Varieties of pipe diameters
Over the years, rolled metal pipes have gained great popularity in the construction industry and other areas.
The distinctive differences of the product are the varieties of pipe diameters. Due to the extensive range, the use of rolled pipes is possible both in the biochemical, mechanical engineering, food and other industries. The internal and external parameters of pipe rolling often have a significant difference, and this is not surprising. Everything depends on the value of the wall thickness, which the manufacturers have set as a constant parameter.
Standard types of pipe diameters
Diameter is one of the established values in determining the parameters of rolled steel pipes according to GOST. If you know the exact value of the diameter and wall thickness, it is easily possible to carry out any financial and technical calculations for upcoming projects.
According to the established GOST standard, all types of pipe diameters are divided into products:
- Large size (more than 500 mm);
- Medium (115-500 mm);
- Small (up to 115 mm).
Steel pipes have good corrosion resistance, which increases the service life of pipe products.
Pipe rolling parameters are set based on the diameters of the products. The values themselves can be calculated either in millimeters or inches.
| Du | Inches | Du | Inches | Du | Inches |
| 6 | 1/8″ | 150 | 6″ | 900 | 36″ |
| 8 | 1/4″ | 175 | 7″ | 1000 | 40″ |
| 10 | 3/8″ | 200 | 8″ | 1050 | 42″ |
| 15 | 1/2″ | 225 | 9″ | 1100 | 44″ |
| 20 | 3/4″ | 250 | 10″ | 1200 | 48″ |
| 25 | 1″ | 275 | 11″ | 1300 | 52″ |
| 32 | 1(1/4)» | 300 | 12″ | 1400 | 56″ |
| 40 | 1(1/2)» | 350 | 14″ | 1500 | 60″ |
| 50 | 2″ | 400 | 16″ | 1600 | 64″ |
| 65 | 2(1/2)» | 450 | 18″ | 1700 | 68″ |
| 80 | 3″ | 500 | 20″ | 1800 | 72″ |
| 90 | 3(1/2)» | 600 | 24″ | 1900 | 76″ |
| 100 | 4″ | 700 | 28″ | 2000 | 80″ |
| 125 | 5″ | 800 | 32″ | 2200 | 88″ |
Sometimes users have a question about how to find out the diameter of a pipe. It's simple! Either look at the markings or use tape. Wrap it around the pipe and remember the size, then multiply by Pi 3.1415.
Main dimensions
So, let's first figure out what diameters there are.
- Nominal;
- Nominal diameter (DN) – nominal value set in millimeters;
- Interior;
- External – one of the main established parameters according to GOST;
- Wall thickness is the second established characteristic according to GOST.
OUTER DIAMETER OF PIPES
If we consider the external parameter, then there are these types of pipe diameters:
- Products with values of 424, 720, 530, 273, 3255, 920 are especially popular;
- Small sizes are used for water supply and heating systems of multi-storey and private buildings;
- Medium sizes are used when installing water pipelines and structures in the oil refining industry;
- Larger sizes are needed for leading oil, water and gas pipelines.
INNER DIAMETER
- If the external parameter does not change, the value of the internal parameter is often very different. When establishing standard dimensions of pipe products, the concept of “nominal diameter (DN)” is used;
- Conditional diameter is the nominal value of the internal parameter, rounded in any case to a larger value. DU – established by GOST 355-52 standard.
- Rolled pipe has an internal parameter value in the range of 6-200 mm.
In addition to millimeters, pipe sizes are measured in inches . 1 inch – 25.4 mm.
Pipe diameter correspondence table
Diameters of steel and water pipes (table)
There are only 4 types:
- Conditional (Nominal value of the internal diameter in mm);
- Nominal;
- External (Main indicator);
- Internal (Required to select the correct fitting).
An important parameter in rolled pipes is the wall thickness, which makes it possible to accurately determine the future load on the walls of the product even at the design stage.
The internal diameter must be known in order to correctly select fittings and additional products for the pipeline.
The external values of pipes with diameters of 17-165 mm have been established, which allow you to select the desired size of the product, focusing on the purpose of the structure being installed.
Pipe wall thickness depending on diameter
As mentioned earlier, the thickness of the walls will determine the design that can exert the appropriate pressure.
Why is standardization needed?
Standardization was created when polymer analogues appeared on the market. Due to the fact that it is possible to connect different materials, the scope of use of pipe rolling has expanded significantly.
Because of this, the dimensions of metal and polymer pipe products are basically always the same.
Established standards make it easier for experts to design and install pipelines. If an expert knows the value of the outer diameter of a steel pipe, then choosing connecting elements and creating a single structure will be easy and simple! Very often, metal structures are distinguished by the length of the product, external and internal values, and wall thickness.
Classification by indicators
All types of pipe diameters are divided among themselves according to two parameters^
By outer diameter
- Up to 115 mm – small;
- 115-500 mm – medium;
- 500-1420 mm – large.
According to the ratio of diameter to pipe wall thickness
- Particularly thin/thin walls;
- Normal;
- Thick/extra thick.
Varieties of pipe diameters are established for specific areas of application. For example, when installing cables for buildings, rolled pipes with a diameter of 10-30 millimeters are used.
Using Pipe Schedule
Rolled metal pipes with a diameter of 40-47 mm are often used in the design and installation of water supply and heating systems in apartments.
Pipes up to 149 mm are usually used for domestic and industrial purposes. Materials that have up to 272 mm are suitable for the oil refining, gas and chemical industries.
Products from 325 mm are used for installation of complex systems, such as heat pipelines and water supply lines. The product, with a diameter of 520-1030 mm, is used for transporting oil, gas, and installing sewers in housing and communal services.
Rolled pipes with an internal diameter of 630 mm are especially popular in construction and when installing road elements (supports, drains).
If you know about all the types of pipe diameters and their characteristics, installing or designing any elements will be quite simple!
Source: https://metallservice24.com/raznovidnosti-diametrov-trub
How to calculate the volume of water in a pipeline
When organizing a heating system, you may need a parameter such as the volume of water that will fit in the pipe. This is necessary when calculating the amount of coolant in the system. For this case, we need a formula for the volume of a cylinder.
Formula for calculating the volume of water in a pipe
There are two ways: first calculate the cross-sectional area (described above) and multiply it by the length of the pipeline. If we calculate everything according to the formula, we will need the internal radius and the total length of the pipeline. Let's calculate how much water will fit in a system of 32 mm pipes 30 meters long.
First, let's convert millimeters to meters: 32 mm = 0.032 m, find the radius (divide in half) - 0.016 m. Substitute into the formula V = 3.14 * 0.0162 * 30 m = 0.0241 m3. It turned out = a little more than two hundredths of a cubic meter. But we are used to measuring the volume of the system in liters. To convert cubic meters into liters, you need to multiply the resulting figure by 1000. It turns out 24.1 liters.
Diameters of steel pipes and their wall thickness in mm. Dependence of one parameter on another
Steel pipes are actively used in various industries and agriculture. Their reliability has been tested by time.
Of course, such products have their drawbacks, in particular, a tendency to corrosion. But everyone is already quite well informed about these shortcomings.
Timely preventive and repair activities make it possible to maintain engineering systems based on metal pipes in perfect order.
The main characteristic of steel pipes is their diameter. We can say that, based on the diameter of the pipe, a decision is made about its use in a particular engineering system, in a particular section of the system.
Features of steel products
In the building materials markets you can find pipes of two main designs:
- welded, having a seam;
- seamless - obtained, for example, by casting.
Steel pipe diameter: outer and inner dimensions
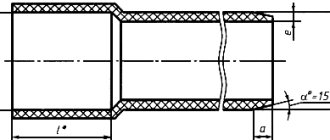
The geometric parameters of a steel pipe - internal and external diameters, wall thickness and length of the product - are regulated by a number of regulatory documents (GOSTs). These documents indicate specific values measured in millimeters and indicate permissible deviations from the mentioned values (as a percentage of the regulated dimensions).
And according to regulatory documents, steel pipes have the following parameters:
- Outer diameter - the distance between two opposite points located on the outside
- Inner diameter - the distance between two opposite points located on the inner surface of the product body
- The wall thickness is half the difference between the outer and inner diameters.
- Conditional diameter is a rounded value of the external dimension, calculated in inches or millimeters.
Moreover, according to GOST, both the length and diameter of steel pipes are related to the method of manufacturing such products. That is, each pipe production technology, and there are only four of them: hot rolled, cold rolled, welded product with a straight seam and welded product with a spiral seam, is characterized by its own assortment.
Therefore, when classifying the standard diameters of steel pipes, we must start from the corresponding production method. After all, only this method allows you to cover the entire “model range” of rental products. And the classification of diameters itself, in this case, will be based on four types of assortments, namely:
↑
This category includes pipes with a diameter from 20 to 550 millimeters. Moreover, according to GOST 8732-78, there are almost seven dozen original products in this assortment. And this is only based on such a criterion as the outer diameter of steel pipes.
The total number of products in this assortment is much larger. After all, each product with an identical outer diameter may have a different wall thickness. This means that the internal diameter of externally similar products will be different.
Do-it-yourself pipe calculation. Step-by-step instructions and calculation example
For example, we have a steel pipe. Let's determine its characteristics and calculate all the described quantities. To carry out measurements we will need the following tools:
- Vernier caliper with Vernier scale. With its help, you can measure the outer and inner diameter of the pipe with an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
- Roulette. It is useful for measuring the length of the pipe.
So, let's say we found out that the length of the pipe is 3 m, the outer diameter is 50 mm, and the inner diameter is 40.8. Having these values, let's calculate all the rest:
- First, let's find the wall thickness. T = (50 – 40.8)/2 = 4.6 mm.
- Inner radius = 40.8 /2 = 20.4 mm.
- Sectional area = 3.14 x 20.42 = 1306.7 sq. mm = 13.07 cu. cm
- Volume of water in the pipe = 13.07 cubic meters. cm x 300 cm = 3921 cubic cm, which is approximately equal to 3.9 liters.
- Pipe weight = (50 - 4.6) x 4.6 x 0.025 = 5.2 kg (1 m!).
This is how you can calculate all the parameters necessary for designing a water supply system.
Standard diameters of steel pipes - table of sizes and fineness of measurement
Knowledge of standards and generally accepted norms greatly simplifies work and makes it easier to choose the optimal solution to an issue in any area. This is also facilitated by systematizing any data, bringing it into a single table. But before moving on to it, the reader’s attention should be focused on some points regarding the diameter of the pipe, regardless of its material and purpose.
In the title, the name of this parameter is indicated in the plural. And this is not only due to the significant range of products.
Experts distinguish several “types” of diameters of steel pipes, and before understanding their numerical expressions, it is necessary to clarify how one differs from the other.
It is ignorance of the nuances of terminology that is often the reason for the wrong choice of samples, misunderstandings between a specialist (for example, a mechanic who arrives on a call, a store manager) and an ordinary consumer, a non-professional in this field.
What are the different pipe diameters?
- Dу – conditional diameter. You need to know it in order to determine whether a given pipe will provide, for example, the required pressure (for water supply) or an acceptable coolant speed (for heating circuits).
- Dн – external. This parameter indicates the convenience of installing the “thread”, attaching samples to a wall or other base, and in some cases, the possibility (or advisability) of passing through surfaces.
- G – threads.
As you can see from the picture, these are not the same thing:
The difference in values is determined by the wall thickness.
Experts also distinguish between nominal and internal diameters. But for the average consumer, these pipe parameters are of no practical importance. The main ones for the “private owner” have already been indicated - Dу and Dн.
How are diameters measured?
This is another “barrier” that prevents the achievement of mutual understanding between a professional and an ordinary person ignorant of such subtleties.
There are 2 dimensions that are used to numerically express the sections of products with a round profile - cm and inches.
Each of us understands centimeters, but specialists, especially when it comes to the diameters of steel pipes that are relatively small (for example, for gas or water), often operate in inches (read more about marking pipes here).
In the Russian Federation there is no abbreviation for inches as such. If you use the abbreviation “dm” by analogy with “cm”, you will get confused - it applies to decimeters. Therefore, the symbol “″” is used, which is placed after the numerical value. For example, 1½″ (one and a half inches).
Table of values
It cannot be considered absolutely complete, but everything that is required for “home and family” is reflected in it. More detailed information is easy to find on specialized websites and in the relevant GOSTs (by the way, there are quite a lot of them).
For the convenience of readers, comparative data for plastic analogues is provided in the right column. These values will be needed if you have to join products made of different materials (steel + plastic).
| Dн (depending on the type of steel pipe, mm) | Du | Dн | ||
| seamless | welded | inches | mm | polymers |
| 16 | 17 | 3/8 | 10 | 16 |
| 20 | 21,3 | ½ | 15 | 20 |
| 26 | 26,8 | ¾ | 20 | 25 |
| 32 | 33,5 | 1 | 25 | 32 |
| 42 | 42,3 | 1 ¼ | 32 | 40 |
| 45 | 48 | 1 ½ | 40 | 50 |
| 57 | 60 | 2 | 50 | 63 |
| 76 | 75,5 | 2 ½ | 65 | 75 |
| 89 | 88,5 | 3 | 80 | 90 |
| 102 | 101,3 | 3 ½ | 90 | 110 |
| 108 | 114 | 4 | 100 | 125 |
| 133 | 140 | 5 | 125 | 140 |
| 159 | 165 | 6 | 150 | 160 |
Source: https://ISmith.ru/material/diametry-stalnyx-trub/