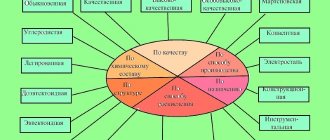
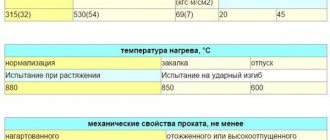
Classification
Requirements for construction steels are regulated by GOST 27772-88* “Rolled steel for building steel structures”. The document defines the range of alloys, provides classification, rules for production, acceptance and use of the metal.
According to GOST, steels are divided into 2 main types according to composition:
- Carbonaceous.
- Alloyed.
Carbon
The amount of the chemical element carbon determines the strength of a steel structure. The more it is, the stronger the metal. Carbon alloys are divided into 3 groups:
- Construction low-alloy steels with a carbon content of less than 0.25%;
- Medium carbon contains 0.25-0.60% carbon;
- High-carbon ones contain more than 0.60% of the chemical element.
Metals with different amounts of carbon are used in the manufacture of building structures of normal tension.
Alloyed
To increase strength, various metals are added to the iron alloy in different quantities. This process is called doping. Based on the number of additives, there are 3 groups of alloys:
- Low alloy – up to 2.5% additional metals;
- Medium alloyed - about 2.5-10% additives;
- Highly alloyed - more than 10% impurities.
Construction steels with additives (alloyed) are considered to be of higher quality than carbon steels. They are used for the manufacture of critical structures in construction, the space industry, mechanical engineering and the railways.
The choice of steel type is determined by GOST and structural calculations.
Structural steels
Any steel, as a rule, is an alloy of iron and carbon, and the content of the latter in it is no more than 2.14%. Carbon gives the alloy hardness, but if it is in excess, the metal becomes too brittle.
The properties of structural building steels are determined mainly by mechanical and technological characteristics. Mechanical ones include tensile strength, elongation, hardness, impact strength;
technological ones -
fluidity, weldability, malleability
, etc.
For structural steels, mainly carbon (0.10...0.20% C) and low-alloy (Si, Mn, Cr, etc.) are used (GOST 19281-73 and GOST 19282-72). They are usually of ordinary quality and are supplied according to their mechanical properties.
Structural steels in the form of sheets and sections are used in construction and mechanical engineering for welded structures, mainly without additional heat treatment. Thus, steel grades 14G2, 18G2, 16GS, 10G2S1, 14KhGS and 15HSND are needed for the manufacture of metal structures, and steel 18G2S, 25G2S and 35GS are needed for reinforced concrete structures.
Steels are classified according to their purpose. Thus, there are instrumental and structural types, grades distinguished by special physical properties. Data in Table 1 below.
Table 1
| Structural steels | Tool steels | Brands with special properties |
| 10ХСНД,20Х2Н4А,15ХМ,20ХМ | U7, U8, U10; U7A; U8A; U10A; U12A | EI69 (45Х14Н14В2М) EI602 (ХН75МБТУ) |
| Steel grades | Mass fraction of elements, % | ||||||||
| GOST 4543 | DIN | ANFOR | Other | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Other |
| 15X | 15Cr3 (1.7015) | 18C3 | 5015 (ASTM) | 0,12-0,18 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,40-0,70 | 0,70-1,00 | <0,30 | |
| 40G | 40Mn4 (1.1157) | 40M5 | 15OM36 (B,S) | 0,37-0,45 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,70-1,00 | <0,30 | ||
| 20G | C21 (1.0432) | A105 (ASTM) | 0,17-0,24 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,70-1,00 | ||||
| 40G2 | 36Mn5 (1.1167) | 154B41H (ASTM) | 0,36-0,44 | 0,17-0,37 | 1,40-1,80 | ||||
| 40X | 42Cr4 (1.7045) | 5140 (ASTM) | 0,36-0,44 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,80-1,10 | |||
| 18ХГ | 16MnCr5 (1.7131) | 16MC5 | 5115 (ASTM) | 0,15-0,21 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,90-1,20 | 0,90-1,20 | ||
| 20MnCr5 (1.7147) | 0,15-0,21 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,90-1,20 | 0,90-1,20 | |||||
| 18ХГТ | 0,17-0,23 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,80-1,10 | 1,00-1,30 | Ti 0.03-0.09 | ||||
| 38ХГМ | 42CrMo4 (1.7225) | 42CD4 | 4140 (ASTM) | 0,34-0,40 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,60-0,90 | 0,80-1,10 | Mo 0.15-0.25 | |
| 27ХГР | 709M40 (B,S) | 0,25-0,31 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,70-1,00 | 0,70-1,00 | ||||
| 38ХС | 0,34-0,42 | 1,00-1,40 | 0,30-0,60 | 1,30-1,60 | |||||
| 30ХМА | 25CrMo4 (1.7218) | 25CD4 | 4130 (ASTM) | 0,26-0,33 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,40-0,70 | 0,80-1,10 | Mo 0.15-0.25 | |
| 30Х3МФ | 31CrMoV9 (1.8519) | 0,27-0,34 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,30-0,60 | 2,30-2,70 | Mo 0.20-0.30 | |||
| 40HFA | 41CrMo4 (1.7223) | 4142 (ASTM) | 0,37-0,44 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,80-1,10 | V 0.10-0.18 | ||
| 40ХН | 40NiCr6 (1.5711) | 3140 (ASTM) | 0,36-0,44 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,80 | 0,45-0,75 | 1,00-1,40 | ||
| 12ХН3А | 655M13 (B,S) | 0,09-0,16 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,30-0,60 | 0,60-0,90 | 2,75-3,15 | |||
| 30ХГСА | 0,28-0,34 | 0,90-1,20 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,80-1,10 | |||||
| 15KhGN2TA | 0,13-0,18 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,70-1,00 | 0,70-1,00 | 1,40-1,80 | Ti 0.03-0.09 | |||
| 40Х2Н2МА | 40CrNiMo6 (1.6565) | 4340 (ASTM) | 0,35-0,42 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,30-0,60 | 1,25-1,65 | 1,35-1,75 | Mo 0.20-0.30 | |
| 818M40 (B,S) | |||||||||
| 18Х2Н4МА | X19NiCrMo4 (1.2764) | 0,14-0,20 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,25-0,55 | 1,35-1,65 | 4,00-4,40 | Mo 0.30-0.40 | ||
| 38Х2Н2МА | 34CrNiMo6 (1.6582) | 4337 (ASTM) | 0,33-0,40 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,25-0,50 | 1,30-1,70 | 1,30-1,70 | Mo 0.20-0.30 | |
| 817M40 (B,S) | |||||||||
| 38Х2МУА | 41CrA1Mo7 (1.8509) | 40CAD6.12 | 0,35-0,42 | 0,20-0,45 | 0,30-0,60 | 1,35-1,65 | Mo 0.20; Al 0.7-1.1 | ||
| 15X | AFNOR | |
| 15X | 15Cr3 (1.7015) | 18C3 |
General characteristics:
steel can be welded without restrictions (except for chemically thermally treated parts).
Not prone to temper brittleness, non-flocene sensitive. Application:
cemented parts - shafts, pins, gears, rollers, which are subject to the requirements of high surface hardness with low core strength.
Types of products supplied:
rolled bars with round and square sections, strip bars, forged bars, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground rods and with special surface finishing.
40X
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN | AISI/SAE |
| 40X | 41Cr4 (1.7035) | 5135; 5140 |
General characteristics:
steel is prone to temper brittleness and is flake-sensitive.
It is difficult to weld and requires heating and subsequent heat treatment. Density at 20°C - 7.82x10 kg/m Application:
for the manufacture of fasteners operating at temperatures not exceeding 425°C.
Axles, shafts, gears, rods, crankshafts, camshafts, rings, racks, spindles, mandrels, axle shafts and other heavy-duty parts. Types of products supplied:
long products with round and square sections, forged bars with round and square sections, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground turned rods and rods with special surface finishing.
18ХГТ
| GOST 4543-71 |
| 18ХГТ |
General characteristics:
steel can be welded without restrictions by resistance and arc welding (except for chemically thermally treated parts).
Non-flocene sensitive, low prone to temper brittleness. Application:
Improved or cemented parts for critical purposes, operating under impact loads, which require increased strength and toughness of the core, as well as high surface strength.
Types of products supplied:
long products with round and square sections, forged bars with round and square sections, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground turned rods and steel with special surface finishing.
38ХС
| GOST 4543-71 |
| 38ХС |
General characteristics:
steel is difficult to weld.
Manual, arc and resistance welding requires heating and subsequent heat treatment. Non-flocene sensitive, has a tendency to temper brittleness. Density at 20°C - 7.6x10 kg/m Application:
shafts, gears, couplings, pins and other small parts to be improved, which require increased strength, elasticity and wear resistance.
Types of products supplied:
long products with round and square sections, forged bars with round and square sections, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground turned rods and steel with special surface finishing.
30ХМА
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN | ASTM |
| 30ХМА | 30CrMo4 (1.7216) | 4130 |
General characteristics:
chrome-molybdenum steel has limited weldability by manual and automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection.
Preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. Flock sensitivity is insignificant. Not prone to temper brittleness. Application:
shafts, gears, pins, flanges, disks, rods and other critical parts operating under conditions of heavy loads and speeds at temperatures up to 450-500°C.
Types of products supplied:
long products with round and square sections, forged bars with round and square sections, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground turned rods and steel with special surface finishing.
40ХН
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN | AISI/SAE/ASTM |
| 40ХН | 40NiCr6 (1.5711) | 3140 |
General characteristics:
difficult-to-weld steel, manual and submerged arc welding.
Electroslag welding is possible. It has increased flake sensitivity and a tendency to temper brittleness. Density at 20°C - 7.83x10 kg/m Application:
rolls of rail and beam and large-section mills for hot rolling of metal.
Axles, shafts, gear wheels, excavator shafts, cylinders and other critical loaded parts subject to vibration and dynamic loads, which require increased strength and toughness. Types of products supplied:
long products with round and square sections, forged bars with round and square sections, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground turned rods and rods with special surface finishing.
12ХН3А
| GOST 4543-71 | AISI/SAE/ASTM |
| 12ХН3А | 655M13 |
General characteristics:
chromium-nickel steel with limited weldability.
Manual and automatic submerged arc welding. Prone to temper brittleness, flake-sensitive. Cutting machinability in the hot-rolled state with a hardness of HB 183-187 is satisfactory. Density at 20°C - 7.85x10 kg/m Application:
claw couplings, gears, shafts, piston pins and other cemented parts that require high strength, ductility and toughness of the core and high surface hardness, operating under impact loads or at negative temperatures.
Types of products supplied:
rolled bars with round and square sections, forged bars, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground bars and bars with special surface finishing.
40Х2Н2МА
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN | AISI/SAE | B.S. |
| 40Х2Н2МА | 40CrNiMo6 (1.6565) | 4340 | 818M40 |
General characteristics:
steel is difficult to weld, heat-resistant up to 450°C.
flake-sensitive, not prone to temper brittleness. Possesses through hardenability in rods up to 50 mm. Manual arc welding requires preheating and subsequent heat treatment. Density at 20°C - 7.85x10 kg/m Application:
heavily loaded parts - crankshafts, connecting rods, gears, claw couplings operating under dynamic loads at temperatures up to 450°C.
Types of products supplied:
rolled bars with round and square sections, forged bars, strip products, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground bars and bars with special surface finishing.
18Х2Н4МА (VA)
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN |
| 18Х2Н4МА(VA) | Х19NiCrMo4 (1.2764) |
General characteristics:
chromium-nickel-molybdenum (tungsten) steel.
Difficult to weld. Heating and subsequent heat treatment are required. Not prone to temper brittleness, flake-sensitive. Density at 20°C - 7.95x10 kg/m Application:
used in a cemented and improved state for the manufacture of critical parts with the requirements of high strength, toughness and wear resistance.
Withstands vibration and dynamic loads well. Can be used in the temperature range from -70 to +450°C. Types of products supplied:
long products and forged bars of round, square and strip sections. Calibrated and ground rods. Rods with special surface finishing.
38Х2МУА
| GOST 4543-71 | DIN |
| 38Х2МУА | 41CrAlMo7 (1.8509) |
General characteristics:
the steel is corrosion-resistant in atmospheric conditions after nitriding.
Not prone to temper brittleness, flake-sensitive. Not suitable for welded structures, heat resistant up to 500°C. Density at 20°C - 7.71x10 kg/m Application:
valve rods of steam turbines, cylinder liners of internal combustion engines, injector needles, axle box plates, plungers.
Nitrided parts operating at temperatures of 450-500°C. Types of products supplied:
rolled bars with round and square sections, strip bars, forged bars, calibrated rolled products with round and hexagonal sections, ground rods and with special surface finishing.
Structural alloy steels
| Steel grades | Mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||||
| GOST 1414-75 | DIN | Other standards | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | S | P | other |
| Structural | ||||||||||
| A12 | 9SMn28 (1.0715) | 230M07 (B,S) | 0,08-0,16 | 0,15-0,35 | 0,70-1,10 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,08-0,2 | 0,08-0,15 | Cu 0.25; Pb 0.15-0.30 |
| AC14 | 0,10-0,17 | 0,12 | 1,00-1,30 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,15-0,30 | 0,10 | Cu 0.25; Pb 0.15-0.30 | ||
| AS35G2 | 35SPb20 (1.0756) | 0,32-0,39 | 0,17-0,37 | 1,35-1,65 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,08-0,13 | 0,04 | Cu 0.25; Pb 0.15-0.30 | |
| TU 14-136-344-98 | ||||||||||
| АВ19ХГН | 0,16-0,21 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,70-1,10 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,035 | 0,035 | Bi 0.12-0.20; Cu 0.30 | ||
| AV35G2 | 0,32-0,39 | 0,17-0,37 | 1,35-1,65 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,08-0,13 | 0,04 | Bi 0.12-0.20; Cu 0.25 | ||
| AB14 | 0,10-0,17 | 0,12 | 1,0-1,30 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,15-0,30 | 0,10 | Cu 0.25; Bi 0.12-0.20 | ||
| X8CrNiS 18.9 (1.4305) | 303 (AISI) | 0,12 | 1,0 | 2,0 | 17,0-19,0 | 8,0-10,0 | 0,28-0,35 | 0,06 | Mo 0.50; W 0.20; Cu 0.30; V 0.20; Ti 0.20 | |
| A12 |
General characteristics:
forging temperature, °C: start - 1200, end - 850. Not applicable for welded structures.
Cutting ability - HB 167-217. Flock-sensitive, not prone to temper brittleness. Application:
axles, rollers, bushings, gear wheels, pinions, pins, screws, bolts and other lightly loaded small parts of complex shapes processed on automatic machines, and which are subject to requirements for surface quality and dimensional accuracy Types of
products supplied:
sectional hot-rolled and calibrated round steel, round steel with special surface finishing, round steel with a machined surface.
AC14
| GOST 4543-71 |
| AC14 |
General characteristics:
lead-containing sulfide-manganese steel with high machinability.
Not applicable for welded structures Application:
intended for processing on machines and automatic machines, as well as for hot pressure processing followed by cutting.
Types of supplied products:
long hot-rolled, calibrated and turned round bars and round steel with special surface finishing.
AV35G2
| GOST 4543-71 |
| AV35G2 |
General characteristics:
structural steel with high machinability.
Not applicable for welded structures. Not sensitive to floc formation; not prone to temper brittleness. Application:
production of car parts by cold machining.
Types of products supplied:
calibrated rolled products of round and hexagonal sections. Delivery condition: in annealed and cold-hardened conditions with preliminary normalization.
1.4305
| DIN 17440 | ASTM 582 |
| X10CrNiS 18.9 | 303 |
General characteristics:
Applicable for such service which requires optimum machinability, high temperature stability and corrosion resistance;
the introduction of lead increases wear resistance during friction, prevents sticking and enveloping of the metal. Application:
production of fasteners and parts in automatic devices
Types of supplied products:
hot-rolled rods O12-70 mm
Delivery condition:
turned in a hardened state
Spring-spring and heat-resistant
| Steel grades | Mass fraction of elements, % | ||||||
| GOST 14959-79 | DIN | SAE/AISI | C | Si | Mn | Cr | other |
| 65G | Ck67 (1.1231) | 1070 | 0,62-0,70 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,90-1,2 | <0,25 | |
| 55С2А | 55Si7 (1.5026) | 9255 | 0,53-0,58 | 1,5-2,0 | 0,60-0,9 | <0,30 | |
| 60С2А | 60Si7 (1.5027) | 9260 | 0,58-0,63 | 1,6-2,0 | 0,60-0,9 | <0,30 | |
| 60S2G | 60SiMn (1.5142) | 0,55-0,65 | 1,8-2,2 | 0,70-1,0 | <0,30 | ||
| 50HFA | 51CrV4 (1.8159) | 0,46-0,54 | 0,17-0,37 | 0,50-0,8 | 0,80-1,1 | V 0.10-0.20 | |
| 60С2ХА | 60SiCr7 (1.7108) | 9262 | 0,56-0,64 | 1,4-1,8 | 0,40-0,7 | 0,70-1,0 | |
| 60С2Н2А | 0,56-0,64 | 1,4-1,8 | 0,40-0,7 | 0,3 | Ni 1.40-1.70 | ||
| 70С2ХА | 71Si7 (1.5029) | 0,65-0,75 | 1,40-1,70 | 0,40-0,6 | 0,20-0,4 | ||
| Note: P and S 0.035% for quality steel, P and S 0.025% for high quality steel 65G | AISI/SAE/ASTM | |
| 65G | Ck65 (1.1230) | 1065 |
General characteristics:
spring steel, insensitive to flocking, prone to temper brittleness with a Mn content of 1%, not used for welded structures.
Density at 20°C - 7.81x10 kg/m. The normal elastic modulus at 20°C is 215 GPa. Specific heat capacity at 20-100°C - 490 J/(kg °C) Application:
springs, springs, thrust washers, brake bands, friction discs, gears, flanges, bearing housings, clamping and feed collets and other parts, which are subject to increased wear resistance requirements, and parts that operate without shock loads.
Types of supplied products:
hot-rolled (without heat treatment) with a hardness of no more than HB285; in a highly tempered state - no more than HB241
60С2А
| GOST 14959-79 | DIN | AAISI/SAE |
| 60С2А | 60Si7 (1.5027) | 9260 |
General characteristics:
forging temperature, °C: start - 1200, end - 800. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, 251-350 mm - in a pit.
Not applicable for welded structures. Non-flocene sensitive, not prone to temper brittleness. Application:
heavily loaded springs, torsion shafts, spring rings, collets, friction discs, Grover washers, etc.
Types of supplied products:
hot-rolled and forged bars, calibrated bars and with special surface finishing.
50HFA
| GOST 14959-79 | DIN | AISI/SAE |
| 50HFA | 50CrMo4 (1.7228) | 4150 |
General characteristics:
spring steel, has a low tendency to grain growth, is not sensitive to flocking, has little tendency to temper brittleness, and is not used for welded structures.
Density at 20°C is 7.80x10 kg/m in air, 251-350mm in a pit. Not applicable for welded structures. Non-flocene sensitive, not prone to temper brittleness. Application:
critical valve springs and springs for cars;
oil seals, springs for sectional piston rings; springs operating at temperatures up to 300°C; springs that are subjected to repeated variable loads during operation during a long operating cycle. Types of products supplied:
rolled products of round, square and rectangular sections, calibrated rolled products and with special surface finishing, forged grades.
15Х5М
| GOST 20072-74 |
| 15Х5М |
General characteristics:
heat-resistant martensitic steel.
Difficult to weld, sensitive to flocking, not prone to temper brittleness. It has increased corrosion resistance in sulfur-containing environments. The temperature at which intense scale formation begins is 650°C. Density at 20°C - 7.75x10 kg/m Application:
housings and internal elements of oil refinery equipment and cracking pipes, pump parts, valves, fasteners with a very long service life (from 50,000 to 100,000 hours) at temperatures up to 600°C.
Types of products supplied:
supplied in a heat-treated state (annealed, tempered or normalized with high tempering) with a hardness of no more than HB217
12Х1МФ
| GOST 20072-74 |
| 12Х1МФ |
General characteristics:
heat-resistant pearlitic steel.
The temperature at which intense scale formation begins is 600°C. The steel has limited weldability: preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. Density at 20°C - 7.8x10 kg/m Application:
pipes of steam superheaters, pipelines and high-pressure collector units;
gas turbine cylinder parts; rods, bolts, studs and other fasteners that operate for a long time (50-100 thousand hours) at temperatures up to 510°C. Types of products supplied: supplied in a heat-treated state (annealed, tempered or normalized with high tempering) or without heat treatment.
Marking of construction steels
The brand indicates the main characteristics of the material. Carbon and alloy steels have different designations, so we will consider them separately.
Decoding carbon steels
It’s easy to decipher the grade of carbon alloy:
- “St” is the designation of construction steel;
- The number indicates the amount of carbon in the alloy in tenths of a percent;
- The letters “kp”, “ps”, “sp” at the end of the designation indicate the boiling type of deoxidation (see below). The absence of additional letters indicates that the steel is calm.
The ratio of steel grade and amount of carbon is presented in the table:
The sulfur content in carbon alloys is not less than 0.045%, phosphorus - not less than 0.055%.
Marking of alloy alloys
Since alloy steels contain various chemical elements, it is necessary to identify them:
An example of a grade of construction steel with alloying additives: 16G2AF. The designation is deciphered as follows:
- 16 – carbon content in the alloy. In our case – 0.16%. If the name has one digit, it should be taken as a hundredth of a percent;
- G – presence of manganese 2%;
- A – nitrogen, about 1%;
- F – vanadium, about 1%.
There are many names of alloyed construction steels.
Designation of structural steel
GOST 27772-88* provides the designation of metals for the manufacture of shaped rolled products, which are designated by the letter “C” (Construction steel) and numbers. To understand what is hidden behind these values, we present the correspondence of alloyed, carbon and accepted construction steels: