When constructing a network that ensures the removal of household wastewater, the depth of the sewer system is critical. If pipes are not hidden in the ground, they can be damaged by transport or destroyed due to exposure to low temperatures. If you deepen them more than necessary, you can upset the balance that allows the system to work by gravity.
Preparation of sewerage inlets into the house
What happens if the depth is incorrectly calculated?
If they are located at a shallow depth, plastic pipes can be damaged when heavy trucks drive across the surface of the ground; theoretically, the pipes can freeze (but in a private house with low water consumption and a low water level in the clearance, this is practically impossible).
If the depth is too great, the pipes can be damaged by the weight of the soil above, especially if the soil has high moisture content. In addition, the volume of labor-intensive excavation work increases significantly; a septic tank or wastewater collection tank will have to be located significantly below ground level.
Important features of laying sewer pipes
- When installing a pipeline system in deep basements or in places with low relief, versions with an extremely low sewer installation depth are provided, in which the installation of a pumping station is provided. The depth of the pressure line must be calculated according to the requirements of regulatory documents.
- Practice has shown that in problem soils (water-saturated, compacted to strong and silty) communications should be laid to a depth of four meters, in dry soils the depth is determined from four to seven meters.
- Communications built with a depth of less than 0.7 meters must necessarily have a sewerage protection zone on the surface of the earth. The security zone is equipped with a system to protect against possible mechanical damage to the pipeline.
- When carrying out projects for laying sewer communications, it is mandatory to take into account the difference in terrain relief lines.
Laying depth of sewer pipes photo
Sewage scheme
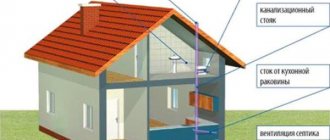
The sewerage system in a private house consists of an internal part and an external part. They have different components and are often made from different materials. In houses and on plots, such systems are installed in a non-pressure way, i.e. The wastewater flows through the system by gravity. Therefore, despite its apparent simplicity, the sewerage system needs to be designed much more than a pressure water supply network. Currently, domestic sewage is collected exclusively from plastic socket pipes.
Internal
The internal sewerage system consists of horizontal sewer pipes and vertical risers (drain pipes) connected to plumbing fixtures (sinks, sinks, bathtubs, toilets) and equipment (washing machines and dishwashers).
The internal sewer network must also have a ventilation pipe leading outside the roof; inspection of risers to clear blockages. For risers and toilet flushes, pipes with an outer diameter of 110 millimeters are used, for connecting a bathtub - 50 millimeters, for washbasins, sinks, washing machines and dishwashers - 40 millimeters.
External
The external sewer line has a more complex design than the internal one. The depth of laying communications, the volume and depth of septic tanks is calculated based on the volume of wastewater, the characteristics of the geological structure of the site, the climatic features of the region, the layout of the site (if there is an entrance to the house or a parking lot above the communications).
If it is not possible to connect the external network to the municipal sewer collector (the distance from the collector to the house is too great), then a wastewater collection site will have to be equipped on the site (cesspool, septic tank, storage tank or treatment facility). For drainage, a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm is needed; reinsurers can use products with a diameter of 150 mm.
Installation
Assembling the pipelines is not difficult at all. They start from the point of exit from the house and gradually approach the point of entry into the septic tank. Sometimes a preliminary rough assembly helps, allowing you to clarify how correctly the calculations have been made and whether the slope and depth of the sewer system in a private house have been observed. Small discrepancies with the calculated values almost always occur, so the ability to make the necessary adjustments during rough assembly is very useful.
The final installation is carried out simultaneously with insulation and sealing of the connections. Particular attention should be paid to bends and entry/exit points of pipelines, where the possibility of ice formation and blockages is highest. After assembly is completed, the system is checked for operability and leaks. If no problems arise, the trench is buried. From this moment on, the sewer system is considered to be put into operation.
Types of tanks, their pros and cons
Each type of container and device for collecting or processing wastewater and waste has its own characteristics. The choice mainly depends on the desires of the owner and financial capabilities.
cesspool
The cesspool is the oldest type of “benefits of civilization.” Modern pits are divided into two types: sealed and filtering. Materials for pits - cinder block, aerated concrete, wood, concrete (concrete rings for wells), plastic containers - from small ones for a small “weekend” dacha to tankers with a volume of 15-20 cubic meters or more.
- Sealed
The wastewater is drained into a sealed cesspool, collected, pumped out and transported. Such pits are installed when the groundwater level is high to prevent contamination, or when there is a large volume of wastewater - it simply does not have time to be processed naturally.
- Filtering
There is no bottom in the filters, there are small holes in the walls - water from the hole seeps into the ground. A filter of sand and gravel with a thickness of at least 15 cm (at least 20 cm in the lower part) is installed around the structure. Such cesspools can be constructed in areas with large groundwater depths.
More often, such “wild filters” are used as wells to collect drainage and storm water. The distance from the bottom of the pit to the groundwater table should be more than one meter. With small volumes of wastewater, filter pits are sometimes made for ordinary wastewater and waste - if the waste remains in the sump for a sufficiently long time, it begins to decompose under the influence of bacteria (which are always present in waste). The result is carbon dioxide, water and a small amount of solid sediment. The water filters into the surrounding soil, sediment accumulates, and must be removed periodically.
Septic tank
A septic tank is essentially a settling tank. This is an element of a comprehensive treatment facility, it is not a complete treatment facility. A septic tank is a container for collecting and treating wastewater from private homes. A process of gravitational settling occurs in it, then the contents are processed using biological products (or not processed and simply pumped out). Then the water can be subjected to other types of purification: forced, chemical, natural purification in the soil. Solid sediment must be removed periodically.
For the construction of septic tanks, cinder block, brick, concrete, polyethylene, polypropylene, and fiberglass are used.
Autonomous industrial installation
An autonomous wastewater treatment plant combines mechanical and biological treatment methods. There are installations designed to treat wastewater from private houses with small and large numbers of residents, cafes, tourist centers, hotels, and domestic sewage from small industrial facilities. The estimated operating time of the treatment system is several decades.
The degree of purification in such installations is 98%, the content of suspended solids at the outlet does not exceed 3 mg/l. After passing through the sand and gravel filter, the water is suitable for discharge into any reservoirs (except those intended for drinking water intake), irrigation, and drainage into the soil.
Structurally, the installations consist of a biorector with aeration, a secondary settling tank and a chamber for clean water. Air is pumped into the bioreactor, which provides optimal conditions for the existence of aerobic bacteria and they process organic matter. Inorganic impurities settle in the sump, then the water enters a clean water tank and is discharged into water bodies or used. To drain water into the ground, a drainage well is installed.
Biological treatment system
In any wastewater, bacteria live and multiply, processing organic substances present in wastewater. The more microorganisms and oxygen there are, the better the bacteria purify the liquid from organic contaminants. Biological treatment requires the presence of containers for collecting wastewater; usually, septic tanks and special biological products are used in private estates for this purpose. The degree of water purification in septic tanks reaches 50-60%.
More complex are systems with wastewater mixing and saturation with oxygen. They began to use aerobic bacteria, which process waste more completely and purify water to a higher degree. A high concentration of bacteria is artificially created in processed products. Such systems purify water up to 95-98%; the water is quite suitable for discharging into natural reservoirs, fisheries reservoirs, and for irrigation. The output water will be clean and transparent, with a slight swampy smell.
Types of sewer system tanks
The sewerage system of a private house can be connected to a public sewerage network or be autonomous. In the second case, a collection well is installed at least 5-7 meters from the house and 50 meters from the water intake well, into which wastewater is discharged.
A reservoir for collecting sewage can serve as:
- a cesspool is the cheapest and easiest option, but is no longer popular at present, as it requires regular cleaning and repairs when the soil settles, but does not protect against unpleasant odors;
- sealed collector - a concrete or plastic tank that is not in contact with the soil and hermetically sealed at the top, does not emit sewage odors, but requires regular cleaning;
- septic tank - a reservoir in which wastewater settles and, after treatment, goes into the soil or drainage ditch, the sediment is gradually destroyed by bacteria and microorganisms, so pumping is not required, you can build a septic tank with your own hands from brick, concrete, series-connected plastic containers;
- a treatment station is the most expensive, effective and environmentally friendly option, the well is manufactured industrially and is a complex structure with filters and a bioreactor; after processing, organic matter is released from the waste mass, used for fertilizers, and purified water, safe for the environment.
How to choose a location for a wastewater receiver and calculate its parameters
The location for the wastewater receiver is determined based on the following regulatory data:
- The distance from the foundation of the house to the wall of the cesspool must be at least 15 m.
- Septic tanks - up to 5 m.
- Drainage and overflow wells - at least 15 m.
- Biological treatment stations and autonomous treatment facilities - up to 3 m from the building foundation.
- The distance to a busy road is at least 5 m.
Placing containers close to the house reduces the number of trenches in a private area, but may cause an unpleasant odor near the house.
There is a recommendation - to place cesspools and drainage wells in the lowest place on the site. For modern cleaning systems this is no longer so relevant. But it is important to place containers and equipment in a place accessible to the access of a vacuum barrel for the evacuation of settling residues in septic tanks. Otherwise, in the event of force majeure situations, the car may not arrive, or green spaces may be damaged.
Experts recommend calculating the capacity of the wastewater receiver based on the composition of the family and the standard water consumption per person - 11.68 m² per month. These consumption standards are accepted by public utilities. As practice shows, people usually do not exceed this consumption rate.
Multiplying the number of family members by 11.68 m², we obtain the monthly volume of wastewater. It is advisable to increase this volume by 10-20% - in case of guests arriving, a total wash, or a delay in the arrival of the sewage disposal truck. The volume of the septic tank is calculated depending on the ability to often call a machine to pump out the contents - this can be once a month, once every two weeks or less.
Pipe selection
At the moment, they refuse to use ceramic or cast iron pipes for laying sewers. This is due to the emergence of more modern options. These include polyvinyl chloride and polypropylene products.
The advantages of such pipes:
- Corrosion resistance.
- Lightweight design.
- Ease of installation. You can cope with the task without any problems with your own hands.
- Cheap materials.
- Microorganisms do not appear inside the pipes.
Among other things, plastic pipes are resistant to chemicals. To clean them, you do not need to select a special solution; you can buy any sewer cleaner.
At what depth should sewer pipes be laid?
The backfill depth is determined by the Code of Rules 32.13330.2012 “Updated edition of SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage. External networks and structures” and some other norms and rules.
Question about bookmark depth
At the household level, if it is possible to connect to public sewer networks, then the best option would be to lay the sewer pipe below the soil freezing level in your region. Utility sewers will definitely be located below this level. But such a deep laying for sewer pipes is not necessary.
Factors influencing the level
The question of the depth of the local sewerage system is primarily influenced by the depth of soil freezing, geological conditions on the site (proximity of groundwater, hard rock, slope of the site), the possibility of deepening the septic tank or treatment plant. The minimum depth should not be less than 0.7 m from the ground surface (after leveling the area), otherwise the entire structure may be damaged by transport. Under roads and car parking areas, the minimum depth is at least 1 m.
Method for calculating the depth of a pipe connected to a storage tank
A septic tank or self-contained treatment plant should not be excessively deep. Excessive deepening of tanks leads to an increase in the volume of excavation and concrete work, complicates the cleaning of tanks; if groundwater is close, it is necessary to take measures to prevent the equipment from “floating” (for example, installing a concrete slab under the bottom).
The septic tank should be located no lower than 1 m from the surface. Treatment plants are similar (the permissible depth is indicated in the passport). The depth of the depth is determined by the supply sewer pipe. If the septic tank is located close to the house, then problems usually do not arise, and the calculation of the depth is carried out according to the formula: depth of the tank pipes = depth of the place where wastewater enters the septic tank = depth of discharge from the house + pipe length multiplied by 0.02 (slope).
Problems arise when the septic tank or treatment plant is located very far from the house. In this case, you need to try to solve the problem by laying the pipe more shallowly and insulating it. If the situation cannot be resolved in this way, then you will have to build an intermediate tank and organize pumping of wastewater using a pump.
Measures to reduce pipe laying depth
In order to take advantage of the opportunity to reduce the depth, some methods are used to eliminate the risk of freezing of sewer lines:
- using a heating cable
- use of high quality plastic pipes
- trench insulation
- increase in diameter and wall thickness
Using a heating cable
This is a successful solution to the issue of heating pipes, the cable is mounted on the outer surface of the pipe, it contains an automatic device that automatically turns on in those sections of the pipeline where problems arise with the temperature dropping below zero degrees.
Heating cable on a sewer pipe photo
Use of high quality plastic pipes
In our age of flourishing chemical industry, polymer pipes used for laying sewer networks have become especially popular. Modern construction of buildings does not provide for the provision of sewer systems with cast iron or asbestos-cement pipelines.
Compared to previous substances for making pipes, their plastic counterpart has quite a few “advantages”, namely:
- increased wear resistance
- plastic pipes are not subject to overgrowing
- no corrosion
- Due to the relative lightness and pliability of the substance, installation of networks does not require unusual skills or physical stress
TIP: polymer sewer pipes are practically not susceptible to freezing; if they are installed and used correctly, there is no stagnation of liquid in them, which can freeze.
Trench insulation
Insulation of the trench with expanded clay, mineral fiber or modern insulation materials. The thickness of the layer that provides thermal insulation varies between ten and eighty millimeters. The thermal insulation layer is covered with waterproofing (special hydrophobic materials) on top.
Increasing diameter and wall thickness
Provided that pipes of increased diameter and high wall thickness are laid, the risk of sewerage freezing is significantly reduced.
In theory, a large volume of waste liquid is also beneficial in reducing the risk of freezing. In practice, it has been established that the volume of wastewater can be significantly lower than the planned volume, which has a bad effect on the freezing factor of the system. The large depths used to lay the network depend precisely on this natural phenomenon; they protect the network from freezing. The thickness of frozen soil in various areas is indicated in Construction Climatology, and the value of soil freezing can be found in construction documentation.
Minimum depth for laying pipelines photo
SNIP for the minimum and maximum depth for a private house below the freezing level
The minimum laying depth of sewer pipes with a diameter of 110-150 mm according to SNiP 2.04.03-85 is allowed 0.3 meters above the soil freezing level. This is due to the fact that the wastewater leaving the house has a positive temperature (most often not lower than +18°C), does not completely fill the section and does not accumulate in the pipe (flows into the collector or septic tank).
The maximum depth to which plastic pipes can be buried is 5-8 m for dry soils, and no more than 4 m for soils with stones and moisture-saturated soils. For deeper penetrations, communications should be laid in trays or cast iron or steel products should be used.
Determining the depth of the sewer system
During the pipe laying process, the following points must be taken into account:
- products must have a sufficient diameter;
- the slope norm is 0.03 meters for each linear meter of pipe. Note that the angle of the sewer pipe is very important, otherwise the system will not work;
- products have different properties depending on the material from which they are made;
- the location of the septic tank and the point of exit of the sewer pipe from the house.
It is important to make the angle of inclination in accordance with SNiP; only in this case will it be possible to achieve spontaneous movement of wastewater and minimize the risk of blockages. You can create as many turning points and pipe connections as you like in your home, but it’s best to avoid them outdoors.
SNIP for minimum and maximum depth at the exit from the house
The minimum depth of the outlet of the sewer pipe of the intra-house system must be equal to the minimum depth of the external network. But if necessary, the outlet can be located higher - it should be insulated and protected from possible damage by transport. The maximum depth is also equal to the maximum depth of external networks.
Depth Reduction Options
If the geological conditions at the site do not allow deepening communications to the required level, then the pipes must be insulated. If the pipes are shallow, it is necessary to take measures to protect communications from damage by transport (lay them in trays).
Optimal tilt amount
The optimal slope when laying the collector from the house is 2 centimeters for every meter. The minimum slope per meter is 8 mm. It is not recommended to make a large slope - this increases the volume of excavation work for long communications, and in some situations can contribute to blockage. The fact is that there is little water in modern tanks; with a large slope of the collector, the water flows quickly, and the most invaluable thing for which the sewer system was created can be delayed (especially if part of the pipe sagged or bent when the soil moved or compacted).
Dependence of sewerage depth on pipe diameter
Compliance with the above parameters is not enough to install a high-quality sewer system. A serious factor is the technical characteristics of the pipes themselves.
First you need to select the material from which the pipeline is made. Metal and ceramics have long faded into the background and now it is best to purchase pipes made of plastic. Plastic is very resistant to various weather conditions, has a long service life, and is easy to transport and carry.
The next parameter is the diameter of the pipe, on which the depth of the sewer system also depends. The larger the diameter of the pipe, the shorter the distance it can be buried in the ground. For example: with an internal pipe diameter of 50 cm and a soil freezing depth of 150 cm, it must be buried 1 m into the ground. The formula by which the laying depth is calculated is quite simple: subtract the internal diameter of the pipeline from the freezing depth. This calculation formula is suitable for any private houses.
After calculating the size of the sewer pipes, you can begin preparing the trench. It is allowed to make trenches as narrow as possible, but it is strictly forbidden to bury them to a shallower depth.
Common problems and their solutions
The most common problem is blockage. Frozen fat in pipes, unfortunately, is practically not dissolved by acids and alkalis - neither liquid “Mole” nor nitric acid will help when clogged with fats. If the cause of the blockage in a large pipe is not clear, and the liquid passes slowly, you can pour out the alkali (“Mole”) and then slowly rinse the system with hot water. If the blockage is due to organic residues, then there is a chance to at least partially clear the pipe and survive until the plumbers arrive. Acid acts much more slowly on organic matter.
When using any chemicals, you must remember the fact that alkalis and acids destroy bacteria in a septic tank or treatment plant and slow down the process of processing sewage.
The advice to pour a couple of buckets of boiling water down the drain can damage siphons and the top of plastic communications and cracks in a faience sink or toilet.
Another problem is the smell. It is necessary to find leaks and seal the communications, and also check that the water plug in the siphon has not dried out (or spilled out through damage). In this case, replace or seal the siphon and add water.
The most serious problem is the destruction of communications due to freezing or damage from heavy equipment or ground shifts. In this situation, you cannot do without digging a trench and replacing the damaged part. To protect against soil shifts, when installing communications, it is necessary to backfill with sand (non-compactable soil) - a layer of 5 cm under the pipe and 10 cm on top of the pipe.
Pipe insulation
If necessary, the pipeline is insulated with material that does not absorb moisture - foil-coated polyethylene foam, polyurethane foam shells. Mineral wool is not suitable for this purpose.
Ventilation
In general, sewer risers must be ventilated. Pipes must be installed above the roof level by at least 500 mm. There are two reasons:
- The entry of air into the system and the removal of aggressive gases reduces corrosion of the metal parts of the system (not relevant for plastic) and protects the premises from the occurrence of unpleasant odors.
- Air access prevents the water seals of the siphons located above from breaking when flushing the toilet.
This issue is very relevant for an apartment building, but in a private building it is not so problematic.
In a private house, the drain riser above the toilet connection level can be narrowed - a pipe of a smaller diameter can be installed. You can abandon the fan pipe and install a special valve that allows air to enter the system. If there is only one toilet connected to the riser, you can refuse ventilation altogether - the volume of a modern tank is small, it leaks through the toilet for almost 10 seconds and therefore does not completely cover the cross-section of the riser and the danger of the water seals breaking is minimal. If there are two toilets and a lot of people live, it is better to install a valve.
Ventilation of a septic tank, cesspool or autonomous treatment plant is a prerequisite for ensuring reliable operation of the structure.
More
You need to know that plastic pipes do not become overgrown with salts, but fats (and suspended particles) can settle on their walls. There are no ways to combat this scourge - the pipes will have to be cleaned every few years. The situation is slightly improved by using liquid rather than abrasive detergents and using a dishwasher.
Rules for installing an external sewer system
When installing the external part of the sewerage pipeline yourself, it is important to follow the rules, the implementation of which will allow you to use the sewerage system for many years without experiencing problems.
- Before installation, a project is drawn up, which reflects the general layout of the pipeline and calculates the parameters and quantity of building materials.
- The drainage system must be protected from hypothermia during the cold period, so the pipes are either laid to the depth of soil freezing or insulated.
Note! If there is an area above the sewer network that is planned to be cleared of snow in winter, to prevent freezing the pipeline is either insulated or its depth is increased.
- The ideal geometry of the sewer system is straight, connecting the outlet of the intra-house sewer network with the place of sewage discharge. If it is impossible to lay a straight pipeline, it is designed in such a way that the number of turns is minimal.
- Right angle turns should be avoided, if this is not possible, two 45 degree corner elements are used to change direction.
- All corners and branches are equipped with inspection wells: tees with a pipe with a plug installed above the soil level. The presence of inspection areas will simplify system maintenance, monitoring its condition and cleaning.
- Under the pipe and on the sides of it, a layer of shock absorption must be poured and compacted; the pipes are poured on top without compaction - the dense bottom and side layers help maintain the geometry of the pipeline, the top layer protects from external loads.
- The sewage disposal network can be equipped with a pump; if it is not there, a gravity system is installed on a slope from the house to the collection well.
- The volume of the wastewater tank is calculated taking into account the number of people living in the house, the volume of water consumed, the type of collection well and the planned frequency of pumping out sewage.
We recommend that you read: How to make a chimney from a steel pipe with your own hands?
Distance when laying water pipes and different types of networks together
Joint laying allows you to save money and reduce the area of underground communications; if the sewerage system crosses the water supply main, it is laid lower in compliance with distance standards. When laying in the ground, the distance must be maintained if the pipelines are laid in protective casings (cases) made of metal, while the sewerage system may be located above the water supply networks.
According to SNiP 2.04.02-84, when laying several water pipelines, the norms of distances between adjacent pipes are selected taking into account the design, organization of installation work and the protection of neighboring areas in the event of a leak in one of them. Distances can be reduced in some sections if the pipelines are placed in a synthetic base, cases, run through tunnels or laid in other ways to prevent their possible damage. The distance must ensure unhindered installation and repair work.
The shortest distance between the water supply and sewerage from:
- 5 m – reinforced concrete or asbestos cement pipes;
- 3 m – cast iron pipes with a circumference above 200 mm;
- 1.5 m – cast iron with a diameter of up to 200 mm;
- 1.5 m – HDPE plastic;
- 1.5 m - in production, taking into account the material of manufacture and the size of the pipes, the physical and chemical parameters of the soil.
When laying a water supply system, the following limits of minimum distances to neighboring networks are accepted:
- 1.5 m – drainage and storm sewers;
- 1 m – low-pressure and medium-pressure gas pipelines;
- 1.5 – 2 m – high-pressure gas pipelines;
- 0.5 m – power electrical cables and communication cables (according to the operating rules for electrical installations of the PEU).
- 1.5 m – heat mains from the external walls of tunnel channels, pipe shells during trench laying, tunnel channels.
- 0.2 m – when pulled in tunnels to the internal walls of fencing structures and adjacent pipelines.
At intersection points, pipeline sections must have a one-way slope and protection from collectors and tunnels, steel casings, monolithic channels made of concrete and reinforced concrete.
Rice. 7 Examples of laying the sewer system of a private house
Depth limits for placing an electric pump in a well
Determining the depth of lowering of the electric pump is always associated with the dynamic and static level of the source. The static level is understood as the distance between the soil surface and the water horizon of the source in the absence of water intake; when drawing up a well passport, it is determined an hour after pumping.
The dynamic level of wells and boreholes is recorded when the electric pump is turned on at full power, which draws water from a given source; it is also equal to the distance between the surfaces of the earth and water. The dynamic threshold is fixed at the equilibrium point of the staying and pumped flow, when the water surface is at a constant level.
Rice. 3 Water level indicators
It is clear that when determining the depth of descent, it is necessary to take into account the dynamic characteristics of the well, that is, the electric pump must be located below the dynamic threshold by at least 1 - 3 m - this is the first indisputable condition.
In addition, such water will become unsuitable not only for drinking, but also for household needs. Therefore, a correctly calculated lowering depth should take this factor into account; the distance to the bottom should not fall lower than 0.5 - 1 m; for powerful electric pumps, the highest limit is chosen and this distance is even increased.
Bookmark standards according to SNiP
The required depth for laying water pipes is 0.5 m (this is the minimum value to maintain the integrity and life of the communication system) below the freezing level of the soil, but it also depends on the geographic area and the nature of the soil.
What materials should the pipe be made of:
- Steel. Structural steel pipes were used in older buildings. Now it is not the most relevant choice, since there are better and more durable materials;
- Cink Steel. An improved version of the previous material. The use of zinc on the surface prevents the negative effects of external factors and increases service life. There is an opinion that this material spoils the quality of water, so it is not used for drinking systems;
- Metal-plastic. The combination of plastic and metal guarantees a long service life. High resistance to adverse external factors;
- HDPE. This material has a number of advantages: low cost, resistant to environmental influences, high flexibility, easy to use.
Distance from the foundation to the well and well for sanitary areas
SNiP 2.04.02-84 establishes three protection zones for deep water intake sources, the minimum boundary of the first zone has the smallest radius and is:
- 30 m – when operating protected water horizons;
- 50 m – with insufficiently isolated water layers;
- 15 or 25 m - used for sources located on a site with a house, if any possibility of contamination of the soil and deep water layer is excluded. Applies to water intake sources located in favorable places in terms of sanitary and geological conditions; standards should be reduced by agreement with local sanitary services.
In the area of the first belt it is prohibited:
- All types of construction work, except for reconstruction, repair or branching of water pipelines.
- The location of any buildings, the location of permanent residents.
- Laying any communications, except those serving water wells or wells.
- The house must have a sewer outlet to the central system or to treatment facilities located behind the first ring.
- If there is no sewerage system, sealed septic tanks are installed in places that prevent sewage from entering the ground of the first zone when the container is emptied.
- Drainage must be arranged beyond the boundaries of the first zone.
Thus, on an individual plot there is no clear distance from a well or borehole to the foundation of a house and outbuildings; the degree of removal depends on the protection of aquifers, the characteristics of the area and can range from 15 to 50 meters. It should be noted that in everyday life, due to the small area of land, other standards apply - wells and boreholes are located much closer to the house.
Rice. 8 Placement of a water source on an individual plot