewater is transported to the general sewer system;
- collectors are necessary to collect aggressive liquid or redirect it to other storage containers;
- Sewage treatment plants are the last link in the sewer network, in which liquid is purified and discharged into water bodies.
The design features of sewer networks are determined by the following factors:
- pipe bends;
- pipeline turns;
- the depth at which groundwater occurs.
Regardless of the type of networks and the above factors, all waste pipes of the system must be at a certain slope, the level of which depends on the cross-section of the pipeline.
Pipe laying depth
An important indicator of SNiP is the depth of pipe laying. It must be greater than the freezing depth of the soil. This parameter depends on the weather conditions of the region and the size of the pipeline. In the middle zone of the country the following standards are used:
Excerpt from SNiP 2.04.03-85 - clause 4.8
- if pipes have a diameter of up to 500 mm, they are placed 0.3 m deep in the ground;
- elements of larger diameter should be laid to a depth of at least 0.7 m.
To reduce the depth of installation, it is necessary to use insulation.
According to SNiP 2.04.03-85, the minimum laying depth is determined by the experience of using such systems in a given area.
What are external networks made of?
The sewer network is a complex system, installed in accordance with SNiP and consisting of the following elements:
- the pipeline consists of pipes of different cross-sections and lengths;
- wells of inspection, drainage, differential and rotary types;
- receivers and outlets for redirecting aggressive liquid to the treatment tank;
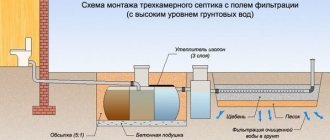
- local treatment facilities. This category of products includes septic tanks, treatment wells, aerators and other engineering structures.
- pumping station if the treatment plant processes wastewater in small volumes;
- auxiliary elements for installation of sewer networks.
The installation of each element of the system must be carried out in accordance with SNiP in order to avoid technical problems associated with sewerage in the future.
Common Mistakes
It is possible to install an external sewage system efficiently and in a short time by avoiding the following mistakes:
- Saving on materials. The difference in cost with cheap analogues may be less than repairing the system.
- Installation of external sewerage pipes in a short time. Pipeline sections must be carefully measured and carefully cut. Angles of inclination must be created in exact accordance with the project.
- Insufficient amount of drainage pipes are laid. If they become clogged or have low throughput, fluid stagnation will occur.
Prices per meter of work on laying external sewerage start from 270 rubles (when installing non-pressure PVC systems with a diameter of 110 mm). For pipe sizes of 500 mm, prices increase to 800 rubles.
Basic requirements that must be observed when designing
To ensure high efficiency of communications and reduce installation costs, it is recommended to develop the sewerage system in parallel with the design of the external water supply system. The construction of the sewer network must be carried out in accordance with sanitary and hygienic standards. Therefore, the primary task of such a project is to determine the type of terrain and type of sewer system. According to one of the points of SNiP, it is necessary to determine the environmental features of the area where the new wastewater disposal network will be located. The main environmental factors include:
- soil feature. Setting this factor will allow you to determine the optimal type of sewage system for the area;
- ground water level. Its determination is mandatory, since if the water level is high, it is necessary to take a number of additional measures before laying the pipeline;
- climatic conditions make it possible to determine the need for thermal insulation materials for the pipeline.
After establishing environmental factors and determining the type of sewer, some of its technical characteristics should be taken into account. In particular, the maximum volume of wastewater and the distance from the communication line to the object. Additionally, according to SNiP, it is necessary to determine the method of passing sewage pipes through water barriers or ravines, if such obstacles exist in the path of the future sewer network.
Design and preparatory work
The project is a mandatory document required when installing a sewer system. It should be included in the plan of the house as a whole. If you have a ready-made option, adapted to a certain climatic zone, you can prepare tools, look for materials and get to work. If the project is created independently, it is better to show the planning result to a specialist.
The installation of external sewerage networks is carried out in accordance with documentation that takes into account:
- soil freezing level;
- depth of groundwater - the installation location is chosen so that wastewater cannot enter aquifers and flood the foundation or basement of the house;
- possibility of access to a sewage treatment plant;
- the volume of the septic tank must correspond to the number of permanent residents; for 3 people, a 4 m3 tank is sufficient;
- location of inspection wells.
When creating an external drainage network, it is important to consider the location of the storm drainage system.
Required materials for installation
To create a project for a future wastewater disposal system, it is necessary to determine not only the above factors, but also the materials from which the sewer network will be built. Wastewater is an aggressive environment that negatively affects various materials, leading to their oxidation and even dissolution. Therefore, the sewer network must be built from materials that are highly resistant to aggressive environments. Therefore, such communications are built from pipes made from the following materials:
- steel or cast iron. They are actively being replaced by polymer pipes, as they are inferior to them in almost everything, from the complexity of installation to durability;
- polyethylene is widely used for the manufacture of sewer pipes. Installation of polyethylene external sewerage must be carried out in a protective casing to prevent direct sunlight, which reduces the properties of polyethylene.
- polypropylene is used mainly for the construction of underground communications, however, SNiP describes the conditions under which pipes made of such material can be used for external networks;
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC) has high strength properties and a very affordable price. It is resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and installation work is completed much faster than with metal pipes.
Thus, PVC pipes are considered the best for the construction of internal and external sewer networks. They differ from each other in wall thickness and length. The surface of PVC pipes is smooth, except in cases where the surface is specially corrugated. PVC corrugated pipes are more practical because they are easier to install on difficult sections of the pipeline. Regardless of whether the surface of the pipes is smooth or corrugated, they can be pressure or non-pressure. In the first case, the pipeline will be able to withstand pressure of up to 10 atmospheres. Through a free-flow PVC pipeline, liquid flows by gravity at a speed of approximately 8 m/s.
Separately, it is worth saying that sometimes reinforced concrete or asbestos cement is used for the construction of external sewer networks. But these materials are relevant only in cases where it is necessary to build a large-diameter sewer system. Such a wastewater system has a low safety margin, and therefore cannot be pressurized and is intended for the natural drainage of aggressive liquid.
Treatment options
You can choose a suitable cleaning system from several types. They all cope well with the task. Therefore, the choice depends on the amount you are willing to spend on its construction.
Accumulation system
Consists of a sealed container. As it fills, it is emptied in different ways. The best option is to pump out sewage using sewage disposal machines.
At the construction stage it is cheaper than other options. However, during operation, the understanding comes that this is not the most economical option - the services of vacuum cleaners have always been expensive.
Septic tank
Installations in which one or more cleaning methods can be used:
- mechanical - settling;
- biological - bacteria;
- chemical.
Recently, septic tanks were built independently, and it looked like they were more like cesspools. Now there are many ready-made installations on sale, of any size and different in price. When choosing a septic tank, you should correctly calculate the required tank volume.
The disadvantage is poor water purification (60 - 70%), which requires the installation of additional filters or the construction of filtration fields.
Biorefinery station
The most effective cleaning method, but also the most expensive. The water passing through such a station can be discharged into reservoirs or used for irrigation.
Installation is possible anywhere, regardless of the ground. Disadvantages include: cost and dependence on electricity.
Features of installation work
By observing SNiP during installation work, it is possible to improve the performance of the sewer system and increase its durability. To effectively drain wastewater naturally, it is very important to set the correct slope of the pipeline. According to SNiP, pipes must be laid at an angle towards the storage well. As a rule, the slope is approximately 2-3 centimeters for every meter of pipeline. As for the cross-section of sewer pipes, pipes with a diameter of 100-110 mm are sufficient to organize drainage from one private house. If the system serves several private houses, then a pipeline with a diameter of at least 200 millimeters is needed.
An important point in design is determining the location for the construction of a prefabricated well. When determining the location, it is necessary to take into account what type of water collector will be installed. This can be a storage well or a septic tank, which not only accumulates, but also processes wastewater. In both cases, it is recommended to select the lowest location on the site to install the wastewater collection point. If preference is given to a simple storage well, then it will need to be emptied periodically using a sewer truck. In this case, it is recommended to choose a place to build a collection point not only in the lowest place, but also as close as possible to the roadway.
Also, do not forget about the construction of intermediate inspection wells at pipeline turns and every 25 meters on straight sections. The presence of inspection wells will simplify the maintenance of the system, especially at turns, where there is always a high probability of sewer pipe clogging.
SNiP for the construction of storm sewers
Is it necessary to adhere to SNiP when constructing storm drains?
Heavy rains and spring thaw become a real problem for many homeowners.
After all, after rain, the site turns into a kind of swamp, and regular flooding of the foundation and walls contributes to their destruction. Let's consider the main points of the construction of such a device as a storm sewer - SNiP, GOST and other requirements that should be taken into account. What is a storm drain? Storm drainage is usually called complex engineering networks that serve to collect and remove moisture from the drained area that falls in the form of precipitation. To construct these schemes, you should be guided by the requirements of SNiP, which address the issues of constructing external sewerage networks.
The SNiP, which regulates the standards that external sewerage networks must comply with, contains the necessary formulas for carrying out calculations when designing a storm sewer system
, the requirements for materials, the depth of pipes and other important aspects of construction are indicated.
Types of storm drainage
There are two types of storm drains:
- Point system.
- Linear system.
Point type storm drainage system
Point diagrams are networks of stormwater inlets and pipes connecting them. In order for the assembled scheme to be durable, safe and effective, the technical conditions for storm drainage provide for the installation of protective grilles on storm inlets, as well as the installation of special filters - sand traps.
Linear storm sewer
A linear scheme is a network of canals that are designed to collect and transport water. According to the requirements of SNiP, storm sewers are installed so that there is a slope towards the main collector.
A closed-type storm sewer consists of a network of storm water inlets connected by pipes laid at depth through which water is discharged to the collector. To maintain and monitor the operation of the system, inspection wells with a diameter of 1 meter are included.
All aspects that will need to be taken into account when developing a project and constructing a storm sewer are set out in the regulatory document SNiP 2.04.01-85.
If for some reason it is not possible to maintain the minimum slope when laying pipes, then pumps are included in the system to pump liquid, since it cannot move by gravity.
Storm drainage elements
Typically, the sewer network includes the following elements:
- Storm water inlets. This is one of the important elements of the system, the main function of which is the local collection of water from the surface of the earth.
- Door pallets. This is an analogue of rainwater inlets that are installed in front of the entrance areas of a house or at the gate.
- Trays or gutters. Elements installed in ditches for water drainage. So that water can move through them by gravity, a slight slope of the storm sewer is provided, directed towards the collector. The materials of trays for linear sewerage
can be different; polymer products are most often used. - Pipes. This element performs the same function as the trays, but the pipes for storm drainage are
not laid in surface trenches, but underground.
To prevent water from seeping through at the joints, sealants are used when laying sewer pipes
. - Sand catchers. These are filter elements that prevent debris and soil particles from entering the drainage system.
- Inspection wells. Elements necessary to control the operation of the system.
Storm sewer calculation
Before starting the construction of a storm drain, you need to make a correct calculation of the storm sewer, for this you need to know:
- Average rainfall in this area.
- Drainage area, that is, the area of roofs, platforms and paths with a waterproof coating.
- Soil properties at the site.
- Locations of already constructed underground communications on the site.
You can calculate what the diameter of a storm drain should be using the formula:
Q = q20 x F x Ψ
Designations in the formula:
Q is the volume of water that the system will have to drain.
q20 – precipitation intensity.
This value depends on the climatic conditions of the area; you can find its value in the tables according to SNiP 2.04.03 - 85.
F is the area of surfaces from which water is planned to be drained. Ψ is a correction factor that depends on the covering material of the site from which water is collected.
The correction factor for roofing is 1.0, for platforms and paths covered with asphalt - 0.95, for concrete coverings - 0.85, for crushed stone coverings - 0.4 (and if the crushed stone is treated with bitumen, then the coefficient will be 0.6).
Pipe depth
The question of what the depth of storm drainage should be is widely discussed in construction forums.
Meanwhile, a completely understandable answer is given in SNiP 2.04.03-85 - the minimum depth of storm drainage is determined by the experience of operating systems in this area.
As a rule, subject to operation in the middle zone and the use of pipes with diameters up to 500 mm, the minimum depth is taken to be 30 cm. In the event that larger diameter pipes are used for the construction of a system such as a storm sewer, their laying depth should not be less than 70 cm.
In order not to carry out complex calculations and not worry about possible errors, it is best to find out what the laying depth should be from people who are involved in the construction of storm sewers in practice.
You can ask your neighbors if they have already finished building external drainage and storm sewer networks, or make inquiries with construction organizations working in this area.
Slope of stormwater pipes
In order to find out the minimum slope of a storm drain, you need to consider:
- Type of drainage;
- Pipe diameter;
- Surface coating.
When using pipes with a diameter of 200 mm, the slope should be 0.7 cm for each meter of pipeline length. If pipes with a cross-section of 150 mm were used, then the slope should be 0.8 cm per meter.
In case of urgent need, SNiP 2.04.03-85 contains a direct indication that in certain sections of the network the minimum slope can be slightly reduced:
- up to 0.5 cm per meter when using pipes measuring 200 mm;
- up to 0.7 cm per meter for pipes with a diameter of 150 mm.
Thus, if local conditions force you to do this, you can “save” up to 2 mm for every meter of pipeline length. Do not forget that SNiP regulates not only the minimum, but also the maximum slope of the pipeline. It should not exceed 1.5 cm for every meter of pipe.
If you exceed this figure, the risk of clogging the structure will increase. The fact is that if the slope is greater than normal, the water quickly leaves, and the sand contained in it settles, as a result of which the inner surface of the pipe quickly silts up.
Construction of storm drainage
In general, installation work on the installation of storm drains is carried out in the same way as when laying external pipelines of a conventional sewer system.
Selection of pipes for the underground part of the pipeline
If external storm sewer networks are installed, SNiP allows the use of the following types of pipes:
- Ceramic;
- Steel;
- Plastic.
Ceramics is a traditional material used for the construction of external sewerage pipelines, including storm water pipes. The disadvantages of the material include its high fragility and significant weight (a meter of pipe with a diameter of 100 mm weighs more than 24 kg). Steel pipes have much less weight (a meter of pipe weighs about 10 kg), but they are prone to corrosion, so it is not profitable to use them for the construction of storm drains.
Recently, for the construction of storm drains, plastic and HDPE pipes have been used for the sewerage system.
. They are light (a meter weighs no more than 5 kg), but durable and resistant to corrosion. In addition, they are easy to connect and do not require welding. Can be used:
- PVC pipes, if external networks are installed, then for their construction you need to use a special type of pipes, they are painted orange;
- Multilayer polymer pipes. Today this is the best option. These pipes have a smooth inner surface, so there is no hydraulic resistance.
Installation of the roofing part
The work goes like this:
- Openings are made in the ceilings for installing rainwater inlets, and all junctions are carefully sealed.
- Drainage pipes are strengthened when constructing a point system or trays when installing a linear storm drain.
- Install drain risers or pipes.
- A unit is assembled for discharging water into a collector or discharging into tray systems.
- All devices are attached to walls and ceilings using clamps. Places for installing clamps are planned in advance, not forgetting to follow the recommended slope values.
Laying the underground part
- Installation begins with the installation of trenches. When constructing systems such as storm sewers, the depth of installation is most often determined not by the depth of freezing, but by the experience of operating the systems at the construction site.
- Trenches are dug with a slope, that is, their depth should gradually increase.
- At the bottom of the trenches there is a sand cushion, the layer height is 20 cm.
- A pit is being prepared for installing the collector.
- Pipes should be laid in the prepared ditches, the pipes should be connected to each other and connected to the collector using conventional fittings.
If the sewer network consists of a single branch more than 10 meters long, then it is worth planning to install a manhole in the middle of it. Such wells should be installed at network branch points.
- Sand traps are installed at the junction of water inlet gutters and stormwater pipe systems.
- Now all that remains is to backfill the trenches and cover the open structures (trays) with gratings on top.
The need to create security zones
Few people know that there is such a thing as a sewerage security zone, including storm sewerage, and meanwhile, SNiP stipulate that a security zone of a certain size be organized near the pipes. Thus, the storm drain protection zone provides for a distance of 5 meters from the pipe walls in each direction. A security zone is a place where it is prohibited:
- Build permanent or temporary structures.
- Set up garbage dumps.
- Arrange parking.
- Plant trees or bushes at a distance of less than three meters from the pipe.
- Block free access to manholes.
So, installing a rainwater drainage system is a necessary measure when landscaping a site. When constructing such systems, it is necessary to strictly comply with the requirements and rules that are formulated in regulatory documents - construction and sanitary rules.
How to calculate the required angle of inclination
The standards in “Storm sewerage SNiP” also allow the owner to calculate the optimal angle of inclination of the pipe. After all, as you know, wastewater is transported in a storm drain, obeying the force of gravity, that is, naturally and without the use of any pumps or other mechanisms.
However, it is not always easy to determine exactly what angle is best to position the pipe to ensure smooth and even transport. Well, SNiP allows you to do this too. Mainly, it all depends on the diameter of the pipe. The calculation is made on the basis of a special table. But in most cases, the average owner can be guided by a simplified scheme:
- for a pipe with a diameter of up to 110 millimeters, a slope of 2 centimeters per linear meter of pipe will be sufficient;
- for pipes with a diameter of 150 millimeters - from 8 to 10 centimeters;
- for a sewer pipe with a diameter of 200 millimeters, a slope of 7 centimeters can be considered optimal;
- finally, for pipes with a diameter of 500 millimeters, the slope should be 30 millimeters per meter of pipe.
Stormwater systems are networks of canals that are needed to collect and transport water. According to the requirements of SNiP, storm sewers are installed so that there is a slope towards the main collector.
Directly in front of the sand trap, the slope should be slightly less in order to ensure uniform distribution of sand and liquid. Otherwise, the flows risk simply mixing with each other.